开发踩坑记录之四:Tomcat内存溢出问题分析
引言
系统平台运行一段时间后,平台出现无法访问的问题,重启对应的服务后平台恢复正常。查看日志发现在凌晨两点零四分之后没有对应的日志输出,直到重启服务后才有日志的正常输出。同时发现在Tomcat的目录下存在hprof文件,即java进程的内存镜像文件。初步猜测Tomcat发生了内存溢出导致服务出现假死现象,即在任务管理器中虽然为运行状态,但是实际已不能正常对外提供服务。
对于hprof文件的分析需要借助于内存分析工具Eclipse Memory Analyzer,通过它寻找到平台发生内存泄露的根源,再根据发生内存泄露的地方以及相关的日志信息定位什么样的业务场景下导致该异常情况的发生,同时采取相关措施防止类似情况再次发生。
- 问题分析过程
- 相关源码分析
- 解决方法
- 总结
一、问题分析过程
使用Eclipse Memory Analyzer分析工具导入java_pid4668.hprof文件进行分析,如下图所示:

颜色最深的区域代表最有可能发生内存泄露的地方,我们可以发现RequestInfo这个对象多达3190个,怀疑这个对象的异常增加同时没有被JVM回收,无法释放已经申请的内存空间,导致内存泄露,直至内存被消耗完,最终产生内存溢出问题,从而造成平台崩溃,使得系统无法正常对外提供服务,我们继续往下分析。

点击对应的RequestInfo项,如上图所示,我们可以发现这个对象所对应的接口地址。这个接口所对应的业务是服务端与客户端之间维持一个websocket的长连接,每隔三十秒客户端向服务端发送心跳,服务端响应心跳以维持客户端在线状态。如果连接建立不成功,客户端每隔三秒就会再次与服务端进行websocket的连接,如此循环往复。
通过查看维护的代码可知,客户端在连接建立不成功时,会将连接对象销毁后再创建新的连接对象,而服务端在连接建立不成功时并未将连接关闭,又重新使用新的连接对象。随着时间的累积,最终导致内存溢出,影响平台的正常运行。
二、相关源码分析
下图描述了一个请求进入Tomcat容器后的流转过程。
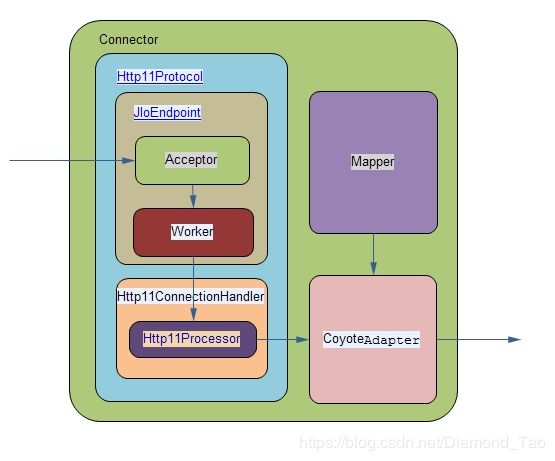
备注:该图片来源于网络
package org.apache.coyote;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/** This can be moved to top level ( eventually with a better name ).
* It is currently used only as a JMX artifact, to aggregate the data
* collected from each RequestProcessor thread.
*/
public class RequestGroupInfo {
//此处源码中的RequestInfo对象通过一个list进行存放
private final ArrayList<RequestInfo> processors = new ArrayList<>();
private long deadMaxTime = 0;
private long deadProcessingTime = 0;
private int deadRequestCount = 0;
private int deadErrorCount = 0;
private long deadBytesReceived = 0;
private long deadBytesSent = 0;
//调用此方法进行请求对象的添加
public synchronized void addRequestProcessor( RequestInfo rp ) {
processors.add( rp );
}
public synchronized void removeRequestProcessor( RequestInfo rp ) {
if( rp != null ) {
if( deadMaxTime < rp.getMaxTime() )
deadMaxTime = rp.getMaxTime();
deadProcessingTime += rp.getProcessingTime();
deadRequestCount += rp.getRequestCount();
deadErrorCount += rp.getErrorCount();
deadBytesReceived += rp.getBytesReceived();
deadBytesSent += rp.getBytesSent();
processors.remove( rp );
}
}
public synchronized long getMaxTime() {
long maxTime = deadMaxTime;
for (RequestInfo rp : processors) {
if (maxTime < rp.getMaxTime()) {
maxTime=rp.getMaxTime();
}
}
return maxTime;
}
// Used to reset the times
public synchronized void setMaxTime(long maxTime) {
deadMaxTime = maxTime;
for (RequestInfo rp : processors) {
rp.setMaxTime(maxTime);
}
}
public synchronized long getProcessingTime() {
long time = deadProcessingTime;
for (RequestInfo rp : processors) {
time += rp.getProcessingTime();
}
return time;
}
public synchronized void setProcessingTime(long totalTime) {
deadProcessingTime = totalTime;
for (RequestInfo rp : processors) {
rp.setProcessingTime( totalTime );
}
}
public synchronized int getRequestCount() {
int requestCount = deadRequestCount;
for (RequestInfo rp : processors) {
requestCount += rp.getRequestCount();
}
return requestCount;
}
public synchronized void setRequestCount(int requestCount) {
deadRequestCount = requestCount;
for (RequestInfo rp : processors) {
rp.setRequestCount( requestCount );
}
}
public synchronized int getErrorCount() {
int requestCount = deadErrorCount;
for (RequestInfo rp : processors) {
requestCount += rp.getErrorCount();
}
return requestCount;
}
public synchronized void setErrorCount(int errorCount) {
deadErrorCount = errorCount;
for (RequestInfo rp : processors) {
rp.setErrorCount( errorCount);
}
}
public synchronized long getBytesReceived() {
long bytes = deadBytesReceived;
for (RequestInfo rp : processors) {
bytes += rp.getBytesReceived();
}
return bytes;
}
public synchronized void setBytesReceived(long bytesReceived) {
deadBytesReceived = bytesReceived;
for (RequestInfo rp : processors) {
rp.setBytesReceived( bytesReceived );
}
}
public synchronized long getBytesSent() {
long bytes=deadBytesSent;
for (RequestInfo rp : processors) {
bytes += rp.getBytesSent();
}
return bytes;
}
public synchronized void setBytesSent(long bytesSent) {
deadBytesSent = bytesSent;
for (RequestInfo rp : processors) {
rp.setBytesSent( bytesSent );
}
}
public void resetCounters() {
this.setBytesReceived(0);
this.setBytesSent(0);
this.setRequestCount(0);
this.setProcessingTime(0);
this.setMaxTime(0);
this.setErrorCount(0);
}
}
在AbstractProtocol类中ConnectionHandler类主要可以调用不同的Processor来处理socket请求,解析完成之后再调用Adapter的方法,将请求转发给容器进行处理。
protected static class ConnectionHandler<S> implements AbstractEndpoint.Handler<S> {
private final AbstractProtocol<S> proto;
private final RequestGroupInfo global = new RequestGroupInfo();
private final AtomicLong registerCount = new AtomicLong(0);
private final Map<S,Processor> connections = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final RecycledProcessors recycledProcessors = new RecycledProcessors(this);
public ConnectionHandler(AbstractProtocol<S> proto) {
this.proto = proto;
}
protected AbstractProtocol<S> getProtocol() {
return proto;
}
protected Log getLog() { return getProtocol().getLog();
}
...
protected void register(Processor processor) {
if (getProtocol().getDomain() != null) {
synchronized (this) {
try {
long count = registerCount.incrementAndGet();
RequestInfo rp =
processor.getRequest().getRequestProcessor();
//
rp.setGlobalProcessor(global);
ObjectName rpName = new ObjectName(
getProtocol().getDomain() +
":type=RequestProcessor,worker="
+ getProtocol().getName() +
",name=" + getProtocol().getProtocolName() +
"Request" + count);
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLog().debug("Register " + rpName);
}
Registry.getRegistry(null, null).registerComponent(rp,
rpName, null);
rp.setRpName(rpName);
} catch (Exception e) {
getLog().warn("Error registering request");
}
}
}
}
}
三、解决办法
在重写WebSocketHandler接口中的afterConnectionClosed以及handleTransportError方法,即在这两个方法中将对应的session进行关闭。
@Override
public void afterConnectionClosed(WebSocketSession session, CloseStatus status) throws Exception {
if (session.isOpen()) {
try {
session.close();
logger.info("Server close this session!");
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("Server close this session has a exception", e);
}
}
}
@Override
public void handleTransportError(WebSocketSession session, Throwable exception) throws Exception {
if (session.isOpen()) {
try {
session.close();
logger.info("Server close this session!");
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("Server close this session has a exception", e);
}
}
}
四、总结
在实际项目中,类似websocket这种资源占用连接,在连接关闭以及连接异常的情况下需要将资源进行释放,避免出现JVM回收不掉创建的对象,最终引起内存溢出,导致平台无法正常运行。