运行环境:win10 64位 py 3.6 pycharm 2018.1.1
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets,cross_validation,ensemble,naive_bayes
def load_data_classification():
digits = datasets.load_digits()
return cross_validation.train_test_split(digits.data,digits.target,test_size=0.25,random_state=0)
def test_GradientBoostingClassifier(*data):
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
clf = ensemble.GradientBoostingClassifier()
clf.fit(X_train,y_train)
print("Traing Score:%f"%clf.score(X_train,y_train))
print("Tesing Score:%f"%clf.score(X_test,y_test))
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=load_data_classification()
test_GradientBoostingClassifier(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
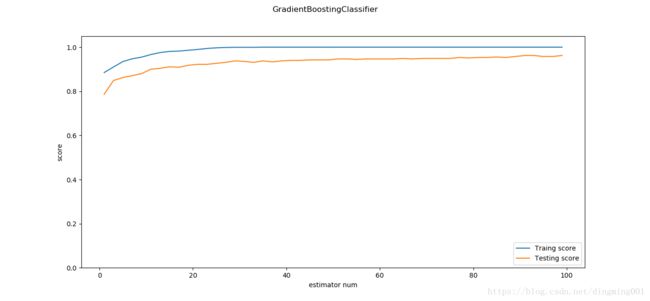
def test_GradientBoostingClassifier_num(*data):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = data
nums = np.arange(1,100,step=2)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
testing_scores=[]
training_scores=[]
for num in nums:
clf = ensemble.GradientBoostingClassifier(n_estimators=num)
clf.fit(X_train,y_train)
training_scores.append(clf.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(clf.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(nums, training_scores, label='Traing score')
ax.plot(nums, testing_scores, label='Testing score')
ax.set_xlabel("estimator num")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc='lower right')
ax.set_ylim(0, 1.05)
plt.suptitle("GradientBoostingClassifier")
plt.show()
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=load_data_classification()
test_GradientBoostingClassifier_num(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
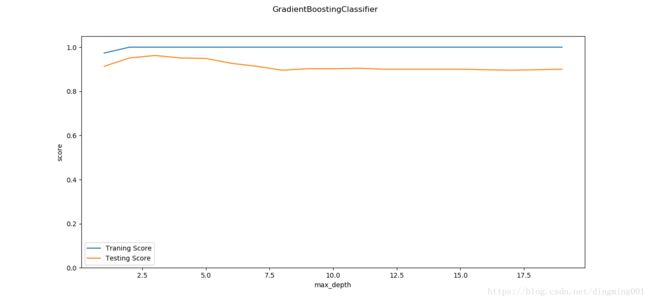
def test_GradientBoostingClassifier_maxdepth(*data):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = data
maxdepths = np.arange(1,20)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
traing_scores = []
testing_scores = []
for maxdepth in maxdepths:
clf = ensemble.GradientBoostingClassifier(max_depth=maxdepth,max_leaf_nodes=None)
clf.fit(X_train,y_train)
traing_scores.append(clf.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(clf.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(maxdepths,traing_scores,label='Traning Score')
ax.plot(maxdepths,testing_scores,label='Testing Score')
ax.set_xlabel("max_depth")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc='best')
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
plt.suptitle('GradientBoostingClassifier')
plt.show()
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = load_data_classification()
test_GradientBoostingClassifier_maxdepth(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
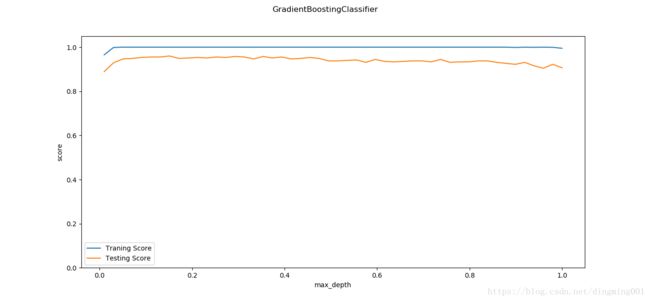
def test_GradientBoostingClassifier_learing(*data):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = data
fig = plt.figure()
learnings = np.linspace(0.01,1.0)
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
traing_scores = []
testing_scores = []
for learning in learnings:
clf = ensemble.GradientBoostingClassifier(learning_rate=learning)
clf.fit(X_train,y_train)
traing_scores.append(clf.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(clf.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(learnings,traing_scores,label='Traning Score')
ax.plot(learnings,testing_scores,label='Testing Score')
ax.set_xlabel("max_depth")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc='best')
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
plt.suptitle('GradientBoostingClassifier')
plt.show()
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = load_data_classification()
test_GradientBoostingClassifier_learing(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
def test_GradientBoostingClassifier_subsample(*data):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = data
fig = plt.figure()
subsamples = np.linspace(0.01,1.0)
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
traing_scores = []
testing_scores = []
for subsample in subsamples:
clf = ensemble.GradientBoostingClassifier(subsample=subsample)
clf.fit(X_train,y_train)
traing_scores.append(clf.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(clf.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(subsamples,traing_scores,label='Traning Score')
ax.plot(subsamples,testing_scores,label='Testing Score')
ax.set_xlabel("subsample")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc='best')
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
plt.suptitle('GradientBoostingClassifier')
plt.show()
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = load_data_classification()
test_GradientBoostingClassifier_subsample(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
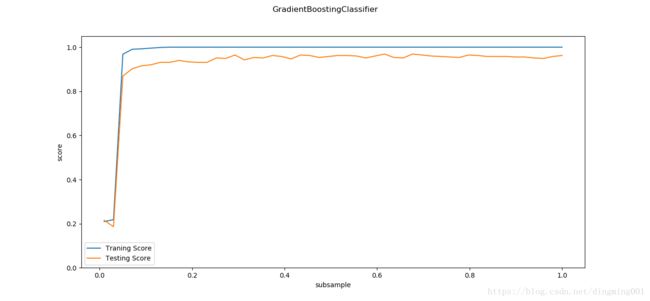
def test_GradientBoostingClassifier_max_features(*data):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = data
fig = plt.figure()
max_features = np.linspace(0.01,1.0)
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
traing_scores = []
testing_scores = []
for features in max_features:
clf = ensemble.GradientBoostingClassifier(max_features=features)
clf.fit(X_train,y_train)
traing_scores.append(clf.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(clf.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(max_features,traing_scores,label='Traning Score')
ax.plot(max_features,testing_scores,label='Testing Score')
ax.set_xlabel("max_features")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc='best')
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
plt.suptitle('GradientBoostingClassifier')
plt.show()
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = load_data_classification()
test_GradientBoostingClassifier_max_features(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
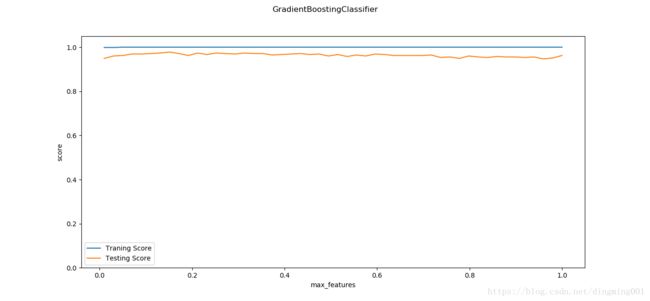
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets,cross_validation,ensemble,naive_bayes
def load_data_regression():
diabetes = datasets.load_diabetes()
return cross_validation.train_test_split(diabetes.data,diabetes.target,test_size=0.25,random_state=0)
def test_GradientBoostingRegressor(*data):
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
regr = ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor()
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
print("Traing Score:%f"%regr.score(X_train,y_train))
print("Tesing Score:%f"%regr.score(X_test,y_test))
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=load_data_regression()
test_GradientBoostingRegressor(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
def test_GradientBoostingRegressor_num(*data):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = data
nums = np.arange(1,200,step=2)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
testing_scores=[]
training_scores=[]
for num in nums:
regr = ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(n_estimators=num)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(nums, training_scores, label='Traing score')
ax.plot(nums, testing_scores, label='Testing score')
ax.set_xlabel("estimator num")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc='lower right')
ax.set_ylim(0, 1.05)
plt.suptitle("GradientBoostingRegressor")
plt.show()
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=load_data_regression()
test_GradientBoostingRegressor_num(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
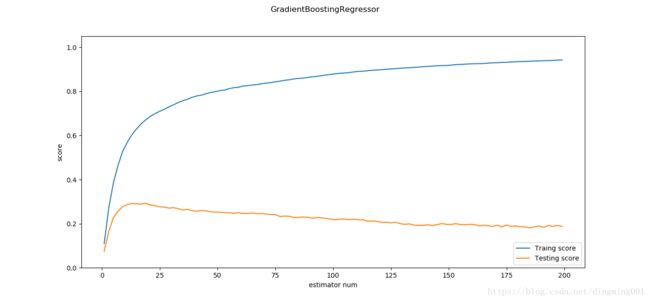
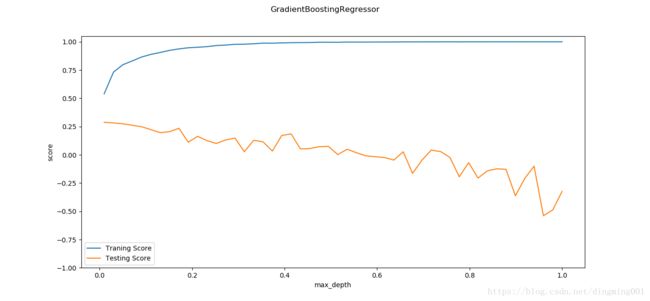
def test_GradientBoostingRegressor_maxdepth(*data):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = data
maxdepths = np.arange(1,20)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
traing_scores = []
testing_scores = []
for maxdepth in maxdepths:
regr = ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(max_depth=maxdepth,max_leaf_nodes=None)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
traing_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(maxdepths,traing_scores,label='Traning Score')
ax.plot(maxdepths,testing_scores,label='Testing Score')
ax.set_xlabel("max_depth")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc='best')
ax.set_ylim(-1,1.05)
plt.suptitle('GradientBoostingRegressor')
plt.show()
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = load_data_regression()
test_GradientBoostingRegressor_maxdepth(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
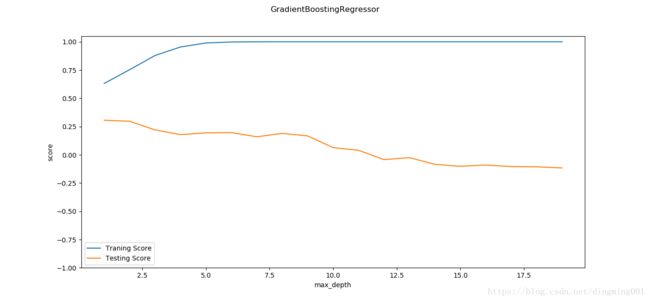
def test_GradientBoostingRegressor_learing(*data):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = data
fig = plt.figure()
learnings = np.linspace(0.01,1.0)
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
traing_scores = []
testing_scores = []
for learning in learnings:
regr = ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(learning_rate=learning)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
traing_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(learnings,traing_scores,label='Traning Score')
ax.plot(learnings,testing_scores,label='Testing Score')
ax.set_xlabel("max_depth")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc='best')
ax.set_ylim(-1,1.05)
plt.suptitle('GradientBoostingRegressor')
plt.show()
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = load_data_regression()
test_GradientBoostingRegressor_learing(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
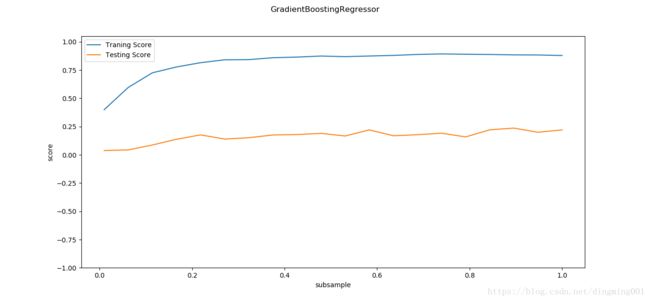
def test_GradientBoostingRegressor_subsample(*data):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = data
fig = plt.figure()
subsamples = np.linspace(0.01,1.0,num=20)
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
traing_scores = []
testing_scores = []
for subsample in subsamples:
regr = ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(subsample=subsample)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
traing_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(subsamples,traing_scores,label='Traning Score')
ax.plot(subsamples,testing_scores,label='Testing Score')
ax.set_xlabel("subsample")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc='best')
ax.set_ylim(-1,1.05)
plt.suptitle('GradientBoostingRegressor')
plt.show()
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = load_data_regression()
test_GradientBoostingRegressor_subsample(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
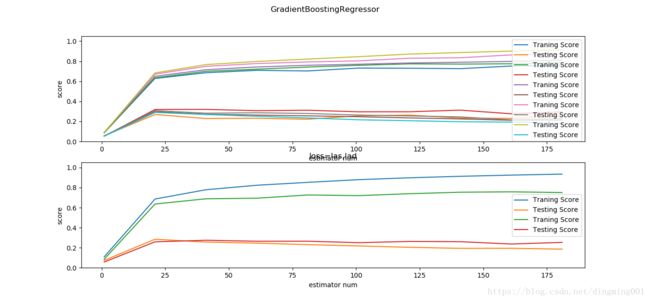
def test_GradientBoostingRegressor_loss(*data):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = data
fig = plt.figure()
nums = np.arange(1,200,step=20)
losses = ["ls","lad","huber"]
ax=fig.add_subplot(2,1,1)
alphas = np.linspace(0.01,1.0,endpoint=False,num=5)
for alpha in alphas:
traing_scores = []
testing_scores = []
for num in nums:
regr = ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(n_estimators=num,loss='huber',alpha=alpha)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
traing_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(nums,traing_scores,label='Traning Score')
ax.plot(nums,testing_scores,label='Testing Score')
ax.set_xlabel("estimator num")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc='best')
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
plt.suptitle('GradientBoostingRegressor')
ax=fig.add_subplot(2,1,2)
for loss in ['ls','lad']:
traing_scores = []
testing_scores = []
for num in nums:
regr = ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(n_estimators=num,loss=loss)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
traing_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(nums,traing_scores,label='Traning Score')
ax.plot(nums,testing_scores,label='Testing Score')
ax.set_xlabel("estimator num")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc='best')
ax.set_title("loss=las,lad")
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
plt.suptitle('GradientBoostingRegressor')
plt.show()
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = load_data_regression()
test_GradientBoostingRegressor_loss(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
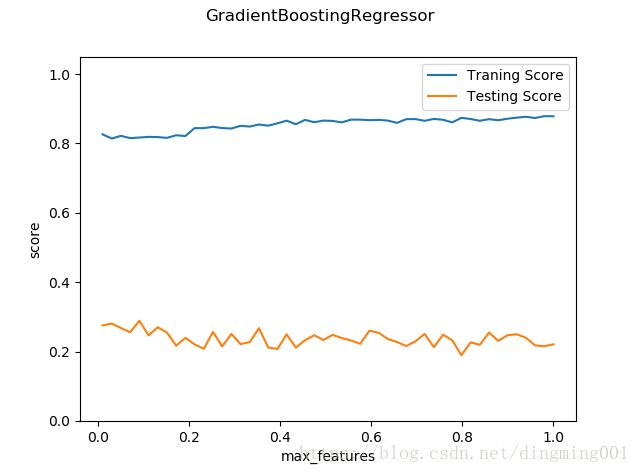
def test_GradientBoostingRegressor_max_features(*data):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = data
fig = plt.figure()
max_features = np.linspace(0.01,1.0)
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
traing_scores = []
testing_scores = []
for features in max_features:
regr = ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(max_features=features)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
traing_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(max_features,traing_scores,label='Traning Score')
ax.plot(max_features,testing_scores,label='Testing Score')
ax.set_xlabel("max_features")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc='best')
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
plt.suptitle('GradientBoostingRegressor')
plt.show()
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = load_data_regression()
test_GradientBoostingRegressor_max_features(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)