linux下libpcap的使用(抓包小程序)
(1)获取网络接口名字和掩码等信息
(2)捕获数据包(单个数据包和多个数据包两种情况)
(3)以太网数据报捕获
(4)ARP数据包捕获
(5)IP数据包捕获
(6)TCP数据包捕获
(7)UDP数据包捕获
(8)ICMP数据包捕获
环境fedora13,vim,gcc
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define max 1024
/*
typedef u_int32_t int_addr_t;
struct in_addr
{
int_addr_t s_addr;
};*/
int call(u_char *argument,const struct pcap_pkthdr* pack,const u_char *content)
{
int m=0,n;
const u_char *buf,*iphead;
u_char *p;
struct ether_header *ethernet;
struct iphdr *ip;
struct tcphdr *tcp;
struct udphdr *udp;
struct icmphdr *icmp;
buf=content;
printf("==================================================\n");
printf("The Frame is \n");
while(m< (pack->len))
{
printf("%02x",buf[m]);
m=m+1;
if(m%16==0)
printf("\n");
else
printf(":");
}
printf("\n");
printf("Grabbed packet of length %d\n",pack->len);
printf("Recieved at ..... %s",ctime((const time_t*)&(pack->ts.tv_sec)));
// printf("Ethernet address length is %d\n",ETHER_HDR_LEN);
ethernet=(struct ether_header *)content;
p=ethernet->ether_dhost;
n=ETHER_ADDR_LEN;
printf("Dest MAC is:");
do{
printf("%02x:",*p++);
}while(--n>0);
printf("\n");
p=ethernet->ether_shost;
n=ETHER_ADDR_LEN;
printf("Source MAC is:");
do{
printf("%02x:",*p++);
}while(--n>0);
printf("\n");
if(ntohs(ethernet->ether_type)==ETHERTYPE_IP)
{
printf("It's a IP packet\n");
ip=(struct iphdr*)(content+14);
printf("IP Version:%d\n",ip->version);
printf("TTL:%d\n",ip->ttl);
printf("Source address:%s\n",inet_ntoa(ip->saddr));
printf("Destination address:%s\n",inet_ntoa(ip->daddr));
printf("Protocol:%d\n",ip->protocol);
switch(ip->protocol)
{
case 6:
printf("The Transport Layer Protocol is TCP\n");
tcp=(struct tcphdr*)(content+14+20);
printf("Source Port:%d\n",ntohs(tcp->source));
printf("Destination Port:%d\n",ntohs(tcp->dest));
printf("Sequence Number:%u\n",ntohl(tcp->ack_seq));
break;
case 17:
printf("The Transport Layer Protocol is UDP\n");
udp=(struct udphdr*)(content+14+20);
printf("Source port:%d\n",ntohs(udp->source));
printf("Destination port:%d\n",ntohs(udp->dest));
break;
case 1:
printf("The Transport Layer Protocol is ICMP\n");
icmp=(struct icmphdr*)(content+14+20);
printf("ICMP Type:%d\n", icmp->type);
switch(icmp->type)
{
case 8:
printf("ICMP Echo Request Protocol\n");
break;
case 0:
printf("ICMP Echo Reply Protocol\n");
break;
default:
break;
}
break;
default:
break;
}
/* if(*iphead==0x45)
{
printf("Source ip :%d.%d.%d.%d\n",iphead[12],iphead[13],iphead[14],iphead[15]);
printf("Dest ip :%d.%d.%d.%d\n",iphead[16],iphead[17],iphead[18],iphead[19]);
}*/
// tcp= (struct tcp_header*)(iphead);
// source_port = ntohs(tcp->tcp_source_port);
// dest_port = ntohs(tcp->tcp_destination_port);
}
else if(ntohs (ethernet->ether_type) == ETHERTYPE_ARP)
{
printf("This is ARP packet.\n");
iphead=buf+14;
if (*(iphead+2)==0x08)
{
printf("Source ip:\t %d.%d.%d.%d\n",iphead[14],iphead[15],iphead[16],iphead[17]);
printf("Dest ip:\t %d.%d.%d.%d\n",iphead[24],iphead[25],iphead[26],iphead[27]);
printf("ARP TYPE: %d (0:request;1:respond)\n",iphead[6]);
}
}
return 0;
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
if(argc!=2)
{
printf("%s \n",argv[0]);
return 0;
}
pcap_t *handle;
pcap_if_t *alldev;
pcap_if_t *p;
char error[100];
struct in_addr net_ip_addr;
struct in_addr net_mask_addr;
struct ether_header *ethernet;
char *net_ip_string;
char *net_mask_string;
char *interface;
u_int32_t net_ip;
u_int32_t net_mask;
struct pcap_pkthdr pack;
const u_char *content;
int i=0,num;
if(pcap_findalldevs(&alldev,error)==-1)
{
printf("find all devices is error\n");
return 0;
}
for(p=alldev;p;p=p->next)
{
printf("%d:%s\n",++i,p->name);
if(p->description)
{
printf("%s\n",p->description);
}
}
if(i==1)
interface=p->name;
else
{
printf("please input which interface you want to use\n");
scanf("%d",&num);
if(num<1||num>i)
{
printf("interface is unavillible\n");
return 0;
}
for(p=alldev,i=1;i<=num;p=p->next,i++)
interface=p->name;
}
/*
if((interface=pcap_lookupdev(error))==NULL)
{
printf("%s\n",error);
return 0;
}*/
if((handle=pcap_open_live(interface,max,1,0,error))==NULL)
{
printf("%s\n",error);
return 0;
}
if(pcap_lookupnet(interface,&net_ip,&net_mask,error)==-1)
{
printf("%s\n",error);
return 0;
}
printf("Interface is:%s\n",interface);
net_ip_addr.s_addr=net_ip;
net_ip_string=inet_ntoa(net_ip_addr);
printf("The ip is:%s\n",net_ip_string);
net_mask_addr.s_addr=net_mask;
net_mask_string=inet_ntoa(net_mask_addr);
printf("The mask is:%s\n",net_mask_string);
pcap_loop(handle,atoi(argv[1]),call,NULL);
pcap_freealldevs(alldev);
return 1;
}
参数为要抓包的个数,抓包结果保存在save文件中。
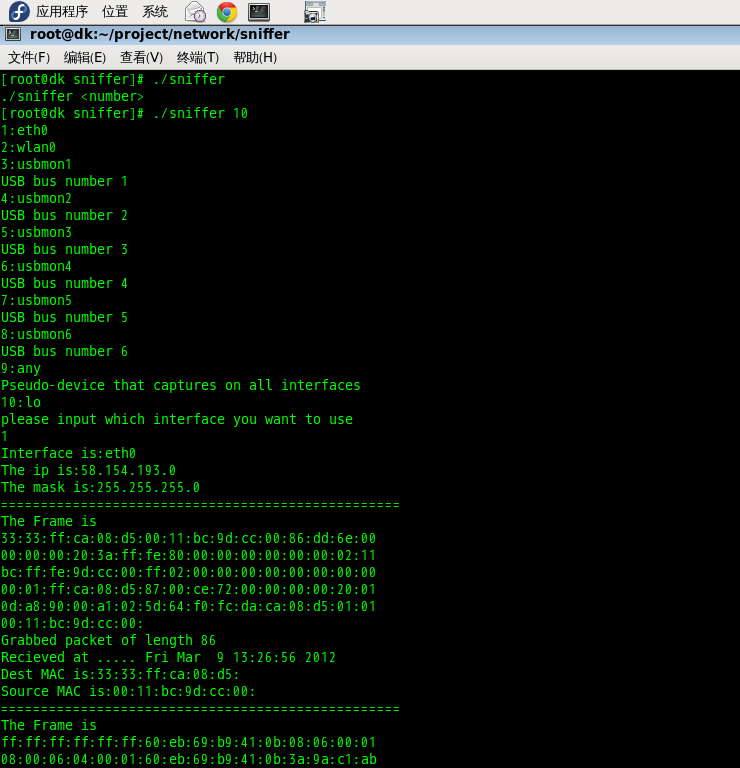
运行部分结果: