前言
近日在学习Binder驱动的binder_work时,发现了如下结构:
struct binder_work{
struct list_head entry;
enum {
...
} type;发现其中引入了list_head链表节点,如此一来binder_work类型也可以看做是个链表了。那么对binder_work也可以加入链表中了,以binder_enqueue_work_ilocked方法为例:
static void
binder_enqueue_work_ilocked(struct binder_work *work,
struct list_head *target_list)
{
BUG_ON(target_list == NULL);
BUG_ON(work->entry.next && !list_empty(&work->entry));
list_add_tail(&work->entry, target_list);//将binder_work的entry成员加入target_list中
}
由此先熟悉kernel中list的实现以及常用方法,以帮助学习Binder内容。
1. 内核链表初始化
1.1 创建型初始化
#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) }
#define LIST_HEAD(name) \
struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)这种方式构造方法十分巧妙,当调用LIST_HEAD(name)时,即为
struct list_head name = { &(name), &(name) }由于list_head结构体的定义为:
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next, *prev;
}; 即把next,prev都指向自身。
1.2 初始化模式型
个人觉得这种方式更容易看懂:
static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list)
{
WRITE_ONCE(list->next, list);//等同于list->net = list;
list->prev = list;
}INIT_LIST_HEAD初始化链表时,实质将头部节点的next以及prev都指向自己。
至于WRITE_ONCE第一次见,stackoverflow的解释是:
1.Read/write "tearing" : replacing a single memory access with many smaller ones. GCC may (and does!) in certain situations replace something like p = 0x01020304; with two 16-bit store-immediate instructions -instead of presumably placing the constant in a register and then a memory access, and so forth. WRITE_ONCE would allow us to say to GCC, "don't do that", like so: WRITE_ONCE(p, 0x01020304);
编译器有可能对读,写操作分割成多条指令,通过该WRITE_ONCE能够将保证这些操作只有一次。
2.C compilers have stopped guaranteeing that a word access is atomic. Any program which is non-race-free can be miscompiled with spectacular results. Not only that, but a compiler may decide to not keep certain values in registers inside a loop, leading to multiple references that can mess up code like this:
C的编译器不能够保证对一个word的访问是原子的。所有可导致多线程竞争的程序都有可能因为编译导致出现不同的结果。
详细的内容可以参考READ_ONCE and WRITE_ONCE
简单而言,有三点好处:
- 使代码更容易理解
- 代码规范的要求
- 能够检测数据竞争(data race)
2. 内核常用操作:
2.1 list_add
-
list_add(struct list_head new, struct list_head head); 将节点插入到链表头部
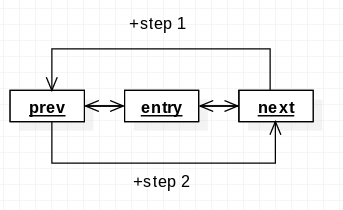
static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next)
{
if (!__list_add_valid(new, prev, next))
return;
next->prev = new;
new->next = next;
new->prev = prev;
WRITE_ONCE(prev->next, new);
}
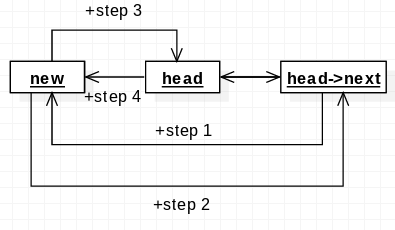
static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(new, head, head->next);
}2.2 list_add_tail
-
list_add_tail(struct list_head new, struct list_head head); 将节点插入到链表尾部
static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(new, head->prev, head);
}尾部加入节点与头部加入节点都是使用了__list_add方法。可以将__list_add参数理解为:
- 第一个为需要加入的节点,两者都为new;
- 第二个为所需要加入的位置的priv,首部加节点的参数为head,尾部加节点的参数为head->priv;
- 第三个为所需要加入的位置,首部加节点的参数为head->next,尾部加节点的位置为head
2.3 list_del
-
list_del(struct list_head *entry);删除一个节点,并将他的指针清除0
static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del_entry(entry);
entry->next = LIST_POISON1;//LIST_POISINO1和LIST_POISON2是两个无效的地址区
entry->prev = LIST_POISON2;
}
static inline void __list_del_entry(struct list_head *entry)
{
if (!__list_del_entry_valid(entry))
return;
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
}
static inline bool __list_del_entry_valid(struct list_head *entry)
{
return true;
}
static inline void __list_del(struct list_head * prev, struct list_head * next)
{
next->prev = prev;
WRITE_ONCE(prev->next, next);
}2.4 list_del_init
-
list_del_init(struct list_head *entry);删除一个节点,并将他的指针再次指向自己本身
static inline void list_del_init(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del_entry(entry);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(entry);
}2.5 list_replace
-
list_replace(struct list_head *old, struct list_head *new);替换链表中的某个节点, old需要被替换的节点, new新的节点
static inline void list_replace(struct list_head *old,
struct list_head *new)
{
new->next = old->next;
new->next->prev = new;
new->prev = old->prev;
new->prev->next = new;
}2.6 list_replace_init
-
list_replace_init(struct list_head *old, struct list_head *new);和上面的区别在于,把替换之后的老的节点进行初始化
static inline void list_replace_init(struct list_head *old,
struct list_head *new)
{
list_replace(old, new);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(old);
}2.7 list_is_last
-
int list_is_last(const struct list_head *list, const struct list_head *head);测试一个节点是否为链表尾节点,list是要测试的节点,head是一个链表头
static inline int list_is_last(const struct list_head *list,
const struct list_head *head)
{
return list->next == head;
}2.8 list_empty
-
int list_empty(const struct list_head *head);测试链表是否为空
static inline int list_empty(const struct list_head *head)
{
return READ_ONCE(head->next) == head;
}