Github地址:https://github.com/LYhiha/wcexe
1.项目相关要求
实现一个统计程序,它能正确统计程序文件中的字符数、单词数、行数,以及还具备其他扩展功能,并能够快速地处理多个文件。
具体功能要求:
基本功能列表:
wc.exe -c file.c //返回文件 file.c 的字符数(实现)
wc.exe -w file.c //返回文件 file.c 的词的数目 (实现)
wc.exe -l file.c //返回文件 file.c 的行数(实现)
扩展功能:
wc.exe -s 递归处理目录下符合条件的文件。(实现)
wc.exe -a 返回更复杂的数据(代码行 / 空行 / 注释行)。(实现)
2.解题思路
2.遇到的困难及解决方法
- 困难描述
1.字符数、单词数、注释行的统计。
2.对main函数传入各项参数处理不好。
3.对递归处理不熟练。
- 做过哪些尝试
1.重新复习了字符串的处理方法。
2.尝试了从main方法传参,但不熟练使用,最后用键盘输入方式输入命令。
3.使用 exe4j 软件把 jar 包转成 .exe 文件
- 是否解决
1.程序基本功能实现,但又瑕疵
- 有何收获
1.重新复习了IO流String类的使用。
2.尝试了从mian方法传参数。
3.首次把代码推上github。
3.解题思路
每个方法实现一个功能,然后在main方法中使用输入流从控制台输入命令,用switch语句判断输入的命令,调用相应的方法,方法需要传入文件路径的参数也控制台输入。
4.设计实现过程
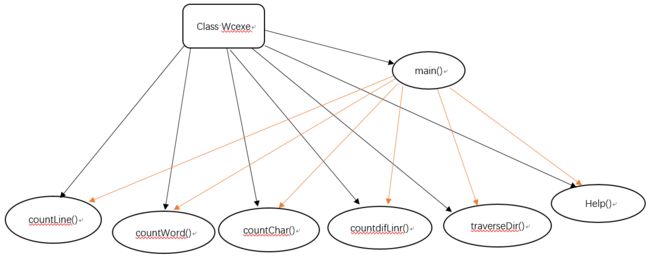
共有一个类Wcexe,类中有6个方法分别实现不同的功能,由main()方法调用。
5.代码说明
1.main:方法:创建输入流从控制台输入命令,对命令进行处理调用相应方法,并循环处理输入的命令。
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
Wcexe wc = null;
while(true) {
System.out.println("请输入命令:(输入wc.exe help获取帮助)");
BufferedReader keyReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String keyInput = keyReader.readLine();
if("-q".equals(keyInput)) {
break;
}
String[] command = keyInput.trim().split(" ");
if(command.length<3) {
}else {
path = command[2];
wc = new Wcexe();
}
switch (command[1]) {
case "-c":
wc.countChar();
break;
case "-w":
wc.countWord();
break;
case "-l":
wc.countLine();
break;
case"-a":
wc.countdifLine();
break;
case"-s":
wc.traverseDir(wc.filepath);
break;
case"help":
Wcexe.help();
break;
default:
System.out.println("请输入正确命令,输入wc.exe help 获取帮助.............");
break;
}
}
}catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("请检查输入命令与文件路径是否正确,重启程序输入wc.exe help 获取帮助.............");
}
}
2.help()方法:打印帮助信息
public static void help() {
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("wc.exe -l 文件名(完整路径) 获取行数");
System.out.println("wc.exe -c 文件名(完整路径)获取字符数");
System.out.println("wc.exe -w 文件名(完整路径) 获取单词数");
System.out.println("wc.exe -a 文件名(完整路径)获取空行,注释行,代码行数");
System.out.println("wc.exe -s 文件夹(完整路径)遍历处理文件夹");
System.out.println(" ");
}
3.countLine()方法:计算行数,使用BufferedReaderd缓冲输入流readLine()方法读取文件,每读一行,行数+1。
public void countLine() throws IOException {
//初始化属性
int lineNum = 0;
FileReader inputReader = new FileReader(filepath);
BufferedReader bufReader = new BufferedReader(inputReader);
String line ;
while( ( line = bufReader.readLine() ) != null) {
lineNum++;
}
System.out.println("总行数:"+lineNum);
bufReader.close();
}
4.countChar()方法:计算字符数,每读取一行存入一字符串,将一行按照空格分割并存进一字符串数组,用for循环获取每个字符串长度并相加。
public void countChar() throws IOException {
int charNum = 0;
FileReader inputReader = new FileReader(filepath);
BufferedReader bufReader = new BufferedReader(inputReader);
String line ;
while( ( line = bufReader.readLine() ) != null) {
String [ ] str = line.split(" ");
for(int i=0;i
5.countWord()方法:计算单词个数,每读取一行,将非英文字符都替换成空格,再以空格分割存进一字符串数组,for循环遍历数组,如果符合给定正则表达式的便将单词数加1。
public void countWord() throws IOException {
int wordNum = 0;
FileReader inputReader = new FileReader(filepath);
BufferedReader bufReader = new BufferedReader(inputReader);
String line ;
while( ( line = bufReader.readLine() ) != null) {
String[] str1=null;
if(!"".equals(line)) {
str1 = line.replaceAll("[^A-Za-z]"," ").trim().split("\\s+");
for(int j = 0;j
6.countdifLine()方法:计算空行、注释行、空行,每读一行用if语句判断,另设置flag标记/* */注释块地开始。
//计算空行、注释行、代码行
public void countdifLine() throws IOException {
int blankLine = 0;
int codeLine = 0;
int annotateLine = 0;
FileReader inputReader = new FileReader(filepath);
BufferedReader bufReader = new BufferedReader(inputReader);
String line;
boolean flag = false;//用于标记/* */注释行
while( ( line = bufReader.readLine() ) != null) {
if(line.trim().startsWith("/*") && line.trim().endsWith("*/")) {
annotateLine++;
}else if(line.trim().startsWith("/*") && !line.trim().endsWith("*/")) {
annotateLine++;
flag = true;
}else if(flag == true&&!line.trim().endsWith("*/")) {
annotateLine++;
}else if(flag == true && line.trim().endsWith("*/")) {
annotateLine++;
flag = false;
}else if(line.trim().startsWith("//") || line.trim().startsWith("}//")) {
annotateLine++;
}else if(line.trim().matches("")) {
blankLine++;
}else{
codeLine++;
}
}
bufReader.close();
System.out.println("代码行"+codeLine);
System.out.println("注释行"+annotateLine);
System.out.println("空 行"+blankLine);
}
7.traverseDir()方法:递归遍历文件夹并处理文件
//遍历文件夹
public void traverseDir(File filepath) {
File[] files;
files = filepath.listFiles();
if(files != null) {
for(File file : files) {
if(file.isFile()) {
path=file.getAbsolutePath();
System.out.println("文件名:"+path);
Wcexe wc1=new Wcexe();
try {//处理遍历到的文件
wc1.countChar();
wc1.countWord();
wc1.countLine();
wc1.countdifLine();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else if(file.isDirectory()) {
traverseDir(file.getAbsoluteFile());//递归
}
}
}
}
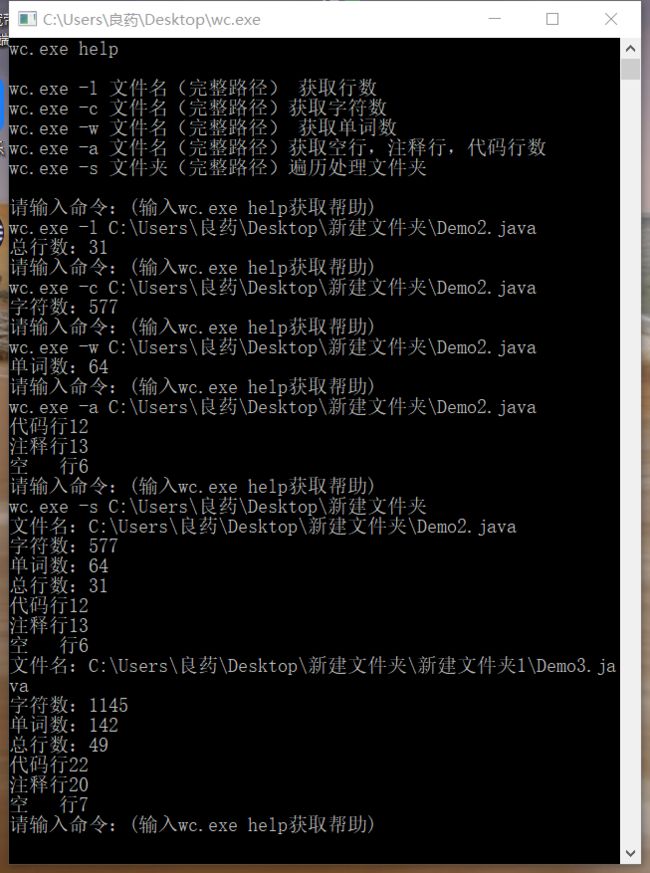
6.测试结果
运行结果:
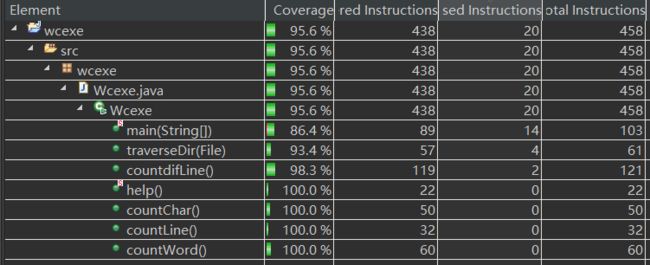
代码覆盖率:
7.PSP
| PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
| Planning |
计划 |
700 | 765 |
| · Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
10 | 5 |
| Development |
开发 |
150 | 160 |
| · Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
90 | 120 |
| · Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
30 | 25 |
| · Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
15 | 15 |
| · Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
30 | 30 |
| · Design |
· 具体设计 |
60 | 70 |
| · Coding |
· 具体编码 |
120 | 150 |
| · Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
30 | 30 |
| · Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
60 | 90 |
| Reporting |
报告 |
45 | 60 |
| · Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
30 | 20 |
| · Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
10 | 15 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
20 | 25 |
| 合计 |
700 | 765 |
8.项目小结
这此的项目开发让我接触了很多新的概念方法,之前写课设时i都是想到神么写什么,以至于写的过程很乱,代码结构混乱,这次有稍稍改变。还有这次初步了解了,单元测试,回归测试,PSP等概念方法,以后尽可能要更多地运用。