timer_create()建立定时器剖析
在程序开发中经常需要使用到定时器
常用的是while(true)与sleep(int)组合的形式简单方便
如果对应用程序精度要求比较低可以直接使用sleep();
本文总结另外一种方法:使用timer_create()函数
其中利用了LINUX系统的信号量机制,注册信号量处理函数
比如信号量:SIGALRM,SIGUSR1
计时精度要求不高的情况下
使用signal函数配合setitimer实现了一个简易的定时器
使用SIGUSR1信号量定时
这里使用SIGUSR1信号量进行测试:
//signalDemo.cpp
//compile : gcc signalDemo.cpp -o testSignal -lrt
#include
#include 为了方便查看程序运行结果,打印中输出时间
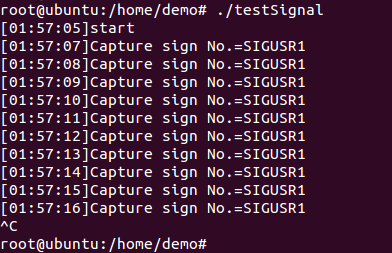
定时器的开始延时2秒;
使用SIGALRM信号量定时
上面程序中使用了信号量SIGUSR1;
如果使用信号量SIGALRM;
(对 CLOCK_REALTIMER来说,默认信号就是SIGALRM)
sleep()函数使用的就是实时时钟CLOCK_REALTIMER
所以使用信号值SIGALRM会中断sleep(int second)函数的休眠;
//timercreate_demo.cpp
#include
#include 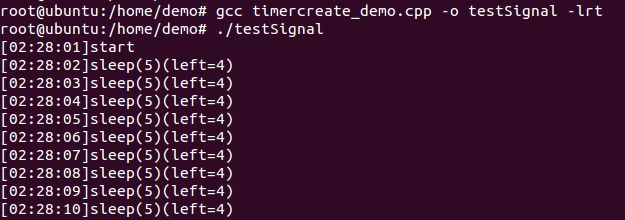
因为timer_settime()中定时器间隔时间为1秒
于是sleep(5)每次都被打断不能按时休眠,剩余4秒未能执行;
SIGALRM信号量不同线程的影响
因为休眠sleep(unsigned int)为线程内操作
所以如果不同线程,信号量SIGALRM是不能中断sleep();
编写程序进行测试
//timercreate_demo.cpp
#include
#include
void SignHandler(int iSignNo);
void testTimerSign();
void printTime();
void *function(void *arg);
int main() {
pthread_t thread1;
pthread_create(&thread1,NULL,function,(char*)"111");
testTimerSign();
while(true);
return 0;
}
void SignHandler(int iSignNo){
if(iSignNo == SIGUSR1){
printf("Capture sign no : SIGUSR1\n");
}else if(SIGALRM == iSignNo){
//printf("Capture sign no : SIGALRM\n");
}else{
printf("Capture sign no:%d\n",iSignNo);
}
}
void testTimerSign(){
struct sigevent evp;
struct itimerspec ts;
timer_t timer;
int ret;
evp.sigev_value.sival_ptr = &timer;
evp.sigev_notify = SIGEV_SIGNAL;
evp.sigev_signo = SIGALRM;
signal(evp.sigev_signo, SignHandler);
ret = timer_create(CLOCK_REALTIME, &evp, &timer);
if(ret) {
perror("timer_create");
}
ts.it_interval.tv_sec = 1;
ts.it_interval.tv_nsec = 0;
ts.it_value.tv_sec = 1;
ts.it_value.tv_nsec = 0;
printTime();
printf("start\n");
ret = timer_settime(timer, 0, &ts, NULL);
if(ret) {
perror("timer_settime");
}
}
void printTime(){
struct tm *cursystem;
time_t tm_t;
time(&tm_t);
cursystem = localtime(&tm_t);
char tszInfo[2048] ;
sprintf(tszInfo, "%02d:%02d:%02d",
cursystem->tm_hour,
cursystem->tm_min,
cursystem->tm_sec);
printf("[%s]",tszInfo);
}
void *function(void *arg){
char *m;
m = (char *)arg;
while(true) {
while(true){
int left = sleep(3);
printTime();
printf("sleep(3)(left=%d)\n", left);
}
}
}
可以看出,在主线程的定时器中的信号量SIGALRM是无法中断子线程thread1的休眠;
函数手册说明
查看函数手册中关于接口的使用:
1查看sigevent的说明
root@ubuntu:/home# man sigevent
NAME
sigevent - structure for notification from asynchronous routines
// 由异步线程通知
SYNOPSIS
union sigval { /* Data passed with notification */
int sival_int; /* Integer value */
void *sival_ptr; /* Pointer value */
};
struct sigevent {
int sigev_notify; /* Notification method */
int sigev_signo; /* Notification signal */
union sigval sigev_value; /* Data passed with
notification */
void (*sigev_notify_function) (union sigval);
/* Function used for thread
notification (SIGEV_THREAD) */
void *sigev_notify_attributes;
/* Attributes for notification thread
(SIGEV_THREAD) */
pid_t sigev_notify_thread_id;
/* ID of thread to signal (SIGEV_THREAD_ID) */
};
DESCRIPTION
The sigevent structure is used by various APIs
about an event (e.g., completion of an asynchronous request,
expiration of a timer, or the arrival of a message).
// 结构体sigevent在各个API中用来描述线程中事件通知的方式
The definition shown in the SYNOPSIS is approximate:
as part of a union. Programs should only employ those
fields relevant to the value specified in sigev_notify.
// sigevent结构体中的一些字段会被定义为共同体的一部分
The sigev_notify field specifies how notification is to be performed
. This field can have one of the following values:
CONFORMING TO
POSIX.1-2001.
SEE ALSO
timer_create(2),...
这里建议查看timer_create(2)的使用说明
root@ubuntu:/home# man sigevent
NAME
sigevent - structure for notification from asynchronous routines
// 由异步线程通知
SYNOPSIS
union sigval { /* Data passed with notification */
int sival_int; /* Integer value */
void *sival_ptr; /* Pointer value */
};
struct sigevent {
int sigev_notify; /* Notification method */
int sigev_signo; /* Notification signal */
union sigval sigev_value; /* Data passed with
notification */
void (*sigev_notify_function) (union sigval);
/* Function used for thread
notification (SIGEV_THREAD) */
void *sigev_notify_attributes;
/* Attributes for notification thread
(SIGEV_THREAD) */
pid_t sigev_notify_thread_id;
/* ID of thread to signal (SIGEV_THREAD_ID) */
};
DESCRIPTION
The sigevent structure is used by various APIs to describe the way
a process is to be notified about an event
(e.g., completion of an asynchronous request, expiration of a
timer, or the arrival of a message).
// 结构体sigevent在各个API中用来描述线程中事件通知的方式
The definition shown in the SYNOPSIS is approximate:
some of the fields in the sigevent structure may be defined as part of a union.
Programs should only employ those fields
relevant to the value specified in sigev_notify.
// sigevent结构体中的一些字段会被定义为共同体的一部分
The sigev_notify field specifies how notification is to be performed.
This field can have one of the following values:
CONFORMING TO
POSIX.1-2001.
SEE ALSO
timer_create(2),...
这里建议查看timer_create(2)的使用说明
root@ubuntu:/home# man 2 timer_create
NAME
timer_create - create a POSIX per-process timer
SYNOPSIS
#include
#include
int timer_create(clockid_t clockid, struct sigevent *sevp,
timer_t *timerid);
Link with -lrt.
Feature Test Macro Requirements for glibc (see feature_test_macros(7)):
timer_create(): _POSIX_C_SOURCE >= 199309L
DESCRIPTION
timer_create() creates a new per-process interval timer.
// 创建一个新的计时器
The ID of the new timer is returned in the buffer pointed to by timerid,
// 返回新的计时器所指向的缓存区的指针
which must be a non-NULL pointer.
This ID is unique within the process, until the timer is deleted.
// ID是唯一值,直到计时器销毁
The new timer is initially disarmed.
// 新的计时器初始默认状态为安静状态
RETURN VALUE
On success, timer_create() returns 0,
and the ID of the new timer is placed in *timerid.
On failure, -1 is returned, and errno is set to indicate the error.
VERSIONS
This system call is available since Linux 2.6.
// 在Linux 2.6 版本之后使用
SEE ALSO
clock_gettime(2), setitimer(2), timer_delete(2), timer_settime(2),
pthreads(7), sigevent(7), signal(7), time(7) .......
EXAMPLE
Program Source
// 使用timer_create API编写的demo源码
在timer_create说明有:
头文件:
signal.h
time.h
编译说明:
Link with -lrt.
推荐一种简单的计时器
来自http://www.cnblogs.com/wenqiang/p/5525261.html
//timercreate_demo.cpp
#include
#include
#include