Java基础回顾---IO(字节流)
IO流是Java基础中很重要的一个知识点,由于IO流的种类繁多,所以在此对其知识点进行整理,方便自己的回顾,总结。
1.IO流概述
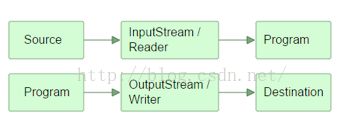
IO是Input和Output的缩写,即输入、输出。其实所谓的输入、输出都是针对运行的程序(CPU、内存)来说的,输入就是向程序所在的内存输入、 输出就是从内存中向外输出,即输入和输出的参照为为程序(内存),这样就比较容易理解IO,IO关注的是原始数据的读取和到目标媒介的输出。流是一组有顺序的,有起点和终点的字节集合,是对数据传输的总称和抽象。流的本质是数据传输(计算机中实际上数据的流动是通过电路,而上面流动的则是电流,电流的电位有低位与高位,即数字的0与1位。从程序的观点来说,通常会将数据目的地(例如内存)与来源(例如文件)之间的数据流动抽象化为一个流(Stream),而其中流动的则是位数据)。
Java IO中根据数据传输特性将其抽象为各种类,方便直观的进行数据操作,这些都在java.io包下。IO流根据处理数据的不同分为字符流和字节流。根据数据流向的不同,又可分为输入流和输出。按照功能的不同,又可以分为节点流和处理流,节点流是直接从一个源读写数据的流(流没有经过包装和修饰),处理流是在对节点流封装的基础上的一种流,例如FileInputStream是一个节点流,可以直接从文件读取,BufferedInputStream包装在FileInputStream外侧,使其具有缓冲功能,就是处理流。
本章节我们先来详细的讲解一下字节流。
2.字节流
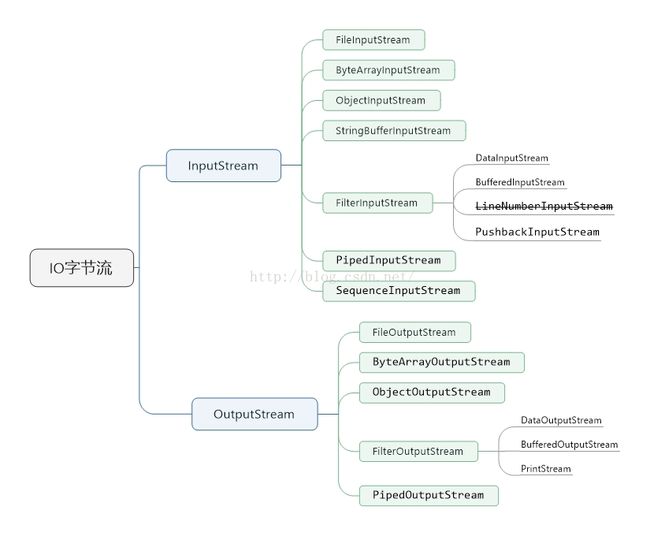
字节流的关系结构图,如下所示:
2.1 InpuStream | OutputStream
InputStream是所有输入字节流的父类,它是一个抽象类,它有最常三个方法:即read()、read(byte[] b)、read(byte[] b , int off , int len )。read()对流进行逐个字节的读取,返回的int是字节的int表达方式,返回 0 到 255 范围内的 int 字节值,如果因为已经到达流末尾而没有可用的字节,则返回值 -1 ,由于一次只会读取一个字节,所以效率很低。read(byte[])从输入流中读取一定数量的字节,并将其存储在缓冲区数组 b 中。以整数形式返回实际读取的字节数。OutputStream是所有输出字节流的父类,也是一个抽象类。
2.2 FileInputStream | FileOutputStream
/**
* 文件流
*
*/
public static void testFileIO() throws IOException{
FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream(new File("F:\\dandan.txt"));
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream(new File("F:\\benben.txt"));
int len = 0;
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
while((len = fin.read(b)) != -1){ //读,使用read(byte[] b)方法
fout.write(b, 0, len); //写
}
fout.flush();
fin.close();
fout.close();
}2.3 ByteArrayInputStream | ByteArrayOutputStream
/**
* ByteArrayInputStream :使用的场景比较少见,在此不再举例
* ByteArrayOutputStream:可以将文件中的数据输出到字节数组中
*/
public static void testByteArrayIO() throws IOException{
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("F:\\dandan.txt"));
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len=fis.read(b)) != -1){
bos.write(b, 0, len);
}
System.out.println(new String(bos.toByteArray()));
fis.close();
bos.close();
}2.4 ObjectInputStream | ObjectOutputStream
/**
* 对象流
* ObjectOutputStream和ObjectInputStream所要读写的对象的类必须实现了Serializable接口
* 注意:对象中的transient和static类型成员变量不会被读取和写入
*/
public static void testObjectIO() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{
Person p = new Person();
p.setId("1001");
p.setName("lixiang");
p.setAge(23);
p.setSex("man");
ObjectOutputStream objout = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("F:\\Person.obj"));
objout.writeObject(p); //将对象写入输出流
objout.flush();
objout.close();
ObjectInputStream objin = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("F:\\Person.obj"));
Person p1 = (Person) objin.readObject(); //从输入流中读取数据
System.out.println(p1.toString());
objin.close();
}
class Person implements Serializable{
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String id ;
private String name;
private int age;
private transient String sex ;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", sex=" + sex + "]";
}
}
2.5 DataInputStream | DataOutputStream
/**
* 数据流:
* DataInputStream 和 DataOutputStream是IO流中的装饰流,继承了FilterInputStream和FilterOutStream
* 允许按照java的基础数据类型读写流中的数据,使用起来比较方便
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void testDataIO() throws IOException{
DataOutputStream dout = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("F:\\data.txt")));
dout.writeInt(100); //写入整数
dout.writeUTF("good good study"); //写入UTF字符串
dout.writeDouble(20.16);
dout.flush();
dout.close();
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("F:\\data.txt")));
System.out.println(dis.readInt()); //按照写入顺序读出
System.out.println(dis.readUTF());
System.out.println(dis.readDouble());
dis.close();
}2.6 BufferedInputStream | BufferedOutputStream
/**
* 缓冲流
*
*/
public static void testBufferedIO() throws IOException{
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("F:\\dandan.txt")));
BufferedOutputStream fout = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("F:\\benben.txt")));
int len = 0;
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
while((len = bis.read(b)) != -1){ //读,使用read(byte[] b)方法
fout.write(b, 0, len); //写
}
fout.flush();
bis.close();
fout.close();
}在上面,总结了几种常见的字节流的使用方法,其实在大部分场景下,我们很少单独使用某个类来实现IO操作,平时都是几个类合起来使用。Java io本身也是采用了装饰者模式,以后有时间会回顾有关装饰者模式的知识总结。