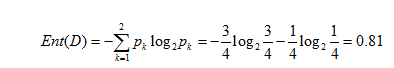王家林人工智能AI第19课:使用决策树在Social Network上构建汽车销售推荐系统老师微信13928463918
王家林人工智能AI第19课:使用决策树在Social Network上构建汽车销售推荐系统老师微信13928463918
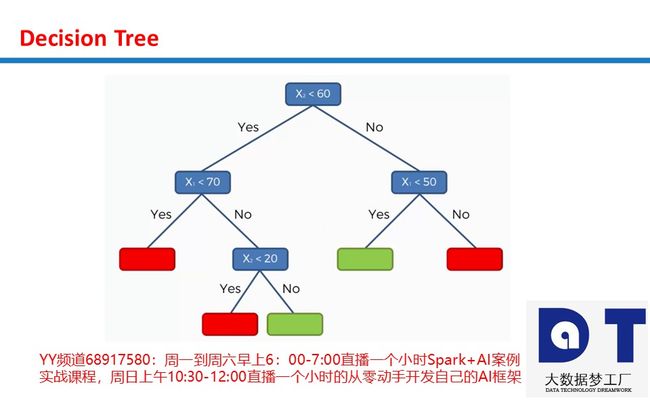
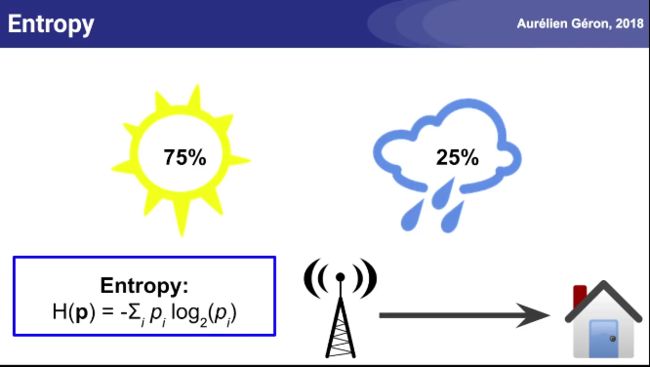
决策树中的熵entropy:
classifier = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion = 'entropy', random_state = 0)熵(Entropy)这个概念最早出现在热力学中,是由德国物理学家及数学家鲁道夫·尤利乌斯·埃马努埃尔·克劳修斯所提出,它的物理意思表示该体系的混乱程度,简单地说,如果该体系下的分子运动杂乱程度增加,该体系的熵也随着增加。 在1948年,信息论之父克劳德·艾尔伍德·香农提出了信息熵的概念, 用来描述随机事件的“混乱”程度,也即该随机事件所有结果所带来平均不确定性。
信息熵的计算就是信息量的数学期望。
信息熵的特点:
(1) 信息熵与事件的可能性数量有关,在概率均等的情况下,存在的可能越多,信息熵越大,信息也约不确定;
假如我们现在投掷一枚硬币,正面和反面的概率都是均等的1/2,那么投掷一枚硬币的信息熵为:
假如我们现在改为投掷一枚骰子,并且每个数字出现的概率都是均等的,为1/6,那么投掷一枚骰子的信息熵为:
(2) 信息熵与事件的概率分布情况有关,概率分布越平均,信息熵越大,当所有概率均等的情况下,信息熵达到最大;
我们知道投掷一枚正反面出现概率都均等为1/2的硬币,信息熵为1.而现在我们刚好有一枚质量分布不均的硬币,它出现正面的概率为3/4,而出现反面的概率只有1/4,那么投掷一枚这样硬币的信息熵为:
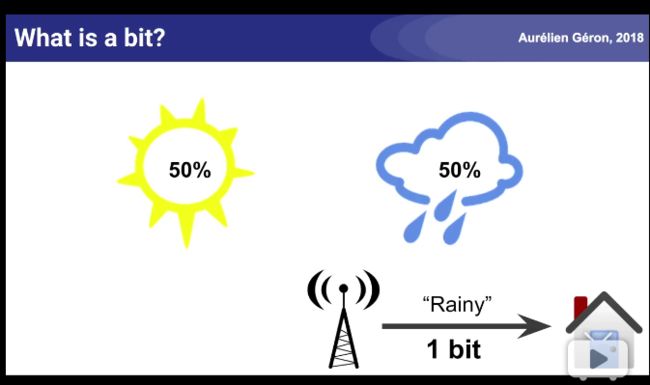
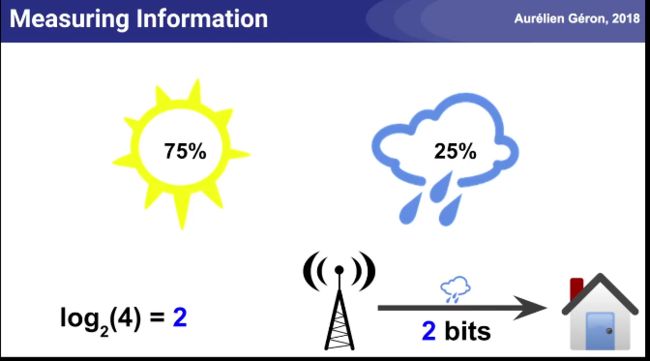
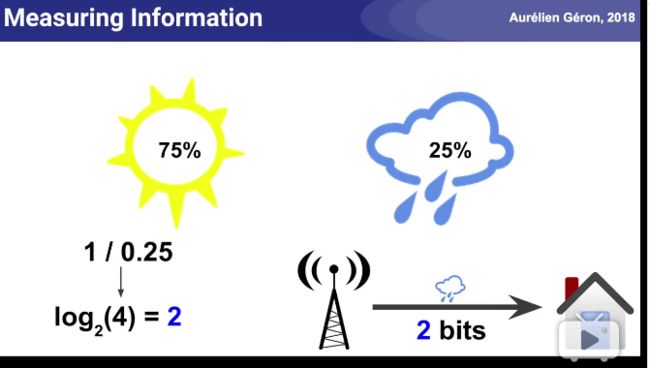
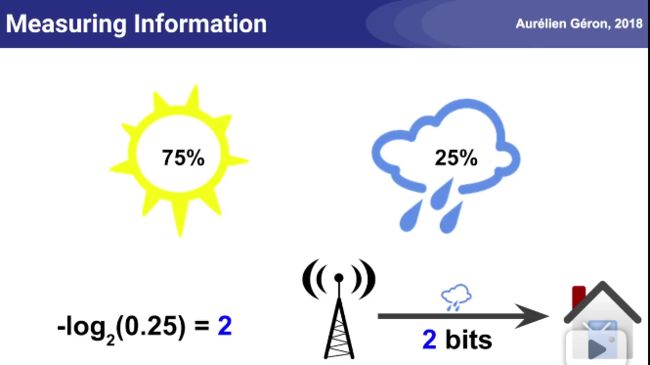
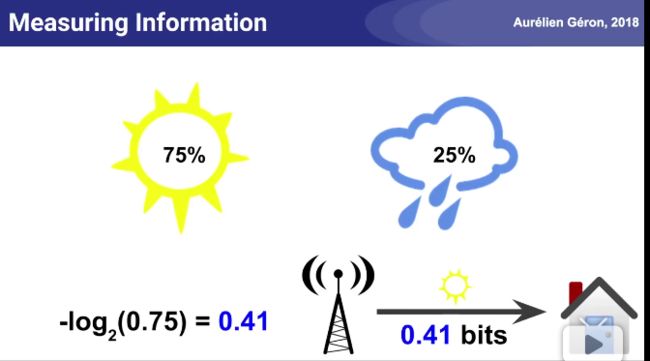
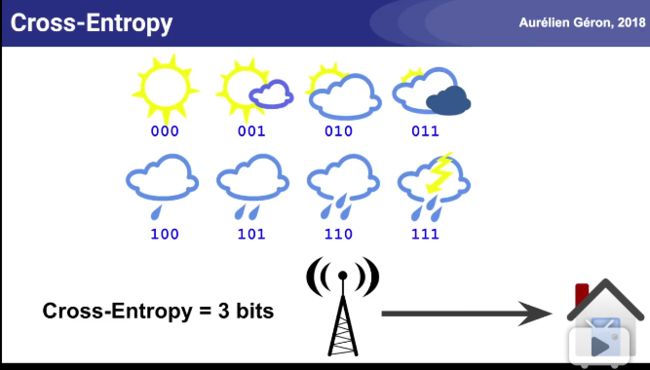
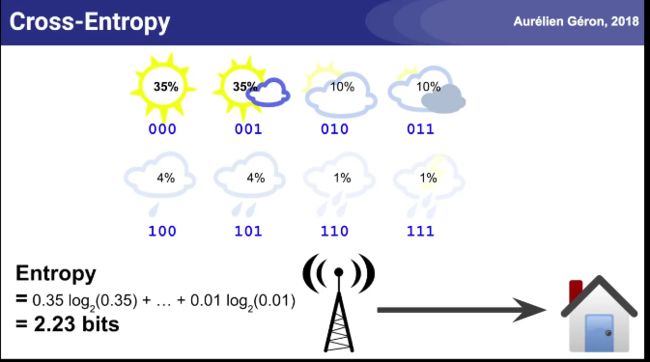
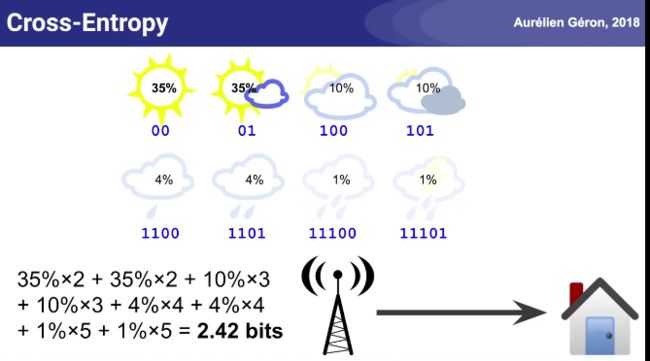
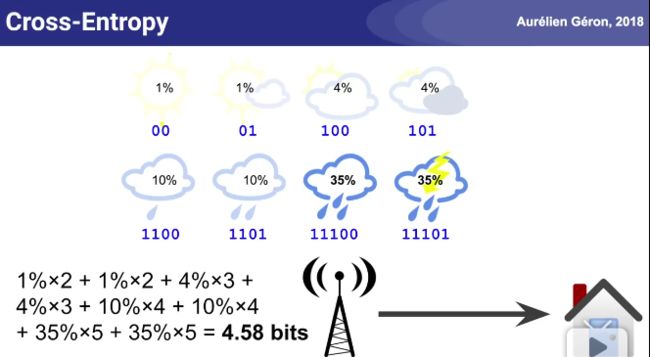
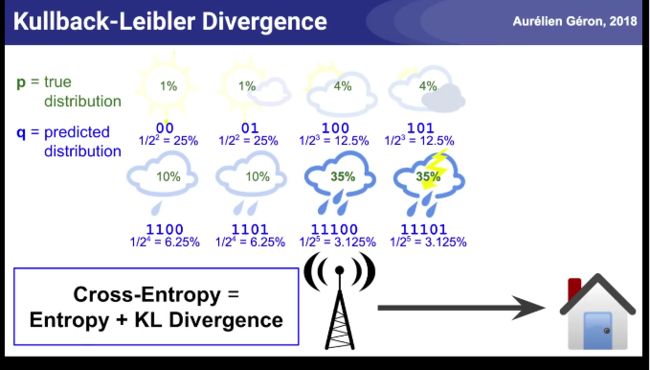
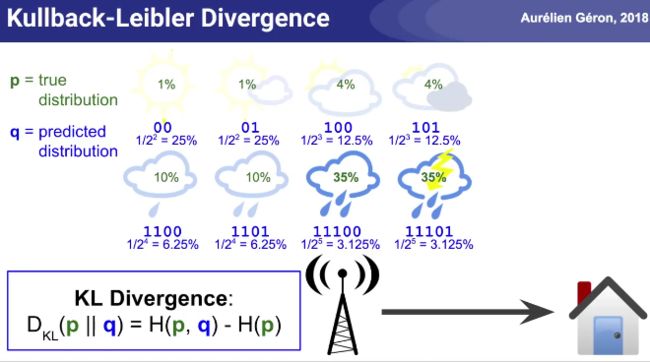
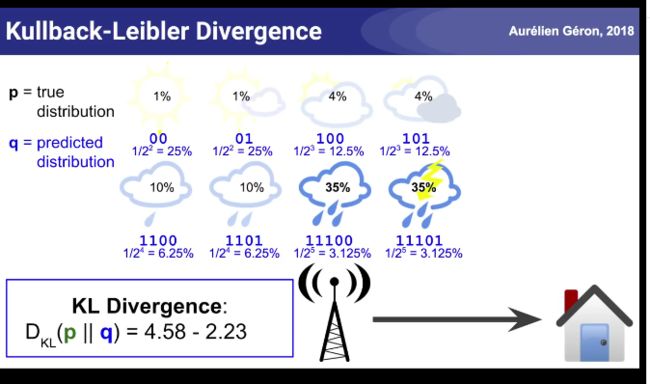
天气预报的信息熵例子:
本节课代码:
# Decision Tree Classification
# Importing the libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
# Importing the dataset
dataset = pd.read_csv('Social_Network_Ads.csv')
X = dataset.iloc[:, [2, 3]].values
y = dataset.iloc[:, 4].values
# Splitting the dataset into the Training set and Test set
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.25, random_state = 0)
# Feature Scaling
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
sc = StandardScaler()
X_train = sc.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = sc.transform(X_test)
# Fitting Decision Tree Classification to the Training set
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
classifier = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion = 'entropy', random_state = 0)
classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Predicting the Test set results
y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test)
# Making the Confusion Matrix
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
# Visualising the Training set results
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
X_set, y_set = X_train, y_train
X1, X2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(start = X_set[:, 0].min() - 1, stop = X_set[:, 0].max() + 1, step = 0.01),
np.arange(start = X_set[:, 1].min() - 1, stop = X_set[:, 1].max() + 1, step = 0.01))
plt.contourf(X1, X2, classifier.predict(np.array([X1.ravel(), X2.ravel()]).T).reshape(X1.shape),
alpha = 0.75, cmap = ListedColormap(('red', 'green')))
plt.xlim(X1.min(), X1.max())
plt.ylim(X2.min(), X2.max())
for i, j in enumerate(np.unique(y_set)):
plt.scatter(X_set[y_set == j, 0], X_set[y_set == j, 1],
c = ListedColormap(('red', 'green'))(i), label = j)
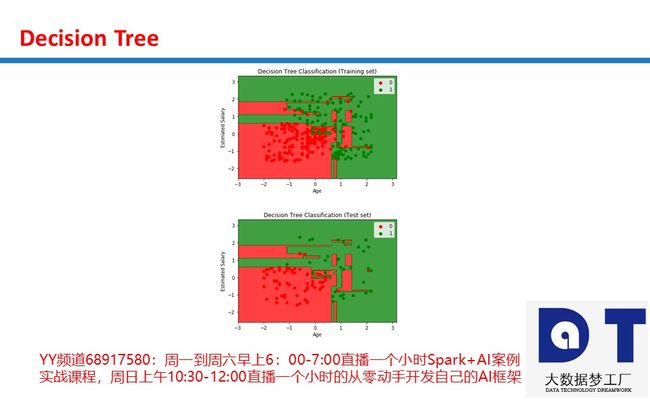
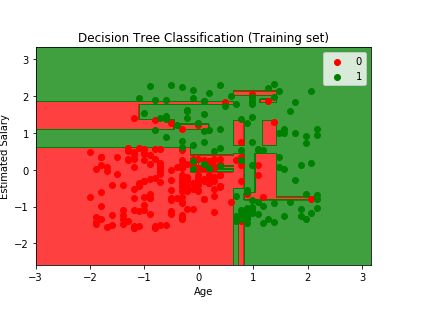
plt.title('Decision Tree Classification (Training set)')
plt.xlabel('Age')
plt.ylabel('Estimated Salary')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# Visualising the Test set results
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
X_set, y_set = X_test, y_test
X1, X2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(start = X_set[:, 0].min() - 1, stop = X_set[:, 0].max() + 1, step = 0.01),
np.arange(start = X_set[:, 1].min() - 1, stop = X_set[:, 1].max() + 1, step = 0.01))
plt.contourf(X1, X2, classifier.predict(np.array([X1.ravel(), X2.ravel()]).T).reshape(X1.shape),
alpha = 0.75, cmap = ListedColormap(('red', 'green')))
plt.xlim(X1.min(), X1.max())
plt.ylim(X2.min(), X2.max())
for i, j in enumerate(np.unique(y_set)):
plt.scatter(X_set[y_set == j, 0], X_set[y_set == j, 1],
c = ListedColormap(('red', 'green'))(i), label = j)
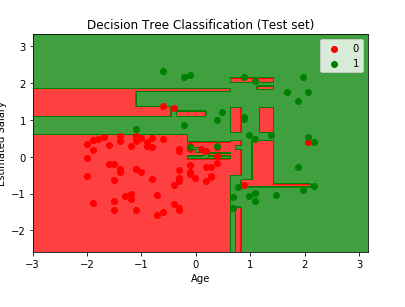
plt.title('Decision Tree Classification (Test set)')
plt.xlabel('Age')
plt.ylabel('Estimated Salary')
plt.legend()
plt.show()运行结果:
3980元团购原价19800元的AI课程,团购请加王家林老师微信13928463918
基于王家林老师独创的人工智能“项目情景投射”学习法,任何IT人员皆可在无需数学和Python语言的基础上的情况下3个月左右的时间成为AI技术实战高手:
1,五节课(分别在4月9-13号早上YY视频直播)教你从零起步(无需Python和数学基础)开发出自己的AI深度学习框架,五节课的学习可能胜过你五年的自我摸索;
2,30个真实商业案例代码中习得AI(从零起步到AI实战专家之路):10大机器学习案例、13大深度学习案例、7大增强学习案例(本文档中有案例的详细介绍和案例实现代码截图);
3,100天的涅槃蜕变,平均每天学习1个小时(周一到周六早上6:00-7:00YY频道68917580视频直播),周末复习每周的6个小时的直播课程(报名学员均可获得所有的直播视频、全部的商业案例完整代码、最具阅读价值的AI资料等)。