CS224n NLP句法分析依赖解析深度学习作业笔记
CS224n NLP句法分析依赖解析深度学习之作业笔记
句法分析的基础内容请参阅CS224n笔记6 句法分析
http://www.hankcs.com/nlp/cs224n-dependency-parsing.html,本文不再赘述。
CS224n assignment2 作业q2_parser_transitions.py学习:
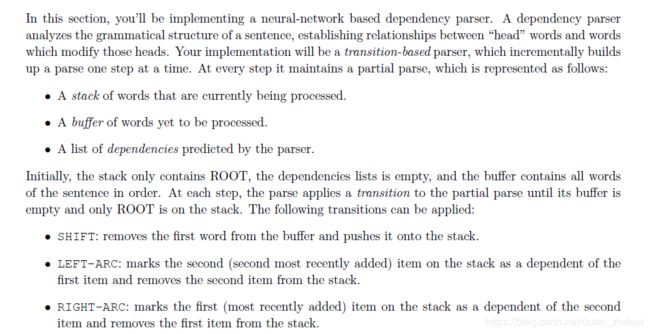
依存句法分析Arc-standard的数据结构: stack,buffer, dependencies 。 (s, b, A)由Stack栈(一个单词需经历入栈、出栈2次操作),buffer缓冲区(队列),依存关系A构成。相应的转换操作包括S,LA,RA 。
q2_parser_transitions.py的代码例子:
SHIFT S操作:["ROOT", "the"], ["cat", "sat"], [] S操作转换为:("ROOT", "the", "cat"), ("sat",), ()
LEFT-ARC LA操作:["ROOT", "the", "cat"], ["sat"], []LA操作转换为: ("ROOT", "cat",), ("sat",), (("cat", "the"),))
RIGHT-ARC RA操作:["ROOT", "run", "fast"], [], [] RA操作转换为: ("ROOT", "run",), (), (("run", "fast"),))PartialParse(sentence).parse 句子解析
#输入要解析的句子: sentence = ["parse", "this", "sentence"]
#传入进行转换解析的操作列表:dependencies = PartialParse(sentence).parse(["S", "S", "S", "LA", "RA", "RA"])
#对解析以后的依存关系排序: dependencies = tuple(sorted(dependencies))
#期望解析成功的依存关系: expected = (('ROOT', 'parse'), ('parse', 'sentence'), ('sentence', 'this'))入站和出站的过程如下:
1,"parse", "this", "sentence" 经过"S", "S", "S" 操作依次入栈,栈中的元素为:ROOT,"parse", "this", "sentence"
2, 进行"LA"操作:栈中"this", "sentence"这2个单词进行PK,sentence指向this,this出栈,栈中的元素为:ROOT,"parse", "sentence"
3, 进行"RA"操作:栈中"parse", "sentence"这2个单词进行PK, parse指向sentence,sentence出栈,栈中的元素为:ROOT,"parse"
4,进行"RA"操作:栈中ROOT,"parse"这2个单词进行PK,ROOT指向parse,parse出栈,栈中的元素为:ROOT
"parse this sentence"句子中的单词经过几轮PK,生成依存关系的结果如下:('ROOT', 'parse'), ('parse', 'sentence'), ('sentence', 'this')
minibatch_parse多个句子解析:
class DummyModel类:
先把句子放到buffer缓存区队列里面,DummyModel predict方法创建转换操作:如果队列中仍有元素,就执行shift操作,将队列中的元素一个个送到stack栈中准备PK;如果队列中无元素了,意味着队列中的元素都入站了要进行PK,如栈中第一个元素(最先入栈的元素是right,DummyModel设置为RA,否则为LA操作(left的情况))。
例如:前2个句子组成一个批次进行解析:
第一句话:["right", "arcs", "only"],
第二句话:["right", "arcs", "only", "again"]
["right", "arcs", "only"]通过DummyModel类的 predict方法创建的转换操作为:[S S S RA RA RA],依次将"right", "arcs", "only"入站,栈中的元素为:ROOT,"right", "arcs", "only", 栈中的第一个元素是right,因此,DummyModel依次生成RA转换操作, 'arcs'指向 'only', only出栈, 'right'指向 'arcs',"arcs"出栈,'ROOT'指向 'right',"right"出栈,最终得到的句子依存关系为:('arcs', 'only'), ('right', 'arcs'), ('ROOT', 'right')。
["right", "arcs", "only", "again"]通过DummyModel类的 predict方法创建的转换操作为:[S S S RA RA RA RA],依次将"right", "arcs", "only", "again"入站,栈中的元素为:ROOT,"right", "arcs", "only", "again", 栈中的第一个元素是right,因此,DummyModel依次生成RA转换操作,"again", "only", "arcs","right"依次出栈,最终得到的句子依存关系为:('only', 'again'), ('arcs', 'only'), ('right', 'arcs'), ('ROOT', 'right')。
第二批次的两句话["left", "arcs", "only"],["left", "arcs", "only", "again"],栈中的第一个元素是left,因此执行的都是LA操作。
["left", "arcs", "only"]通过DummyModel类的 predict方法创建的转换操作为:[S S S LA LA LA],依次将"left", "arcs", "only"入站,栈中的元素为:ROOT,"left", "arcs", "only", 栈中的第一个元素是left,因此,DummyModel依次生成LA转换操作, 'only'指向 'arcs', arcs出栈,栈中的元素为:ROOT,"left","only",然后 'only'指向 'left',"left"出栈, 栈中的元素为:ROOT, "only" , 'only'指向 'ROOT',"ROOT"出栈,最终得到的句子依存关系为: ('only', 'arcs'), ('only', 'left'), ('only', 'ROOT')
#输入要解析的多个句子列表:sentences = [["right", "arcs", "only"],
["right", "arcs", "only", "again"],
["left", "arcs", "only"],
["left", "arcs", "only", "again"]]
#批次解析: deps = minibatch_parse(sentences, DummyModel(), 2) DummyModel()模型中提供要转换的动作。2是批次大小batch_size
#期望解析的依存关系: deps[0]:(('ROOT', 'right'), ('arcs', 'only'), ('right', 'arcs')))
deps[1]: (('ROOT', 'right'), ('arcs', 'only'), ('only', 'again'), ('right', 'arcs')))
deps[2]: (('only', 'ROOT'), ('only', 'arcs'), ('only', 'left')))
deps[3]: (('again', 'ROOT'), ('again', 'arcs'), ('again', 'left'), ('again', 'only')))q2_parser_transitions.py代码如下:
class PartialParse(object):
def __init__(self, sentence):
"""Initializes this partial parse.
Your code should initialize the following fields:
self.stack: The current stack represented as a list with the top of the stack as the
last element of the list.
self.buffer: The current buffer represented as a list with the first item on the
buffer as the first item of the list
self.dependencies: The list of dependencies produced so far. Represented as a list of
tuples where each tuple is of the form (head, dependent).
Order for this list doesn't matter.
The root token should be represented with the string "ROOT"
Args:
sentence: The sentence to be parsed as a list of words.
Your code should not modify the sentence.
"""
# The sentence being parsed is kept for bookkeeping purposes. Do not use it in your code.
self.sentence = sentence
### YOUR CODE HERE
self.stack = ['ROOT']
self.buffer = sentence[:]
self.dependencies = []
### END YOUR CODE
def parse_step(self, transition):
"""Performs a single parse step by applying the given transition to this partial parse
Args:
transition: A string that equals "S", "LA", or "RA" representing the shift, left-arc,
and right-arc transitions.
"""
### YOUR CODE HERE
if transition == "S":
self.stack.append(self.buffer[0])
self.buffer.pop(0)
elif transition == "LA":
self.dependencies.append((self.stack[-1], self.stack[-2]))
self.stack.pop(-2)
else:
self.dependencies.append((self.stack[-2], self.stack[-1]))
self.stack.pop(-1)
### END YOUR CODE
def parse(self, transitions):
"""Applies the provided transitions to this PartialParse
Args:
transitions: The list of transitions in the order they should be applied
Returns:
dependencies: The list of dependencies produced when parsing the sentence. Represented
as a list of tuples where each tuple is of the form (head, dependent)
"""
for transition in transitions:
self.parse_step(transition)
return self.dependencies
def minibatch_parse(sentences, model, batch_size):
"""Parses a list of sentences in minibatches using a model.
Args:
sentences: A list of sentences to be parsed (each sentence is a list of words)
model: The model that makes parsing decisions. It is assumed to have a function
model.predict(partial_parses) that takes in a list of PartialParses as input and
returns a list of transitions predicted for each parse. That is, after calling
transitions = model.predict(partial_parses)
transitions[i] will be the next transition to apply to partial_parses[i].
batch_size: The number of PartialParses to include in each minibatch
Returns:
dependencies: A list where each element is the dependencies list for a parsed sentence.
Ordering should be the same as in sentences (i.e., dependencies[i] should
contain the parse for sentences[i]).
"""
### YOUR CODE HERE
# refer: https://github.com/zysalice/cs224/blob/master/assignment2/q2_parser_transitions.py
partial_parses = [PartialParse(s) for s in sentences]
unfinished_parse = partial_parses
while len(unfinished_parse) > 0:
minibatch = unfinished_parse[0:batch_size]
# perform transition and single step parser on the minibatch until it is empty
while len(minibatch) > 0:
transitions = model.predict(minibatch)
for index, action in enumerate(transitions):
minibatch[index].parse_step(action)
minibatch = [parse for parse in minibatch if len(parse.stack) > 1 or len(parse.buffer) > 0]
# move to the next batch
unfinished_parse = unfinished_parse[batch_size:]
dependencies = []
for n in range(len(sentences)):
dependencies.append(partial_parses[n].dependencies)
### END YOUR CODE
return dependencies
def test_step(name, transition, stack, buf, deps,
ex_stack, ex_buf, ex_deps):
"""Tests that a single parse step returns the expected output"""
pp = PartialParse([])
pp.stack, pp.buffer, pp.dependencies = stack, buf, deps
pp.parse_step(transition)
stack, buf, deps = (tuple(pp.stack), tuple(pp.buffer), tuple(sorted(pp.dependencies)))
assert stack == ex_stack, \
"{:} test resulted in stack {:}, expected {:}".format(name, stack, ex_stack)
assert buf == ex_buf, \
"{:} test resulted in buffer {:}, expected {:}".format(name, buf, ex_buf)
assert deps == ex_deps, \
"{:} test resulted in dependency list {:}, expected {:}".format(name, deps, ex_deps)
print ("{:} test passed!".format(name))
def test_parse_step():
"""Simple tests for the PartialParse.parse_step function
Warning: these are not exhaustive
"""
test_step("SHIFT", "S", ["ROOT", "the"], ["cat", "sat"], [],
("ROOT", "the", "cat"), ("sat",), ())
test_step("LEFT-ARC", "LA", ["ROOT", "the", "cat"], ["sat"], [],
("ROOT", "cat",), ("sat",), (("cat", "the"),))
test_step("RIGHT-ARC", "RA", ["ROOT", "run", "fast"], [], [],
("ROOT", "run",), (), (("run", "fast"),))
def test_parse():
"""Simple tests for the PartialParse.parse function
Warning: these are not exhaustive
"""
sentence = ["parse", "this", "sentence"]
dependencies = PartialParse(sentence).parse(["S", "S", "S", "LA", "RA", "RA"])
dependencies = tuple(sorted(dependencies))
expected = (('ROOT', 'parse'), ('parse', 'sentence'), ('sentence', 'this'))
assert dependencies == expected, \
"parse test resulted in dependencies {:}, expected {:}".format(dependencies, expected)
assert tuple(sentence) == ("parse", "this", "sentence"), \
"parse test failed: the input sentence should not be modified"
print ("parse test passed!")
class DummyModel:
"""Dummy model for testing the minibatch_parse function
First shifts everything onto the stack and then does exclusively right arcs if the first word of
the sentence is "right", "left" if otherwise.
"""
def predict(self, partial_parses):
return [("RA" if pp.stack[1] is "right" else "LA") if len(pp.buffer) == 0 else "S"
for pp in partial_parses]
def test_dependencies(name, deps, ex_deps):
"""Tests the provided dependencies match the expected dependencies"""
deps = tuple(sorted(deps))
assert deps == ex_deps, \
"{:} test resulted in dependency list {:}, expected {:}".format(name, deps, ex_deps)
def test_minibatch_parse():
"""Simple tests for the minibatch_parse function
Warning: these are not exhaustive
"""
sentences = [["right", "arcs", "only"],
["right", "arcs", "only", "again"],
["left", "arcs", "only"],
["left", "arcs", "only", "again"]]
deps = minibatch_parse(sentences, DummyModel(), 2)
test_dependencies("minibatch_parse", deps[0],
(('ROOT', 'right'), ('arcs', 'only'), ('right', 'arcs')))
test_dependencies("minibatch_parse", deps[1],
(('ROOT', 'right'), ('arcs', 'only'), ('only', 'again'), ('right', 'arcs')))
test_dependencies("minibatch_parse", deps[2],
(('only', 'ROOT'), ('only', 'arcs'), ('only', 'left')))
test_dependencies("minibatch_parse", deps[3],
(('again', 'ROOT'), ('again', 'arcs'), ('again', 'left'), ('again', 'only')))
print ("minibatch_parse test passed!")
if __name__ == '__main__':
test_parse_step()
test_parse()
test_minibatch_parse()
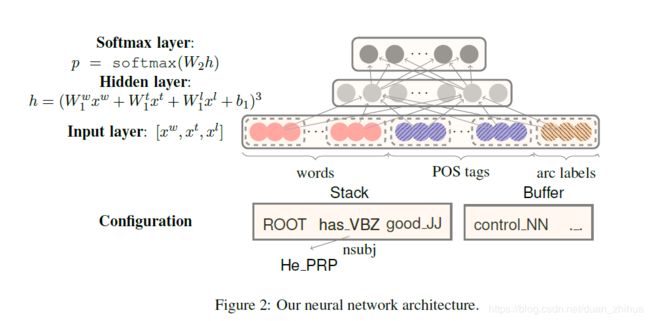
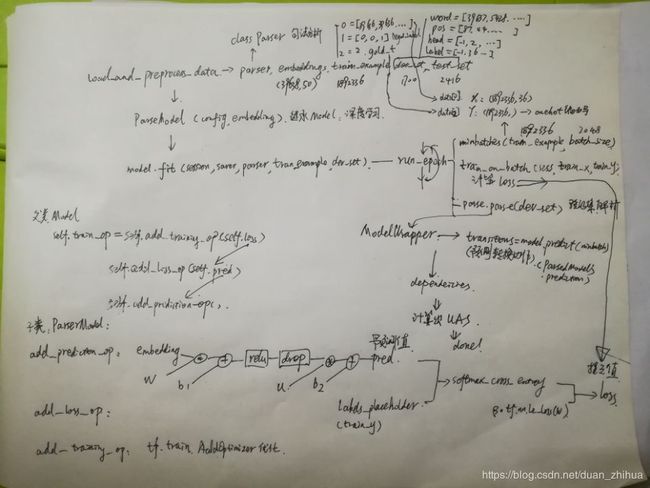
CS224n assignment2 作业q2_parser_model.py学习:
本次作业实现一个基于神经网络的依存句法分析器,使用softmax分类器预测正确的转换操作。
深度学习网络结构如下:
斯坦福大学提供了句法分析的数据源文件,数据文件是人工标注形成的。
训练集数据源train.conll记录如下:
.......
1 Ms. _ PROPN NNP _ 2 compound _ _
2 Haag _ PROPN NNP _ 3 nsubj _ _
3 plays _ VERB VBZ _ 0 root _ _
4 Elianti _ PROPN NNP _ 3 dobj _ _
5 . _ PUNCT . _ 3 punct _ _
.......文件中的每个句子以空行分隔,每个句子从1开始编号,句子中的每个单词一行,1行有10列,参考网上资料,每列的定义如下:
0. ID:单词索引,每个新句子从1开始的整数;可能是多个词的标记的范围。
1. FORM:Word单词或标点符号。
2. LEMMA:词形的词条或词干。
3. UPOSTAG:从Google通用POS标签的修订版本中提取的通用词性标签。
4. XPOSTAG:语言特定的词性标签;下划线如果不可用。
5. FEATS:来自通用特征清单或来自定义的语言特定扩展的形态特征列表;下划线如果不可用。
6. HEAD:当前令牌的头部,它是ID的值或零(0)。
7. DEPREL:通用斯坦福与HEAD(root iff HEAD = 0)的依赖关系或者定义的语言特定的子类型之一。
8. DEPS:二级依赖项列表(head-deprel对)。
9. MISC:任何其他注释。
第4列词性解释的说明,例如:
NNP: noun, proper, singular 名词,单数
VBZ: verb, present tense,3rd person singular 动词,一般现在时第三人称单数
第7列依赖关系的说明,例如:
nsubj : nominal subject,名词主语
dobj : direct object直接宾语
punct: punctuation标点符号
验证集dev.conll的格式如下:
1 Influential _ ADJ JJ _ 2 amod _ _
2 members _ NOUN NNS _ 10 nsubj _ _
3 of _ ADP IN _ 6 case _ _
4 the _ DET DT _ 6 det _ _
5 House _ PROPN NNP _ 6 compound _ _
6 Ways _ PROPN NNPS _ 2 nmod _ _
7 and _ CONJ CC _ 6 cc _ _
8 Means _ PROPN NNP _ 9 compound _ _
9 Committee _ PROPN NNP _ 6 conj _ _
10 introduced _ VERB VBD _ 0 root _ _
......测试集的格式:
1 No _ ADV DT _ 7 discourse _ _
2 , _ PUNCT , _ 7 punct _ _
3 it _ PRON PRP _ 7 nsubj _ _
4 was _ VERB VBD _ 7 cop _ _
5 n't _ PART RB _ 7 neg _ _
6 Black _ PROPN JJ _ 7 compound _ _
7 Monday _ PROPN NNP _ 0 root _ _
8 . _ PUNCT . _ 7 punct _ _
.......en-cw词向量的格式:
......
''alabama'' -1.99981 -0.240157 -0.597358 0.282017 1.90753 -0.1756 -0.412226 1.82043 0.459125 -0.875625 -1.48324 0.527355 0.23079 0.0563458 -0.434202 -0.23701 -0.461489 -1.0859 -1.2836 -1.6587 -0.324906 -0.359099 -0.383356 0.302803 -0.356627 1.05563 0.125849 0.947028 -0.384615 0.661425 2.19244 -1.07033 0.564551 -1.36917 0.819228 -0.47918 1.64099 0.538061 -0.299839 -1.13484 1.59743 0.271243 0.333574 -1.06259 0.473146 0.802993 1.24637 -0.0298284 -1.16564 -1.55788
''angel'' -0.826045 -0.0102042 -0.27299 1.40068 -0.283138 0.935602 -0.43502 -0.402933 -1.40289 -0.25715 2.02683 -0.228278 1.59202 1.08971 0.501361 -0.56396 0.537273 -0.706518 -1.75152 0.351134 1.13729 -0.441985 -0.324955 -0.124531 1.78251 -0.520803 -1.4151 -1.35754 -0.601823 1.2412 -0.111517 -0.262058 -0.404138 -1.52515 -0.713882 0.13644 -1.43873 -0.846919 0.561326 -0.343231 0.228051 -0.348782 -0.316699 -1.37365 -0.655157 1.68428 1.99759 -2.06295 -0.481767 -0.283251
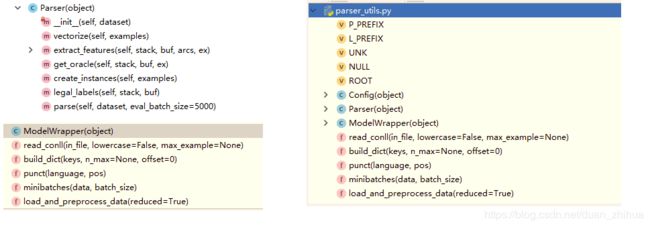
...... q2_parser_model.py 主要包括两方面的内容(句子依存特征提取,神经网络模型):
-
句子依存关系特征的提取:单词特征、词性特征、依存关系的特征。
句子依存分析涉及的类及方法:
- 深度学习神经网络的构建、训练、预测。
神经网络涉及的类:
q2_parser_model.py 重要的数据结构:
训练数据集、验证数据集、测试数据集,如:
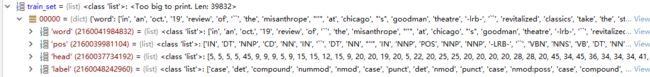
train_set = read_conll(os.path.join(config.data_path, config.train_file),
lowercase=config.lowercase)train_set 列表的大小为39832,train_set的每一个元素是一个字典,
如:Ms. Haag plays Elianti. 的记录
1 Ms. _ PROPN NNP _ 2 compound _ _
2 Haag _ PROPN NNP _ 3 nsubj _ _
3 plays _ VERB VBZ _ 0 root _ _
4 Elianti _ PROPN NNP _ 3 dobj _ _
5 . _ PUNCT . _ 3 punct _ _read_conll方法对Ms. Haag plays Elianti. 解析如下:
{'word': ['ms.', 'haag', 'plays', 'elianti', '.'], #记录句子的单词内容
'pos': ['NNP', 'NNP', 'VBZ', 'NNP', '.'], #记录词性
'head': [2, 3, 0, 3, 3], #记录head索引位置
'label': ['compound', 'nsubj', 'root', 'dobj', 'punct']} #记录句法分析的内容
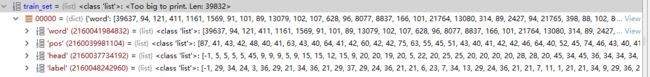
调用parser.vectorize(train_set)实现train_set训练集向量化,train_set训练集进行向量化转换的数据结构如下,将word、pos、label中的每个元素从token标识编号字典tok2id中查找对应的编号,转换为数字的格式,将word、pos、head、label对应的编号列表作为字典返回。 vec_examples.append({'word': word, 'pos': pos, 'head': head, 'label': label}) 。vectorize向量化以后的train_set 列表的大小为39832,train_set的每一个元素是一个字典,如:
{'word': [39637, 553, 13081, 3339, 21767, 90], #记录句子的单词内容
'pos': [87, 42, 42, 54, 42, 47], #记录词性
'head': [-1, 2, 3, 0, 3, 3], #记录head索引位置
'label': [-1, 29, 26, 0, 12, 11]} #记录句法分析的内容
然后,train_set 经过create_instances转换为train_examples数据结构。train_set 是train.conll中的句子集合(39832个句子),train.conll的数据记录数是989859,不计分隔的空行数,每个单词需入栈、出栈,因此转换以后的train_set的大小为1892336,train_set的每一个元素的第0个元素是36个特征值,第2个元素是转换的操作(0: 'L', 1: 'R', 2: 'S'),第2个元素是在神经网络模型中需进行预测的目标值。
Parser解析类中的数据结构,如:
token标识与编号的对应关系tok2id,id2tok:
设置各个label的前缀:
P_PREFIX = '
:'
L_PREFIX = '
UNK = '
NULL = '
ROOT = '
1.tok2id 加入句法分析的内容:将label转换成标签编码的格式:L_PREFIX前缀 + 标签: 编号
{'
tok2id 的句法分析中NULL的情况。如:'
2.tok2id 加入词性解释的内容: 将pos转换成pos编码的格式: P_PREFIX 前缀 + 词性: 编号
如:在tok2id句法分析之后增加词性的内容:
'
:NN': 40, '
:IN': 41, '
:NNP': 42, '
:DT': 43, '
:JJ': 44, '
:NNS': 45, '
:,': 46, '
:.': 47, '
:CD': 48, '
:RB': 49, '
:VBD': 50, '
:VB': 51, '
:CC': 52, '
:TO': 53, '
:VBZ': 54, '
:VBN': 55, '
:PRP': 56, '
:VBG': 57, '
:VBP': 58, '
:MD': 59, '
:POS': 60, '
:PRP$': 61, '
:$': 62, '
:``': 63, "
:''": 64, '
::': 65, '
:WDT': 66, '
:JJR': 67, '
:NNPS': 68, '
:RP': 69, '
:WP': 70, '
:WRB': 71, '
:JJS': 72, '
:RBR': 73, '
:-RRB-': 74, '
:-LRB-': 75, '
:EX': 76, '
:RBS': 77, '
:PDT': 78, '
:FW': 79, '
:WP$': 80, '
:#': 81, '
:UH': 82, '
:SYM': 83, '
:LS': 84}
tok2id 的词性解析中UNK,NULL,ROOT的情况,如'
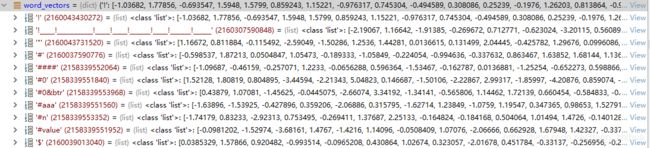
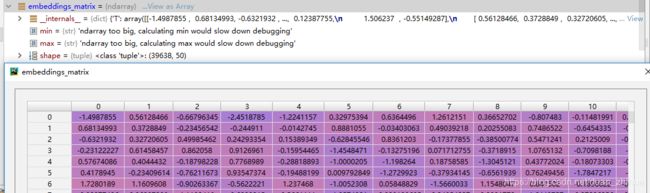
: : : 3.tok2id 加入单词word的内容: 将word转换成word编码的格式: word : 编号 4.遍历tok2id,将token与编号的关系转换为编号与token的关系: id2tok 转换操作trans的数据结构: 转换操作trans 词向量word_vectors, 从en-cw.txt文件中加载词向量(130000),key值是单词,value值是50维的词向量 : 词向量矩阵embeddings_matrix:随机数初始化词向量矩阵 embeddings_matrix :shape为(39638, 50) , 39638是n_tokens的大小;循环遍历tok2id中的每一个单词,如果token(或者小写的token)在word_vectors词向量字典里面,那么获取word_vectors词向量50维的数据作为词向量矩阵embeddings_matrix对应索引的词向量参数。embeddings_matrix[i] = word_vectors[token]。 q2_parser_model.py 关键的算法及模型: (1)句子依存关系特征提取算法: parser_utils.py的get_oracle方法传入stack,buffer,ex三个参数,其中ex为训练集向量化以后的数据,stack为栈,buffer为缓冲区队列,get_oracle方法返回一个转换操作(0为left-arc,1为right-arc,2为SHIFT)。如果栈的长度小于2,返回self.n_trans - 1;如果栈中大于2个元素,分别获取栈顶第一个元素i0和第二个元素i1,获取ex训练集head列表对应的head值,ex训练集label句法对应的值,根据各种情况判断返回哪一种转换操作。 parser_utils.py的extract_features方法根据stack, buf, arcs, ex参数提取特征向量,分别获取栈stack、缓冲区buf中ex['word']的前3个单词,获取单词的特征向量(3+ 3),如果为空,使用NULL填充;分别获取栈stack、缓冲区buf中ex['pos']的前3个单词,获取词性的特征向量(3+ 3),如果为空,使用P_NULL填充;合计3+3+3+3=12个。 然后循环遍历 for i in range(2),分两种情况: 2,如果i大于等于栈的长度,(栈中小于2个元素) parser_utils.py的create_instances方法产生训练集,返回all_instances,其中的每个元素的格式(self.extract_features(stack, buf, arcs, ex), legal_labels, gold_t)。instances的每一个元素是一个元组,元组的第一个元素是句子特征,第二个元素是legal_labels如[0, 0, 1];第三个元素是gold_t,使用get_oracle(self, stack, buf, ex)方法根据ex中head返回一个转换操作,用数字代替,0为left-arc,1为right-arc,2为SHIFT。 (2)深度学习神经网络模型: 神经网络模型使用全连接神经网络加sotfmax分类(句法依存特征==>嵌入词向量==>Relu(xW + b1)==>Dropout ===>pred(h_dropU + b2)===>softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits ==> tf.nn.l2_loss ===> tf.train.AdamOptimizer) 1,load_and_preprocess_data函数返回解析器,词嵌入矩阵,训练集(特征提取),验证集,测试集 2,创建模型类实例model = ParserModel(config, embeddings),其中ParserModel继承Model 4,测试集解析: test_set 的大小为1700,sentences 列表的每一个元素sentence是一个列表,元素为每句长度的range列表,如: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37] ,sentence_id_to_idx 是一个系统编号对应一个句子编号: {2351680779720: 0, 2351659480264: 1, 2351680782280: 2, 2351680781448: 3, ......dependencies = minibatch_parse(sentences, model, eval_batch_size) 其中UAS的计算: 正确的依赖关系数与总的依赖关系数的比值。例如: https://github.com/duanzhihua/cs224n-learning-camp
如:....... 'friendlier': 39624, '78.50': 39625, '75.625': 39626, '87.375': 39627, 'neidl': 39628, 'mattis': 39629, 'gracious': 39630, '275-a-share': 39631, 'f.c': 39632, 'adversarial': 39633, 'hardball': 39634,
tok2id 的单词word中UNK,NULL,ROOT的情况,如'
如{0: '
编号对应转换: id2tran: {0: 'L', 1: 'R', 2: 'S'}
转换对应编号: tran2id :{'L': 0, 'R': 1, 'S': 2} def get_oracle(self, stack, buf, ex):
if len(stack) < 2:
return self.n_trans - 1
i0 = stack[-1]
i1 = stack[-2]
h0 = ex['head'][i0]
h1 = ex['head'][i1]
l0 = ex['label'][i0]
l1 = ex['label'][i1]
if self.unlabeled:
if (i1 > 0) and (h1 == i0):
return 0
elif (i1 >= 0) and (h0 == i1) and \
(not any([x for x in buf if ex['head'][x] == i0])):
return 1
else:
return None if len(buf) == 0 else 2
else:
if (i1 > 0) and (h1 == i0):
return l1 if (l1 >= 0) and (l1 < self.n_deprel) else None
elif (i1 >= 0) and (h0 == i1) and \
(not any([x for x in buf if ex['head'][x] == i0])):
return l0 + self.n_deprel if (l0 >= 0) and (l0 < self.n_deprel) else None
else:
return None if len(buf) == 0 else self.n_trans - 1
1,如果i小于栈的长度:
分别获取堆栈顶部两个单词的第一个和第二个最左/最右边的子项,单词get_lc(k),get_rc(k)的ex['word']的单词特征lc[0]、rc[0]、lc[1]、rc[1](4*2 );堆栈顶部两个单词的最左边或最左边节点的最右边或最右边节点llc[0]、rrc[0]ex[‘word']的单词特征(2*2);self.use_pos为True,需分别获取堆栈顶部两个单词的第一个和第二个最左/最右边的子项,单词get_lc(k),get_rc(k)的ex['pos']的词性特征lc[0]、rc[0]、lc[1]、rc[1](4*2 );堆栈顶部两个单词的最左边或最左边节点的最右边或最右边节点llc[0]、rrc[0]ex['pos']的词性特征(2*2);合计4*2+2*2 +4*2+2*2 = 24 这里self.use_dep设置为False。
共计12+24=36个特征。
则设置NULL空特征 (6*2+6*2 =24)
共计12+24=36个特征。 def extract_features(self, stack, buf, arcs, ex):
if stack[0] == "ROOT":
stack[0] = 0
def get_lc(k):
return sorted([arc[1] for arc in arcs if arc[0] == k and arc[1] < k])
def get_rc(k):
return sorted([arc[1] for arc in arcs if arc[0] == k and arc[1] > k],
reverse=True)
p_features = []
l_features = []
features = [self.NULL] * (3 - len(stack)) + [ex['word'][x] for x in stack[-3:]]
features += [ex['word'][x] for x in buf[:3]] + [self.NULL] * (3 - len(buf))
if self.use_pos:
p_features = [self.P_NULL] * (3 - len(stack)) + [ex['pos'][x] for x in stack[-3:]]
p_features += [ex['pos'][x] for x in buf[:3]] + [self.P_NULL] * (3 - len(buf))
for i in range(2):
if i < len(stack):
k = stack[-i-1]
lc = get_lc(k)
rc = get_rc(k)
llc = get_lc(lc[0]) if len(lc) > 0 else []
rrc = get_rc(rc[0]) if len(rc) > 0 else []
features.append(ex['word'][lc[0]] if len(lc) > 0 else self.NULL)
features.append(ex['word'][rc[0]] if len(rc) > 0 else self.NULL)
features.append(ex['word'][lc[1]] if len(lc) > 1 else self.NULL)
features.append(ex['word'][rc[1]] if len(rc) > 1 else self.NULL)
features.append(ex['word'][llc[0]] if len(llc) > 0 else self.NULL)
features.append(ex['word'][rrc[0]] if len(rrc) > 0 else self.NULL)
if self.use_pos:
p_features.append(ex['pos'][lc[0]] if len(lc) > 0 else self.P_NULL)
p_features.append(ex['pos'][rc[0]] if len(rc) > 0 else self.P_NULL)
p_features.append(ex['pos'][lc[1]] if len(lc) > 1 else self.P_NULL)
p_features.append(ex['pos'][rc[1]] if len(rc) > 1 else self.P_NULL)
p_features.append(ex['pos'][llc[0]] if len(llc) > 0 else self.P_NULL)
p_features.append(ex['pos'][rrc[0]] if len(rrc) > 0 else self.P_NULL)
if self.use_dep:
l_features.append(ex['label'][lc[0]] if len(lc) > 0 else self.L_NULL)
l_features.append(ex['label'][rc[0]] if len(rc) > 0 else self.L_NULL)
l_features.append(ex['label'][lc[1]] if len(lc) > 1 else self.L_NULL)
l_features.append(ex['label'][rc[1]] if len(rc) > 1 else self.L_NULL)
l_features.append(ex['label'][llc[0]] if len(llc) > 0 else self.L_NULL)
l_features.append(ex['label'][rrc[0]] if len(rrc) > 0 else self.L_NULL)
else:
features += [self.NULL] * 6
if self.use_pos:
p_features += [self.P_NULL] * 6
if self.use_dep:
l_features += [self.L_NULL] * 6
features += p_features + l_features
assert len(features) == self.n_features
return features
create_instances方法将训练集train的每个单词根据栈顶2个单词的关系衍生出36个特征(X值,后续在神经网络中作为inputs_batch喂入input_placeholder占位数据,然后再embedding_lookup查询词向量,送入深度学习神经网络进行训练);create_instances方法对于每一个单词通过get_oracle获取一个转换动作作为目标值(y值) 。 def create_instances(self, examples):
all_instances = []
succ = 0
for id, ex in enumerate(logged_loop(examples)):
n_words = len(ex['word']) - 1
# arcs = {(h, t, label)}
stack = [0]
buf = [i + 1 for i in range(n_words)]
arcs = []
instances = []
for i in range(n_words * 2):
gold_t = self.get_oracle(stack, buf, ex)
if gold_t is None:
break
legal_labels = self.legal_labels(stack, buf)
assert legal_labels[gold_t] == 1
instances.append((self.extract_features(stack, buf, arcs, ex),
legal_labels, gold_t))
if gold_t == self.n_trans - 1:
stack.append(buf[0])
buf = buf[1:]
elif gold_t < self.n_deprel:
arcs.append((stack[-1], stack[-2], gold_t))
stack = stack[:-2] + [stack[-1]]
else:
arcs.append((stack[-2], stack[-1], gold_t - self.n_deprel))
stack = stack[:-1]
else:
succ += 1
all_instances += instances
return all_instances
parser, embeddings, train_examples, dev_set, test_set = load_and_preprocess_data(debug)
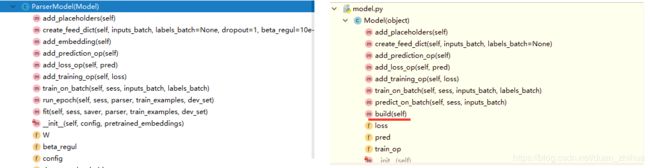
model初始化传入config, embeddings参数,调用父类Model的build方法,在子类ParserModel重载实现
add_placeholders()、add_prediction_op()、add_loss_op(self.pred)、add_training_op(self.loss)
3,模型训练
model.fit(session, saver, parser, train_examples, dev_set)
UAS, dependencies = parser.parse(test_set)
dependencies是一个列表,每个元素的第一个值、第二个值的关系,如: [(2, 1), (6, 5), (6, 4), (6, 3), (6, 7), (9, 8), (6, 9), (2, 6), (10, 2), (14, 13), (14, 12), (20, 19), (20, 18), (20, 17), (20, 16), (22, 21), (22, 20), (22, 15), (22, 23), (14, 22), (11, 14), (10, 11), (10, 24), (28, 27), (28, 26), (31, 30), (31, 32), (33, 31), (33, 29), (36, 35), (36, 34), (33, 36), (28, 33), (25, 28), (10, 25), (10, 37), (0, 10)]