CmokeryC++开源项目学习
1. Cmockery简介:
Cmockery是Google发布的用于C单元测试的一个轻量级框架,该框架有以下几个特点:
- 免费且开源,google提供技术支持;
- 轻量级的框架,测试快速简单;
- 避免使用复杂的编译器特性,对老版本的编译器的兼容性好;
- 不强制要求待测代码必须依赖C99标准,对许多嵌入式系统的开发很有用;
2. Linux下编译:
cd 到Cmockery目录下,执行下面命令:
- sudo ./configure
- sudo make
- sudo make install
库文件安装到:/usr/local/lib
头文件安装到:/usr/local/include/google
此时还需要加载一下Cmockery库:
cd /usr/local/lib
执行命令:sudo ldconfig
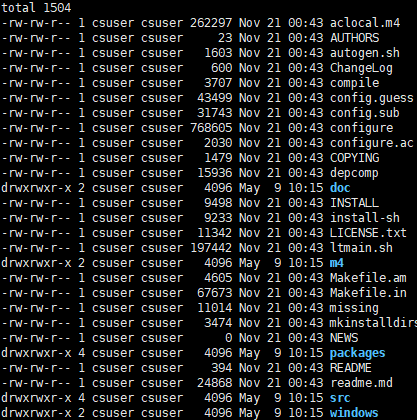
项目编译前,有下述文件:
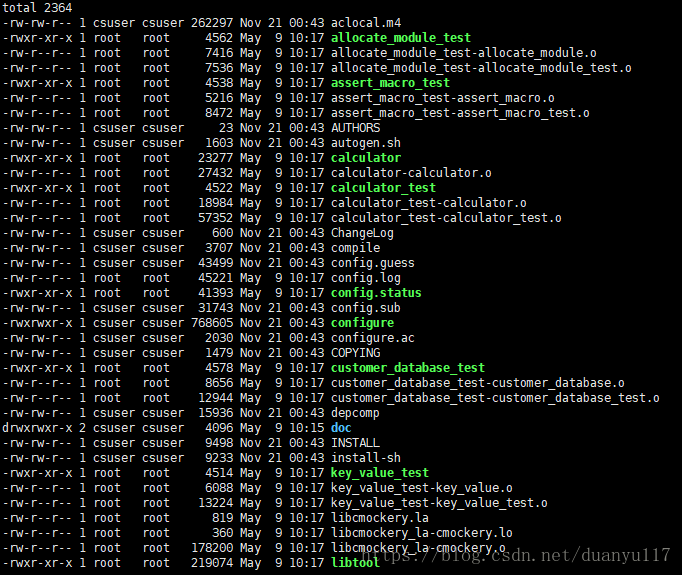
项目编译完,生成了项目中供学习的多个可执行文件:
可在目录下直接运行使用
3. Cmockery的测试实例学习:
下面的内容主要根据Cmockery的手册来展开:
动机
现今的许多C开源测试框架相当复杂,且对于最新的编译器技术有所依赖,使得这些测试框架的使用有一定的局限性。
Cmockery只需要待测试程序与标准C链接,最大限度地减少与标准库文件的冲突,而且,Cmockery尽量避免使用编译器中新的特性,具有更好的兼容性。
概述
Cmockery的测试和Cmockery库、标准C库、待测模块链接在一起,最终被编译成一个可独立运行的程序。测试过程中,待测模块的任何外部信息都应被模拟,即使用测试用例中定义的函数返回值来替换。即使待测代码在实际运行环境和测试环境的运行存在差异,仍可视为有效的测试。因为Cmockery的测试目的在于大吗模块在功能层面上的逻辑测试,不必要求所有的行为都和目标环境一致。
测试执行
Cmockery单元测试用例是签名为void function(void **state)的函数 .
Cmockery 测试程序将(多个)测试用例的函数指针初始化到一个表中,使用unit_test*() 宏. 这个表会传给 run_tests() 宏来执行测试用例。
run_tests() 将适当的异常/信号句柄,以及其他数据结构的指针装入到测试函数。
当单元测试结束时,run_tests() 会显示出各种定义的测试是否成功。
run_test.c文件如下:
#include
#include
#include
#include
// A test case that does nothing and succeeds.
void null_test_success(void **state) {//签名为(void** state)的函数作为单元测试用例)
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
const UnitTest tests[] = { //多个测试用例的函数指针初始化UnitTest的数组中
unit_test(null_test_success),
};
return run_tests(tests); //将初始化的表传递给run_tests函数来执行测试用例,返回测试用例的结果
} 异常处理
测试函数被run_tests() 执行之前,断言/信号句柄会被一个句柄重载,它可以在异常发生时,显示错误并退出测试函数。 如果一个异常发生在测试函数的外部,例如Cmockery本身,程序将终止执行并返回错误码。
出错处理
当测试函数执行run_tests() 时,如果出现错误,当前的测试函数将中断,测试程序继续执行下一测试函数。
测试失败的通过CMockery函数fail() 给出最终的标志。导致Cmockery库测试失败的事件如下:
- 断言
- 异常
- 内存泄漏
- 装载和拆除函数不匹配
- 模拟返回值出错
- 模拟返回值没用
- 预计参数值出错
- 预计参数值没用
断言
运行时的断言宏和C标准库的assert() 相似,需要在待测模块中使用Cmockery的mock_assert() 函数重定义。 通常mock_assert() 表示 测试的失败 . 如果一个函数被expect_assert_failure() 宏调用, 那么在这个函数中就要调用mock_assert() ,测试将进行。若没有调用mock_assert() ,表示这个函数测试失败。
mock_module的使用
asset_module.c文件:
#include
// If unit testing is enabled override assert with mock_assert().
#if UNIT_TESTING
extern void mock_assert(const int result, const char* const expression,
const char * const file, const int line);
#undef assert
#define assert(expression) \
mock_assert((int)(expression), #expression, __FILE__, __LINE__);
#endif // UNIT_TESTING
void increment_value(int * const value) {
assert(value);
(*value) ++;
}
void decrement_value(int * const value) {
if (value) {
(*value) --;
}
} assert_module_test.c文件:
#include
#include
#include
#include
extern void increment_value(int * const value);
/* This test case will fail but the assert is caught by run_tests() and the
* next test is executed. */
void increment_value_fail(void **state) {
increment_value(NULL);
}
// This test case succeeds since increment_value() asserts on the NULL pointer.
void increment_value_assert(void **state) {
expect_assert_failure(increment_value(NULL));
}
/* This test case fails since decrement_value() doesn't assert on a NULL
* pointer. */
void decrement_value_fail(void **state) {
expect_assert_failure(decrement_value(NULL));
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
const UnitTest tests[] = {
unit_test(increment_value_fail),
unit_test(increment_value_assert),
unit_test(decrement_value_fail),
};
return run_tests(tests);
} 断言宏
Cmockery提供了一系列的断言宏,在测试程序的使用方法和C标准中的用法一致。 当断言错误发生时,Cmockery的断言宏会将这个这个错误输出到标准错误流,并把这个测试标记为失败。 由于标准C库中assert()的是限制,Cmockery的assert_true() 和 assert_false() 宏只能显示导致断言失败的表达式。Cmockery中和具体类型相关的断言宏, assert_{类型}_equal() and assert_{类型}_not_equal(), 显示那些导致断言失败的数据, 这样可以增加数据的可视化,辅助调试那些出错的测试用例。
Cmockery项目中提供了以下断言函数:
assert_true(c)
assert_false(c)
assert_int_equal(a, b)
assert_int_not_equal(a, b)
assert_string_equal(a, b)
assert_string_not_equal(a, b)
assert_memory_equal(a, b, size)
assert_memory_not_equal(a, b, size)
assert_in_range(value, minimum, maximum)
assert_not_in_range(value, minimum, maximum)
assert_in_set(value, values, number_of_values)
assert_not_in_set(value, values, number_of_values) assert_macro.c文件:
#include
static const char* status_code_strings[] = {//状态码的字符串数组
"Address not found",
"Connection dropped",
"Connection timed out",
};
const char* get_status_code_string(const unsigned int status_code) {//根据状态码在数组中查找,返回该状态码的字符串
return status_code_strings[status_code];
};
unsigned int string_to_status_code(const char* const status_code_string) {//查找传入的表示状态的字符串与状态数组中哪个匹配,匹配出状态码
unsigned int i;
for (i = 0; i < sizeof(status_code_strings) /
sizeof(status_code_strings[0]); i++) {
if (strcmp(status_code_strings[i], status_code_string) == 0) {
return i;
}
}
return ~0U;
} assert_macro_test.c文件:
#include
#include
#include
#include
extern const char* get_status_code_string(const unsigned int status_code); //将两个待测试函数包含进来
extern unsigned int string_to_status_code(
const char* const status_code_string);
/* This test will fail since the string returned by get_status_code_string(0)
* doesn't match "Connection timed out". */
void get_status_code_string_test(void **state) {
assert_string_equal(get_status_code_string(0), "Address not found");
assert_string_equal(get_status_code_string(1), "Connection timed out");
}
// This test will fail since the status code of "Connection timed out" isn't 1
void string_to_status_code_test(void **state) {
assert_int_equal(string_to_status_code("Address not found"), 0);
assert_int_equal(string_to_status_code("Connection timed out"), 1);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
const UnitTest tests[] = { //将要测试的函数传入数组中
unit_test(get_status_code_string_test),
unit_test(string_to_status_code_test),
};
return run_tests(tests); //通过运行函数run_tests执行测试
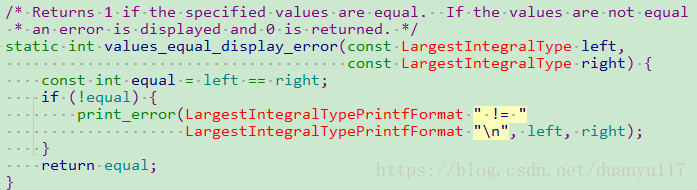
} 例子中的assert_int_equal函数最终调用cmockery.c文件中的函数实现:
该函数中最终由values_equal_display_error函数决定最终的返回值:
同样的,assert_string_equal函数的底层实现也可在源码中查到,调用了字符串比较函数strcmp。
动态内存分配
为了能用Cmockery测试待测模块中的内存泄漏,缓存溢出和underflows问题,应该将对malloc() 、 calloc() 和free()的调用分别替换成test_malloc() 、test_calloc() 和 test_free() 。每次释放块内存是使用test_free() ,如果一个内存块被 标记为测试失败 ,它将检测内存崩溃。所有块的内存分配使用 test_*() 函数,Cmockery库将跟踪它们。当测试完成时,如果有任何分配的块没有被释放(内存泄漏), 这些信息会被记录,此测试标记为失败。
为了简单起见,Cmockery会在同一进程中执行所有的测试。因此,一个测试程序的所有测试用例,共用一个单独的地址空间, 也就是说,一个测试用例的内存崩溃,会导致整个测试程序的提前结束。
allocate_module.c文件:
#ifdef HAVE_CONFIG_H
#include "config.h"
#endif
#ifdef HAVE_MALLOC_H
#include
#endif
#include
#if UNIT_TESTING
extern void* _test_malloc(const size_t size, const char* file, const int line);
extern void* _test_calloc(const size_t number_of_elements, const size_t size,
const char* file, const int line);
extern void _test_free(void* const ptr, const char* file, const int line);
#define malloc(size) _test_malloc(size, __FILE__, __LINE__)
#define calloc(num, size) _test_calloc(num, size, __FILE__, __LINE__)
#define free(ptr) _test_free(ptr, __FILE__, __LINE__)
#endif // UNIT_TESTING
void leak_memory() {
int * const temporary = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int));//调用底层的_test_malloc函数
*temporary = 0; //内存泄漏
}
void buffer_overflow() {
char * const memory = (char*)malloc(sizeof(int));
memory[sizeof(int)] = '!'; //越界检测
free(memory);//调用底层的_test_free函数
}
void buffer_underflow() {
char * const memory = (char*)malloc(sizeof(int));
memory[-1] = '!'; //下溢出
free(memory);
} allocate_module_test.c文件:
#include
#include
#include
#include
extern void leak_memory();
extern void buffer_overflow();
extern void buffer_underflow();
// Test case that fails as leak_memory() leaks a dynamically allocated block.
void leak_memory_test(void **state) {
leak_memory();
}
// Test case that fails as buffer_overflow() corrupts an allocated block.
void buffer_overflow_test(void **state) {
buffer_overflow();
}
// Test case that fails as buffer_underflow() corrupts an allocated block.
void buffer_underflow_test(void **state) {
buffer_underflow();
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { //对多个测试函数同时测试
const UnitTest tests[] = {
unit_test(leak_memory_test),
unit_test(buffer_overflow_test),
unit_test(buffer_underflow_test),
};
return run_tests(tests);
} 底层的_test_free函数的实现如下:
// Use the real free in this function.
#undef free
void _test_free(void* const ptr, const char* file, const int line) {
unsigned int i;
char *block = (char*)ptr;
MallocBlockInfo *block_info;
_assert_true((int)ptr, "ptr", file, line);
block_info = (MallocBlockInfo*)(block - (MALLOC_GUARD_SIZE +
sizeof(*block_info)));
// Check the guard blocks.
{
char *guards[2] = {block - MALLOC_GUARD_SIZE,
block + block_info->size};
for (i = 0; i < ARRAY_LENGTH(guards); i++) {
unsigned int j;
char * const guard = guards[i];
for (j = 0; j < MALLOC_GUARD_SIZE; j++) {
const char diff = guard[j] - MALLOC_GUARD_PATTERN;
if (diff) {
print_error(
"Guard block of 0x%08x size=%d allocated by "
SOURCE_LOCATION_FORMAT " at 0x%08x is corrupt\n",
(size_t)ptr, block_info->size,
block_info->location.file, block_info->location.line,
(size_t)&guard[j]);
_fail(file, line);
}
}
}
}
list_remove(&block_info->node, NULL, NULL);
block = block_info->block;
memset(block, MALLOC_FREE_PATTERN, block_info->allocated_size);
free(block);
}
#define free test_free底层的_test_malloc函数实现如下:
// Use the real malloc in this function.
#undef malloc
void* _test_malloc(const size_t size, const char* file, const int line) {
char* ptr;
MallocBlockInfo *block_info;
ListNode * const block_list = get_allocated_blocks_list();
const size_t allocate_size = size + (MALLOC_GUARD_SIZE * 2) +
sizeof(*block_info) + MALLOC_ALIGNMENT;
char* const block = (char*)malloc(allocate_size);
assert_true(block);
// Calculate the returned address.
ptr = (char*)(((size_t)block + MALLOC_GUARD_SIZE + sizeof(*block_info) +
MALLOC_ALIGNMENT) & ~(MALLOC_ALIGNMENT - 1));
// Initialize the guard blocks.
memset(ptr - MALLOC_GUARD_SIZE, MALLOC_GUARD_PATTERN, MALLOC_GUARD_SIZE);
memset(ptr + size, MALLOC_GUARD_PATTERN, MALLOC_GUARD_SIZE);
memset(ptr, MALLOC_ALLOC_PATTERN, size);
block_info = (MallocBlockInfo*)(ptr - (MALLOC_GUARD_SIZE +
sizeof(*block_info)));
set_source_location(&block_info->location, file, line);
block_info->allocated_size = allocate_size;
block_info->size = size;
block_info->block = block;
block_info->node.value = block_info;
list_add(block_list, &block_info->node);
return ptr;
}
#define malloc test_malloc模拟测试
一个单元测试最好能将待测函数或模块从外部依赖中隔离。 这就会用到模拟函数,它通过动态或静态方式链接到待测模块中去。 当被测代码直接引用外部函数时,模拟函数必须静态链接。 动态链接是一个简单的过程,将一个函数指针放到一个表中,给待测模块中一个测试用例定义的模拟函数引用。
will_return
为了简化模拟函数的实现,Cmockery 提供了给模拟函数的每个测试用例存放返回值的功能,使用的是 will_return() 函数。然后,这些值将通过每个模拟函数调用mock() 返回。 传给will_return() 的值,将分别添加到每个函数所特有的队列中去。连续调用 mock() ,将从函数的队列中移除一个返回值。 这使一个模拟函数通过多次调用mock() ,来返回(多个)输出参数和(一个)返回值成为可能。 此外,一个模拟函数多次调用(多个)返回值的做法也是可以的。
will_return的使用:
database.h文件:
typedef struct DatabaseConnection DatabaseConnection;
/* Function that takes an SQL query string and sets results to an array of
* pointers with the result of the query. The value returned specifies the
* number of items in the returned array of results. The returned array of
* results are statically allocated and should not be deallocated using free()
*/
typedef unsigned int (*QueryDatabase)(
DatabaseConnection* const connection, const char * const query_string,
void *** const results);
// Connection to a database.
struct DatabaseConnection {
const char *url;
unsigned int port;
QueryDatabase query_database;
};
// Connect to a database.
DatabaseConnection* connect_to_database(const char * const url,
const unsigned int port);customer_database.c文件:
#include
#include
#include
#ifdef _WIN32
#define snprintf _snprintf
#endif // _WIN32
// Connect to the database containing customer information.
DatabaseConnection* connect_to_customer_database() {
return connect_to_database("customers.abcd.org", 321);
}
/* Find the ID of a customer by his/her name returning a value > 0 if
* successful, 0 otherwise. */
unsigned int get_customer_id_by_name(
DatabaseConnection * const connection,
const char * const customer_name) {
char query_string[256];
int number_of_results;
void **results;
snprintf(query_string, sizeof(query_string),
"SELECT ID FROM CUSTOMERS WHERE NAME = %s", customer_name);
number_of_results = connection->query_database(connection, query_string,
&results);
if (number_of_results != 1) {
return -1;
}
return (unsigned int)results[0];
} customer_database_test.c文件:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
extern DatabaseConnection* connect_to_customer_database();
extern unsigned int get_customer_id_by_name(
DatabaseConnection * const connection, const char * const customer_name);
// Mock query database function.
unsigned int mock_query_database(
DatabaseConnection* const connection, const char * const query_string,
void *** const results) {
*results = (void**)((unsigned)mock());
return (unsigned int)mock();
}
// Mock of the connect to database function.
DatabaseConnection* connect_to_database(const char * const database_url,
const unsigned int port) {
return (DatabaseConnection*)((unsigned)mock());
}
void test_connect_to_customer_database(void **state) {
will_return(connect_to_database, 0x0DA7ABA53);
assert_int_equal((int)connect_to_customer_database(), 0x0DA7ABA53);
}
/* This test fails as the mock function connect_to_database() will have no
* value to return. */
void fail_connect_to_customer_database(void **state) {
assert_true(connect_to_customer_database() ==
(DatabaseConnection*)0x0DA7ABA53);
}
void test_get_customer_id_by_name(void **state) {
DatabaseConnection connection = {
"somedatabase.somewhere.com", 12345678, mock_query_database
};
// Return a single customer ID when mock_query_database() is called.
int customer_ids = 543;
will_return(mock_query_database, &customer_ids);
will_return(mock_query_database, 1);
assert_int_equal(get_customer_id_by_name(&connection, "john doe"), 543);
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
const UnitTest tests[] = {
unit_test(test_connect_to_customer_database),
unit_test(test_get_customer_id_by_name),
};
return run_tests(tests);
} 参数检测
除了存储模拟函数的返回值之外,Cmockery还提供了对模拟函数参数期望值的存储功能,使用的是 expect_*()函数,一个模拟函数的参数可以通过check_expected()宏来做有效的验证.
连续调用expect_*()宏,是用队列中的一个参数值来检测给定的参数。 check_expected()检测一个的函数参数,它与expect_*()相对应,即将出队的值。 如果参数检验失败,这个测试将标记为失败。 此外,如果调用check_expected()时,队列中没有参数值出队,测试也会失败。
expect_*()的使用:
product_database.c文件:
#include
// Connect to the database containing customer information.
DatabaseConnection* connect_to_product_database() {
return connect_to_database("products.abcd.org", 322);
} product_database_test.c文件:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
extern DatabaseConnection* connect_to_product_database();
/* Mock connect to database function.
* NOTE: This mock function is very general could be shared between tests
* that use the imaginary database.h module. */
DatabaseConnection* connect_to_database(const char * const url,
const unsigned int port) {
check_expected(url);
check_expected(port);
return (DatabaseConnection*)((unsigned)mock());
}
void test_connect_to_product_database(void **state) {
expect_string(connect_to_database, url, "products.abcd.org");
expect_value(connect_to_database, port, 322);
will_return(connect_to_database, 0xDA7ABA53);
assert_int_equal((int)connect_to_product_database(), 0xDA7ABA53);
}
/* This test will fail since the expected URL is different to the URL that is
* passed to connect_to_database() by connect_to_product_database(). */
void test_connect_to_product_database_bad_url(void **state) {
expect_string(connect_to_database, url, "products.abcd.com");
expect_value(connect_to_database, port, 322);
will_return(connect_to_database, 0xDA7ABA53);
assert_int_equal((int)connect_to_product_database(), 0xDA7ABA53);
}
/* This test will fail since the mock connect_to_database() will attempt to
* retrieve a value for the parameter port which isn't specified by this
* test function. */
void test_connect_to_product_database_missing_parameter(void **state) {
expect_string(connect_to_database, url, "products.abcd.org");
will_return(connect_to_database, 0xDA7ABA53);
assert_int_equal((int)connect_to_product_database(), 0xDA7ABA53);
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
const UnitTest tests[] = {
unit_test(test_connect_to_product_database),
unit_test(test_connect_to_product_database_bad_url),
unit_test(test_connect_to_product_database_missing_parameter),
};
return run_tests(tests);
} 测试状态
Cmockery允许每个测试用例多次装载和卸载函数的做法,装载函数,通过unit_test_setup() 或unit_test_setup_teardown() 宏给出, 支持多个测试用例公共的通用初始化; 此外,卸载函数,通过unit_test_teardown() 或 unit_test_setup_teardown() 宏,给出一个测试用例在执行失败情况下的代码路径。
unit_test_setup_teardown()的使用
key_value.c文件:
#include
#include
#include
typedef struct KeyValue {
unsigned int key;
const char* value;
} KeyValue;
static KeyValue *key_values = NULL;
static unsigned int number_of_key_values = 0;
void set_key_values(KeyValue * const new_key_values,
const unsigned int new_number_of_key_values) {
key_values = new_key_values;
number_of_key_values = new_number_of_key_values;
}
// Compare two key members of KeyValue structures.
int key_value_compare_keys(const void *a, const void *b) {
return (int)((KeyValue*)a)->key - (int)((KeyValue*)b)->key;
}
// Search an array of key value pairs for the item with the specified value.
KeyValue* find_item_by_value(const char * const value) {
unsigned int i;
for (i = 0; i < number_of_key_values; i++) {
if (strcmp(key_values[i].value, value) == 0) {
return &key_values[i];
}
}
return NULL;
}
// Sort an array of key value pairs by key.
void sort_items_by_key() {
qsort(key_values, number_of_key_values, sizeof(*key_values),
key_value_compare_keys);
} key_valur_test.c文件:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
/* This is duplicated here from the module setup_teardown.c to reduce the
* number of files used in this test. */
typedef struct KeyValue {
unsigned int key;
const char* value;
} KeyValue;
void set_key_values(KeyValue * const new_key_values,
const unsigned int new_number_of_key_values);
extern KeyValue* find_item_by_value(const char * const value);
extern void sort_items_by_key();
static KeyValue key_values[] = {
{ 10, "this" },
{ 52, "test" },
{ 20, "a" },
{ 13, "is" },
};
void create_key_values(void **state) {
KeyValue * const items = (KeyValue*)test_malloc(sizeof(key_values));
memcpy(items, key_values, sizeof(key_values));
*state = (void*)items;
set_key_values(items, sizeof(key_values) / sizeof(key_values[0]));
}
void destroy_key_values(void **state) {
test_free(*state);
set_key_values(NULL, 0);
}
void test_find_item_by_value(void **state) {
unsigned int i;
for (i = 0; i < sizeof(key_values) / sizeof(key_values[0]); i++) {
KeyValue * const found = find_item_by_value(key_values[i].value);
assert_true(found);
assert_int_equal(found->key, key_values[i].key);
assert_string_equal(found->value, key_values[i].value);
}
}
void test_sort_items_by_key(void **state) {
unsigned int i;
KeyValue * const kv = *state;
sort_items_by_key();
for (i = 1; i < sizeof(key_values) / sizeof(key_values[0]); i++) {
assert_true(kv[i - 1].key < kv[i].key);
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
const UnitTest tests[] = {
unit_test_setup_teardown(test_find_item_by_value, create_key_values,
destroy_key_values),
unit_test_setup_teardown(test_sort_items_by_key, create_key_values,
destroy_key_values),
};
return run_tests(tests);
} 实例
一个很小基于命令行的计算器程序 calculator.c与计算器程序的测试程序 calculator_test.c ,它包含了本文所涉及的所有特性的一个实例
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/oncoding/article/details/4324421