Spring--IOC容器初始化之Resource定位
IOC容器初始化主要分三步,第一步是Resource定位,即首先要找到要加载的BeanDefinition的资源在哪
对于每一种等待被加载的资源都会有与之相匹配的ApplicationContext的实现类来进行加载,例如加载文件用到的FileSystemXmlApplicationContext类,以及ClasspathXmlApplicationContext等
接下来将以FIleSystemXmlApplicationContext来讲述如何进行Resource定位的:
FileSystemXMLApplicationContext的基本情况
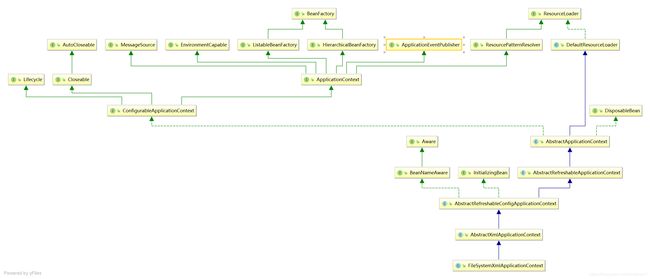
1、主要类的继承图
在类的继承图中可看到FileSystemXMLApplicationContext类的超类中继承了AbstractApplicationContext类,而AbstractApplicationContext继承了DefaultResourceLoader类,使得其具有了资源加载的功能。
2、FileSystemXMLApplicationContext类的具体实现
7个构造方法
//无参构造方法
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext() {
}
/**
* 传入父上下文
* @param parent
*/
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) {
super(parent);
}
//传入单个文件路径
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation) throws BeansException {
this(new String[] {configLocation}, true, null);
}
//传入多个文件路径
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String... configLocations) throws BeansException {
this(configLocations, true, null);
}
//传入文件路径数组以及父应用上下文
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException {
this(configLocations, true, parent);
}
//传入文件路径数组即是否刷新容器的标志
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh) throws BeansException {
this(configLocations, refresh, null);
}
/**
* 以上的四个构造方法最终都是调用此方法
* 该方法需要传入三个参数
* configLocations:需要加载的文件的路径
* refresh:是否刷新容器
* parent:父应用上下文
* refresh()方法是IOC容器初始化的入口
* @param configLocations
* @param refresh
* @param parent
* @throws BeansException
*/
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
//从此处开始IOC容器的初始化
refresh();
}
}重写了超类DefaultResourceLoader中的根据路径获取资源的方法
/**
* 根据路径获取资源
* 将路径包装成一个FileSystemResource对象
* @param path
* @return
*/
@Override
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
if (path != null && path.startsWith("/")) {
path = path.substring(1);
}
return new FileSystemResource(path);
}Resource定位
入口为FileSystemXmlApplicationContext类中调用refresh方法
/**
*
* @throws BeansException
* @throws IllegalStateException
*/
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
//startupShutdownMonitor是一个Object,用来管理容器的刷新和destroy
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
/**
* 为刷新准备好应用上下文
* ①设置好开始时间startupDate
* ②是否关闭closed设置为false
* ③是否活跃的active设置为true
* ④初始化属性资源
* ⑤检测所有被标记为必需的资源是否是可解析的
* ⑥创建好一个存放早期应用事件的Set容器
*/
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
/**
* 创建好一个ConfigurableListableBeanFactory对象
* ①检测是否已经有bean工厂,如果有,则将其destroy并且close
* ②创建一个DefaultListableBeanFactory
* ③获取资源的位置并通过DefaultListableBeanFactory来加载资源
* ④返回ConfigurableListableBeanFactory对象
*/
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
//下面的代码省略
}
} 紧接着会调用obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法。
在调用过程中会创建DefaultListableBeanFactory对象
加载资源主要是通过loadBeanDefinitions()方法来实现的,如下:
在加载资源前会先创建一个XmlBeanDeginitionReader来对资源进行读取
@Override
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.
//在此处创建一个XmlBeanDefinitionReader对象来对资源进行加载
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
// resource loading environment.
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
//加载资源的入口
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}接下来获取资源的路径
资源有两种路径形式,一种是Resource类型的,一种是String类型的
/**
* 两种类型的资源
* 一种是Resource类型的
* 一种是String类型的
* @param reader
* @throws BeansException
* @throws IOException
*/
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources();
if (configResources != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);
}
}然后获取资源加载器ResourceLoader
根据ResourceLoader的类型不同对资源有不同的获取方法
当为ResourcePatternResolver类型时,将ResourceLoader强转类型后调用getResource()方法定位资源
否则,直接调用DefaultResourceLoader的getResource()方法定位资源。
到此资源的定位结束,接下来开始资源的真正载入与注册。
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, Set actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader == null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Cannot import bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available");
}
/**
* 当ResourceLoader为ResourcePatternResolver类型时
* 调用其getResource()方法定位资源
*/
if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {
// Resource pattern matching available.
try {
Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location);
int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resources);
if (actualResources != null) {
for (Resource resource : resources) {
actualResources.add(resource);
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]");
}
return loadCount;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
/**
* 否则调用DefaultResourceLoader的getResource()方法定位资源
*/
// Can only load single resources by absolute URL.
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location);
int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
if (actualResources != null) {
actualResources.add(resource);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location [" + location + "]");
}
return loadCount;
}
}