java学习之路个人总结三
1、异常的相关处理
在java中,一般用try......catch......来捕捉异常:try...catch...finally
throws 表示当前方法不做异常处理,而是让方法调用去处理异常
throw 表示直接抛出一个异常
例:
public class Demo2 {
public static void testFinally(){
String str="123a";
try{
int a=Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println(a);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("exception");
return;
}finally{
System.out.println("finally end");
}
System.out.println("end");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
testFinally();
}
}
2、Exception和RuntimeExecption区别 :
自定义异常类 例:
public class TestCustomException {
public static void test()throws CustomException{
throw new CustomException("自定义异常");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
test();
} catch (CustomException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3、java日期类 可以根据相关知识得出想要的时间
Date类 Canlendar类 SimpleDateFormat类(例如下)
import java.util.Date;
/**
* 日期类date
* @author 小誉
*
*/
public class Testdate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date=new Date();
System.out.println("当前日期:"+date);
}
}
4、String 与 StringBuffer
5、Match类 与数学相关的一个类
例:
public class TestMath {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("最大值:"+Math.max(1,2));
System.out.println("最小值:"+Math.min(1,2));
System.out.println("四舍五入:"+Math.round(12.6));
System.out.println("四舍五入:"+Math.round(12.4));
System.out.println("3的四次方:"+Math.pow(3,4));
System.out.println("25的平方根:"+Math.sqrt(25));
}
}
6、泛型:使用泛型可以指代任意对象类型
首先,定义一个简单的Box类:
public
class
Box {
private
String object;
public
void
set(String object) {
this
.object = object; }
public
String get() {
return
object; }
}
这是最常见的做法,这样做的一个坏处是Box里面现在只能装入String类型的元素,今后如果我们需要装入Integer等其他类型的元素,还必须要另外重写一个Box,代码得不到复用,使用泛型可以很好的解决这个问题。
public
class
Box {
// T stands for "Type"
private
T t;
public
void
set(T t) {
this
.t = t; }
public
T get() {
return
t; }
}
这样我们的Box类便可以得到复用,我们可以将T替换成任何我们想要的类型:
Box integerBox =
new
Box();
Box doubleBox =
new
Box();
Box stringBox =
new
Box();
看完了泛型类,接下来我们来了解一下泛型方法。声明一个泛型方法很简单,只要在返回类型前面加上一个类似
public
class
Util {
public
static
boolean
compare(Pair p1, Pair p2) {
return
p1.getKey().equals(p2.getKey()) &&
p1.getValue().equals(p2.getValue());
}
}
public
class
Pair {
private
K key;
private
V value;
public
Pair(K key, V value) {
this
.key = key;
this
.value = value;
}
public
void
setKey(K key) {
this
.key = key; }
public
void
setValue(V value) {
this
.value = value; }
public
K getKey() {
return
key; }
public
V getValue() {
return
value; }
}
Pair p1 =
new
Pair<>(
1
,
"apple"
);
Pair p2 =
new
Pair<>(
2
,
"pear"
);
boolean
same = Util.compare(p1, p2);
通配泛型:
public class Test {
/**通配泛型
* tong'pei
* @param a
*/
private static void take(Demo a){
a.print();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo
take(dog);
Demo
take(cat);
Demo
take(animal);
}
}
ArrayList类(例)
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class TestArrayList {
private static void printArrayList(ArrayList
System.out.println("当前的集合元素:");
for(int i=0;i
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList
//添加元素
arrayList.add("张三");
arrayList.add("李四");
printArrayList(arrayList);
//将指定元素插入此列表中指定的位置
arrayList.add(1,"张小三");
printArrayList(arrayList);
//将指定的元素替代此列表中指定位置上的元素。
arrayList.set(2,"李小四");
printArrayList(arrayList);
//一处此列表中指定位置上的元素
arrayList.remove(0);
printArrayList(arrayList);
}
}
Linkedlist类(例)
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class TestLinkedList {
private static void printLinkedList(LinkedList
System.out.print("当前元素集合:");
for(int i=0;i
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList
linkedList.add("张三");
linkedList.add("李四");
linkedList.add("王麻子");
linkedList.add("小三");
linkedList.add("小四");
printLinkedList(linkedList);
//返回此列表中首次出现的指定元素的索引,如果此列表中不包含该元素,则返回 -1。
System.out.println(linkedList.indexOf("李四"));
printLinkedList(linkedList);
//获取但不移除此列表的第一个元素;如果此列表为空,则返回 null。
System.out.println(linkedList.peekFirst());
printLinkedList(linkedList);
//获取但不移除此列表的最后一个元素;如果此列表为空,则返回 null。
System.out.println(linkedList.peekLast());
printLinkedList(linkedList);
//获取并移除此列表的第一个元素;如果此列表为空,则返回 null。
System.out.println(linkedList.pollFirst());
printLinkedList(linkedList);
//获取并移除此列表的最后一个元素;如果此列表为空,则返回 null。
System.out.println(linkedList.pollLast());
printLinkedList(linkedList);
}
}
8、Iterator或foreach遍历集合
Set集合:
![]()
HashSet类
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import com.java234.chap07.sec01集合.Student;
public class TestHashSet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* HashSet是无序的
* 不循序有重复的值
*/
HashSet
hs.add("1");
hs.add("2");
hs.add("2");
hs.add("4");
hs.add("5");
/**
* 用Iterator遍历集合
*/
Iterator
while(it.hasNext()){
String s=it.next();
System.out.println(s+" ");
}
}
}
Map集合:
![]()
HashMap类
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import com.java234.chap07.sec01集合.Student;
public class TestHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap
hashMap.put("1号",new Student("张三",10));
hashMap.put("2号",new Student("李四",20));
hashMap.put("3号",new Student("王麻子",30));
//通过key,获取value
Student s=hashMap.get("1号");
System.out.println(s.getName()+":"+s.getAge());
Iterator
while(it.hasNext()){
String key=it.next();//获取key
Student student=hashMap.get(key);//通过key获取value
System.out.println("key="+key+"value={"+student.getName()+" , "+student.getAge()+"}");
}
}
}
9、java多线程:同时对多项任务加以控制
java多线程实现:继承Thread类 实现Runnable接口
例如 实现Runnable接口
public class Thread2 implements Runnable{
private int baoZi=1;
private String threadName;
public Thread2(String threadName) {
super();
this.threadName = threadName;
}
@Override
public synchronized void run() {
while(baoZi<=10){
System.out.println(threadName+"吃第"+baoZi+"包子");
baoZi++;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*Thread2 t1=new Thread2("张三线程");
Thread2 t2=new Thread2("李四线程");
Thread t11=new Thread(t1);
Thread t12=new Thread(t2);
t11.start();
t12.start();*/
Thread2 t1=new Thread2("超级张三线程");
Thread t11=new Thread(t1);
Thread t12=new Thread(t1);
Thread t13=new Thread(t1);
//实现资源共享
t11.start();
t12.start();
t13.start();
}
}
10、线程状态:
11、线程的常用方法:
例如:Yield();
public class Demo5 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
//获取当前线程
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
Thread t=Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(t.getName()+":"+i);//返回线程的名称
if(i==5){
System.out.println("线程礼让:");
Thread.currentThread().yield();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo5 demo1=new Demo5();
new Thread(demo1,"线程A").start();
new Thread(demo1,"线程B").start();
}
}
12、String简单介绍:
JFrame容器:
import java.awt.Color;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class JFrameTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame jFrame=new JFrame("JFrame窗体");
/*Container c=jFrame.getContentPane();
c.setBackground(Color.RED);*/
jFrame.getContentPane().setBackground(Color.RED);// 设置容器的背景颜色
jFrame.setLocation(400,200);//设置容器的位置
jFrame.setSize(500,200);//设置容器大小
jFrame.setVisible(true);//让容器显示
}
}
JButton: 按钮
import java.awt.Color;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class JButtonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame jFrame=new JFrame("JButton测试");
JButton jb=new JButton("这是一个按钮");
jFrame.add(jb);
jFrame.setLocation(400,200);//设置容器的位置
jFrame.setSize(500,200);//设置容器大小
jFrame.setVisible(true);//让容器显示
jFrame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}
13、布局
FlowLayout流式布局:此布局使所有组件像流水一样依次进行排列
BorderLayout:将区域分为东西南北五个区域
GridLayout表格布局:以表格的形式布局
例如 BorderLayout:
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class BorderLayoutTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame jFrame=new JFrame("BorderLayout测试");
//jFrame.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
jFrame.setLayout(new BorderLayout(5,5));
jFrame.add(new JButton("东"),BorderLayout.EAST);
jFrame.add(new JButton("西"),BorderLayout.WEST);
jFrame.add(new JButton("南"),BorderLayout.SOUTH);
jFrame.add(new JButton("北"),BorderLayout.NORTH);
jFrame.add(new JButton("中"),BorderLayout.CENTER);
jFrame.setLocation(400,200);//设置容器的位置
jFrame.setSize(500,200);//设置容器大小
jFrame.setVisible(true);//让容器显示
jFrame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}
15、JLabel组件
文本框组件 :
Jpanel轻量级容器
根据以上内容 可运用相关知识写一个简单界面 例:
import java.awt.GridLayout;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JPasswordField;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
import javax.swing.border.EmptyBorder;
public class JPanelTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame jFrame=new JFrame("JPanel面板测试");
JPanel jPanel=new JPanel();
jPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(3,2,10,10));
jPanel.setBorder(new EmptyBorder(10,10,10,10));//设置边距
jFrame.add(jPanel);
JLabel j1=new JLabel("用户名:");
JTextField jtf=new JTextField();
JLabel j12=new JLabel("密码:");
JPasswordField jpf=new JPasswordField();
JButton jb1=new JButton("登录");
JButton jb2=new JButton("重置");
jPanel.add(j1);
jPanel.add(jtf);
jPanel.add(j12);
jPanel.add(jpf);
jPanel.add(jb1);
jPanel.add(jb2);
jFrame.setLocation(400,200);//设置容器的位置
jFrame.setSize(250,150);//设置容器大小
jFrame.setVisible(true);//让容器显示
jFrame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}
16、Swing事情处理:(例如写一个简单面板)
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
class MyWindowAdapter extends WindowAdapter{
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.windowClosing(e);
System.out.println("窗口关闭......");
}
}
public class EventTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame jFrame=new JFrame("Swing事情");
//MyWindowAdapter myWindowAdapter=new MyWindowAdapter();
//jFrame.addWindowListener(myWindowAdapter);
jFrame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.windowClosing(e);
System.out.println("窗口关闭......");
}
});
jFrame.setLocation(400,200);//设置容器的位置
jFrame.setSize(500,200);//设置容器大小
jFrame.setVisible(true);//让容器显示
jFrame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}
Swing综合示例 例子:
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JComboBox;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
import javax.tools.JavaCompiler;
public class SwingTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame jFrame=new JFrame("Swing综合示例测试");
jFrame.setLayout(null); //使用绝对布局
final JTextField num1Txt=new JTextField();
final JTextField num2Txt=new JTextField();
///JLabel fuHao=new JLabel("+",JLabel.CENTER);
String fuHao[]={"+","-","*","/"};
final JComboBox jcb=new JComboBox(fuHao);
final JTextField resultTxt=new JTextField();
JButton jb=new JButton("=");
jb.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String num1=num1Txt.getText();//获取第一个数字文本
String num2=num2Txt.getText();//获取第个二数字文本
String fuHao=(String)jcb.getSelectedItem();
int result=0;
if("+".equals(fuHao)){
result=Integer.parseInt(num1)+Integer.parseInt(num2);
}else if("-".equals(fuHao)){
result=Integer.parseInt(num1)-Integer.parseInt(num2);
}else if("*".equals(fuHao)){
result=Integer.parseInt(num1)*Integer.parseInt(num2);
}else if("/".equals(fuHao)){
result=Integer.parseInt(num1)/Integer.parseInt(num2);
}
//int result=Integer.parseInt(num1)+Integer.parseInt(num2);
resultTxt.setText(result+"");
}
});
num1Txt.setBounds(20, 30, 50, 25);
//fuHao.setBounds(80, 30, 40, 25);
jcb.setBounds(80,30,40,25);
num2Txt.setBounds(130, 30, 50, 25);
jb.setBounds(190, 30, 50, 25);
resultTxt.setBounds(250, 30, 50, 25);
jFrame.add(num1Txt);
//jFrame.add(fuHao);
jFrame.add(jcb);
jFrame.add(num2Txt);
jFrame.add(jb);
jFrame.add(resultTxt);
jFrame.setLocation(400,200);//设置容器的位置
jFrame.setSize(350,150);//设置容器大小
jFrame.setVisible(true);//让容器显示
jFrame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}
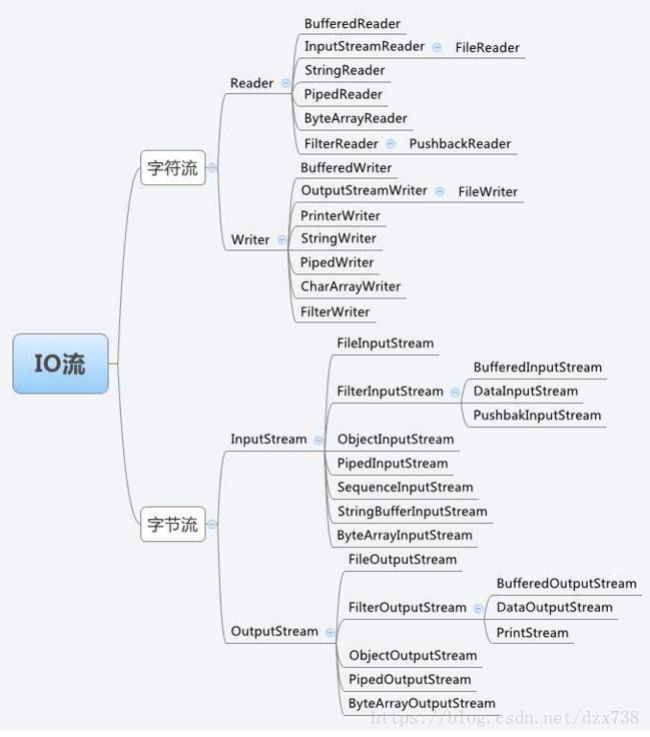
17、IO流(个人认为有所需要时现学现用):
18、文件操作File类
19、字节输入输出流
字符输入输出流:
例:输出流
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.Reader;
import java.io.WriteAbortedException;
import java.io.Writer;
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File file=new File("G://测试文件.txt");
Writer out=new FileWriter(file);
String str="我爱中华!!!";
out.write(str); //将字符串写入输出流
out.close(); //关闭输出流
}
}