对于日志来说,最常见的需求就是收集、存储、查询、展示,开源社区正好有相对应的开源项目:logstash(收集)、elasticsearch(存储+搜索)、kibana(展示),我们将这三个组合起来的技术称之为ELKStack,所以说ELKStack指的是Elasticsearch、Logstash、Kibana技术栈的结合
一、环境介绍
1、操作系统
CentOS Linux release 7.6.1810 (Core)2、软件版本
- elasticsearch-2.3.5
- kibana-4.5.4-1.x86_64
- logstash-2.3.4-1.noarch
3、主机分配
| 服务 | IP地址 | 主机名 |
|---|---|---|
| elasticsearch | 10.201.1.145 | k8s-m1 |
| elasticsearch | 10.201.1.146 | k8s-n1 |
| logstash | 10.201.1.145 | k8s-n1 |
| kibana | 10.201.1.146 | k8s-n1 |
二、安装部署
1、在145/146两台服务器安装elasticsearch
- 安装Java
yum install -y java- 安装RPM软件包
rpm -ivh elasticsearch-2.3.5.rpm
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable elasticsearch.service
rpm -ql elasticsearch- 先修改145配置文件(取消注释做如下修改)
grep '^[a-z]' /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
cluster.name: myes #节点名称,所有节点要保持一致
node.name: k8s-m1 #节点名称,一般设置为主机名,不能和其他节点重复
path.data: /data/es-data #数据存放路径
path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch #log存放路径
bootstrap.mlockall: true #保证内存不被放到交换分区里面
network.host: 10.201.1.145 #当前主机IP
http.port: 9200 #服务端口- 再来修改146配置文件
grep '^[a-z]' /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
cluster.name: myes
node.name: k8s-n1
path.data: /data/es-data
path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch
bootstrap.mlockall: true #保证内存不被放到交换分区里面
network.host: 10.201.1.146
http.port: 9200
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["10.201.1.145", "10.201.1.146"] #单播的方式发布自己的服务,让其他es节点识别- 创建配置文件中所需目录,并赋予权限
mkdir -p /data/es-data
chown -R elasticsearch:elasticsearch /data/es-data- 启动服务
/etc/init.d/elasticsearch start
tail -f /var/log/elasticsearch/myes.log
netstat -lntpu|grep 9200- 在145主机上安装常用插件,插件需要查看是否适用当前版本
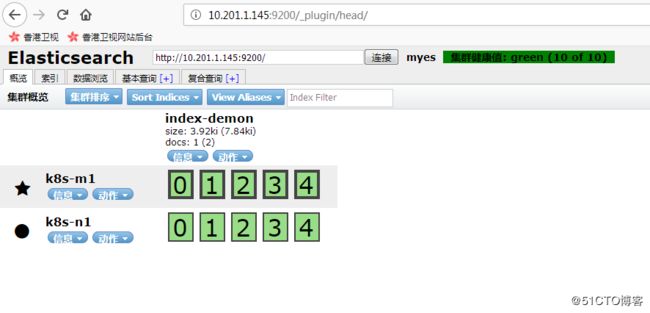
安装head插件
/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/plugin install mobz/elasticsearch-head浏览器访问插件,查看状态
http://10.201.1.145:9200/_plugin/head/
如下图示,表明安装正常
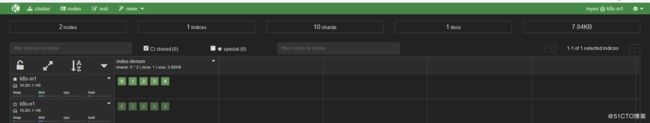
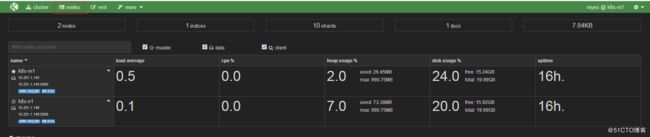
安装kopf插件
/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/plugin install lmenezes/elasticsearch-kopf浏览器访问插件,查看状态
http://10.201.1.145:9200/_plugin/kopf/
如下图示,表明安装正常
- 至此,两台elasticsearch 已经搭建完成
2、145安装logstash
-
logstash的运行需要依赖Java环境,前面已经安装过
- RPM安装软件包
rpm -ivh logstash-2.3.4-1.noarch.rpm
rpm -ql logstash- 验证使用logstash的一些插件(具体参考官方文档)
命令行模式下验证:
/opt/logstash/bin/logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { stdout{} }' #标准的输入和输出
/opt/logstash/bin/logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { stdout{ codec => rubydebug} }'
/opt/logstash/bin/logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { elasticsearch { hosts => ["10.201.1.145"] index => "logstash-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"} }' #将输入输出到es中,并创建索引写入配置文件形式验证(默认读取的目录为/etc/logstash/conf.d/):
cat file.conf
input{
file{
path => ["/var/log/messages", "/var/log/secure"]
type => "system-log"
start_position => "beginning"
}
}
filter{
}
output{
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["10.201.1.145:9200"]
index => "system-log-%{+YYYY.MM}"
}
}- 下面列举常用的收集日志方法
- 收集系统日志,和java日志
cat /etc/logstash/conf.d/file.conf
input{
file{ #file 是收集本地文件
path => ["/var/log/messages", "/var/log/secure"] #收集的路径
type => "system-log" #索引和指定的类型,为下面做判断
start_position => "beginning" #从头开始收集
}
file{
path => "/var/log/elasticsearch/myes.log"
type => "es-log"
start_position => "beginning"
codec => multiline{ #使用codec插件,相当于转换格式,使用多行合并参数,适合java日志收集
pattern => "^\[" # 设置正则匹配。根据自己java日志格式来设置
negate => true
what => "previous" #匹配到正则则和上文合并
}
}
}
filter{
}
output{
if [type] == "system-log" { #做判断,区分不同的日志类型
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["10.201.1.145:9200"]
index => "system-log-%{+YYYY.MM}"
}
}
if [type] == "es-log" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["10.201.1.145:9200"]
index => "es-log-%{+YYYY.MM}"
}
}
}
- 收集nginx日志
需要先把nginx的日志类型改为json
log_format access_log_json '{"user_ip":"$http_x_real_ip","lan_ip":"$remote_addr","log_time":"$time_iso8601","user_req":"$request","http_code":"$status","body_bytes_sent":"$body_bytes_sent","req_time":"$request_time","user_ua":"$http_user_agent"}';写配置文件
cat /etc/logstash/conf.d/nginx.conf
input{
file {
path => "/var/log/nginx/access.log_json"
codec => "json"
}
}
filter{
}
output{
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["10.201.1.145:9200"]
index => "nginx-access-log-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}- 收集rsyslog日志log
修改要收集日志主机的rsyslog配置文件
[root@k8s-m1 ~]# tail -2 /etc/rsyslog.conf
*.* @@10.201.1.146:514
# ### end of the forwarding rule ###编写收集配置文件
[root@k8s-n1 ~]# cat rsyslog.conf
input{
syslog {
type => "system-syslog"
port => 514
}
}
filter{
}
output{
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["10.201.1.146:9200"]
index => "system-syslog-%{+YYYY.MM}"
}
}- 收集TCP日志
编写配置文件
[root@k8s-n1 ~]# cat tcp.conf
input{
tcp {
port => 6666
mode => "server"
type => "tcp"
}
}
output{
stdout {
codec => rubydebug
}
}用另一台机器,发信息验证(下面列举几种方法)
yum -y install nc
echo "lxd" | nc 10.201.1.146 6666
nc 10.201.1.146 6666 < /etc/resolv.conf
echo "123" > /dev/tcp/10.201.1.146/6666- 收集Apache日志
[root@k8s-m1 ~]# cat apache.conf
input {
file {
path => "/var/log/httpd/access_log"
type => "apache_log"
start_position => "beginning"
}
}
filter {
grok {
match => { "message" => "%{COMBINEDAPACHELOG}" }
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["10.201.1.145:9200"]
index => "apache-log-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}前台运行,然后去登录es查看收集的日志
http://10.201.1.145:9200/_plugin/head/
/opt/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/file.conf - 至此,logstash安装完毕,功能正常使用
3、146安装kibana
Kibana 是为 Elasticsearch 设计的开源分析和可视化平台。你可以使用 Kibana 来搜索,查看存储在 Elasticsearch 索引中的数据并与之交互。你可以很容易实现高级的数据分析和可视化,以图表的形式展现出来。
- RPM安装kibana
rpm -ivh kibana-4.5.4-1.x86_64.rpm
rpm -ql kibana- 修改配置文件
grep '^[a-z]' /opt/kibana/config/kibana.yml
server.port: 5601
server.host: "0.0.0.0"
elasticsearch.url: "http://10.201.1.145:9200"
kibana.index: ".kibana"- 启动服务
/etc/init.d/kibana start
netstat -lntpu | grep 5601- 初次访问kibana,并做初始化配置
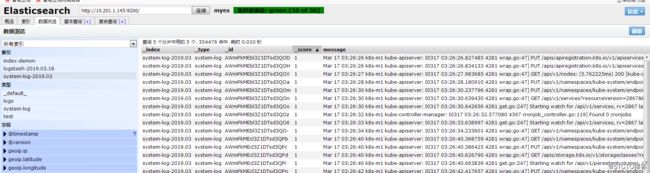
浏览器访问:http://10.201.1.146:5601
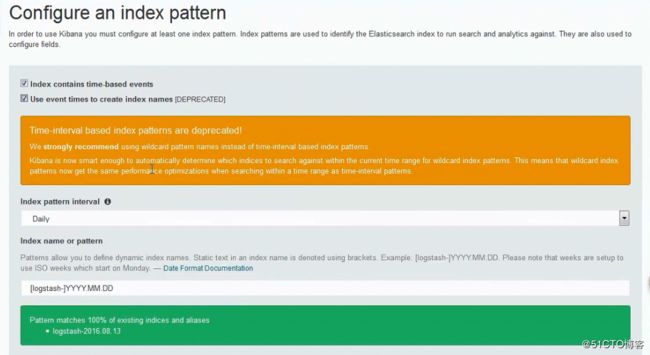
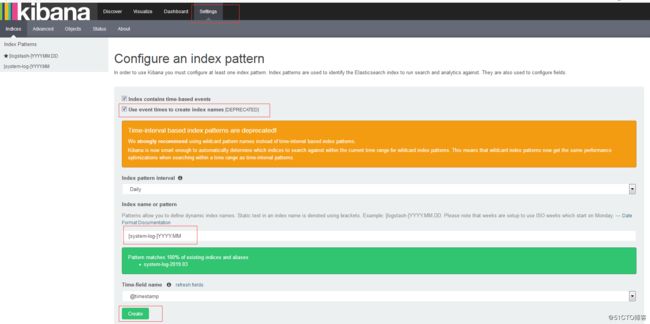
添加在es中创建的索引
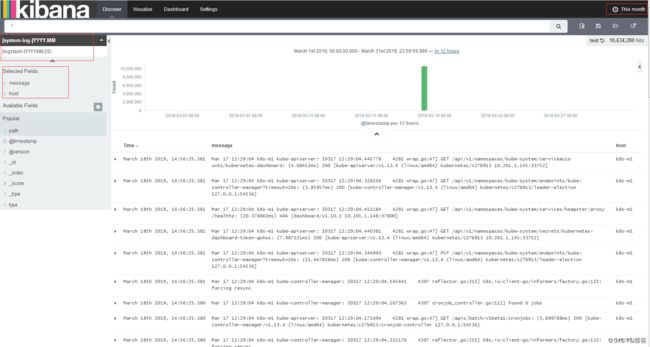
查看收集到的日志信息
- 至此,kibana搭建完成,测试OK