minimize.m:共轭梯度法更新BP算法权值
作者:凯鲁嘎吉 - 博客园 http://www.cnblogs.com/kailugaji/
Carl Edward Rasmussen在高斯机器学习的MATLAB代码中写到一个优化类的函数:minimize.m,同时,Geoff Hinton在用BP算法精调深度自编码网络时,也借鉴了这个函数minimize.m,下面来简单聊一聊这个函数的大致机理。
matlab函数minimum.m用来查找(非线性)多元函数的(局部)最小值。用户必须提供一个函数,该函数返回所有变量的值和偏导数。该函数基于具有Wolfe-Powel条件的多项式插值,使用Polak-Ribiere共轭梯度和近似线性搜索。
作用:Minimize a differentiable multivariate function.
1. 线性搜索技术——确定迭代步长
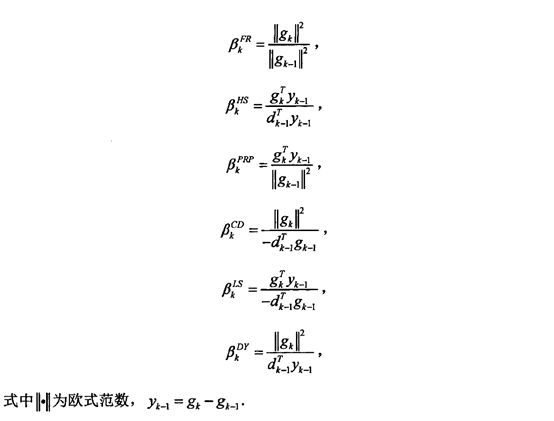
2. 非线性共轭梯度法——确定搜索方向
3. MATLAB代码详解
function [X, fX, i] = minimize(X, f, length, varargin) %X是权值偏置 f输出的是代价函数和偏导 3次线性搜索 每层网络对应的节点数Dim和训练数据data %f是一个函数的名称,它主要是用来计算网络中的代价函数以及代价函数对各个参数X的偏导函数,f的参数值分别为X,以及minimize函数后面的P1,P2,P3,…使用共轭梯度法进行优化的最大线性搜索长度为length。 %返回值X为3次线性搜索最优化后得到的权值参数,是一个列向量,fX为在此最优参数X下的代价函数,i为线性搜索的长度(即迭代的次数)。 % Minimize a differentiable multivariate function. % % Usage: [X, fX, i] = minimize(X, f, length, P1, P2, P3, ... ) %更新参数W和b,ΔW=步长*方向,Δb=步长*方向。步长用Wolfe不确定线性搜索进行计算,而下降的方向用Polack-Ribiere共轭梯度进行计算。最终输出更新完之后的参数W,b %最小化连续微分多元函数。 %起点由“ X”(D乘1)给定,并且在字符串“ f”中命名的函数必须返回函数值和偏导数向量。 %共轭梯度的Polack-Ribiere风格用于计算搜索方向,并且使用二次多项式和三次多项式逼近以及Wolfe-Powell停止准则的线搜索以及斜率比方法来猜测初始步长。 %此外,还要进行大量检查,以确保正在进行探索,并且推断不会无边无际。 %“length”给出了运行的长度:如果为正,则给出最大的线性搜索次数;如果为负,则其绝对值给出最大的函数求值次数。 %当函数的长度变长或无法进一步进行处理时(即,我们处于最小状态,或由于数值问题而接近时,我们无法进一步接近),该函数将返回。 %如果函数在几次迭代中终止,则可能表明函数值和导数不一致(即,“ f”函数的实现中可能存在错误)。 %函数返回找到的解“ X”,函数值“ fX”的向量表示进展,“ i”使用的迭代次数(线性搜索或函数评估,取决于“length”的符号)。 %当函数的长度增加或无法进一步处理时(即,我们处于(局部)最小值,或由于数值问题而接近),函数将返回。 %注意:如果函数在几次迭代中终止,则可能表明函数值和导数不一致(即,“ f”函数的实现中可能存在错误)。 %函数返回找到的解“ X”,函数值“ fX”的向量表示进展,“ i”使用的迭代次数(行搜索或函数评估,取决于“长度”的符号)。 INT = 0.1; % don't reevaluate within 0.1 of the limit of the current bracket不要在当前括号限制的0.1以内重新评估 EXT = 3.0; % extrapolate maximum 3 times the current step-size外推最大值为当前步长的3倍 MAX = 20; % max 20 function evaluations per line search每次线性搜索最多20个函数求值 RATIO = 10; % maximum allowed slope ratio最大允许斜率 SIG = 0.1; RHO = SIG/2; % SIG和RHO是控制Wolfe-Powell条件的常数。 % SIG是先前斜率和新斜率(搜索方向上的导数)之间允许的最大绝对比率,因此将SIG设置为低(正)值将强制线搜索中的更高精度。 % RHO是期望值的最小允许分数(从线性搜索中起始点的斜率开始)。 % 常数必须满足00 S='Linesearch'; %线性搜索 else S='Function evaluation'; %函数求值 end i = 0; % zero the run length counter 运行长度计数器清零 ls_failed = 0; % no previous line search has failed先前的线性搜索没有失败 [f0 df0] = feval(f, X, varargin{:}); % get function value and gradient fX = f0; i = i + (length<0); % count epochs?! s = -df0; d0 = -s'*s; % initial search direction (steepest) and slope初始搜索方向(最陡,负梯度方向)和斜率 x3 = red/(1-d0); % initial step is red/(|s|+1) 初始步长 while i < abs(length) % while not finished i = i + (length>0); % count iterations?! X0 = X; F0 = f0; dF0 = df0; % make a copy of current values if length>0, M = MAX; else M = min(MAX, -length-i); end %用p1、p2外推p3 while 1 % keep extrapolating as long as necessary x2 = 0; f2 = f0; d2 = d0; f3 = f0; df3 = df0; success = 0; while ~success && M > 0 try M = M - 1; i = i + (length<0); % count epochs?! [f3 df3] = feval(f, X+x3*s, varargin{:}); %权值(t+1)=权值(t)+初始步长*初始搜索方向 if isnan(f3) || isinf(f3) || any(isnan(df3)+isinf(df3)), error(''), end success = 1; catch % catch any error which occured in f x3 = (x2+x3)/2; % bisect and try again %步长等分,选取新搜索点 end end if f3 < F0, X0 = X+x3*s; F0 = f3; dF0 = df3; end % keep best values d3 = df3'*s; % new slope if d3 > SIG*d0 || f3 > f0+x3*RHO*d0 || M == 0 % are we done extrapolating? break end x1 = x2; f1 = f2; d1 = d2; % move point 2 to point 1 x2 = x3; f2 = f3; d2 = d3; % move point 3 to point 2 A = 6*(f1-f2)+3*(d2+d1)*(x2-x1); % make cubic extrapolation B = 3*(f2-f1)-(2*d1+d2)*(x2-x1); x3 = x1-d1*(x2-x1)^2/(B+sqrt(B*B-A*d1*(x2-x1))); % num. error possible, ok! if ~isreal(x3) || isnan(x3) || isinf(x3) || x3 < 0 % num prob | wrong sign? x3 = x2*EXT; % extrapolate maximum amount elseif x3 > x2*EXT % new point beyond extrapolation limit? x3 = x2*EXT; % extrapolate maximum amount elseif x3 < x2+INT*(x2-x1) % new point too close to previous point? x3 = x2+INT*(x2-x1); end end % end extrapolation %插值p2、p3和p4 while (abs(d3) > -SIG*d0 || f3 > f0+x3*RHO*d0) && M > 0 % keep interpolating if d3 > 0 || f3 > f0+x3*RHO*d0 % choose subinterval x4 = x3; f4 = f3; d4 = d3; % move point 3 to point 4 else x2 = x3; f2 = f3; d2 = d3; % move point 3 to point 2 end if f4 > f0 x3 = x2-(0.5*d2*(x4-x2)^2)/(f4-f2-d2*(x4-x2)); % quadratic interpolation 二次插值 else A = 6*(f2-f4)/(x4-x2)+3*(d4+d2); % cubic interpolation 三次插值 B = 3*(f4-f2)-(2*d2+d4)*(x4-x2); x3 = x2+(sqrt(B*B-A*d2*(x4-x2)^2)-B)/A; % num. error possible, ok! end if isnan(x3) || isinf(x3) x3 = (x2+x4)/2; % if we had a numerical problem then bisect end x3 = max(min(x3, x4-INT*(x4-x2)),x2+INT*(x4-x2)); % don't accept too close [f3 df3] = feval(f, X+x3*s, varargin{:}); if f3 < F0, X0 = X+x3*s; F0 = f3; dF0 = df3; end % keep best values M = M - 1; i = i + (length<0); % count epochs?! d3 = df3'*s; % new slope end % end interpolation %用Polack-Ribiere共轭梯度法更新搜索方向 if abs(d3) < -SIG*d0 && f3 < f0+x3*RHO*d0 % if line search succeeded X = X+x3*s; f0 = f3; fX = [fX' f0]'; % update variables fprintf('%s %6i; Value %4.6e\r', S, i, f0); s = (df3'*df3-df0'*df3)/(df0'*df0)*s - df3; % Polack-Ribiere 共轭梯度方向 搜索方向的更新公式 df0 = df3; % swap derivatives d3 = d0; d0 = df0'*s; if d0 > 0 % new slope must be negative s = -df0; d0 = -s'*s; % otherwise use steepest direction 负梯度方向 end x3 = x3 * min(RATIO, d3/(d0-realmin)); % slope ratio but max RATIO ls_failed = 0; % this line search did not fail else X = X0; f0 = F0; df0 = dF0; % restore best point so far if ls_failed || i > abs(length) % line search failed twice in a row break; % or we ran out of time, so we give up end s = -df0; d0 = -s'*s; % try steepest x3 = 1/(1-d0); ls_failed = 1; % this line search failed end end fprintf('\n');
4. 参考文献
[1]汪丹戎. 非线性共轭梯度法及全局收敛性分析[D].长江大学,2016.
[2] Quadratic and Cubic Search for a Minimum
[3] 2006, Carl Edward Rasmussen, Minimize
[4] 2011, Conjugate Gradient Back-propagation with Modified Polack Rebier updates for training feed forward neural network
[5] 景慧丽. 无约束最优化问题的算法研究与实现[D].西安科技大学,2009.
[6] 数值优化(Numerical Optimization)学习系列-线搜索方法(LineSearch)