题目链接:UVA 11178
Description
Input
Output
Sample Input
Sample Output
Solution
题意
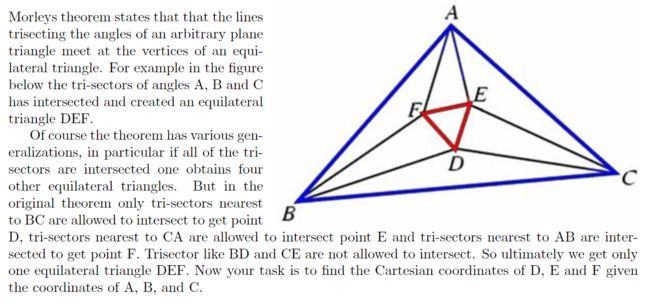
\(Morley's\ theorem\) 指任意三角形的每个内角的三等分线相交的三角形为等边三角形。
给出三角形的每个点的坐标,求根据 \(Morley's\ theorem\) 构造的等边三角形的三个点的坐标。
题解
对于点 \(D\),只需求直线 \(BC\) 绕点 \(B\) 旋转 \(\frac{1}{3} \angle ABC\) 的直线与直线 \(CB\) 绕点 \(C\) 旋转 \(\frac{1}{3} \angle ACB\) 的直线的交点。其他两点类似。
Code
#include
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef double db;
const db eps = 1e-10;
const db pi = acos(-1.0);
const ll inf = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const ll maxn = 1e5 + 10;
inline int dcmp(db x) {
if(fabs(x) < eps) return 0;
return x > 0? 1: -1;
}
class Point {
public:
double x, y;
Point(double x = 0, double y = 0) : x(x), y(y) {}
void input() {
scanf("%lf%lf", &x, &y);
}
Point operator+(const Point a) {
return Point(x + a.x, y + a.y);
}
Point operator-(const Point a) {
return Point(x - a.x, y - a.y);
}
bool operator<(const Point &a) const {
return (!dcmp(y - a.y))? dcmp(x - a.x) < 0: y < a.y;
}
db dis2() {
return x * x + y * y;
}
db dis() {
return sqrt(dis2());
}
db dot(const Point a) {
return x * a.x + y * a.y;
}
db cross(const Point a) {
return x * a.y - y * a.x;
}
db ang(Point a) {
return acos(dot(a) / (a.dis() * dis()));
}
Point Rotate(double rad) {
return Point(x * cos(rad) - y * sin(rad), x * sin(rad) + y * cos(rad));
}
};
typedef Point Vector;
class Line {
public:
Point s, e;
db angle;
Line() {}
Line(Point s, Point e) : s(s), e(e) {}
inline void input() {
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf", &s.x, &s.y, &e.x, &e.y);
}
int toLeftTest(Point p) {
if((e - s).cross(p - s) > 0) return 1;
else if((e - s).cross(p - s) < 0) return -1;
return 0;
}
Point crosspoint(Line l) {
double a1 = (l.e - l.s).cross(s - l.s);
double a2 = (l.e - l.s).cross(e - l.s);
double x = (s.x * a2 - e.x * a1) / (a2 - a1);
double y = (s.y * a2 - e.y * a1) / (a2 - a1);
if(dcmp(x) == 0) x = 0;
if(dcmp(y) == 0) y = 0;
return Point(x, y);
}
};
Point get_crosspoint(Point A, Point B, Point C) {
Vector v1 = C - B;
db a1 = v1.ang(A - B);
v1 = v1.Rotate(a1 / 3.0);
v1 = v1 + B;
Vector v2 = B - C;
db a2 = v2.ang(A - C);
v2 = v2.Rotate(-a2 / 3.0);
v2 = v2 + C;
Line l1 = Line(B, v1);
Line l2 = Line(C, v2);
return l1.crosspoint(l2);
}
int main() {
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T--) {
Point a, b, c;
a.input(); b.input(); c.input();
Point d, e, f;
d = get_crosspoint(a, b, c);
e = get_crosspoint(b, c, a);
f = get_crosspoint(c, a, b);
printf("%.6lf %.6lf %.6lf %.6lf %.6lf %.6lf\n", d.x, d.y, e.x, e.y, f.x, f.y);
}
return 0;
}