本文包含以下打钩知识点:
- [x] Collections类是什么?Collection 和 Collections的区别?
- [ ] 为什么 Collection 不从 Cloneable 和 Serializable 接口继承
- [ ] 说出几点 Java 中使用 Collections 的最佳实践?
Collection和Collections的区别
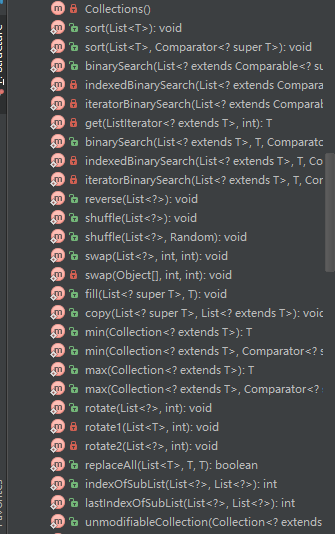
Collections
java.util.Collections,是不属于java的集合框架的,它是集合类的一个工具类/帮助类。此类不能被实例化, 服务于java的Collection框架。
它包含有关集合操作的静态多态方法,实现对各种集合的搜索、排序、线程安全等操作。如:
常用的有:
(1)排序 sort(Collection)
如Collections.sort(List
使用sort方法可以根据元素的自然顺序对指定列表按升序进行排序。列表中的所有元素都必须实现Comparable接口, 而且必须是使用指定比较器可相互比较的。
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static > void sort(List list) {
list.sort(null);
}
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
public static void sort(List list, Comparator c) {
list.sort(c);
}
简单示例:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = Arrays.asList("one two three four five".split(" "));
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println(list);
}
}
运行结果:
[five, four, one, three, two] //(按字母排序)
(2)混排 shuffle(Collection)
如Collections.shuffle(List list)
基于随机源的输入随机排序该List,这个算法对实现一个碰运气的游戏非常有用,在生成测试案例时也十分有用。
简单示例:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = Arrays.asList("one two three four five".split(" "));
Collections.shuffle(list);
System.out.println(list);
}
}
运行结果:
[three, five, four, one, two]
(3)反转 reverse(Collection)
如Collections.reverse(List list)
使用reverse()反转集合中元素的顺序
简单示例:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = Arrays.asList("one two three four five".split(" "));
Collections.reverse(list);
System.out.println(list);
}
}
运行结果:
[five, four, three, two, one]
(4)替换所有元素 fill(List list,Object o)
使用指定元素替换集合中的所有元素。
简单示例:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = Arrays.asList("one two three four five".split(" "));
Collections.fill(list, "zero");
System.out.println(list);
}
}
运行结果:
[zero, zero, zero, zero, zero]
(5)拷贝 copy(List list1,List list2)
将集合list2中的元素全部复制到list1中,并且覆盖相应索引的元素。目标list1至少与源list2一样长。
简单示例:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list1 = Arrays.asList("one two three four five".split(" "));
List list2 = Arrays.asList("一 二 三 四 五".split(" "));
Collections.copy(list1, list2);
System.out.println(list1);
}
}
运行结果:
[一, 二, 三, 四, 五]
(6)rotate(List list,int m)
根据指定的距离m循环移动列表中的元素。集合中的元素向后移m个位置,在后面被遮盖的元素循环到前面来。
简单示例:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list1 = Arrays.asList("one two three four five".split(" "));
Collections.rotate(list1, 2);
System.out.println(list1);
}
}
运行结果:
[four, five, one, two, three]
(7)最小(大)元素 min(),max()
根据指定比较器产生的顺序,返回给定Collection的最小(大)元素。
min(Collection),min(Collection,Comparator)
max(Collection),max(Collection,Comparator)
简单示例:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(10);
list.add(40);
list.add(20);
list.add(50);
System.out.println(Collections.min(list));
System.out.println(Collections.max(list));
}
}
运行结果:
10
50
(8)indexOfSublist(List list,List sublist)
查找sublist在list中首次出现位置的索引。返回指定源列表中第一次出现指定目标列表的起始位置。
简单示例:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = Arrays.asList("one two three four five".split(" "));
List subList=Arrays.asList("three four five".split(" "));
System.out.println(Collections.indexOfSubList(list,subList));
}
}
运行结果:
2
(9)lastIndexOfSublist(List list,List sublist)
返回指定列表中最后一次出现指定目标列表的起始位置。
(10)swap(List list,int m,int n)
交换集合中指定元素索引m,n的位置。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = Arrays.asList("one two three four five".split(" "));
Collections.swap(list, 2, 3);
System.out.println(list);
}
}
运行结果:
[one, two, four, three, five]
Collection
Collection是最基本的集合接口,一个Collection代表一组Object,即Collection的元素。它的直接继承接口有List,Set和Queue。
Collection接口,Set、List接口参考
Java中集合类框架及基本接口
参考资料:
Collections类常用方法总结
Collection与Collections的区别