第1章 ssh补充
1.1 ssh服务相关命令操作方法
ssh –p52113 wuhuang@10.0.0.41 [命令]
l SSH连接远程主机命令的基本语法;
l -p(小写)接端口,默认22端口时可以省略-p22;
l “@”前面为用户名,如果用当前用户连接,可以不指定用户。
l “@”后面为要连接的服务器的IP. 更多用法
l -A 携带私钥认证文件,登录远程主机中
通过man ssh查询更多帮助信息。
1.2 scp
scp -P22 -rp /tmp/wuhuang wuhuang@10.0.0.143:/tmp
说明:scp命令有推和拉的概念
l -P (大写,注意和ssh命令的不同)接端口,默认22端口时可以省略-P22;
l -r 递归,表示拷贝目录;
l -p 表示在拷贝前后保持文件或目录属性;
l -l limit 限制速度。
l /tmp/wuhuang为本地的目录。
l “@”前为用户名,“@”后为要连接的服务器的IP。
l IP后的:/tmp目录,为远端的目标目录。
1.3 sftp
sftp -oPort=52113 wuhuang@10.0.0.142 --- 实现ftp协议中控制链路建立
l -oPort=52113 --- 指定连接ssh服务端口
l sftp> --- 进入到ftp控制命令行中
l bye --- Quit sftp 退出ftp控制界面命令
l ls --- 显示出sftp服务端文件或目录数据信息
l lls --- 显示出sftp客户端(本地)文件或目录数据信息
l pwd --- 检查当前登录到sftp服务端之后,所在路径信息
l lpwd --- 检查当前登录到sftp服务端之后,客户端所在路径信息
l get --- 从ftp服务端下载数据
l put --- 从ftp客户端上传数据
l mget --- 批量下载数据
l mput --- 批量上传数据
第2章 ssh+key
2.1 部署好基于ssh秘钥认证的环境
2.1.1 第一步:创建秘钥对
ssh-keygen -t rsa
2.1.2 第二步:分发公钥
ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub 172.16.1.41
2.2 实现批量部署ssh+key环境时遇到的问题
2.2.1 创建秘钥对时需要进行交互,输入回车
1) 需要确认私钥保存路径
解决方法:ssh-keygen -t rsa -f /root/.ssh/id_rsa
-f filename #Specifies the filename of the key file. 指定私钥文件保存路径信息参数
2) 需要确认私钥密码信息
解决方法:ssh-keygen -t rsa -f /root/.ssh/id_rsa -P ""
-N new_passphrase #Provides the new passphrase. 提供了新的密码
-P passphrase #Provides the (old) passphrase 提供旧密码
2.2.2 分发公钥时,需要输入yes和密码信息
解决方法:
sshpass -p123456 ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub "172.16.1.41 -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no"
sshpass -p123456 #指定密码为123456,忽略交互
如果端口号不是默认的22号端口,例如是52114
sshpass -p123456 ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub "172.16.1.7 -p52114"
[root@m01 ~]# cat /usr/bin/ssh-copy-id …… ssh $1 "exec sh -c 'cd; umask 077; test -d .ssh || mkdir .ssh ; cat >> .ssh/authorized_keys && (test -x /sbin/restorecon && /sbin/restorecon .ssh .ssh/authorized_keys >/dev/null 2>&1 || true)'" || exit 1 …… 说明: 1. exec sh -c --- 在脚本中临时设置环境变量信息 2. cd --- 切换到当前用户家目录 3. umask 077 --- 设置临时的umask值,使发布过去的公钥信息是600的权限 4. test -d .ssh || mkdir .ssh --- 判断当前用户家目录是否存在.ssh目录,如果不存在就进行创建 5. cat >> .ssh/authorized_keys && ...省略... ---- 将当前主机秘钥对中公钥信息复制到远程主机上,在远 程主机接收到公钥信息后,将信息保存到.ssh/authorized_keys 总体含义:远程登录到相应主机上, 将公钥信息保存到远程主机相应用户家目录中的.ssh/authorized_keys 并将authorized_keys权限设置为600 |
shift:一个shift可以理解为忽略在命令行中的第一个参数(执行第二次忽略第一个参数,执行第三次忽略前两个参数,依次忽略)
脚本内容 [root@m01 scripts]# cat shift.sh #!/bin/bash until [ $# -eq 0 ] do echo $* shift done 执行结果 [root@m01 scripts]# sh shift.sh 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 2 3 4 5 6 3 4 5 6 4 5 6 5 6 6 |
2.3 编写免交互批量分发公钥脚本
2.3.1 编写脚本
脚本内容 [root@m01 scripts]# cat fenfa.sh #!/bin/bash
# create key pair \rm /root/.ssh/id_rsa* -f #避免.ssh下已有公钥信息,下次在创建时,会提示是否覆盖 ssh-keygen -t rsa -f /root/.ssh/id_rsa -P "" &>/dev/null #免交互创建秘钥对
# fenfa #免交互分发公钥 for ip in 7 8 31 41 do echo =====================172.16.1.$ip fenfa info========================== sshpass -p123456 ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub "172.16.1.$ip -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no" echo =====================172.16.1.$ip fenfa end=========================== echo "" done |
2.3.2 测试
[root@m01 scripts]# sh fenfa.sh =====================172.16.1.7 fenfa info========================== Now try logging into the machine, with "ssh '172.16.1.7 -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no'", and check in:
.ssh/authorized_keys
to make sure we haven't added extra keys that you weren't expecting.
=====================172.16.1.7 fenfa end===========================
=====================172.16.1.8 fenfa info========================== Warning: Permanently added '172.16.1.8' (RSA) to the list of known hosts. Now try logging into the machine, with "ssh '172.16.1.8 -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no'", and check in:
.ssh/authorized_keys
to make sure we haven't added extra keys that you weren't expecting.
=====================172.16.1.8 fenfa end===========================
=====================172.16.1.31 fenfa info========================== Now try logging into the machine, with "ssh '172.16.1.31 -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no'", and check in:
.ssh/authorized_keys
to make sure we haven't added extra keys that you weren't expecting.
=====================172.16.1.31 fenfa end===========================
=====================172.16.1.41 fenfa info========================== Now try logging into the machine, with "ssh '172.16.1.41 -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no'", and check in:
.ssh/authorized_keys
to make sure we haven't added extra keys that you weren't expecting.
=====================172.16.1.41 fenfa end===========================
说明:执行脚本时后面不加参数的话,会先连接到172.16.1.7,在连接到31,然后从31在连接到41 |
2.4 编写批量管理脚本
2.4.1 编写脚本
[root@m01 scripts]# cat batch.sh #!/bin/bash
#batch
for ip in 7 8 31 41
do
echo =====================172.16.1.$ip host info==========================
ssh 172.16.1.$ip $1 #$1 表示第一个参数
echo ""
done 说明:执行脚本时后面不加参数的话,会先连接到172.16.1.7,在连接到31,然后从31在连接到41 |
2.4.2 测试
[root@m01 scripts]# sh batch.sh hostname #批量查看每个主机的主机名 =====================172.16.1.7 host info========================== web01
=====================172.16.1.8 host info========================== web02
=====================172.16.1.31 host info========================== nfs01
=====================172.16.1.41 host info========================== backup |
[root@m01 scripts]# sh batch.sh free -m #批量查看每个主机的内存信息 =====================172.16.1.7 host info========================== total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 485984 252840 233144 228 26956 121208 -/+ buffers/cache: 104676 381308 Swap: 204796 0 204796
=====================172.16.1.8 host info========================== total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 485984 258228 227756 236 27088 124804 -/+ buffers/cache: 106336 379648 Swap: 204796 0 204796
=====================172.16.1.31 host info========================== total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 485984 248468 237516 228 25568 117744 -/+ buffers/cache: 105156 380828 Swap: 204796 0 204796
=====================172.16.1.41 host info========================== total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 485984 239944 246040 228 25412 114812 -/+ buffers/cache: 99720 386264 Swap: 204796 0 204796
|
[root@m01 scripts]# sh batch.sh uptime #批量查看每个主机的负载信息 =====================172.16.1.7 host info========================== 11:18:17 up 1:25, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
=====================172.16.1.8 host info========================== 11:18:18 up 1:24, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
=====================172.16.1.31 host info========================== 11:18:18 up 1:31, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
=====================172.16.1.41 host info========================== 11:18:18 up 1:26, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
|
[root@m01 scripts]# sh batch.sh yum install libselinux-python -y #批量安装ansible被管理端软件 |
第3章 实现多台主机之间,彼此相互访问都是基于秘钥的
3.1 方法1(思路:多台主机的秘钥都一样)
3.1.1 第一步:在一台主机上创建秘钥对
[root@m01 ~]# ssh-keygen -t rsa Generating public/private rsa key pair. Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa): Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): Enter same passphrase again: Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa. Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub. The key fingerprint is: 50:c8:08:88:32:8e:ad:ad:e2:3e:9c:c1:b3:1f:ad:92 root@m01 The key's randomart image is: +--[ RSA 2048]----+ |.... o .. | |= . o. | |+o . | |... . | |.o S | |.+. . | |..*. . | |oE o | |+o+o | +-----------------+ [root@m01 ~]# ll .ssh/ total 8 -rw------- 1 root root 1675 Feb 3 11:34 id_rsa -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 390 Feb 3 11:34 id_rsa.pub |
3.1.2 第二步:将公钥复制到authorized_keys
[root@m01 ~]# cd .ssh/ [root@m01 .ssh]# cp id_rsa.pub authorized_keys [root@m01 .ssh]# ll total 12 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 390 Feb 3 11:36 authorized_keys -rw------- 1 root root 1675 Feb 3 11:34 id_rsa -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 390 Feb 3 11:34 id_rsa.pub |
3.1.3 第三步:将authorized_keys权限设为600
[root@m01 .ssh]# chmod 600 authorized_keys |
3.1.4 第四步:将 .ssh目录远程复制到其他主机
[root@m01 ~]# rsync -rp .ssh [email protected]:/root [root@m01 ~]# rsync -rp .ssh [email protected]:/root [root@m01 ~]# rsync -rp .ssh [email protected]:/root [root@m01 ~]# rsync -rp .ssh [email protected]:/root |
3.1.5 第五步:测试
[root@m01 ~]# ssh 172.16.1.7 hostname web01 [root@m01 ~]# ssh 172.16.1.8 hostname web02 [root@m01 ~]# ssh 172.16.1.31 hostname nfs01 [root@m01 ~]# ssh 172.16.1.41 hostname backup 实现彼此之间的访问不需要密码 |
3.2 方法2
思路:每台主机分别创建自己的秘钥对,再将公钥分发给其他主机
此种方法比较繁琐,当有多台主机时工作量会加大
第4章 利用xshell实现基于秘钥连接虚拟主机
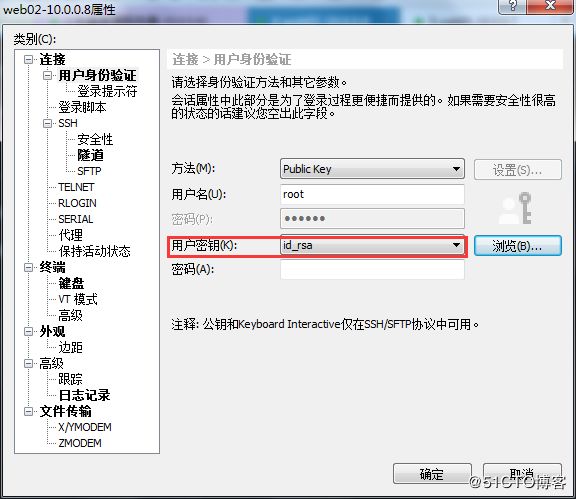
4.1 第一步:设置用户身份验证方式
4.2 第二步:将主机私钥传输到宿主机
[root@web02 .ssh]# sz id_rsa |
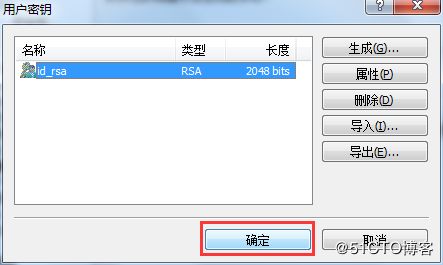
4.3 第三步:创建用户秘钥
4.4 第四步:修改ssh服务端配置文件并重启服务
[root@web02 .ssh]# vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config 66 PasswordAuthentication no [root@web02 .ssh]# /etc/init.d/sshd reload Reloading sshd: [ OK ] |
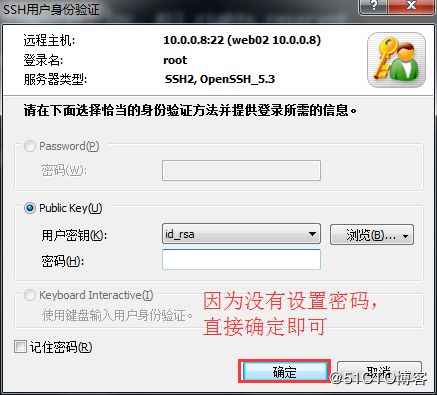
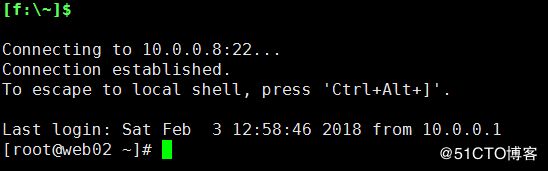
4.5 第五步:重新连接测试
注:因为这些主机的秘钥对都是一样的,所以都可以利用xshell实现基于秘钥连接