Google Dapper和Alibaba EagleEye都是用于大规模分布式系统的业务链路监控,2者都是基于ThreadLocal来透传Trace信息,那么ThreadLocal是什么,为什么会被用来传递Trace信息?
什么是业务链路监控系统:
一个复杂的分布式web系统,前端的一次用户操作,对应的是后端几十甚至上百个应用和服务的调用,这些调用有串行的、并行的,那么如何确定前端的一次操作背后调用了哪些应用、服务、接口,这些调用的先后顺序又是怎样,业务链路监控系统就是用来解决这个痛点的。
实现原理:
从流量入口(通常是前端的一次Http调用)开始,传递Trace(TraceId,RpcId,UserData),在整个业务链路上传递Trace信息,从前端、服务层到数据层一层一层传递下去,这样根据TraceId就可以识别具体调用属于哪条链路
Trace信息是如何在链路内透传:
Trace信息相当于在业务链路中的埋点信息
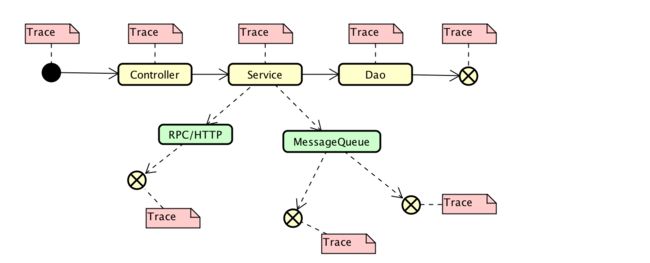
如下图:链路的调用分2种,系统内部的调用通常是线程内的调用,而经过RPC、HTTP、异步消息调用都是不同系统(不同线程间)的调用
2种场景的Trace信息透传:
线程/进程间传递使用参数传递:客户端调用服务端、异步消息调用属于信息从一个应用的线程转移到另外一个应用的线程,在2个线程之间传递Trace信息使用参数传递
线程内传递使用ThreadLocal:线程内部的方法之间调用,无论调用了多少个方法,都是一个线程内部的调用,这些方法间传递Trace信息使用ThreadLocal
-
线程间透传
- HTTP:通过Http head或者body传递Trace信息。
- RPC:通过自定义的rpc协议(根据rpc框架实现的不同,各个公司有不同的rpc协议实现)传递Trace信息。
- MQ:通过消息头或者消息体携带Trace信息实现Trace信息从消息的生产者向消费者传递。
-
线程内透传:
- ThreadLocal:进入线程时,将Trace信息存储在ThreadLocal变量中,出线程时,从ThreadLocal变量中取出Trace信息,作为参数传递到下一个线程(应用系统)。
ThreadLocal是什么?
上面讲了业务链路监控系统是如何实现无侵入式的Trace信息透传,那么ThreadLocal是什么,为什么可以实现线程内的数据传递。
首先,ThreadLocal是一个老家伙,它在jdk1.2的时候就已经存在了,首先看下ThreadLocal的注释:
/**
* This class provides thread-local variables. These variables differ from
* their normal counterparts in that each thread that accesses one (via its
* {@code get} or {@code set} method) has its own, independently initialized
* copy of the variable. {@code ThreadLocal} instances are typically private
* static fields in classes that wish to associate state with a thread (e.g.,
* a user ID or Transaction ID).
*
* For example, the class below generates unique identifiers local to each
* thread.
* A thread's id is assigned the first time it invokes {@code ThreadId.get()}
* and remains unchanged on subsequent calls.
*
* import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
*
* public class ThreadId {
* // Atomic integer containing the next thread ID to be assigned
* private static final AtomicInteger nextId = new AtomicInteger(0);
*
* // Thread local variable containing each thread's ID
* private static final ThreadLocal threadId =
* new ThreadLocal() {
* @Override protected Integer initialValue() {
* return nextId.getAndIncrement();
* }
* };
*
* // Returns the current thread's unique ID, assigning it if necessary
* public static int get() {
* return threadId.get();
* }
* }
*
* Each thread holds an implicit reference to its copy of a thread-local
* variable as long as the thread is alive and the {@code ThreadLocal}
* instance is accessible; after a thread goes away, all of its copies of
* thread-local instances are subject to garbage collection (unless other
* references to these copies exist).
*
* @author Josh Bloch and Doug Lea
* @since 1.2
*/
public class ThreadLocal {
}
ThreadLocal变量特殊的地方在于:对变量值的任何操作实际都是对这个变量在线程中的一份copy进行操作,不会影响另外一个线程中同一个ThreadLocal变量的值。
例如定义一个ThreadLocal变量,值类型为Integer:
ThreadLocal tLocal = new ThreadLocal();
ThreadLocal提供的几个主要接口:
- set(T value):设置ThreadLocal变量在当前线程中copy的值。
- get():获取当前ThreadLocal变量在当前线程中copy的值。
- remove():移除当前ThreadLocal变量在当前线程中copy的值。
- initialValue():初始化ThreadLocal变量在当前线程中copy的值
范例代码:
package com.wow.testcode.threadlocal;
/**
* Created by arthur.hw on 2017/8/17.
*/
public class TestThreadLocal {
private ThreadLocal seq = new ThreadLocal() {
@Override
protected TestBean initialValue() {
return new TestBean();
}
};
public TestBean addSeq() {
System.out.println("thread --> " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " --> " + seq.get());
seq.get().setId(seq.get().getId() + 1);
return seq.get();
}
public void setSeq(TestBean testbean) {
this.seq.set(testbean);
}
public TestBean getSeq() {
return this.seq.get();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestThreadLocal tlocal = new TestThreadLocal();
TestBean testbean = new TestBean();
tlocal.setSeq(testbean);
tlocal.addSeq();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new NewTestThread(tlocal, testbean));
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new NewTestThread(tlocal, testbean));
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
package com.wow.testcode.threadlocal;
/**
* Created by arthur.hw on 2017/8/17.
*/
public class NewTestThread implements Runnable {
private TestThreadLocal seq;
private TestBean testBean;
public NewTestThread(TestThreadLocal seq, TestBean testBean) {
this.seq = seq;
this.testBean = testBean;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("thread inner--> " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " --> " + this.seq.getSeq());
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("thread --> " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " --> seq = "
+ seq.addSeq().getId());
}
}
}
package com.wow.testcode.threadlocal;
/**
* Created by arthur.hw on 2017/8/17.
*/
public class TestBean {
private Integer id = 0;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
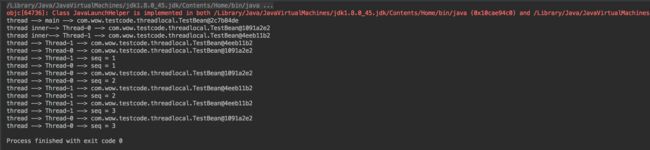
执行结果:
结果分析:
- thread0和thread1中对ThreadLocal变量seq的操作并没有相互影响。
- 主线程在thread1启动前修改seq值对thread1无影响,thread1中seq初始值仍然是0。
- 三个线程中调用get方法获取到的是不同的TestBean对象
ThreadLocal变量线程独立的原理:
直接看ThreadLocal变量的赋值:
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
- getMap的作用是返回线程对象t的threadLocals属性的值
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
线程对象的threadLocals属性定义如下:
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
getMap返回的是线程对象t的threadLocals属性,一个ThreadLocalMap对象
- createMap(t,value)的作用是初始化线程对象t的属性threadLocals的值:
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
- 综上看,ThreadLocal.set(T value)的逻辑是:
首先获取当前线程对象t,然后调用getMap(t)获取t.threadLocals,如果获取到的t.threadLocals为空,就调用createMap(t,value)对t.threadLocals进行初始化赋值,否则调用map.set(this,value)覆盖t.threadLocals的值。
一个线程中调用ThreadLocal变量的get/set方法获取和修改的是当前线程中存储的value,当前线程无法修改另外一个线程的存储的value,这就是ThreadLocal变量线程独立的原因。
但是如果不同线程的value通过调用set方法指向同一个对象,ThreadLocal就丧失了线程独立性,范例代码:
package com.wow.testcode.threadlocal;
/**
* Created by arthur.hw on 2017/8/17.
*/
public class TestThreadLocal {
private ThreadLocal seq = new ThreadLocal();
public TestBean addSeq() {
System.out.println("thread --> " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " --> " + seq.get());
seq.get().setId(seq.get().getId() + 1);
return seq.get();
}
public void setSeq(TestBean testbean) {
this.seq.set(testbean);
}
public TestBean getSeq(){
return this.seq.get();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestThreadLocal tlocal = new TestThreadLocal();
TestBean testbean = new TestBean();
tlocal.setSeq(testbean);
tlocal.addSeq();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new NewTestThread(tlocal, testbean));
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new NewTestThread(tlocal, testbean));
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
package com.wow.testcode.threadlocal;
/**
* Created by arthur.hw on 2017/8/17.
*/
public class NewTestThread implements Runnable {
private TestThreadLocal seq;
private TestBean testBean;
public NewTestThread(TestThreadLocal seq, TestBean testBean) {
this.seq = seq;
this.testBean = testBean;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 线程运行前,将ThreadLocal变量的值赋值为外部的testBean对象
this.seq.setSeq(testBean);
System.out.println("thread inner--> " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " --> " + this.seq.getSeq());
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("thread --> " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " --> seq = "
+ seq.addSeq().getId());
}
}
}
package com.wow.testcode.threadlocal;
/**
* Created by arthur.hw on 2017/8/17.
*/
public class TestBean {
private Integer id = 0;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
和前面代码的区别在于,线程运行前,调用set方法将value置为外部的testBean变量,看运行结果:
所以ThreadLocal线程独立的前提是:不要使用set方法设置value为同一个对象,ThreadLocal对象会自动在线程第一次调用get方法中调用initialValue()方法生成一个类型的实例作为value。