1.JavaScript 中的所有事物都是对象:字符串、数值、数组、函数...
此外,JavaScript 允许自定义对象。
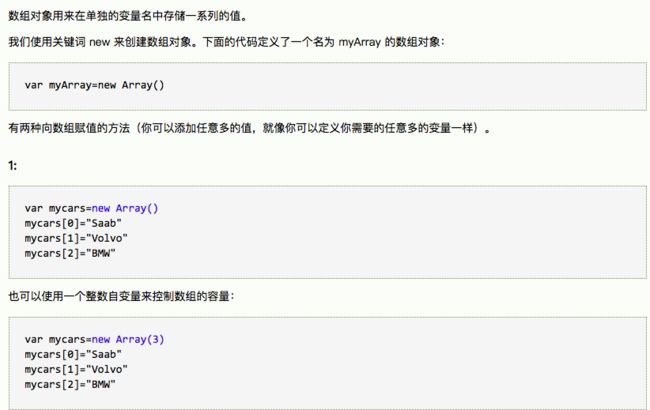
2.创建直接的实例,这个例子创建了对象的一个新实例,并向其添加了四个属性:
person=new Object();
person.firstname="Bill";
person.lastname="Gates";
person.age=56;
person.eyecolor="blue";
替代语法(使用对象 literals):
person={firstname:"John",lastname:"Doe",age:50,eyecolor:"blue"};
3.使用对象构造器
本例使用函数来构造对象:
实例
function person(firstname,lastname,age,eyecolor)
{
this.firstname=firstname;
this.lastname=lastname;
this.age=age;
this.eyecolor=eyecolor;
}
创建 JavaScript 对象实例
一旦有了对象构造器,就可以创建新的对象实例,就像这样:
var myFather=new person("Bill","Gates",56,"blue");
var myMother=new person("Steve","Jobs",48,"green");
4.JavaScript 类
JavaScript 是面向对象的语言,但 JavaScript 不使用类。
在 JavaScript 中,不会创建类,也不会通过类来创建对象(就像在其他面向对象的语言中那样)。
JavaScript 基于 prototype,而不是基于类的。
5.var y=123e5;// 12300000
var z=123e-5;// 0.00123
6.八进制和十六进制
如果前缀为 0,则 JavaScript 会把数值常量解释为八进制数,如果前缀为 0 和 "x",则解释为十六进制数。
实例
var y=0377;
var z=0xFF;
提示:绝不要在数字前面写零,除非您需要进行八进制转换。
7.数字属性和方法
属性:
MAX VALUE
MIN VALUE
NEGATIVE INFINITIVE
POSITIVE INFINITIVE
NaN
prototype
constructor
方法:
toExponential()
toFixed()
toPrecision()
toString()
valueOf()
8.字符串样式
document.write("Fontcolor: " + txt.fontcolor("Red") + "
")
9.JavaScript String(字符串)对象 实例
(1)document.write(txt.length)计算字符串的长度
(2)document.write("Fontcolor: " + txt.fontcolor("Red") + "
")document.write("Fontsize: " + txt.fontsize(16) + "
")
document.write("Lowercase: " + txt.toLowerCase() +
")document.write("Uppercase: " + txt.toUpperCase() + "
")为字符串添加样式
(3)var str="Hello world!"
document.write(str.indexOf("Hello") + "
")
document.write(str.indexOf("World") + "
")
document.write(str.indexOf("world"))
输出0,-1,6indexOf() 方法
(4)var str="Hello world!"document.write(str.match("world") + "
")
document.write(str.match("World") + "
")
document.write(str.match("worlld") + "
")
document.write(str.match("world!"))
输出world,null,null,world!match() 方法
(5)var str="Visit Microsoft!"
document.write(str.replace(/Microsoft/,"你好"))如何替换字符串中的字符 - replace()
8.返回当日的日期和时间
如何使用 Date() 方法获得当日的日期。
document.write(Date())
getTime()
getTime() 返回从 1970 年 1 月 1 日至今的毫秒数。
var d=new Date();
document.write("从 1970/01/01 至今已过去 " + d.getTime() + " 毫秒");
从 1970/01/01 至今已过去 1510461729190 毫秒
var d=new Date()
var weekday=new Array(7)
weekday[0]="星期日"
weekday[1]="星期一"
weekday[2]="星期二"
weekday[3]="星期三"
weekday[4]="星期四"
weekday[5]="星期五"
weekday[6]="星期六"
document.write("今天是" + weekday[d.getDay()])
显示时钟
function startTime()
{
var today=new Date()
var h=today.getHours()
var m=today.getMinutes()
var s=today.getSeconds()
// add a zero in front of numbers<10
m=checkTime(m)
s=checkTime(s)
document.getElementById('txt').innerHTML=h+":"+m+":"+s
t=setTimeout('startTime()',500)
}
function checkTime(i)
{
if (i<10)
{i="0" + i}
return i
}
var myDate=new Date()myDate.setFullYear(2008,7,9)
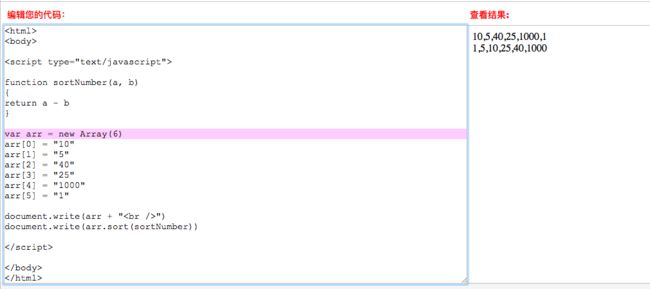
9.arr和arr2是两个数组,合并数组的方法是:
document.write(arr.concat(arr2))
10.document.write(arr.join());用数组的元素组成字符串 - join()
11
12.
13.document.write(Math.random())
使用 random() 来返回 0 到 1 之间的随机数。
document.write(Math.round(0.60) + "
")document.write(Math.round(0.50) + "
")
document.write(Math.round(0.49) + "
")
document.write(Math.round(-4.40) + "
")
document.write(Math.round(-4.60))
如何使用 round()。四舍五入1,1,0,-4,-5
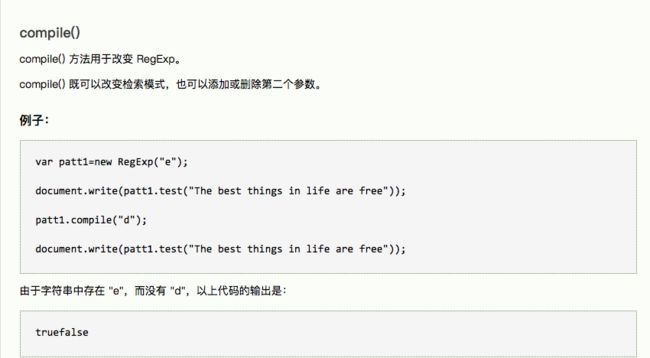
14.RegExp 对象用于规定在文本中检索的内容。
什么是 RegExp?
RegExp 是正则表达式的缩写。
当检索某个文本时,可以使用一种模式来描述要检索的内容。RegExp 就是这种模式。
简单的模式可以是一个单独的字符。
更复杂的模式包括了更多的字符,并可用于解析、格式检查、替换等等。
可以规定字符串中的检索位置,以及要检索的字符类型,等等。
15.
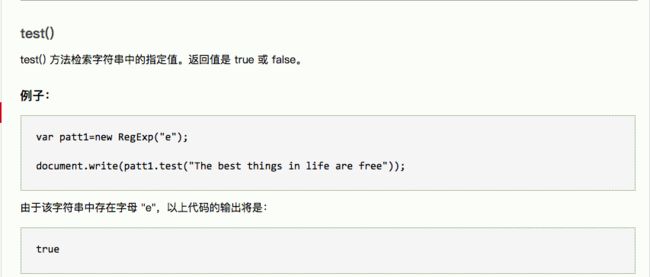
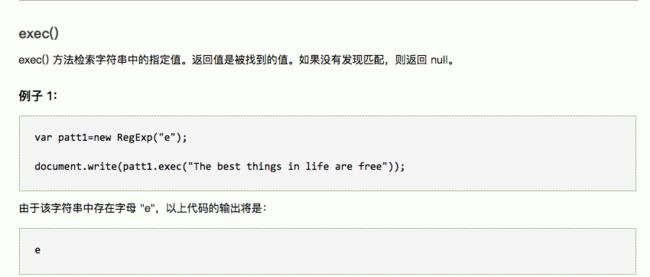
16.RegExp 对象的方法
RegExp 对象有 3 个方法:test()、exec() 以及 compile()。