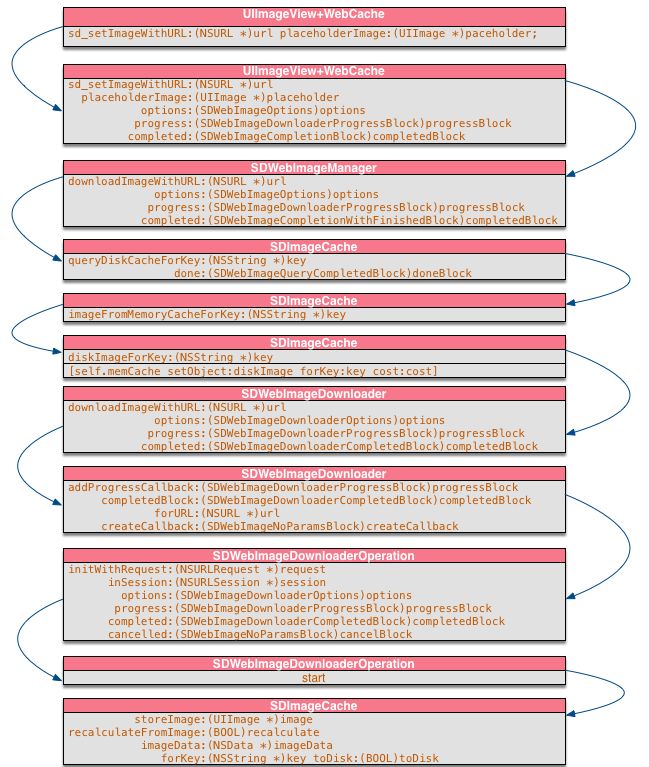
在SDWebImage源码解析(一)中,我从宏观上介绍了SDWebImage项目,并详细介绍了UIImageView+WebCache和SDWebImageManager两个类。现在我们继续研究SDWebImageDownloader和SDImageCache。
SDWebImageDownloader
Asynchronous downloader dedicated and optimized for image loading.
SDWebImageDownloader是专用的且优化的图片异步加载器。先了解一下下载选项:
typedef NS_OPTIONS(NSUInteger, SDWebImageDownloaderOptions) {
//默认的使用模式,前往下载,返回进度block信息,完成时调用completedBlock
SDWebImageDownloaderLowPriority = 1 << 0,
// 渐进式下载,如果设置了这个选项,会在下载过程中,每次接收到一段返回数据就会调用一次完成回调,回调中的image参数为未下载完成的部分图像,可以实现将图片一点点显示出来的功能
SDWebImageDownloaderProgressiveDownload = 1 << 1,
// 默认情况下请求不使用NSURLCache,如果设置该选项,则以默认的缓存策略来使用NSURLCache
SDWebImageDownloaderUseNSURLCache = 1 << 2,
// 如果从NSURLcache缓存中读取图片,则在调用完成block的时候,传递空的image或者imageData
SDWebImageDownloaderIgnoreCachedResponse = 1 << 3,
// 在iOS 4+系统上,允许程序进入后台后继续下载图片。该操作通过向系统申请额外时间来完成后台下载。如果后台任务终止,则操作将被取消
SDWebImageDownloaderContinueInBackground = 1 << 4,
//通过设置NSMutableURLRequest.HTTPShouldHandleCookies = YES来处理存储在NSHTTPCookieStore中的cookie
SDWebImageDownloaderHandleCookies = 1 << 5,
// 允许不受信任的SSL证书。主要用于测试目的(生产环境慎用)
SDWebImageDownloaderAllowInvalidSSLCertificates = 1 << 6,
// 将图片下载放到高优先级队列中
SDWebImageDownloaderHighPriority = 1 << 7,
};
再看看下载顺序:
typedef NS_ENUM(NSInteger, SDWebImageDownloaderExecutionOrder) {
//默认的下载顺序,先进先出
SDWebImageDownloaderFIFOExecutionOrder,
//后进先出
SDWebImageDownloaderLIFOExecutionOrder
};
SDWebImageDownloader也定义了三个block:
// 下载进度回调(返回已经接收的图片数据的大小,未接收的图片数据的大小)
typedef void(^SDWebImageDownloaderProgressBlock)(NSInteger receivedSize, NSInteger expectedSize);
// 下载完成回调,返回图片数据或错误
typedef void(^SDWebImageDownloaderCompletedBlock)(UIImage *image, NSData *data, NSError *error, BOOL finished);
//过滤HTTP请求的Header
typedef NSDictionary *(^SDWebImageDownloaderHeadersFilterBlock)(NSURL *url, NSDictionary *headers);
类方法分别是:
//给每个HTTP下载请求头的指定field设置值。
- (void)setValue:(NSString *)value forHTTPHeaderField:(NSString *)field;
//返回HTTP特定field的值
- (NSString *)valueForHTTPHeaderField:(NSString *)field;
//设置一个SDWebImageDownloaderOperation的子类作为下载请求的默认NSOperation
- (void)setOperationClass:(Class)operationClass;
//创建一个SDWebImageDownloader异步下载实例,图片下载完成或错误时,通知delegate回调。方法返回一个 SDWebImageOperation
- (id )downloadImageWithURL:(NSURL *)url
options:(SDWebImageDownloaderOptions)options
progress:(SDWebImageDownloaderProgressBlock)progressBlock
completed:(SDWebImageDownloaderCompletedBlock)completedBlock;
// 设置下载队列为挂起状态
- (void)setSuspended:(BOOL)suspended;
//取消队列中的所有操作。
- (void)cancelAllDownloads;
实际上,SDWebImageDownloader管理一个下载队列downloadQueue,默认最大的并行操作个数是6。队列中每一个SDWebImageDownloaderOperation实例才是真正的下载请求执行者。
我们重点研究核心下载方法
- (id )downloadImageWithURL:(NSURL *)url
options:(SDWebImageDownloaderOptions)options
progress:(SDWebImageDownloaderProgressBlock)progressBlock
completed:(SDWebImageDownloaderCompletedBlock)completedBlock;
该方法就是调用了另外一个关键方法:
- (void)addProgressCallback:(SDWebImageDownloaderProgressBlock)progressBlock
completedBlock:(SDWebImageDownloaderCompletedBlock)completedBlock
forURL:(NSURL *)url
createCallback:(SDWebImageNoParamsBlock)createCallback {
// url作为URLCallbacks的key,如果为nil ,直接调用completedBlock。
if (url == nil) {
if (completedBlock != nil) {
completedBlock(nil, nil, nil, NO);
}
return;
}
//将所有下载任务的网络响应处理放到barrierQueue队列中。
//并设置栅栏来确保同一时间只有一个线程操作URLCallbacks属性
dispatch_barrier_sync(self.barrierQueue, ^{
BOOL first = NO;
if (!self.URLCallbacks[url]) {
self.URLCallbacks[url] = [NSMutableArray new];
first = YES;
}
// Handle single download of simultaneous download request for the same URL
//修改url对应的URLCallbacks
//URLCallbacks是一个字典: key是url, value是数组
//数组的元素是字典,key是callback类型字符串,value是callback的block
NSMutableArray *callbacksForURL = self.URLCallbacks[url];
NSMutableDictionary *callbacks = [NSMutableDictionary new];
if (progressBlock) callbacks[kProgressCallbackKey] = [progressBlock copy];
if (completedBlock) callbacks[kCompletedCallbackKey] = [completedBlock copy];
[callbacksForURL addObject:callbacks];
self.URLCallbacks[url] = callbacksForURL;
//第一次请求这个url 才去真正做http请求
if (first) {
createCallback();
}
});
}
该方法为下载的操作添加回调的块, 在下载进行时, 或者在下载结束时执行一些操作。图片下载的progressBlock和completedBlock回调由一个字典URLCallbacks管理。字典的key是图片的url,value 是一个数组,数组只包含一个元素,这个元素的类型是NSMutableDictionary类型,这个字典的key为NSString类型代表着回调类型,value为block,是对应的回调。由于允许多个图片同时下载,因此可能会有多个线程同时操作URLCallbacks属性。为了保证线程安全,将下载操作作为一个个任务放到barrierQueue队列中,并设置栅栏来确保同一时间只有一个线程操作URLCallbacks属性
两个回调对应的key分别是
static NSString *const kProgressCallbackKey = @"progress";
static NSString *const kCompletedCallbackKey = @"completed";
如果URLCallbacks没有url这个key,说明是第一次请求这个url,需要调用createCallback创建下载任务,即使用
- (id)initWithRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request
inSession:(NSURLSession *)session
options:(SDWebImageDownloaderOptions)options
progress:(SDWebImageDownloaderProgressBlock)progressBlock
completed:(SDWebImageDownloaderCompletedBlock)completedBlock
cancelled:(SDWebImageNoParamsBlock)cancelBlock
初始化SDWebImageDownloaderOperation实例。
下载任务使用NSMutableURLRequest,默认超时时间是15秒。
在progress block中我们取出存储在URLCallbacks中的progressBlock
SDWebImageDownloader *sself = wself;
if (!sself) return;
__block NSArray *callbacksForURL;
dispatch_sync(sself.barrierQueue, ^{
callbacksForURL = [sself.URLCallbacks[url] copy];
});
for (NSDictionary *callbacks in callbacksForURL) {
//异步提交, 当前线程直接返回
//callbacks在main_queue中并行执行
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
SDWebImageDownloaderProgressBlock callback = callbacks[kProgressCallbackKey];
if (callback)
callback(receivedSize, expectedSize);
});
}
对已经接收到的大小和期待的大小调用callback;
在completed block中我们取出存储在URLCallbacks中的completedBlock
SDWebImageDownloader *sself = wself;
if (!sself) return;
__block NSArray *callbacksForURL;
dispatch_barrier_sync(sself.barrierQueue, ^{
callbacksForURL = [sself.URLCallbacks[url] copy];
if (finished) {
[sself.URLCallbacks removeObjectForKey:url];
}
});
for (NSDictionary *callbacks in callbacksForURL) {
SDWebImageDownloaderCompletedBlock callback = callbacks[kCompletedCallbackKey];
if (callback)
callback(image, data, error, finished);
}
对image和data调用callback;
在cancelled block中,我们移除存储在URLCallbacks的数组。
初始化完成后,再设置operation的参数:
//是否解压下载的图片,默认是YES,但是会消耗掉很多内存,如果遇到内存不足的crash时,将值设为NO。
operation.shouldDecompressImages = wself.shouldDecompressImages;
//设置证书
if (wself.urlCredential) {
operation.credential = wself.urlCredential;
} else if (wself.username && wself.password) {
operation.credential = [NSURLCredential credentialWithUser:wself.username
password:wself.password
persistence:NSURLCredentialPersistenceForSession];
}
//设置队列优先级
if (options & SDWebImageDownloaderHighPriority) {
operation.queuePriority = NSOperationQueuePriorityHigh;
} else if (options & SDWebImageDownloaderLowPriority) {
operation.queuePriority = NSOperationQueuePriorityLow;
}
最后将这个SDWebImageDownloaderOperation实例添加到downloadQueue队列中去。如果下载执行顺序是LIFO,还要加上任务的依赖
//加入操作队列后, operation 真正开始执行start
//所有的下载任务放在downloadQueue队列中
[wself.downloadQueue addOperation:operation];
if (wself.executionOrder == SDWebImageDownloaderLIFOExecutionOrder) {
//加上任务的依赖,也就是说依赖的任务都完成后,才能执行当前任务
[wself.lastAddedOperation addDependency:operation];
wself.lastAddedOperation = operation;
}
SDWebImageDownloaderOperation
现在我们来研究一下上面提到的SDWebImageDownloaderOperation类。
SDWebImageDownloaderOperation是NSOperation的子类,遵循SDWebImageOperation, NSURLSessionTaskDelegate,NSURLSessionDataDelegate协议,并重写了start方法。在start方法中真正处理HTTP请求和URL链接。
首先监测下载状态:
//管理下载状态,如果已取消,则重置当前下载并设置完成状态为YES
if (self.isCancelled) {
self.finished = YES;
[self reset];
return;
}
如果是iOS4.0以上的版本,还需要考虑是否在后台执行:
Class UIApplicationClass = NSClassFromString(@"UIApplication");
BOOL hasApplication = UIApplicationClass && [UIApplicationClass respondsToSelector:@selector(sharedApplication)];
if (hasApplication && [self shouldContinueWhenAppEntersBackground]) {
//如果设置了在后台执行,则进行后台执行
__weak __typeof__ (self) wself = self;
UIApplication * app = [UIApplicationClass performSelector:@selector(sharedApplication)];
self.backgroundTaskId = [app beginBackgroundTaskWithExpirationHandler:^{
// 如果在系统规定时间内任务还没有完成(一般是10分钟),结束后台任务
__strong __typeof (wself) sself = wself;
if (sself) {
[sself cancel];
[app endBackgroundTask:sself.backgroundTaskId];
sself.backgroundTaskId = UIBackgroundTaskInvalid;
}
}];
}
Version3.8中,下载已经由原先的NSURLConnection切换到了NSURLSession了:
NSURLSession *session = self.unownedSession;
if (!self.unownedSession) {
NSURLSessionConfiguration *sessionConfig = [NSURLSessionConfiguration defaultSessionConfiguration];
sessionConfig.timeoutIntervalForRequest = 15;
//为任务创建会话,我们给delegateQueue设置nil来创建一个顺序操作队列去执行所有的代理方法和完成回调。
self.ownedSession = [NSURLSession sessionWithConfiguration:sessionConfig
delegate:self
delegateQueue:nil];
session = self.ownedSession;
}
self.dataTask = [session dataTaskWithRequest:self.request];
self.executing = YES;
self.thread = [NSThread currentThread];
创建好任务后开始执行请求。 如果任务创建成功,可能需要调用progressBlock回调并发送下载开始的通知;如果创建失败,直接执行完成回调,并传递一个connection没有初始化的错误:
//开启任务
[self.dataTask resume];
if (self.dataTask) {
if (self.progressBlock) {
self.progressBlock(0, NSURLResponseUnknownLength);
}
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
// 在主线程中发送开始下载的通知
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationName:SDWebImageDownloadStartNotification object:self];
});
} else {
//如果session创建失败,直接执行完成回调,并传递一个connection没有初始化的错误
if (self.completedBlock) {
self.completedBlock(nil, nil, [NSError errorWithDomain:NSURLErrorDomain code:0 userInfo:@{NSLocalizedDescriptionKey : @"Connection can't be initialized"}], YES);
}
}
任务开始后,我们需要关注NSURLSessionDataDelegate的几个代理方法。
首先是
- (void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session
dataTask:(NSURLSessionDataTask *)dataTask
didReceiveResponse:(NSURLResponse *)response
completionHandler:(void (^)(NSURLSessionResponseDisposition disposition))completionHandler
此代理方法告诉delegate已经接受到服务器的初始应答, 准备接下来的数据任务的操作。这里主要可讲的是对返回码为304的处理。在HTTP的返回码中,304表示服务端资源未改变,可直接使用客户端未过期的资源,我们需要取消operation并返回缓存中的image。
其次是
- (void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session dataTask:(NSURLSessionDataTask *)dataTask didReceiveData:(NSData *)data
此代理方法告诉delegate已经接收到部分数据,拼接数据。
- (void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session dataTask:(NSURLSessionDataTask *)dataTask didReceiveData:(NSData *)data {
//添加新收到的部分数据
[self.imageData appendData:data];
//如果SDWebImageDownloaderOptions选择了逐步下载模式而且还在下载中,需要实时更新下载的资源
if ((self.options & SDWebImageDownloaderProgressiveDownload) && self.expectedSize > 0 && self.completedBlock) {
//已经下载的总大小
const NSInteger totalSize = self.imageData.length;
// 利用现有的数据创建一个CGImageSourceRef对象
CGImageSourceRef imageSource = CGImageSourceCreateWithData((__bridge CFDataRef)self.imageData, NULL);
//首次进入,从这些包含图像信息的数据中取出图像的长、宽、方向等信息以备使用
if (width + height == 0) {
CFDictionaryRef properties = CGImageSourceCopyPropertiesAtIndex(imageSource, 0, NULL);
if (properties) {
NSInteger orientationValue = -1;
CFTypeRef val = CFDictionaryGetValue(properties, kCGImagePropertyPixelHeight);
if (val) CFNumberGetValue(val, kCFNumberLongType, &height);
val = CFDictionaryGetValue(properties, kCGImagePropertyPixelWidth);
if (val) CFNumberGetValue(val, kCFNumberLongType, &width);
val = CFDictionaryGetValue(properties, kCGImagePropertyOrientation);
if (val) CFNumberGetValue(val, kCFNumberNSIntegerType, &orientationValue);
CFRelease(properties);
//绘制到Core Graphics时,会丢失方向信息,这意味着有时候由initWithCGIImage创建的图片 // 的方向会不对,所以在这边先保存这个信息并在后面使用
orientation = [[self class] orientationFromPropertyValue:(orientationValue == -1 ? 1 : orientationValue)];
}
}
//下载未完成
if (width + height > 0 && totalSize < self.expectedSize) {
// 使用现有的数据创建部分图片对象,如果数据中存有多张图片,则取第一张
CGImageRef partialImageRef = CGImageSourceCreateImageAtIndex(imageSource, 0, NULL);
#ifdef TARGET_OS_IPHONE
// Workaround for iOS anamorphic image
// 对下载下来的图片做个颜色空间转换等处理
if (partialImageRef) {
const size_t partialHeight = CGImageGetHeight(partialImageRef);
CGColorSpaceRef colorSpace = CGColorSpaceCreateDeviceRGB();
CGContextRef bmContext = CGBitmapContextCreate(NULL, width, height, 8, width * 4, colorSpace, kCGBitmapByteOrderDefault | kCGImageAlphaPremultipliedFirst);
CGColorSpaceRelease(colorSpace);
if (bmContext) {
CGContextDrawImage(bmContext, (CGRect){.origin.x = 0.0f, .origin.y = 0.0f, .size.width = width, .size.height = partialHeight}, partialImageRef);
CGImageRelease(partialImageRef);
partialImageRef = CGBitmapContextCreateImage(bmContext);
CGContextRelease(bmContext);
}
else {
CGImageRelease(partialImageRef);
partialImageRef = nil;
}
}
#endif
if (partialImageRef) {
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageWithCGImage:partialImageRef scale:1 orientation:orientation];
NSString *key = [[SDWebImageManager sharedManager] cacheKeyForURL:self.request.URL];
// 对图片进行缩放
UIImage *scaledImage = [self scaledImageForKey:key image:image];
if (self.shouldDecompressImages) {
// 对图片解压缩
image = [UIImage decodedImageWithImage:scaledImage];
}
else {
image = scaledImage;
}
CGImageRelease(partialImageRef);
dispatch_main_sync_safe(^{
if (self.completedBlock) {
self.completedBlock(image, nil, nil, NO);
}
});
}
}
CFRelease(imageSource);
}
//调用progressBlock,实时更新图像信息
if (self.progressBlock) {
self.progressBlock(self.imageData.length, self.expectedSize);
}
}
另外还有NSURLSessionTaskDelegate的两个代理方法:
//告诉delegate, task已经完成,直接调用completedBlock,刷新UIImageView。
- (void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session task:(NSURLSessionTask *)task didCompleteWithError:(NSError *)error
//需要请求认证
- (void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session task:(NSURLSessionTask *)task didReceiveChallenge:(NSURLAuthenticationChallenge *)challenge completionHandler:(void (^)(NSURLSessionAuthChallengeDisposition disposition, NSURLCredential *credential))completionHandler
这里就不再一一赘述了。
SDImageCache
现在我们研究缓存部分,即SDImageCache类。
SDImageCache maintains a memory cache and an optional disk cache. Disk cache write operations are performed asynchronous so it doesn’t add unnecessary latency to the UI.
SDImageCache维持了一个内存缓存memCache和一个可选的磁盘缓存fileManager,磁盘缓存的写操作时异步的。
内存缓存是用NSCache实现的,以Key-Value的形式存储图片,当内存不够的时候会清除所有缓存图片。磁盘缓存则是缓存到沙盒中,文件替换方式是以时间为单位,剔除时间大于一周的图片文件。
先来看看几个重要的属性:
//同SDWebImageDownloader的属性
//是否解压下载的图片,默认是YES,但是会消耗掉很多内存,如果遇到内存不足的crash时,将值设为NO。
@property (assign, nonatomic) BOOL shouldDecompressImages;
//是否使用内存缓存,默认YES
@property (assign, nonatomic) BOOL shouldCacheImagesInMemory;
//内存缓存的最大像素量
@property (assign, nonatomic) NSUInteger maxMemoryCost;
//内存缓存的最大对象数
@property (assign, nonatomic) NSUInteger maxMemoryCountLimit;
//图片在缓存中的最长寿命,默认1周,超期删除
@property (assign, nonatomic) NSInteger maxCacheAge;
//最大缓存大小
@property (assign, nonatomic) NSUInteger maxCacheSize;
再看看几个重要的方法:
//用指定的命名空间来初始化一个cache
//创建磁盘缓存路径,调用initWithNamespace:diskCacheDirectory方法
- (id)initWithNamespace:(NSString *)ns;
//创建memCache和fileManager,初始化diskCachePath等属性
- (id)initWithNamespace:(NSString *)ns diskCacheDirectory:(NSString *)directory;
//将key对应的image存储到内存缓存和磁盘缓存中
- (void)storeImage:(UIImage *)image forKey:(NSString *)key;
//将key对应的image存储到内存缓存,是否同时存入磁盘中由参数toDisk决定
- (void)storeImage:(UIImage *)image forKey:(NSString *)key toDisk:(BOOL)toDisk;
//功能同上,参数recalculate指明imageData是否可用或者应该从UIImage重新构造;参数imageData是由服务器返回,可以用于磁盘存储,这样可以避免将image转换为一个可存储/压缩的图片以节省CPU。
- (void)storeImage:(UIImage *)image recalculateFromImage:(BOOL)recalculate imageData:(NSData *)imageData forKey:(NSString *)key toDisk:(BOOL)toDisk;
//真正将key对应的image存储到磁盘缓存中
- (void)storeImageDataToDisk:(NSData *)imageData forKey:(NSString *)key;
//异步查询disk cache
- (NSOperation *)queryDiskCacheForKey:(NSString *)key done:(SDWebImageQueryCompletedBlock)doneBlock;
//同步查询memory cache
- (UIImage *)imageFromMemoryCacheForKey:(NSString *)key;
//先检测memory cache,再监测disk cache并存到memory cache里
- (UIImage *)imageFromDiskCacheForKey:(NSString *)key;
//从memory cache 中删除image,并从disk cache中异步删除
- (void)removeImageForKey:(NSString *)key fromDisk:(BOOL)fromDisk withCompletion:(SDWebImageNoParamsBlock)completion;
//清空memory cache,收到内存警告时调用
- (void)clearMemory;
// 清空disk cache
- (void)clearDisk;
//清空disk cache ,非阻塞方法,立即返回
- (void)clearDiskOnCompletion:(SDWebImageNoParamsBlock)completion;
//清除disk cache中所有过期image
- (void)cleanDisk;
//清除disk cache中所有过期image,非阻塞方法,立即返回
- (void)cleanDiskWithCompletionBlock:(SDWebImageNoParamsBlock)completionBlock;
//同步获取disk cache 使用的cache 大小,利用NSFileManager的enumeratorAtPath方法遍历disk cache文件累计fileSize
- (NSUInteger)getSize;
//同步获取disk cache的图片数量
- (NSUInteger)getDiskCount;
//异步获取disk cache的图片数量和缓存大小
- (void)calculateSizeWithCompletionBlock:(SDWebImageCalculateSizeBlock)completionBlock;
//监测key对应的图片是否在disk cache中,方法先按照defaultCachePathForKey生成的path寻找,如果没有则对path删除扩展名,再寻找。
- (BOOL)diskImageExistsWithKey:(NSString *)key;
//功能同上,异步的
- (void)diskImageExistsWithKey:(NSString *)key completion:(SDWebImageCheckCacheCompletionBlock)completionBlock;
//根据指定的key生成cache 路径,为disk cache 使用
- (NSString *)cachePathForKey:(NSString *)key inPath:(NSString *)path;
//指定的key默认的cache 路径,调用上面的方法,第二个参数为self.diskCachePath
- (NSString *)defaultCachePathForKey:(NSString *)key;
disk cache的文件名是key做MD5后的字符串:
- (NSString *)cachedFileNameForKey:(NSString *)key {
const char *str = [key UTF8String];
if (str == NULL) {
str = "";
}
unsigned char r[CC_MD5_DIGEST_LENGTH];
CC_MD5(str, (CC_LONG)strlen(str), r);
NSString *filename = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%@",
r[0], r[1], r[2], r[3], r[4], r[5], r[6], r[7], r[8], r[9], r[10],
r[11], r[12], r[13], r[14], r[15], [[key pathExtension] isEqualToString:@""] ? @"" : [NSString stringWithFormat:@".%@", [key pathExtension]]];
return filename;
}
我们重点研究怎么存储到缓存中的,storeImage:forKey:和storeImage:forKey:toDisk:最终都是调用storeImage:recalculateFromImage:imageData:forKey:toDisk:方法的。
如果需要存储到memory cache中,首先存入memory cache。
if (self.shouldCacheImagesInMemory) {
NSUInteger cost = SDCacheCostForImage(image);
[self.memCache setObject:image forKey:key cost:cost];
}
如果需要存储到disk cache,在子线程中串行存储到disk cache中:
dispatch_async(self.ioQueue, ^{//串行队列
NSData *data = imageData;
if (image && (recalculate || !data)) {
#if TARGET_OS_IPHONE
// 确定图片是png还是jpeg. imageData为nil而且有alapha通道,当作png处理
// PNG图片的前八个字节是137 80 78 71 13 10 26 10
int alphaInfo = CGImageGetAlphaInfo(image.CGImage);
BOOL hasAlpha = !(alphaInfo == kCGImageAlphaNone ||
alphaInfo == kCGImageAlphaNoneSkipFirst ||
alphaInfo == kCGImageAlphaNoneSkipLast);
BOOL imageIsPng = hasAlpha;
// 如果imageData有值,查看前缀
if ([imageData length] >= [kPNGSignatureData length]) {
imageIsPng = ImageDataHasPNGPreffix(imageData);
}
if (imageIsPng) {
// PNG
data = UIImagePNGRepresentation(image);
}
else {
//JPEGP
data = UIImageJPEGRepresentation(image, (CGFloat)1.0);
}
#else
data = [NSBitmapImageRep representationOfImageRepsInArray:image.representations usingType: NSJPEGFileType properties:nil];
#endif
}
//真正存储到磁盘中
[self storeImageDataToDisk:data forKey:key];
});
最终真正存储到磁盘中的方法是:
- (void)storeImageDataToDisk:(NSData *)imageData forKey:(NSString *)key {
//监测imageData
if (!imageData) {
return;
}
//创建目录
if (![_fileManager fileExistsAtPath:_diskCachePath]) {
[_fileManager createDirectoryAtPath:_diskCachePath withIntermediateDirectories:YES attributes:nil error:NULL];
}
// 获取默认的缓存路径
NSString *cachePathForKey = [self defaultCachePathForKey:key];
// 将路径转化为 NSUrl
NSURL *fileURL = [NSURL fileURLWithPath:cachePathForKey];
//存储文件
[_fileManager createFileAtPath:cachePathForKey contents:imageData attributes:nil];
//禁用iCloud备份
if (self.shouldDisableiCloud) {
[fileURL setResourceValue:[NSNumber numberWithBool:YES] forKey:NSURLIsExcludedFromBackupKey error:nil];
}
}
再来看看图片查询的几个方法。在SDWebImageManager中的downloadImageWithURL:options:progress:completed方法中使用到了imageCache的queryDiskCacheForKey:done方法。这是SDImageCache里面查询图片的入口。
首先,从memory cache中查询,如果找到图片就直接使用并返回:
UIImage *image = [self imageFromMemoryCacheForKey:key];
if (image) {
doneBlock(image, SDImageCacheTypeMemory);
return nil;
}
否则,去disk cache中查询,同样是在子线程的同步队列中执行。如果找到,还需要监测是否需要存储到memory cache中:
NSOperation *operation = [NSOperation new];
dispatch_async(self.ioQueue, ^{
if (operation.isCancelled) {
return;
}
@autoreleasepool {
UIImage *diskImage = [self diskImageForKey:key];
if (diskImage && self.shouldCacheImagesInMemory) {
NSUInteger cost = SDCacheCostForImage(diskImage);
[self.memCache setObject:diskImage forKey:key cost:cost];
}
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
doneBlock(diskImage, SDImageCacheTypeDisk);
});
}
});
其中,在memory cache 中查询很简单,直接使用字典方法objectForKey:
- (UIImage *)imageFromMemoryCacheForKey:(NSString *)key {
return [self.memCache objectForKey:key];
}
在disk cache中查询,需要根据key构造各种可能的路径。最后如果找到,需要缩放或者解压缩:
// 构造各种可能路径去查询
- (NSData *)diskImageDataBySearchingAllPathsForKey:(NSString *)key {
NSString *defaultPath = [self defaultCachePathForKey:key];
NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:defaultPath];
if (data) {
return data;
}
// 考虑文件扩展名
data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:[defaultPath stringByDeletingPathExtension]];
if (data) {
return data;
}
NSArray *customPaths = [self.customPaths copy];
for (NSString *path in customPaths) {
NSString *filePath = [self cachePathForKey:key inPath:path];
NSData *imageData = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:filePath];
if (imageData) {
return imageData;
}
imageData = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:[filePath stringByDeletingPathExtension]];
if (imageData) {
return imageData;
}
}
return nil;
}
//从disk cache中查询
- (UIImage *)diskImageForKey:(NSString *)key {
NSData *data = [self diskImageDataBySearchingAllPathsForKey:key];
if (data) {
UIImage *image = [UIImage sd_imageWithData:data];
//缩放
image = [self scaledImageForKey:key image:image];
if (self.shouldDecompressImages)
//解压缩
image = [UIImage decodedImageWithImage:image];
}
return image;
}
else {
return nil;
}
}
最后来看看图片的清理方式。移除指定key对应的图片有一系列方法,最终调用的方法是:
- (void)removeImageForKey:(NSString *)key fromDisk:(BOOL)fromDisk withCompletion:(SDWebImageNoParamsBlock)completion {
if (key == nil) {
return;
}
//先从memory cache 中移除
if (self.shouldCacheImagesInMemory) {
[self.memCache removeObjectForKey:key];
}
//再从disk cache 中移除
if (fromDisk) {
dispatch_async(self.ioQueue, ^{
[_fileManager removeItemAtPath:[self defaultCachePathForKey:key] error:nil];
if (completion) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
completion();
});
}
});
} else if (completion){
completion();
}
}
而清空cache有两种方式,即完全清空与部分清空。对于memory cache是完全清空的:
- (void)clearMemory {
[self.memCache removeAllObjects];
}
对于disk cache,两种方式都有可能。完全清空的方式是直接把文件夹移除掉:
- (void)clearDiskOnCompletion:(SDWebImageNoParamsBlock)completion
{
dispatch_async(self.ioQueue, ^{
[_fileManager removeItemAtPath:self.diskCachePath error:nil];
[_fileManager createDirectoryAtPath:self.diskCachePath
withIntermediateDirectories:YES
attributes:nil
error:NULL];
if (completion) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
completion();
});
}
});
}
部分清空是根据参数配置移除文件,使文件的总大小小于最大使用空间。清理策略有两个:
- 文件的缓存有效期:默认是一周。如果文件的缓存时间超过这个时间值,则将其移除。
- 最大缓存空间大小:如果所有缓存文件的总大小超过最大缓存空间,则会按照文件最后修改时间的逆序,以每次一半的递归来移除那些过早的文件,直到缓存的实际大小小于我们设置的最大使用空间。
- (void)cleanDiskWithCompletionBlock:(SDWebImageNoParamsBlock)completionBlock {
dispatch_async(self.ioQueue, ^{
NSURL *diskCacheURL = [NSURL fileURLWithPath:self.diskCachePath isDirectory:YES];
NSArray *resourceKeys = @[NSURLIsDirectoryKey, NSURLContentModificationDateKey, NSURLTotalFileAllocatedSizeKey];
// 通过文件的枚举器来获取缓存文件的有用的属性
NSDirectoryEnumerator *fileEnumerator = [_fileManager enumeratorAtURL:diskCacheURL
includingPropertiesForKeys:resourceKeys
options:NSDirectoryEnumerationSkipsHiddenFiles
errorHandler:NULL];
NSDate *expirationDate = [NSDate dateWithTimeIntervalSinceNow:-self.maxCacheAge];
NSMutableDictionary *cacheFiles = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
NSUInteger currentCacheSize = 0;
//遍历cache 目录,删除过期文件,存储文件属性
NSMutableArray *urlsToDelete = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init];
for (NSURL *fileURL in fileEnumerator) {
NSDictionary *resourceValues = [fileURL resourceValuesForKeys:resourceKeys error:NULL];
//跳过文件夹
if ([resourceValues[NSURLIsDirectoryKey] boolValue]) {
continue;
}
//记录待删除的过期文件 并continue
NSDate *modificationDate = resourceValues[NSURLContentModificationDateKey];
if ([[modificationDate laterDate:expirationDate] isEqualToDate:expirationDate]) {
[urlsToDelete addObject:fileURL];
continue;
}
//没删除的文件,存储文件的资源属性 计算文件总大小
NSNumber *totalAllocatedSize = resourceValues[NSURLTotalFileAllocatedSizeKey];
currentCacheSize += [totalAllocatedSize unsignedIntegerValue];
[cacheFiles setObject:resourceValues forKey:fileURL];
}
//删除过期文件
for (NSURL *fileURL in urlsToDelete) {
[_fileManager removeItemAtURL:fileURL error:nil];
}
//剩下的cache总大小依然超出配置的cache最大值,执行第二次清理
//首先清除最老的文件,每次清理一半,递归
if (self.maxCacheSize > 0 && currentCacheSize > self.maxCacheSize) {
const NSUInteger desiredCacheSize = self.maxCacheSize / 2;
// 所有文件按照修改时间排序
NSArray *sortedFiles = [cacheFiles keysSortedByValueWithOptions:NSSortConcurrent
usingComparator:^NSComparisonResult(id obj1, id obj2) {
return [obj1[NSURLContentModificationDateKey] compare:obj2[NSURLContentModificationDateKey]];
}];
//删除文件 直到desiredCacheSize大小
for (NSURL *fileURL in sortedFiles) {
if ([_fileManager removeItemAtURL:fileURL error:nil]) {
NSDictionary *resourceValues = cacheFiles[fileURL];
NSNumber *totalAllocatedSize = resourceValues[NSURLTotalFileAllocatedSizeKey];
currentCacheSize -= [totalAllocatedSize unsignedIntegerValue];
if (currentCacheSize < desiredCacheSize) {
break;
}
}
}
}
if (completionBlock) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
completionBlock();
});
}
});
}
至此,我们已经把SDWebImage最主要的几个模块分析清楚了,我们可以绘制一个流程图来对各个模块的工作流做个总结:
延伸
最后,我们延伸一点知识,讲讲前面提到的dispatch_main_sync_safe宏、dispatch_main_async_safe宏以及SDWebImageDecoder的作用。
这两个宏比较简单,直接看代码:
#define dispatch_main_sync_safe(block)\
if ([NSThread isMainThread]) {\
block();\
} else {\
dispatch_sync(dispatch_get_main_queue(), block);\
}
#define dispatch_main_async_safe(block)\
if ([NSThread isMainThread]) {\
block();\
} else {\
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), block);\
}
即保证当前代码在主线程中执行,上面是同步调用,下面是异步调用。
判断主线程的目的是避免出现死锁问题:
*** 如果在主线程中执行dispatch_sync(dispatch_get_main_queue(), block) 同步操作时,会出现死锁问题,因为主线程正在执行当前代码,根本无法将block添加到主队列中 ***
SDWebImageDecoder用来解压缩图片,关于为什么从磁盘读取image后要做一次解压缩,参考了v2panda的解释,仅供大家参考。
因为通过 imageNamed 创建 UIImage 时,系统实际上只是在 Bundle 内查找到文件名,然后把这个文件名放到 UIImage 里返回,并没有进行实际的文件读取和解码。当 UIImage 第一次显示到屏幕上时,其内部的解码方法才会被调用,同时解码结果会保存到一个全局缓存去。在图片解码后,App 第一次退到后台和收到内存警告时,该图片的缓存才会被清空,其他情况下缓存会一直存在。具体的说就是一个UIImage加载了jpeg或者png,当UIImageView将要显示这个UIImage的时候会先把png和jpeg解码成未压缩格式,所以SDWebImage有一个decodeImage方法,就是把这一步放在了异步线程做,防止tableViewCell中的imageView加载图片的时候在主线程解码图片,导致滑动卡顿。这样效率很低,但是只有瞬时的内存需求。为了提高效率通过SDWebImageDecoder将包装在Data下的资源解压,然后画在另外一张图片上,这样这张新图片就不再需要重复解压了,这种做法是典型的空间换时间的做法,如下从硬盘中去图片时,分别对图片进行了缩放和解压缩操作。