大纲
- 数据中心联盟DCA《可信区块链:第2部分 总体要求和评价指标》
- 日本政府针对区块链平台的评估细则
- 新加坡国立大学联合浙江大学推出BlockBench
《可信区块链:第2部分 总体要求和评价指标》
http://www.jianshu.com/p/1c64a830884d 《可信区块链:第2部分 总体要求和评价指标》
1 范围 1
2 术语和定义 1
3 总体要求 1
4 评价指标 1
4.1 数据处理基本功能 1
4.2 身份认证 2
4.3 查询历史数据 2
4.4 节点管理 2
4.5 故障恢复能力 2
4.6 应用层稳定性 2
4.7 共识机制有效性 3
4.8 数据可审计性 3
4.9 妥善的私钥管理措施 4
4.10 密码技术合规性 4
4.11 吞吐率要求 4
4.12 核心技术自主可控 4
4.13 数据私密性 4
4.14 最小硬件要求 5
(日本政府)针对区块链平台的评估细则
http://www.meti.go.jp/english/press/2017/0329_004.html Document Titled “Evaluation Forms for Blockchain-based Systems ver. 1.0” Released,(Release date:March 29, 2017)
Summary of the Evaluation Forms for Blockchain-Based Systems ver. 1.0 (英文PDF:1,268KB),
Full text of the Survey Report on Establishing Evaluation Forms for Blockchain-Based Systems (in Japanese) (日文PDF:2,627KB)
Blockchain technologies are expected to be applied in a wide variety of fields, including IoT. To promote this technology from neutral assessment, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) has released a document titled “Evaluation Forms for Blockchain-based Systems ver. 1.0.”
1. Background
Blockchain technologies are new types of technology used for trading virtual currencies, e.g., Bitcoins. The important features of blockchain technology are that it is extremely difficult to falsify compared to conventional systems, and that inexpensive systems that cause no downtime in effect could be built. Due to these features, the technologies are expected to be applied in a wide variety of fields, including IoT.
However, no evaluation indices or criteria had been established to adequately assess the features of the technologies and to compare them with existing systems. This causes the public anxiety on the one hand and unreasonable hopes for the technology on the other, leading to a potential unwillingness to introduce the technologies. Blockchain-based systems have tradeoff unique to the nature of blockchain technologies, e.g., due to consensus-building by nodes. This is one of the factors that makes it difficult to evaluate blockchain technologies in the same way as the the conventional system-evaluation methods.
Bearing these challenges in mind, METI held interviews with people from both domestic and foreign companies and other experts in the field of blockchain technologies, held discussions based on the interviews and studied new evaluation forms that will allow users to make comparisons between conventional systems and blockchain-based systems and that will comprehensively cover a variety of systems, and organized tradeoffs between evaluation items. Following these efforts, METI compiled these discussion results into the Evaluation Forms for Blockchain-based Systems Report, the world’s first comprehensive evaluation method for this field.
Figure 1: Conceptual diagram comparing a conventional system and a blockchain-based system
- Outline of the report
(1) Intended scope of evaluation forms in this report
In discussing the introduction of a blockchain-based system, METI aimed to formulate evaluation forms by which system vendors and other stakeholders would be able to compare systems in terms of features and functionality. To this end, METI examined blockchain-based systems as a whole, including related sub-systems, and blockchain platforms.
Consequently, the evaluation forms are expected to be utilized not only in the comparison between a conventional system and a blockchain-based system, but also in the comparison between different blockchain-based systems (see Figure 2).
[图片上传中。。。(2)]Figure 2: Study of the scope of evaluation in discussing evaluation forms (conceptual diagram)
(2) Elements of the evaluation forms
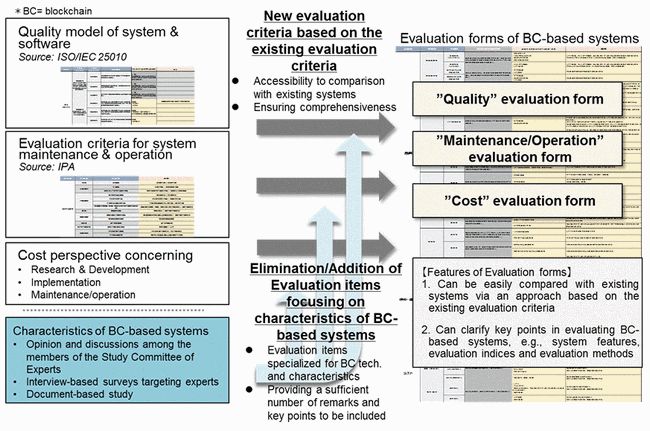
METI organized the evaluation forms within three major categories: quality, maintenance/operation, and cost effectiveness.
These categories will contribute to assisting system vendors, the expected users of blockchain technologies, in using the evaluation forms in conjunction with existing system-evaluation methods.
In this context, concerning the sections closely related to blockchain technologies, the quality category includes excerpts from ISO/IEC25010 (system and software quality models) and the maintenance/operation category includes excerpts from Chapter 4 (Maintenance), System Reference Manual (2005), a compilation of evaluation criteria for conventional systems, published by the Information-Technology Promotion Agency, Japan (IPA). The cost effectiveness category is a collection of points which system vendors should recognize in deciding pricing for customers (see Figure 3).
METI also clarified key points that users should be aware of in evaluating various systems, based on a consideration of features of blockchain technologies in which various evaluation items and characteristics are in tradeoff relationship.
For details of the evaluation forms, see the Appendices.
Figure 3: Study for elements of the evaluation forms
(3) How to utilize the evaluation forms
The evaluation forms formulated by METI are expected to be utilized for the following purposes:
Comparing a conventional system and a blockchain-based system to evaluate replacement options
Evaluating the results of demonstration tests of systems using blockchain technologies
The evaluation forms are expected to contribute to popularizing common evaluation methods or criteria among a variety of evaluators or system vendors, thereby assisting such evaluators in comparing and referring to a variety of evaluation results.
Appendices:
- Summary of the Evaluation Forms for Blockchain-Based Systems ver. 1.0 (下载PDF:1,268KB)
- Full text of the Survey Report on Establishing Evaluation Forms for Blockchain-Based Systems (in Japanese) (下载PDF:2,627KB)
新加坡国立大学联合浙江大学推出BlockBench
2017-05-12 众享比特 新加坡国立大学联合浙江大学推出BlockBench
英文:http://www.peersafe.cn/blockbench/blockbench.pdf
中文:http://www.peersafe.cn/blockbench/blockbench_zh.pdf 【关注】
论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.04057 (to appear in ACM SIGMOD 2017)
代码:http://www.comp.nus.edu.sg/~dbsystem/blockbench/
近日,新加坡国立大学和浙江大学联合推出了一个私有区块链的评估框架——BlockBench,通过对目前最成熟的能够支持智能合约功能的三个区块链平台——Hyperledger Fabric,、Ethereum 、Parity 开展对BlockBench的设计,该框架将能广泛地支持未来的区块链平台。其“在区块链中加入数据库设计”的结论,与众享比特在2017年1月发布的ChainSQL(基于区块链的数据库应用平台)的理念不谋而合。
众享比特团队第一时间对BlockBench白皮书进行了翻译,以下为容要点:
在发布的BlockBench白皮书中,通过对现有问题的分析,强调区块链与智能合约的必要性,希望设计一种通用的基准架构来测试区块链处理数据的工作范围,该框架能帮助区块链应用开发者评估区块链的能力,以满足应用设计的需要,同时可帮助区块链开发者识别并改进性能瓶颈。
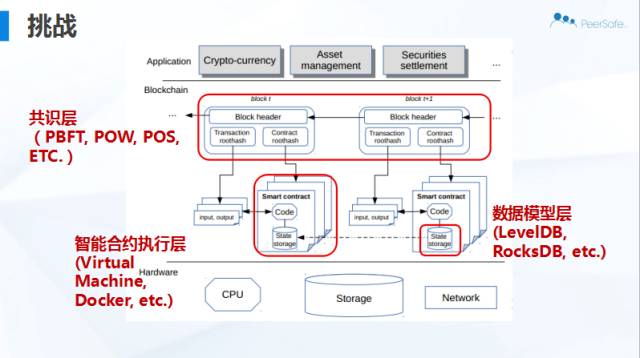
在设计评估框架前,首先要面临目前存在的三个主要挑战:
- 区块链系统中包括许多部分,我们观察到,不同平台之间的每一个细节上都存在各种各样的设计选择。
- 目前有多种区块链平台供大家选择,然而并不是所有平台都达到了成熟设计、实施以及建立用户群基础的程度。
- 目前的区块链平台中缺少面向数据库的工作负载结构。
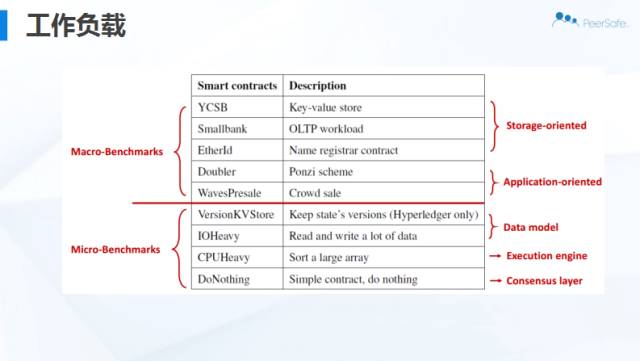
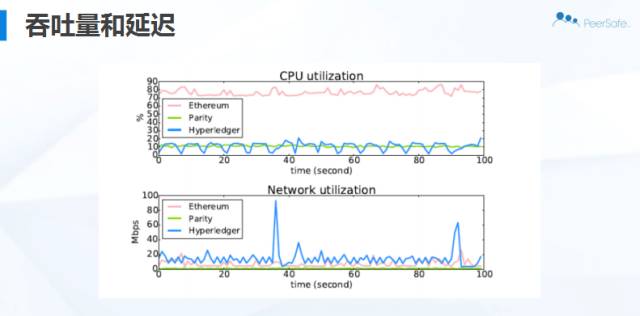
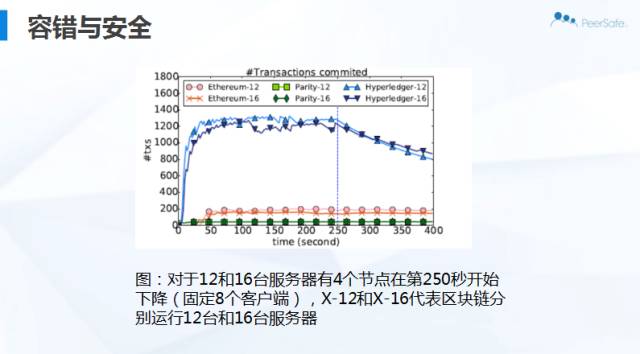
他们在宏观、微观层面的性能基准测试如下图:
三个系统基于YCSB的CPU和网络资源利用率:
网络和节点的开销测试
面对挑战,“在区块链中加入数据库设计”能够解决问题
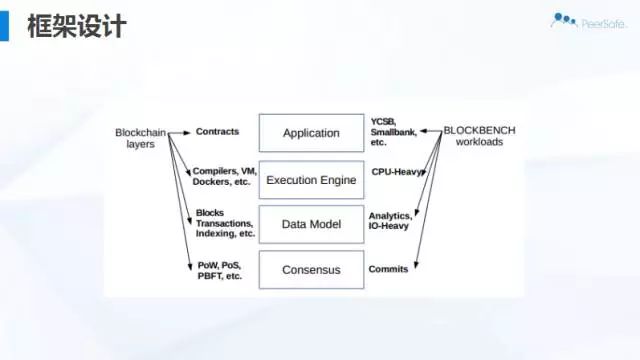
在区块链中加入数据库设计
将存储、执行引擎和共识层彼此分离,然后独立优化和扩展。 我们的系统UStore表明,针对区块链数据结构设计的存储能够比现有的实现方式获得更好的性能。
拥抱新的硬件
对于区块链,使用可信硬件可以修改底层的拜占庭容错协议,从而减少网络消息。
Parity和Ethereum这样的系统可以利用多核CPU和大内存来改善合约执行和I/O性能。
分片
在拜占庭故障中,数据库系统中使用的现有一致性协议不再起作用。尽管如此,分片数据库系统的设计可以为实现更可扩展的区块链分片协议提供参照。
支持声明语言
拥有一套可以以声明方式组合的高级操作,便于定义复杂的智能合约。
声明式语言也开辟了低级优化的机会,加快合约执行的可能。
分片的主要挑战是确保多个分片之间的一致性。
结论
据我们所知,BlockBench是评估私有区块链系统的首个综合基准框架。
- 希望我们的结果将成为进一步开収区块链技术的基础。
- 更多信息:
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.04057 (to appear in ACM SIGMOD 2017)
Code+Workloadsat project web site: http://www.comp.nus.edu.sg/~dbsystem/blockbench/
作者:
Anh Dinh, Ji Wang, Gang Chen, RuiLiu, Beng Chin Ooi
National University of Singapore x Zhejiang University
我们相信,新加坡国立大学和浙江大学联合研究的结果,将成为进一步开发区块链技术的基础。众享比特也将在自主研发的ChainSQL基础上,推进区块链应用的开发。
http://www.peersafe.cn/blockbench/ BlockBench文档中英文下载
http://www.chainsql.net/ ChainSQL白皮书下载