网络文件系统Netwrok File System,类似于wiin10的网络共享
功能:通过网络让不同主机系统之间可以共享文件或目录
集群中,用来存储共享视频,图片文件等静态资源文件
NFS传输数据使用端口是随机的,功能太多,所用的端口不一定,客户端咋知道端口?RPC(Remote Procedure Call)协议/服务来
NFS服务的主要任务是共享文件系统数据,文件系统数据的共享离不开权限问题
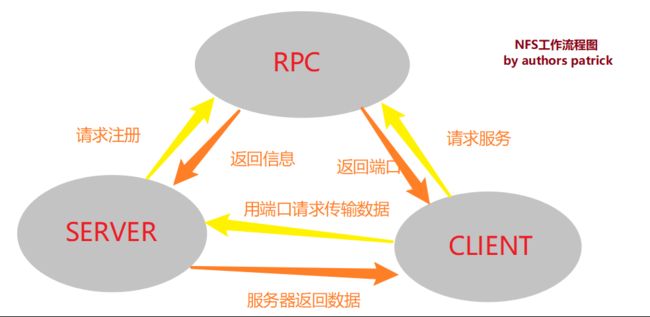
工作流程图

配置权限设置参数关系表

软件包
nfs-utils:NFS的主程序,包括rpc,nfsd、rpc.mountd
rpcbind:RPC的主程序,用来做好端口和功能对应映射工作,使用的端口是111
优缺点
优点:容易上手,数据在文件系统之上,部署快速,服务稳定
缺点:存在单点故障,后期通过负载均衡弥补,安全性一般,但用于内网问题不大
实践
部署环境
| 服务器系统 | 角色 | IP |
|---|---|---|
| 6.5 | nfs-server | 192.168.2.22 |
| 6.5 | nfs-client1 | 192.168.2.11 |
| 6.5 | nfs-client2 | 192.168.2.33 |
[root@NFS_22 ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release
CentOS release 6.5 (Final)
[root@NFS_22 ~]# uname -a
Linux NFS_22 2.6.32-431.el6.i686 #1 SMP Fri Nov 22 00:26:36 UTC 2013 i686 i686 i386 GNU/Linux
服务器
软件列表
1、安装rpcbind和nfs-utils两个程序
[root@NFS_22 ~]# rpm -qa rpcbind nfs-utils #不用管道命令更高效
rpcbind-0.2.0-11.el6.i686
nfs-utils-1.2.3-39.el6.i686
[root@NFS_22 ~]# yum -y install rpcbind nfs-utils
[root@NFS_22 ~]# /etc/init.d/rpcbind status
rpcbind (pid 2500) is running...
2、启动rpcbind和nfs服务
[root@NFS_22 ~]# rpcinfo -p localhost #检查RPC服务是否启动,正常启动会返回端口信息
program vers proto port service
100000 4 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 3 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 2 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 4 udp 111 portmapper
100000 3 udp 111 portmapper
100000 2 udp 111 portmapper
[root@NFS_22 ~]# chkconfig --list |grep rpcbind #默认rpcbind开机启自启动,查看一下
rpcbind 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
[root@NFS_22 ~]# /etc/init.d/nfs start #启动nfs服务
Starting NFS services: [ OK ]
Starting NFS quotas: [ OK ]
Starting NFS mountd: [ OK ]
Starting NFS daemon: [ OK ]
Starting RPC idmapd: [ OK ]
[root@NFS_22 ~]# rpcinfo -p localhost #再次查看RPC端口管理器变多了
100003 2 tcp 2049 nfs
100003 3 tcp 2049 nfs
100003 4 tcp 2049 nfs
100227 2 tcp 2049 nfs_acl
100227 3 tcp 2049 nfs_acl
100003 2 udp 2049 nfs
100003 3 udp 2049 nfs
100003 4 udp 2049 nfs
[root@NFS_22 ~]# man rpc.mountd #进程很多,去手册找一下
3、开机自启动两个服务,两年方式
[root@NFS_22 ~]# LANG=en #英文单词比较方便查看
[root@NFS_22 ~]# chkconfig rpcbind on
[root@NFS_22 ~]# chkconfig nfs on #俩大哥开机自启动,最后查看一下
[root@NFS_22 ~]# chkconfig --list |egrep 'nfs\b|rpcbind'
nfs 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
rpcbind 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
[root@NFS_22 ~]# tail -2 /etc/rc.local #大哥说,高级的开机自启动都是放置到/etc/rc.local中的
/etc/init.d/rpcbind start
/etc/init.d/nfs start
4、配置共享目录的权限,指定文件的默认用户,写入测试文件
[root@NFS_22 ~]# mkdir -p /data
[root@NFS_22 ~]# touch /data/ram.txt
#nfsnobody 是nfs的默认用户,把共享目录交给默认用户,也可以 直接777,但777不太好
[root@NFS_22 ~]# chown -R nfsnobody.nfsnobody /data/ #-R 递归 继承
[root@NFS_22 ~]# ls -ld /data/
drwxr-xr-x. 2 nfsnobody nfsnobody 4096 Oct 11 18:47 /data/
[root@NFS_22 ~]# grep nfs /etc/passwd
nfsnobody❌65534:65534:Anonymous NFS User:/var/lib/nfs:/sbin/nologin
5、配置/etc/exports主配置文件
[root@NFS_22 ~]# cat /etc/exports -A #这个文件本来就是空的,啥都没有
[root@NFS_22 ~]# man exports #里面有很多exports如何配置的信息
[root@NFS_22 ~]# tail -2 /etc/exports #配置信息,格式是目录 地址(读写rw,只读ro,同步sync等操作)
#share /data by ram for test
/data 192.168.2.0/24(rw,sync)
[root@NFS_22 ~]# exportfs -rv #修改配置文件/etc/exports后,需要重新加载NFS配置,执行命令,不需要重启服务
exporting 192.168.2.0/24:/data
6、服务器当小白鼠,先挂载做测试
[root@NFS_22 ~]# showmount -e localhost #在服务器本地查看挂载情况
Export list for localhost:
/data 192.168.2.0/24
[root@NFS_22 ~]# cat /var/lib/nfs/etab #就是将主配置文件加载到这里,会添加一些默认的参数
/data192.168.2.0/24(rw,sync,wdelay,hide,nocrossmnt,secure,root_squash,no_all_squash,no_subtree_check,secure_locks,acl,anonuid=65534,anongid=65534,sec=sys,rw,root_squash,no_all_squash)
[root@NFS_22 ~]# mount -t nfs 192.168.2.22:/data /mnt/ #把服务器当做客户机挂载来测试
[root@NFS_22 ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/vg_moban-lv_root 18G 2.3G 15G 14% /
tmpfs 503M 0 503M 0% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 485M 32M 428M 7% /boot
192.168.2.22:/data 18G 2.3G 15G 14% /mnt
service nfs reload =/etc/init.d/nfs reload #success
客户端
1、安装rpcbind和nfs-utils两个程序
[root@NFS_22 ~]# rpm -qa rpcbind nfs-utils #不用管道命令更高效
rpcbind-0.2.0-11.el6.i686
nfs-utils-1.2.3-39.el6.i686
[root@NFS_22 ~]# yum -y install rpcbind nfs-utils
[root@NFS_22 ~]# /etc/init.d/rpcbind status
rpcbind (pid 2500) is running...
2、启动rpcbind,不用启动nfs
[root@Backup_11 ~]# showmount -e 192.168.2.22
Export list for 192.168.2.22:
/data 192.168.2.0/24
[root@Backup_11 ~]# mount -t nfs 192.168.2.22:/data /mnt/ #-t指定挂载文件的类型
[root@Backup_11 ~]# df -h #display free -h human 按照人类可读的方式显示
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/vg_moban-lv_root 18G 2.3G 15G 14% /
tmpfs 503M 0 503M 0% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 485M 32M 428M 7% /boot
192.168.2.22:/data 18G 2.3G 15G 14% /mnt
3、关闭防火墙
4、挂载共享目录
[root@Backup_11 ~]# mount
/dev/mapper/vg_moban-lv_root on / type ext4 (rw)
proc on /proc type proc (rw)
sysfs on /sys type sysfs (rw)
devpts on /dev/pts type devpts (rw,gid=5,mode=620)
tmpfs on /dev/shm type tmpfs (rw,rootcontext="system_u:object_r:tmpfs_t:s0")
/dev/sda1 on /boot type ext4 (rw)
none on /proc/sys/fs/binfmt_misc type binfmt_misc (rw)
sunrpc on /var/lib/nfs/rpc_pipefs type rpc_pipefs (rw)
192.168.2.22:/data on /mnt type nfs (rw,vers=4,addr=192.168.2.22,clientaddr=192.168.2.11)
5、测试,给挂载的文件下的ram.txt目录增加内容,所有挂载该共享文件的系统都可以查看
备份服务器挂载测试
[root@Backup_11 ~]# ls /mnt/
ram.txt
[root@Backup_11 ~]# echo 9999 >/mnt/ram.txt
NFS服务器本地挂载查看
[root@NFS_22 ~]# cat /mnt/ram.txt
9999
在本地源文件查看,over
[root@NFS_22 ~]# cat /data/ram.txt
9999
防火墙
服务器的防火墙控制,仅允许内部IP网段访问
iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.2.0/24 -j ACCEPT