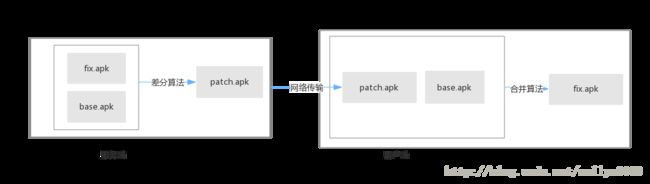
tinker修复的过程包含两个过程,一方面服务端产生补丁包的过程;另一方面用户端获得补丁包之后的修复工程,简单的流程可以用如下的图描述:
服务端补丁产生过程主要是tinker 定义的gradle插件来完成。我们在文章的后面会详细介绍gradle插件的细节。
我们首先来分析用户端的逻辑。一个完整的apk解压之后基本上包括dex文件,资源文件和so文件。前面的文章中已经详细介绍了dex文件的修复过程,本章主要介绍资源文件和so文件的修复。
资源文件的修复
资源文件的修复过程发生在客户端。包含两个主要的过程,首先是客户端获取到patch.apk之后,和本地的base.apk的合并过程,这个过程根据BSD算法将patch的资源文件和base的资源文件合并,最后打包到fix.apk中;另一个是资源文件的加载过程,主要的功能是引导base.apk使用fix.apk中的资源(这里有个关键点:虽然我们在用户端有了fix.apk,但是我们的fix.apk并没有安装,启动应用的还是base.apk,只是引导base.apk使用fix.apk里面的dex文件,资源文件,so文件)。我们主要介绍资源文件的加载。资源文件的合并主要是算法,我们这里不做介绍,感兴趣的读者可以在tinker源码中自行学习BSPatch.java。
public static boolean loadTinkerResources(Context context, boolean tinkerLoadVerifyFlag, String directory, Intent intentResult) {
if (resPatchInfo == null || resPatchInfo.resArscMd5 == null) {
return true;
}
String resourceString = directory + "/" + RESOURCE_PATH + "/" + RESOURCE_FILE;
File resourceFile = new File(resourceString);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (tinkerLoadVerifyFlag) {
if (!SharePatchFileUtil.checkResourceArscMd5(resourceFile, resPatchInfo.resArscMd5)) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to load resource file, path: " + resourceFile.getPath() + ", expect md5: " + resPatchInfo.resArscMd5);
ShareIntentUtil.setIntentReturnCode(intentResult, ShareConstants.ERROR_LOAD_PATCH_VERSION_RESOURCE_MD5_MISMATCH);
return false;
}
Log.i(TAG, "verify resource file:" + resourceFile.getPath() + " md5, use time: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
}
try { TinkerResourcePatcher.monkeyPatchExistingResources(context, resourceString);
Log.i(TAG, "monkeyPatchExistingResources resource file:" + resourceString + ", use time: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
} catch (Throwable e) {
Log.e(TAG, "install resources failed");
//remove patch dex if resource is installed failed
try {
SystemClassLoaderAdder.uninstallPatchDex(context.getClassLoader());
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
Log.e(TAG, "uninstallPatchDex failed", e);
}
intentResult.putExtra(ShareIntentUtil.INTENT_PATCH_EXCEPTION, e);
ShareIntentUtil.setIntentReturnCode(intentResult, ShareConstants.ERROR_LOAD_PATCH_VERSION_RESOURCE_LOAD_EXCEPTION);
return false;
}
return true;
}
resourceString 局部变量代表的是fix.apk的资源文件。首先检查文件的的md5是否正确。然后再TinkerResourcePatcher中完成资源加载。
public static void monkeyPatchExistingResources(Context context, String externalResourceFile) throws Throwable {
if (externalResourceFile == null) {
return;
}
for (Field field : new Field[]{packagesFiled, resourcePackagesFiled}) {
Object value = field.get(currentActivityThread);
for (Map.Entry> entry
: ((Map>) value).entrySet()) {
Object loadedApk = entry.getValue().get();
if (loadedApk == null) {
continue;
}
if (externalResourceFile != null) {
resDir.set(loadedApk, externalResourceFile);
}
}
}
// Create a new AssetManager instance and point it to the resources installed under
if (((Integer) addAssetPathMethod.invoke(newAssetManager, externalResourceFile)) == 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not create new AssetManager");
}
// Kitkat needs this method call, Lollipop doesn't. However, it doesn't seem to cause any harm
// in L, so we do it unconditionally.
ensureStringBlocksMethod.invoke(newAssetManager);
for (WeakReference wr : references) {
Resources resources = wr.get();
//pre-N
if (resources != null) {
// Set the AssetManager of the Resources instance to our brand new one
try {
assetsFiled.set(resources, newAssetManager);
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
// N
Object resourceImpl = resourcesImplFiled.get(resources);
// for Huawei HwResourcesImpl
Field implAssets = ShareReflectUtil.findField(resourceImpl, "mAssets");
implAssets.setAccessible(true);
implAssets.set(resourceImpl, newAssetManager);
}
clearPreloadTypedArrayIssue(resources);
resources.updateConfiguration(resources.getConfiguration(), resources.getDisplayMetrics());
}
}
// Handle issues caused by WebView on Android N.
// Issue: On Android N, if an activity contains a webview, when screen rotates
// our resource patch may lost effects.
// publicSourceDirField.set(context.getApplicationInfo(), externalResourceFile);
if (!checkResUpdate(context)) {
throw new TinkerRuntimeException(ShareConstants.CHECK_RES_INSTALL_FAIL);
}
}
主要的功能在两个for循环中。外层的for循环是两个Field对象packagesFiled和resourcePackagesFiled,他们分别代表ActivityThread中的成员mPackages和mResourcePackages。里层的for循环分别修改这两个Field对象中的成员resDir,也就是LoadedApk的成员mResDir。这里主要通过反射修改系统文件的属性,实现资源的加载。后面的流程主要对android系统版本兼容处理。
为什么修改了ActivityThread的属性mPackages,mResourcePackages和LoadedApk类的mResDir属性就可以实现Base.apk加载Fix.apk的资源?我们从Android源码的角度分析一下。
通常我们获取某一资源的代码如下:context.getResource().getxxxx,这里的context我们知道是ContextImpl类。ContextImpl的方法getResource()得到的是它的属性mResources,mResources代表了一个资源包,也就是说如果这里的mResources代表的是Fix.apk的资源包,我们就完成了资源的加载。mResources是如何初始化的呢?
final void init(LoadedApk packageInfo,
IBinder activityToken, ActivityThread mainThread,
Resources container, String basePackageName) {
mPackageInfo = packageInfo;
mBasePackageName = basePackageName != null ? basePackageName : packageInfo.mPackageName;
mResources = mPackageInfo.getResources(mainThread);
if (mResources != null && container != null
&& container.getCompatibilityInfo().applicationScale !=
mResources.getCompatibilityInfo().applicationScale) {
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, "loaded context has different scaling. Using container's" +
" compatiblity info:" + container.getDisplayMetrics());
}
mResources = mainThread.getTopLevelResources(
mPackageInfo.getResDir(), container.getCompatibilityInfo());
}
mMainThread = mainThread;
mContentResolver = new ApplicationContentResolver(this, mainThread);
setActivityToken(activityToken);
}
在ContextImpl初始化的时候对mResources 赋值。ActivityThread的方法getTopLevelResources和LoadedApk的方法getResources都可以对mResources ,最终都是调用的
Resources getTopLevelResources(String resDir, CompatibilityInfo compInfo) {
ResourcesKey key = new ResourcesKey(resDir, compInfo.applicationScale);
Resources r;
synchronized (mPackages) {
// Resources is app scale dependent.
if (false) {
Slog.w(TAG, "getTopLevelResources: " + resDir + " / "
+ compInfo.applicationScale);
}
WeakReference wr = mActiveResources.get(key);
r = wr != null ? wr.get() : null;
//if (r != null) Slog.i(TAG, "isUpToDate " + resDir + ": " + r.getAssets().isUpToDate());
if (r != null && r.getAssets().isUpToDate()) {
if (false) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Returning cached resources " + r + " " + resDir
+ ": appScale=" + r.getCompatibilityInfo().applicationScale);
}
return r;
}
}
//if (r != null) {
// Slog.w(TAG, "Throwing away out-of-date resources!!!! "
// + r + " " + resDir);
//}
AssetManager assets = new AssetManager();
if (assets.addAssetPath(resDir) == 0) {
return null;
}
//Slog.i(TAG, "Resource: key=" + key + ", display metrics=" + metrics);
DisplayMetrics metrics = getDisplayMetricsLocked(null, false);
r = new Resources(assets, metrics, getConfiguration(), compInfo);
if (false) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Created app resources " + resDir + " " + r + ": "
+ r.getConfiguration() + " appScale="
+ r.getCompatibilityInfo().applicationScale);
}
synchronized (mPackages) {
WeakReference wr = mActiveResources.get(key);
Resources existing = wr != null ? wr.get() : null;
if (existing != null && existing.getAssets().isUpToDate()) {
// Someone else already created the resources while we were
// unlocked; go ahead and use theirs.
r.getAssets().close();
return existing;
}
// XXX need to remove entries when weak references go away
mActiveResources.put(key, new WeakReference(r));
return r;
}
}
这里逻辑很清晰了。利用resDir设置AssetManager的属性,并创建Resource对象,resource对象和resDir一一对应。这里resDir参数是LoadedApk的属性mResourecDir。因此整个逻辑实现就是如果我们修改LoadedApk的属性mResourceDir是Fix.apk的资源,ContextImpl的属性mResource就代表了Fix.apk的资源。如下的图说明了他们之间的关系:
So文件的加载
so的修复过程也是在用户端完成的。首先是根据BSD算法修复so,然后在使用so文件的地方加载。
so文件加载机制
SO文件加载的时机和Dex、资源的加载有些不一样,Dex和资源的加载都是系统在特定的时机自动去加载,而SO加载的时机则是让开发者自己控制.开发者可以通过System类对外暴露出来的两个静态方法load和loadLibarary加载SO.这两个方法都拿ClassLoader再通过Runtime实现的。
- Sytem.loadLibrary 方法是加载app安装过之后自动从apk包中释放到/data/data/packagename/lib下对应的SO文件。如果要使用这样的方式加载fix.apk中的so文件,需要利用反射修改DexPathList的属性nativeLibraryDirectorie,具体的方法可以参考前面文章中Dex文件的加载过程。
- System.load 方法可以根据开发者指定的路径加载SO文件,例如/data/data/packagename/tinker/patch-xxx/lib/libtest.so,这是Tinker使用的方式,开发者不用修改任何代码,只要指定路径就可以加载Fix.apk的so文件。
Gradle插件
为什么要用gradle插件
- 根据上面的分析,用户端要先得到patch.apk,才完成后面的修复和加载的过程,patch.apk是客户端修复的关键。tinker中的Gradle插件就是完成patch.apk的。
- 另外,dex文件的差分和合并对比的是字节码,BSD算法的差分和合并对比的是二进制文件,那么这里隐含了一条规则,服务端的fix.apk的Dex文件的混淆,以及资源文件的R文件的属性需要和base.apk的一样。以及对于代码超出65536的方法,需要分包的应用,分包方法也需要和base.apk一样。这些也是gradle插件需要处理的问题。
Tinker中gradle插件的流程
简单的流程如下:在fix.apk编译之前按照需要修复的base.apk的资源id映射生成map文件;按照base.apk的混淆规则映射fix.apk的混淆规则等,以及按照base.apk的multidex的分包方式编译出fix.apk,最后产生差分的补丁patch.apk。
Tinker 中gradle插件的设计
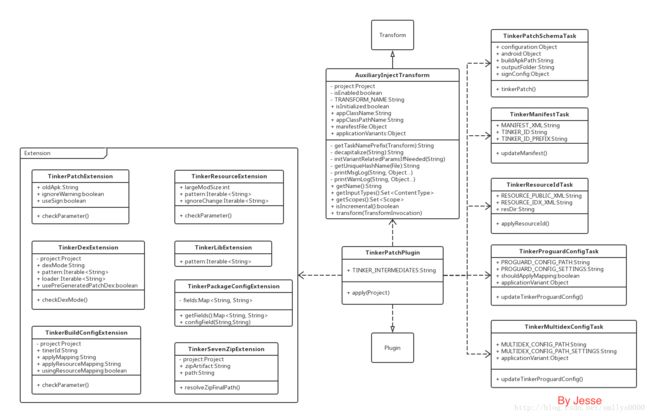
tinker定义了5个task来完成patch.apk的产生过程。如下图是tinker插件的类图,
TinkerManifestTask 主要是在AndroidManifest.xml中插入 meta-data TINKER_ID ,它是用来在客户端合并补丁的时候验证old.apk中的TINKER_ID是否一致。
@(工作-待办)TaskAction
def updateManifest() {
String tinkerValue = project.extensions.tinkerPatch.buildConfig.tinkerId
if (tinkerValue == null || tinkerValue.isEmpty()) {
throw new GradleException('tinkerId is not set!!!')
}//校验gradle配置的tinkerId的值
tinkerValue = TINKER_ID_PREFIX + tinkerValue
writeManifestMeta(manifestPath, TINKER_ID, tinkerValue)//像AndriodManifest.xml插入Tinkerid
addApplicationToLoaderPattern()
File manifestFile = new File(manifestPath)
if (manifestFile.exists()) {//修改后的AndriodManifest.xml拷贝到app\build\intermediates\tinker_intermediates下
FileOperation.copyFileUsingStream(manifestFile, project.file(MANIFEST_XML))
project.logger.error("tinker gen AndroidManifest.xml in ${MANIFEST_XML}")
}
}
TinkerManifestTask首先根据读取gradle配置的tinkerid,校验是否合法。然后往AndroidManifest.xm插入tinkerid,并拷贝到app\build\intermediates\tinker_intermediates。
TinkerResourceIdTask根据gradle配置的applyResourceMapping文件,产生public.xml和idx.xml,使得new.apk在编译资源文件的时候,按照public.xml指定的id分配给资源
def applyResourceId() {
String resourceMappingFile = project.extensions.tinkerPatch.buildConfig.applyResourceMapping
if (!FileOperation.isLegalFile(resourceMappingFile)) {
project.logger.error("apply resource mapping file ${resourceMappingFile} is illegal, just ignore")
return
}
project.extensions.tinkerPatch.buildConfig.usingResourceMapping = true
PatchUtil.generatePublicResourceXml(aaptResourceCollector, idsXml, publicXml)
FileOperation.copyFileUsingStream(publicFile, project.file(RESOURCE_PUBLIC_XML))
FileOperation.copyFileUsingStream(idxFile, project.file(RESOURCE_IDX_XML))
}
}
TinkerMultidexConfigTask 如果开启了multiDex 会在编译中根据gradle的配置和默认配置生成出要keep在main dex中的proguard信息文件,然后copy出这个文件,方便开发者使用multiDexKeepProguard进行配置.首先打开文件并写入默认配置.文件路径也在tinker_intermediates下
@TaskAction
def updateTinkerProguardConfig() {
File file = project.file(MULTIDEX_CONFIG_PATH)
print(file.getAbsolutePath())
project.logger.error("try update tinker multidex keep proguard file with ${file}")
// Create the directory if it doesn't exist already
file.getParentFile().mkdirs()
StringBuffer lines = new StringBuffer()
lines.append("\n")
.append("#tinker multidex keep patterns:\n")
.append(MULTIDEX_CONFIG_SETTINGS)
.append("\n")
.append("#your dex.loader patterns here\n")
Iterable loader = project.extensions.tinkerPatch.dex.loader
for (String pattern : loader) {
if (pattern.endsWith("*")) {
if (!pattern.endsWith("**")) {
pattern += "*"
}
}
lines.append("-keep class " + pattern + " {\n" +
" *;\n" +
"}\n")
.append("\n")
}
// Write our recommended proguard settings to this file
FileWriter fr = new FileWriter(file.path)
try {
for (String line : lines) {
fr.write(line)
}
} finally {
fr.close()
}
File multiDexKeepProguard = null
try {
multiDexKeepProguard = applicationVariant.getVariantData().getScope().getManifestKeepListProguardFile()
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
try {
multiDexKeepProguard = applicationVariant.getVariantData().getScope().getManifestKeepListFile()
} catch (Throwable e) {
project.logger.error("can't find getManifestKeepListFile method, exception:${e}")
}
}
if (multiDexKeepProguard == null) {
project.logger.error("auto add multidex keep pattern fail, you can only copy ${file} to your own multiDex keep proguard file yourself.")
return
}
FileWriter manifestWriter = new FileWriter(multiDexKeepProguard, true)
try {
for (String line : lines) {
manifestWriter.write(line)
}
} finally {
manifestWriter.close()
}
}
TinkerProguardConfigTask如果开启了混淆,就会在gradle插件中构建出该任务,主要的作用是将tinker中默认的混淆信息和基准包的mapping信息加入混淆列表,这样就可以通过gradle配置自动帮开发者做一些类的混淆设置,并且可以通过applymapping的基准包的mapping文件达到在混淆上补丁包和基准包一致的目的.首先打开在编译路径下的混淆文件,为后面写入默认的keep规则做准备.文件的路径同样在tinker_intermediates下
@TaskAction
def updateTinkerProguardConfig() {
def file = project.file(PROGUARD_CONFIG_PATH)
project.logger.error("try update tinker proguard file with ${file}")
// Create the directory if it doesnt exist already
file.getParentFile().mkdirs()
// Write our recommended proguard settings to this file
FileWriter fr = new FileWriter(file.path)
String applyMappingFile = project.extensions.tinkerPatch.buildConfig.applyMapping
//write applymapping
if (shouldApplyMapping && FileOperation.isLegalFile(applyMappingFile)) {
project.logger.error("try add applymapping ${applyMappingFile} to build the package")
fr.write("-applymapping " + applyMappingFile)
fr.write("\n")
} else {
project.logger.error("applymapping file ${applyMappingFile} is illegal, just ignore")
}
fr.write(PROGUARD_CONFIG_SETTINGS)
fr.write("#your dex.loader patterns here\n")
//they will removed when apply
Iterable loader = project.extensions.tinkerPatch.dex.loader
for (String pattern : loader) {
if (pattern.endsWith("*") && !pattern.endsWith("**")) {
pattern += "*"
}
fr.write("-keep class " + pattern)
fr.write("\n")
}
fr.close()
// Add this proguard settings file to the list
applicationVariant.getBuildType().buildType.proguardFiles(file)
def files = applicationVariant.getBuildType().buildType.getProguardFiles()
project.logger.error("now proguard files is ${files}")
}
TinkerPatchSchemaTask 负责校验Extensions的参数和环境是否合法和补丁生成
@TaskAction
def tinkerPatch() {
configuration.checkParameter()
configuration.buildConfig.checkParameter()
configuration.res.checkParameter()
configuration.dex.checkDexMode()
configuration.sevenZip.resolveZipFinalPath()
InputParam.Builder builder = new InputParam.Builder()
if (configuration.useSign) {
if (signConfig == null) {
throw new GradleException("can't the get signConfig for this build")
}
builder.setSignFile(signConfig.storeFile)
.setKeypass(signConfig.keyPassword)
.setStorealias(signConfig.keyAlias)
.setStorepass(signConfig.storePassword)
}
builder.setOldApk(configuration.oldApk)
.setNewApk(buildApkPath)
.setOutBuilder(outputFolder)
.setIgnoreWarning(configuration.ignoreWarning)
.setDexFilePattern(new ArrayList(configuration.dex.pattern))
.setDexLoaderPattern(new ArrayList(configuration.dex.loader))
.setDexMode(configuration.dex.dexMode)
.setSoFilePattern(new ArrayList(configuration.lib.pattern))
.setResourceFilePattern(new ArrayList(configuration.res.pattern))
.setResourceIgnoreChangePattern(new ArrayList(configuration.res.ignoreChange))
.setResourceLargeModSize(configuration.res.largeModSize)
.setUseApplyResource(configuration.buildConfig.usingResourceMapping)
.setConfigFields(new HashMap(configuration.packageConfig.getFields()))
.setSevenZipPath(configuration.sevenZip.path)
.setUseSign(configuration.useSign)
InputParam inputParam = builder.create()
Runner.gradleRun(inputParam);
}
总结
- Tinker 和其他的类加载方式的修复方案相比,利用差分算法,最大限度的减小的补丁包的大小,这一点对于移动应用来说非常重要。
- Tinker的修复包中不能引入新的四大组件,不能修改androidManifest文件。