Canny 边缘检测算法
Steps:
- 高斯滤波平滑
- 计算梯度大小和方向
- 非极大值抑制
- 双阈值检测和连接
代码结构:
Canny Edge Detection
| Gaussian_Smoothing
| | convolution.py
| | | convolution()
| | gaussion_smoothing.py
| | | dnorm()
| | | gaussian_kernel()
| | | gaussian_blur()
| Sobel_Filter
| | sobel.py
| | | sobel_edge_detection()
| Canny.py
| | non_max_suppression()
| | threshold()
| | hysteresis()
| | main()代码解读:
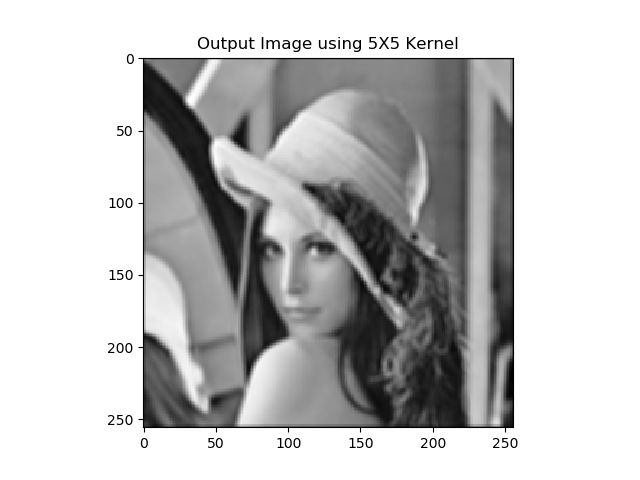
1. 高斯滤波平滑
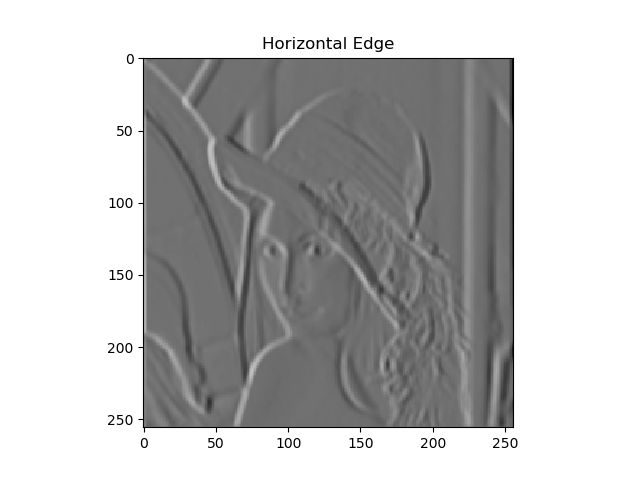
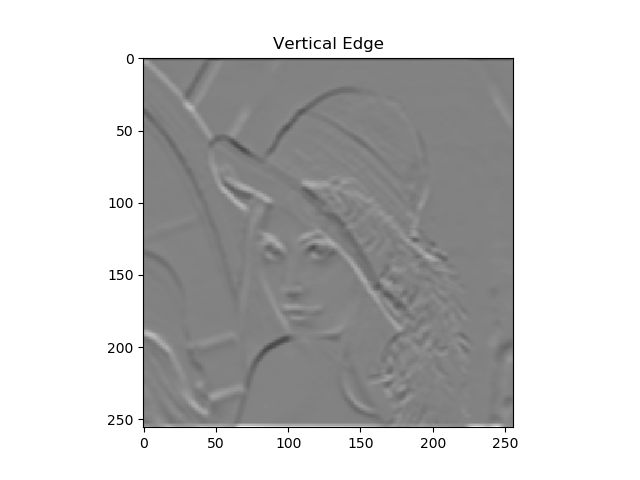
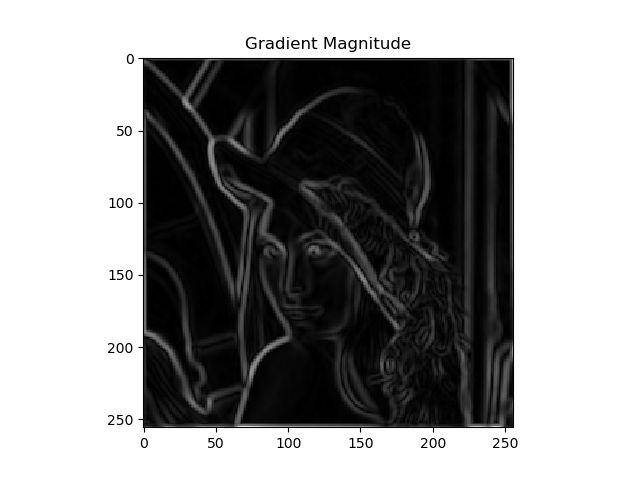
2. 计算梯度大小和方向
水平方向和竖直方向
梯度图:
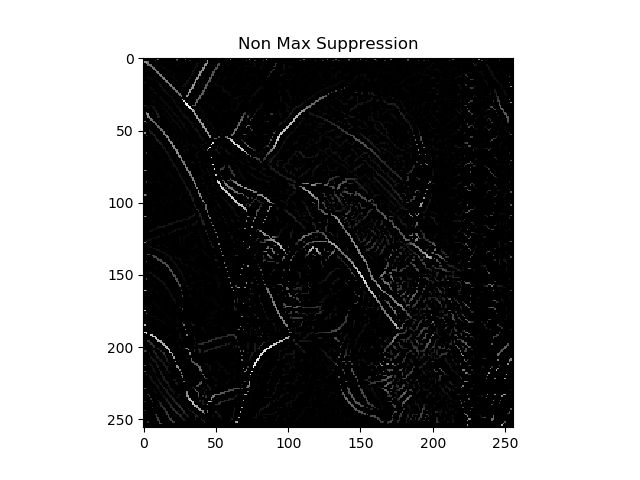
3. 非极大值抑制
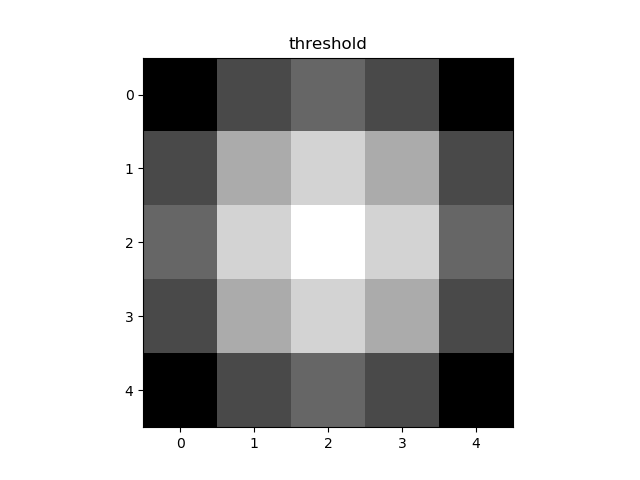
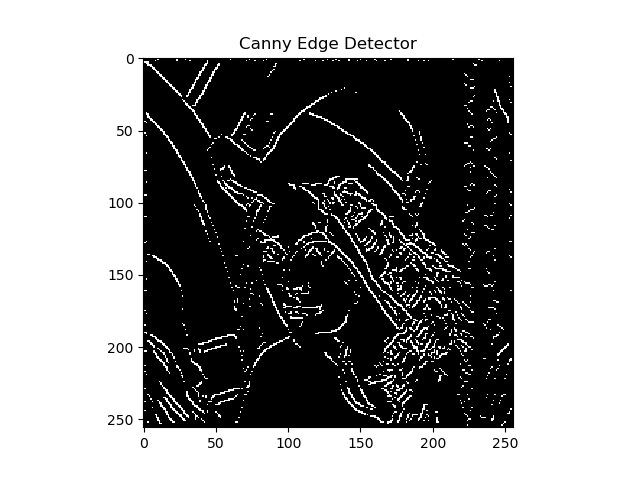
4. 双阈值检测和连接
以下是代码:
import numpy as np
import cv2
import argparse
from Computer_Vision.Canny_Edge_Detection.sobel import sobel_edge_detection
from Computer_Vision.Canny_Edge_Detection.gaussian_smoothing import gaussian_blur
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def non_max_suppression(gradient_magnitude, gradient_direction, verbose):
image_row, image_col = gradient_magnitude.shape
output = np.zeros(gradient_magnitude.shape)
PI = 180
for row in range(1, image_row - 1):
for col in range(1, image_col - 1):
direction = gradient_direction[row, col]
if (0 <= direction < PI / 8) or (15 * PI / 8 <= direction <= 2 * PI):
before_pixel = gradient_magnitude[row, col - 1]
after_pixel = gradient_magnitude[row, col + 1]
elif (PI / 8 <= direction < 3 * PI / 8) or (9 * PI / 8 <= direction < 11 * PI / 8):
before_pixel = gradient_magnitude[row + 1, col - 1]
after_pixel = gradient_magnitude[row - 1, col + 1]
elif (3 * PI / 8 <= direction < 5 * PI / 8) or (11 * PI / 8 <= direction < 13 * PI / 8):
before_pixel = gradient_magnitude[row - 1, col]
after_pixel = gradient_magnitude[row + 1, col]
else:
before_pixel = gradient_magnitude[row - 1, col - 1]
after_pixel = gradient_magnitude[row + 1, col + 1]
if gradient_magnitude[row, col] >= before_pixel and gradient_magnitude[row, col] >= after_pixel:
output[row, col] = gradient_magnitude[row, col]
if verbose:
plt.imshow(output, cmap='gray')
plt.title("Non Max Suppression")
plt.show()
return output
def threshold(image, low, high, weak, verbose=False):
output = np.zeros(image.shape)
strong = 255
strong_row, strong_col = np.where(image >= high)
weak_row, weak_col = np.where((image <= high) & (image >= low))
output[strong_row, strong_col] = strong
output[weak_row, weak_col] = weak
if verbose:
plt.imshow(output, cmap='gray')
plt.title("threshold")
plt.show()
return output
def hysteresis(image, weak):
image_row, image_col = image.shape
top_to_bottom = image.copy()
for row in range(1, image_row):
for col in range(1, image_col):
if top_to_bottom[row, col] == weak:
if top_to_bottom[row, col + 1] == 255 or top_to_bottom[row, col - 1] == 255 or top_to_bottom[row - 1, col] == 255 or top_to_bottom[
row + 1, col] == 255 or top_to_bottom[
row - 1, col - 1] == 255 or top_to_bottom[row + 1, col - 1] == 255 or top_to_bottom[row - 1, col + 1] == 255 or top_to_bottom[
row + 1, col + 1] == 255:
top_to_bottom[row, col] = 255
else:
top_to_bottom[row, col] = 0
bottom_to_top = image.copy()
for row in range(image_row - 1, 0, -1):
for col in range(image_col - 1, 0, -1):
if bottom_to_top[row, col] == weak:
if bottom_to_top[row, col + 1] == 255 or bottom_to_top[row, col - 1] == 255 or bottom_to_top[row - 1, col] == 255 or bottom_to_top[
row + 1, col] == 255 or bottom_to_top[
row - 1, col - 1] == 255 or bottom_to_top[row + 1, col - 1] == 255 or bottom_to_top[row - 1, col + 1] == 255 or bottom_to_top[
row + 1, col + 1] == 255:
bottom_to_top[row, col] = 255
else:
bottom_to_top[row, col] = 0
right_to_left = image.copy()
for row in range(1, image_row):
for col in range(image_col - 1, 0, -1):
if right_to_left[row, col] == weak:
if right_to_left[row, col + 1] == 255 or right_to_left[row, col - 1] == 255 or right_to_left[row - 1, col] == 255 or right_to_left[
row + 1, col] == 255 or right_to_left[
row - 1, col - 1] == 255 or right_to_left[row + 1, col - 1] == 255 or right_to_left[row - 1, col + 1] == 255 or right_to_left[
row + 1, col + 1] == 255:
right_to_left[row, col] = 255
else:
right_to_left[row, col] = 0
left_to_right = image.copy()
for row in range(image_row - 1, 0, -1):
for col in range(1, image_col):
if left_to_right[row, col] == weak:
if left_to_right[row, col + 1] == 255 or left_to_right[row, col - 1] == 255 or left_to_right[row - 1, col] == 255 or left_to_right[
row + 1, col] == 255 or left_to_right[
row - 1, col - 1] == 255 or left_to_right[row + 1, col - 1] == 255 or left_to_right[row - 1, col + 1] == 255 or left_to_right[
row + 1, col + 1] == 255:
left_to_right[row, col] = 255
else:
left_to_right[row, col] = 0
final_image = top_to_bottom + bottom_to_top + right_to_left + left_to_right
final_image[final_image > 255] = 255
return final_image
if __name__ == '__main__':
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("-i", "--image", required=True, help="Path to the image")
ap.add_argument("-v", "--verbose", type=bool, default=False, help="Path to the image")
args = vars(ap.parse_args())
image = cv2.imread(args["image"])
blurred_image = gaussian_blur(image, kernel_size=9, verbose=False)
edge_filter = np.array([[-1, 0, 1], [-2, 0, 2], [-1, 0, 1]])
gradient_magnitude, gradient_direction = sobel_edge_detection(blurred_image, edge_filter, convert_to_degree=True, verbose=args["verbose"])
new_image = non_max_suppression(gradient_magnitude, gradient_direction, verbose=args["verbose"])
weak = 50
new_image = threshold(new_image, 5, 20, weak=weak, verbose=args["verbose"])
new_image = hysteresis(new_image, weak)
plt.imshow(new_image, cmap='gray')
plt.title("Canny Edge Detector")
plt.show()References
hahahha