小文件下载
如果文件比较小,下载方式会比较多
直接用NSData的+ (id)dataWithContentsOfURL:(NSURL *)url;
利用NSURLConnection发送一个HTTP请求(默认是get请求)去下载
如果是下载图片,还可以利用SDWebImage框架
如果是大文件下载,建议使用或者使用NSURLSession第三方框架
HTTP Range的示例
通过设置请求头Range可以指定位置每次从网路下载数据包的大小
Range示例
bytes=0-499 从0到499的头500个字节
bytes=500-999 从500到999的第二个500字节
bytes=500- 从500字节以后的所有字节
bytes=-500 最后500个字节
bytes=500-599,800-899 同时指定几个范围
Range小结
- 用于分隔
前面的数字表示起始字节数
后面的数组表示截止字节数,没有表示到末尾
, 用于分组,可以一次指定多个Range,不过很少用
第三方解压缩框架——SSZipArchive
下载地址:https://github.com/samsoffes/ssziparchive
注意:需要引入libz.dylib框架
Unzipping
NSString *zipPath = @"path_to_your_zip_file";
NSString *destinationPath = @"path_to_the_folder_where_you_want_it_unzipped";
[SSZipArchive unzipFileAtPath:zipPath toDestination:destinationPath];
Zipping
NSString *zippedPath = @"path_where_you_want_the_file_created";
NSArray *inputPaths = [NSArray arrayWithObjects:
[[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"photo1" ofType:@"jpg"],
[[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"photo2" ofType:@"jpg"]
nil];
[SSZipArchive createZipFileAtPath:zippedPath withFilesAtPaths:inputPaths];
第三方解压缩框架——ZipArchive
下载地址:https://github.com/ZipArchive/ZipArchive
需要引入libz.dylib框架
导入头文件Main.h
创建压缩文件
- (BOOL)createZipFileAtPath:(NSString *)path
withFilesAtPaths:(NSArray *)paths; - (BOOL)createZipFileAtPath:(NSString *)path
withContentsOfDirectory:(NSString *)directoryPath;
解压
- (BOOL)unzipFileAtPath:(NSString *)path
toDestination:(NSString *)destination
文件上传的步骤
设置请求头
[request setValue:@"multipart/form-data; boundary=分割线" forHTTPHeaderField:@"Content-Type"];
设置请求体
非文件参数
--分割线\r\n
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="参数名"\r\n
\r\n
参数值
\r\n
文件参数
--分割线\r\n
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="参数名"; filename="文件名"\r\n
Content-Type: 文件的MIMEType\r\n
\r\n
文件数据
\r\n
参数结束的标记
--分割线--\r\n
multipart/form-data格式小结
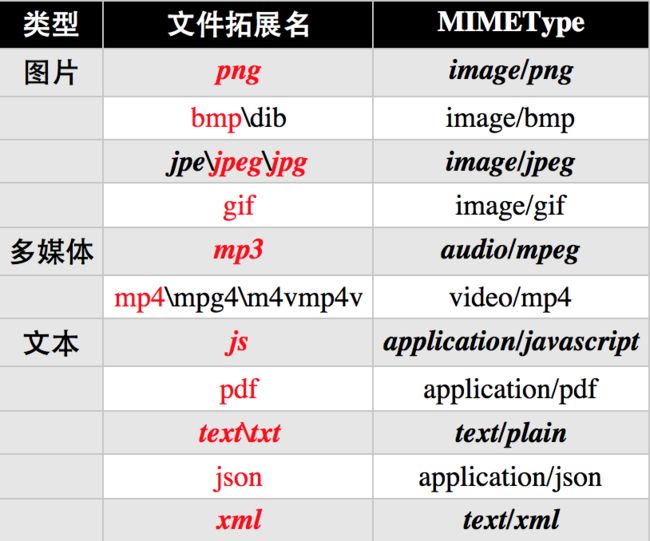
部分文件的MIMEType
获得文件的MIMEType
利用NSURLConnection
(NSString *)MIMEType:(NSURL *)url
{
1.创建一个请求
NSURLRequest *request = [NSURLRequest requestWithURL:url];
2.发送请求(返回响应)
NSURLResponse *response = nil;
[NSURLConnection sendSynchronousRequest:request
returningResponse:&response error:nil];
3.获得MIMEType
return response.MIMEType;
}
获得文件的MIMEType
C语言API
- (NSString *)mimeTypeForFileAtPath:(NSString *)path
{
if (![[NSFileManager alloc] init]
fileExistsAtPath:path]) {
return nil;
}
CFStringRef UTI =UTTypeCreatePreferredIdentifierForTag(kUTTagClassFilenameExtension,
(CFStringRef)[path pathExtension], NULL);
CFStringRef MIMEType = UTTypeCopyPreferredTagWithClass (UTI,
kUTTagClassMIMEType);
CFRelease(UTI);
if (!MIMEType) {
return
@"application/octet-stream";
}
return NSMakeCollectable(MIMEType);
}
1.0 文件下载
- 1.1 小文件下载
(1)第一种方式(NSData)
使用NSDta直接加载网络上的url资源(不考虑线程)
-(void)dataDownload
{
1.确定资源路径
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://120.25.226.186:32812/resources/images/minion_01.png"];
2.根据URL加载对应的资源
NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:url];
3.转换并显示数据
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageWithData:data];
self.imageView.image = image;
}
(2)第二种方式(NSURLConnection-sendAsync)
使用NSURLConnection发送异步请求下载文件资源
-(void)connectDownload
{
1.确定请求路径
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://120.25.226.186:32812/resources/images/minion_01.png"];
2.创建请求对象
NSURLRequest *request = [NSURLRequest requestWithURL:url];
3.使用NSURLConnection发送一个异步请求
[NSURLConnection sendAsynchronousRequest:request queue:[NSOperationQueue
mainQueue] completionHandler:^(NSURLResponse * _Nullable
response, NSData * _Nullable data, NSError *
_Nullable connectionError) {
4.拿到并处理数据
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageWithData:data];
self.imageView.image = image;
}];
}
(3)第三种方式(NSURLConnection-delegate)
使用NSURLConnection设置代理发送异步请求的方式下载文件
-(void)connectionDelegateDownload
{
1.确定请求路径
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://120.25.226.186:32812/resources/videos/minion_01.mp4"];
2.创建请求对象
NSURLRequest *request = [NSURLRequest requestWithURL:url];
3.使用NSURLConnection设置代理并发送异步请求
[NSURLConnection connectionWithRequest:request delegate:self];
}
pragma
mark--NSURLConnectionDataDelegate
当接收到服务器响应的时候调用,该方法只会调用一次
-(void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection
didReceiveResponse:(NSURLResponse *)response
{
创建一个容器,用来接收服务器返回的数据
self.fileData = [NSMutableData data];
获得当前要下载文件的总大小(通过响应头得到)
NSHTTPURLResponse *res = (NSHTTPURLResponse *)response;
self.totalLength = res.expectedContentLength;
NSLog(@"%zd",self.totalLength);
拿到服务器端推荐的文件名称
self.fileName = res.suggestedFilename;
}
当接收到服务器返回的数据时会调用
该方法可能会被调用多次
-(void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection
didReceiveData:(NSData *)data
{
拼接每次下载的数据
[self.fileData appendData:data];
计算当前下载进度并刷新UI显示
self.currentLength = self.fileData.length;
NSLog(@"%f",1.0* self.currentLength/self.totalLength);
self.progressView.progress = 1.0*self.currentLength/self.totalLength;
}
当网络请求结束之后调用
-(void)connectionDidFinishLoading:(NSURLConnection
*)connection
{
文件下载完毕把接受到的文件数据写入到沙盒中保存
1.确定要保存文件的全路径
caches文件夹路径
NSString *caches = [NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSCachesDirectory,
NSUserDomainMask, YES) lastObject];
NSString *fullPath = [caches stringByAppendingPathComponent:self.fileName];
2.写数据到文件中
[self.fileData writeToFile:fullPath atomically:YES];
NSLog(@"%@",fullPath);
}
当请求失败的时候调用该方法
-(void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection
didFailWithError:(NSError *)error
{
NSLog(@"%s",__func__);
}
- 3.2 大文件的下载
(1)实现思路
边接收数据边写文件以解决内存越来越大的问题
(2)核心代码
当接收到服务器响应的时候调用,该方法只会调用一次
-(void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection
didReceiveResponse:(NSURLResponse *)response
{
0.获得当前要下载文件的总大小(通过响应头得到)
NSHTTPURLResponse *res = (NSHTTPURLResponse *)response;
self.totalLength = res.expectedContentLength;
NSLog(@"%zd",self.totalLength);
创建一个新的文件,用来当接收到服务器返回数据的时候往该文件中写入数据
1.获取文件管理者
NSFileManager *manager = [NSFileManager defaultManager];
2.拼接文件的全路径
caches文件夹路径
NSString *caches = [NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSCachesDirectory,
NSUserDomainMask, YES) lastObject];
NSString *fullPath = [caches stringByAppendingPathComponent:res.suggestedFilename];
self.fullPath = fullPath;
3.创建一个空的文件
[manager createFileAtPath:fullPath contents:nil
attributes:nil];
}
当接收到服务器返回的数据时会调用
该方法可能会被调用多次
-(void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection
didReceiveData:(NSData *)data
{
1.创建一个用来向文件中写数据的文件句柄
注意当下载完成之后,该文件句柄需要关闭,调用closeFile方法
NSFileHandle *handle = [NSFileHandle fileHandleForWritingAtPath:self.fullPath];
2.设置写数据的位置(追加)
[handle
seekToEndOfFile];
3.写数据
[handle writeData:data];
4.计算当前文件的下载进度
self.currentLength += data.length;
NSLog(@"%f",1.0* self.currentLength/self.totalLength);
self.progressView.progress = 1.0*self.currentLength/self.totalLength;
}
- 1.3 大文件断点下载
(1)实现思路
在下载文件的时候不再是整块的从头开始下载,而是看当前文件已经下载到哪个地方,然后从该地方接着往后面下载。可以通过在请求对象中设置请求头实现。
(2)解决方案(设置请求头)
2.创建请求对象
NSMutableURLRequest *request = [NSMutableURLRequest requestWithURL:url];
2.1 设置下载文件的某一部分
只要设置HTTP请求头的Range属性, 就可以实现从指定位置开始下载
表示头500个字节:Range: bytes=0-499
表示第二个500字节:Range: bytes=500-999
表示最后500个字节:Range: bytes=-500
表示500字节以后的范围:Range: bytes=500-
NSString *range = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"bytes=%zd-",self.currentLength];
[request setValue:range forHTTPHeaderField:@"Range"];
(3)注意点(下载进度并判断是否需要重新创建文件)
获得当前要下载文件的总大小(通过响应头得到)
NSHTTPURLResponse *res = (NSHTTPURLResponse *)response;
注意点:res.expectedContentLength获得是本次请求要下载的文件的大小(并非是完整的文件的大小)
因此:文件的总大小 == 本次要下载的文件大小+已经下载的文件的大小
self.totalLength = res.expectedContentLength +self.currentLength;
NSLog(@"----------------------------%zd",self.totalLength);
0 判断当前是否已经下载过,如果当前文件已经存在,那么直接返回
if (self.currentLength >0) {
return;
}
- 1.4 输出流
(1)使用输出流也可以实现和NSFileHandle相同的功能
(2)如何使用
1.创建一个数据输出流
第一个参数:二进制的流数据要写入到哪里
第二个参数:采用什么样的方式写入流数据,如果YES则表示追加,如果是NO则表示覆盖
NSOutputStream *stream = [NSOutputStream outputStreamToFileAtPath:fullPath append:YES];
只要调用了该方法就会往文件中写数据
如果文件不存在,那么会自动的创建一个
[stream open];
self.stream = stream;
2.当接收到数据的时候写数据
使用输出流写数据
第一个参数:要写入的二进制数据
第二个参数:要写入的数据的大小
[self.stream write:data.bytes maxLength:data.length];
3.当文件下载完毕的时候关闭输出流
关闭输出流
[self.stream close];
self.stream = nil;
- 1.5 使用多线程下载文件思路
01 开启多条线程,每条线程都只下载文件的一部分(通过设置请求头中的Range来实现)
02 创建一个和需要下载文件大小一致的文件,判断当前是那个线程,根据当前的线程来判断下载的数据应该写入到文件中的哪个位置。(假设开5条线程来下载10M的文件,那么线程1下载0-2M,线程2下载2-4M一次类推,当接收到服务器返回的数据之后应该先判断当前线程是哪个线程,假如当前线程是线程2,那么在写数据的时候就从文件的2M位置开始写入)
03 代码相关:使用NSFileHandle这个类的seekToFileOfSet方法,来向文件中特定的位置写入数据。
04 技术相关
a.每个线程通过设置请求头下载文件中的某一个部分
b.通过NSFileHandle向文件中的指定位置写数据
2.0 文件的压缩和解压缩
(1)说明
使用ZipArchive来压缩和解压缩文件需要添加依赖库(libz),使用需要包含Main文件,如果使用cocoaPoads来安装框架,那么会自动的配置框架的使用环境
(2)相关代码
压缩文件的第一种方式
第一个参数:压缩文件要保存的位置
第二个参数:要压缩哪几个文件
[Main createZipFileAtPath:fullpath withFilesAtPaths:arrayM];
压缩文件的第二种方式
第一个参数:文件压缩到哪个地方
第二个参数:要压缩文件的全路径
[Main createZipFileAtPath:fullpath withContentsOfDirectory:zipFile];
如何对压缩文件进行解压
第一个参数:要解压的文件
第二个参数:要解压到什么地方
[Main unzipFileAtPath:unZipFile toDestination:fullpath];
2.0 文件的上传
- 2.1 文件上传步骤
(1)确定请求路径
(2)根据URL创建一个可变的请求对象
(3)设置请求对象,修改请求方式为POST
(4)设置请求头,告诉服务器我们将要上传文件(Content-Type)
(5)设置请求体(在请求体中按照既定的格式拼接要上传的文件参数和非文件参数等数据)
001 拼接文件参数
002 拼接非文件参数
003 添加结尾标记
(6)使用NSURLConnection sendAsync发送异步请求上传文件
(7)解析服务器返回的数据
- 2.2 文件上传设置请求体的数据格式
请求体拼接格式
分隔符:----WebKitFormBoundaryhBDKBUWBHnAgvz9c
01.文件参数拼接格式
--分隔符
Content-Disposition:参数
Content-Type:参数
空行
文件参数
02.非文件拼接参数
--分隔符
Content-Disposition:参数
空行
非文件的二进制数据
03.结尾标识
--分隔符--
- 2.3 文件上传相关代码
- (void)upload
{
1.确定请求路径
NSURL
*url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://120.25.226.186:32812/upload"];
2.创建一个可变的请求对象
NSMutableURLRequest *request = [NSMutableURLRequest requestWithURL:url];
3.设置请求方式为POST
request.HTTPMethod = @"POST";
4.设置请求头
NSString *filed = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"multipart/form-data;
boundary=%@",Kboundary];
[request setValue:filed forHTTPHeaderField:@"Content-Type"];
5.设置请求体
NSMutableData *data = [NSMutableData data];
5.1
文件参数
--分隔符
Content-Disposition:参数
Content-Type:参数
空行
文件参数
[data appendData:[[NSString stringWithFormat:@"--%@",Kboundary]
dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]];
[data appendData:KnewLine];
[data appendData:[@"Content-Disposition: form-data;
name="file"; filename="test.png""dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]];
[data appendData:KnewLine];
[data appendData:[@"Content-Type: image/png"
dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]];
[data appendData:KnewLine];
[data appendData:KnewLine];
[data appendData:KnewLine];
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"test"];
NSData *imageData = UIImagePNGRepresentation(image);
[data appendData:imageData];
[data appendData:KnewLine];
5.2
非文件参数
--分隔符
Content-Disposition:参数
空行
非文件参数的二进制数据
[data appendData:[[NSString stringWithFormat:@"--%@",Kboundary]
dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]];
[data appendData:KnewLine];
[data appendData:[@"Content-Disposition: form-data;
name="username"" dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]];
[data appendData:KnewLine];
[data appendData:KnewLine];
[data appendData:KnewLine];
NSData *nameData = [@"wending ding" dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
[data appendData:nameData];
[data appendData:KnewLine];
5.3
结尾标识
--分隔符--
[data appendData:[[NSString stringWithFormat:@"--%@--",Kboundary]
dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]];
[data appendData:KnewLine];
request.HTTPBody = data;
6.发送请求
[NSURLConnection sendAsynchronousRequest:request queue:[NSOperationQueue mainQueue] completionHandler:^(NSURLResponse * __nullable response, NSData * __nullable data, NSError
-
__nullable connectionError) {
7.解析服务器返回的数据NSLog(@"%@",[NSJSONSerialization
JSONObjectWithData:data options:kNilOptions error:nil]);}];
}
- 2.4 如何获得文件的MIMEType类型
(1)直接对该对象发送一个异步网络请求,在响应头中通过response.MIMEType拿到文件的MIMEType类型
如果想要及时拿到该数据,那么可以发送一个同步请求
- (NSString *)getMIMEType
{
NSString *filePath = @"/Users/文顶顶/Desktop/备课/其它/swift.md";
NSURLResponse *response = nil;
[NSURLConnection sendSynchronousRequest:[NSURLRequest requestWithURL:[NSURL
fileURLWithPath:filePath]] returningResponse:&response error:nil];
return response.MIMEType;
}
对该文件发送一个异步请求,拿到文件的MIMEType
- (void)MIMEType
{
NSString *file = @"file:///Users/Edison/Desktop/test.png";
[NSURLConnection sendAsynchronousRequest:[NSURLRequest
requestWithURL:[NSURL fileURLWithPath:@"/Users/Edison/Desktop/test.png"]] queue:[NSOperationQueue mainQueue]
completionHandler:^(NSURLResponse * __nullable response, NSData * __nullable data,
NSError * __nullableconnectionError) {
NSLog(@"%@",response.MIMEType);
}];
}
(2)通过UTTypeCopyPreferredTagWithClass方法
注意:需要依赖于框架MobileCoreServices
- (NSString *)mimeTypeForFileAtPath:(NSString *)path
{
if (![[[NSFileManager alloc] init]
fileExistsAtPath:path]) {
return nil;
}
CFStringRef UTI = UTTypeCreatePreferredIdentifierForTag(kUTTagClassFilenameExtension, (__bridge CFStringRef)[path pathExtension],NULL);
CFStringRef MIMEType = UTTypeCopyPreferredTagWithClass (UTI,
kUTTagClassMIMEType);
CFRelease(UTI);
if (!MIMEType) {
return
@"application/octet-stream";
}
return (__bridge
NSString *)(MIMEType);
}
**************************黑马笔记****************************
一、大文件下载
1.方案:利用NSURLConnection和它的代理方法
1> 发送一个请求
1.URL
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://localhost:8080/MJServer/resources/videos.zip"];
2.请求
NSURLRequest *request
= [NSURLRequest requestWithURL:url];
3.下载(创建完conn对象后,会自动发起一个异步请求)
[NSURLConnection
connectionWithRequest:request delegate:self];
2> 在代理方法中处理服务器返回的数据
在接收到服务器的响应时:
1.创建一个空的文件
2.用一个句柄对象关联这个空的文件,目的是:方便后面用句柄对象往文件后面写数据
- (void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection
didReceiveResponse:(NSURLResponse *)response
{
文件路径
NSString
*caches = [NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSCachesDirectory,
NSUserDomainMask, YES) lastObject];
NSString
*filepath = [caches stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"videos.zip"];
创建一个空的文件 到 沙盒中
NSFileManager *mgr = [NSFileManager defaultManager];
[mgr createFileAtPath:filepath contents:nil
attributes:nil];
创建一个用来写数据的文件句柄
self.writeHandle = [NSFileHandle fileHandleForWritingAtPath:filepath];
}
在接收到服务器返回的文件数据时,利用句柄对象往文件的最后面追加数据
- (void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection
didReceiveData:(NSData *)data
{
移动到文件的最后面
[self.writeHandle seekToEndOfFile];
将数据写入沙盒
[self.writeHandle writeData:data];
}
在所有数据接收完毕时,关闭句柄对象
- (void)connectionDidFinishLoading:(NSURLConnection
*)connection
{
关闭文件
[self.writeHandle closeFile];
self.writeHandle = nil;
}
2.注意点:千万不能用NSMutableData来拼接服务器返回的数据
二、NSURLConnection发送异步请求的方法
1.block形式
- 除开大文件下载以外的操作,都可以用这种形式
[NSURLConnection
sendAsynchronousRequest:<#(NSURLRequest *)#> queue:<#(NSOperationQueue
*)#> completionHandler:^(NSURLResponse *response, NSData *data, NSError
*connectionError) {
}];
2.代理形式
- 一般用在大文件下载
1.URL
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://localhost:8080/MJServer/login?username=123&pwd=123"];
2.请求
NSURLRequest *request = [NSURLRequest requestWithURL:url];
3.下载(创建完conn对象后,会自动发起一个异步请求)
[NSURLConnection connectionWithRequest:request delegate:self];
三、NSURLSession
1.使用步骤
1> 获得NSURLSession对象
2> 利用NSURLSession对象创建对应的任务(Task)
3> 开始任务([task
resume])
2.获得NSURLSession对象
1> [NSURLSession sharedSession]
2>NSURLSessionConfiguration
*cfg = [NSURLSessionConfiguration defaultSessionConfiguration];
self.session = [NSURLSession
sessionWithConfiguration:cfg delegate:self
delegateQueue:[NSOperationQueue mainQueue]];
3.任务类型
1>
NSURLSessionDataTask
- 用途:用于非文件下载的GET\POST请求
NSURLSessionDataTask
*task = [self.session
dataTaskWithRequest:request];
NSURLSessionDataTask *task = [self.session dataTaskWithURL:url];
NSURLSessionDataTask *task = [self.session dataTaskWithURL:url
completionHandler:^(NSData *data, NSURLResponse *response, NSError *error) {
}];
2>
NSURLSessionDownloadTask
- 用途:用于文件下载(小文件、大文件)
NSURLSessionDownloadTask *task = [self.session
downloadTaskWithRequest:request];
NSURLSessionDownloadTask *task = [self.session
downloadTaskWithURL:url];
NSURLSessionDownloadTask *task = [self.session
downloadTaskWithURL:url completionHandler:^(NSURL *location, NSURLResponse *response, NSError *error) {
}];