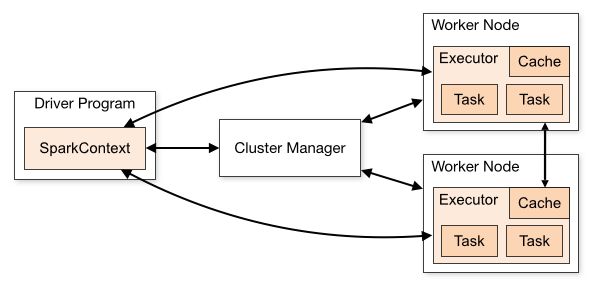
本文以Spark 1.6 Standalone模式为例,介绍用户提交Spark Job后的Job的执行流程。大体流程如下图所示
用户提交Job后会生成SparkContext对象,SparkContext向Cluster Manager(在Standalone模式下是Spark Master)申请Executor资源,并将Job分解成一系列可并行处理的task,然后将task分发到不同的Executor上运行,Executor在task执行完后将结果返回到SparkContext。
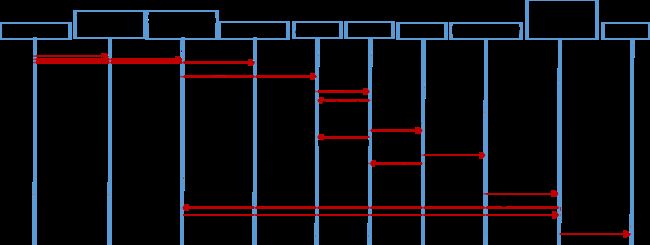
下面首先介绍SparkContext申请Executor资源的过程,整个过程如下图所示。
整个过程分为8步:
- SparkContext创建TaskSchedulerImpl,SparkDeploySchedulerBackend和DAGScheduler
// Create and start the scheduler
val (sched, ts) = SparkContext.createTaskScheduler(this, master)
_schedulerBackend = sched
_taskScheduler = ts
_dagScheduler = new DAGScheduler(this)
DAGScheduler负责将Job划分为不同的Stage,并在每个Stage内化为出一系列可并行处理的task,然后将task递交给TaskSchedulerImpl调度。此过程之后详谈。
TaskSchedulerImpl负责通过SparkDeploySchedulerBackend来调度任务(task),目前实现了FIFO调度和Fair调度。注意如果是Yarn模式,则是通过YarnSchedulerBackend来进行调度。
- SparkDeploySchedulerBackend创建AppClient,并通过一些回调函数来得到Executor信息
client = new AppClient(sc.env.actorSystem, masters, appDesc, this, conf)
client.start()
SparkDeploySchedulerBackend与AppClient间的回调函数如下:
private[spark] trait AppClientListener {
def connected(appId: String): Unit
/** Disconnection may be a temporary state, as we fail over to a new Master. */
def disconnected(): Unit
/** An application death is an unrecoverable failure condition. */
def dead(reason: String): Unit
def executorAdded(fullId: String, workerId: String, hostPort: String, cores: Int, memory: Int)
def executorRemoved(fullId: String, message: String, exitStatus: Option[Int]): Unit
}
- AppClient向Master注册Application
try {
registerWithMaster()
} catch {
case e: Exception =>
logWarning("Failed to connect to master", e)
markDisconnected()
context.stop(self)
}
Applicent通过Akka与Master进行交互得到Executor和Master的信息,然后通过回调SparkDeploySchedulerBackend的函数。
- Master向Woker发送LaunchExecutor消息,同时向AppClient发送ExecutorAdded消息
Master收到RegisterApplication信息后,开始分配Executor资源。目前有两种策略(摘抄原话):There are two modes of launching executors. The first attempts to spread out an application's executors on as many workers as possible, while the second does the opposite (i.e. launch them on as few workers as possible). The former is usually better for data locality purposes and is the default.
case RegisterApplication(description) => {
if (state == RecoveryState.STANDBY) {
// ignore, don't send response
} else {
logInfo("Registering app " + description.name)
val app = createApplication(description, sender)
registerApplication(app)
logInfo("Registered app " + description.name + " with ID " + app.id)
persistenceEngine.addApplication(app)
sender ! RegisteredApplication(app.id, masterUrl)
schedule() //分配Executor资源
}
}
然后向Worker发送LauchExecutor消息,
private def launchExecutor(worker: WorkerInfo, exec: ExecutorDesc): Unit = {
logInfo("Launching executor " + exec.fullId + " on worker " + worker.id)
worker.addExecutor(exec)
worker.actor ! LaunchExecutor(masterUrl,
exec.application.id, exec.id, exec.application.desc, exec.cores, exec.memory)
exec.application.driver ! ExecutorAdded(
exec.id, worker.id, worker.hostPort, exec.cores, exec.memory)
}
注意:The number of cores assigned to each executor is configurable. When this is explicitly set, multiple executors from the same application may be launched on the same worker if the worker has enough cores and memory. Otherwise, each executor grabs all the cores available on the worker by default, in which case only one executor may be launched on each worker.
- Worker创建ExecutorRunner,并向Master发送ExecutorStateChanged的消息
val manager = new ExecutorRunner(
appId,
execId,
appDesc.copy(command = Worker.maybeUpdateSSLSettings(appDesc.command, conf)),
cores_,
memory_,
self,
workerId,
host,
webUi.boundPort,
publicAddress,
sparkHome,
executorDir,
akkaUrl,
conf,
appLocalDirs, ExecutorState.LOADING)
executors(appId + "/" + execId) = manager
manager.start()
coresUsed += cores_
memoryUsed += memory_
master ! ExecutorStateChanged(appId, execId, manager.state, None, None)
- ExecutorRunner创建CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend
在函数fetchAndRunExecutor中,
val builder = CommandUtils.buildProcessBuilder(appDesc.command, memory,
sparkHome.getAbsolutePath, substituteVariables)
其中appDesc.command是(在SparkDeploySchedulerBackend中定义)
val command = Command("org.apache.spark.executor.CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend",
args, sc.executorEnvs, classPathEntries ++ testingClassPath, libraryPathEntries, javaOpts)
- CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend向SparkDeploySchedulerBackend发送RegisterExecutor消息
override def onStart() {
logInfo("Connecting to driver: " + driverUrl)
rpcEnv.asyncSetupEndpointRefByURI(driverUrl).flatMap { ref =>
// This is a very fast action so we can use "ThreadUtils.sameThread"
driver = Some(ref)
ref.ask[RegisteredExecutor.type](
RegisterExecutor(executorId, self, hostPort, cores, extractLogUrls))
}(ThreadUtils.sameThread).onComplete {
// This is a very fast action so we can use "ThreadUtils.sameThread"
case Success(msg) => Utils.tryLogNonFatalError {
Option(self).foreach(_.send(msg)) // msg must be RegisteredExecutor
}
case Failure(e) => logError(s"Cannot register with driver: $driverUrl", e)
}(ThreadUtils.sameThread)
}
- CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend在接收到SparkDeploySchedulerBackend发送的RegisteredExecutor消息后,创建Executor
override def receive: PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
case RegisteredExecutor =>
logInfo("Successfully registered with driver")
val (hostname, _) = Utils.parseHostPort(hostPort)
executor = new Executor(executorId, hostname, env, userClassPath, isLocal = false)
至此Executor创建成功,:)。