虽然我写了这文章,但是我不建议这种做法,原因很简单,这是把简单事情复杂化。
什么是Cucumber?什么是BDD?这里不细讲,不懂的直接查看官方:https://cucumber.io/
什么是Rest Assured?传送门:https://github.com/rest-assured/rest-assured
以下以java为开发语言,快速搭建一个cucumber+Rest Assured的api自动化测试平台。
1. 用IDEA 新建一个Maven工程,并pom文件添加如下配置:
info.cukes
cucumber-java8
1.2.4
test
info.cukes
cucumber-java
1.2.4
info.cukes
cucumber-html
0.2.3
com.jayway.restassured
rest-assured
2.9.0
org.testng
testng
6.9.10
log4j
log4j
1.2.17
org.slf4j
slf4j-log4j12
1.7.5
provided
net.javacrumbs.json-unit
json-unit
1.13.0
com.fasterxml.jackson.core
jackson-databind
2.8.1
- 新建个ApiTools类,并对Rest Assured进程二次封装,主要是Post 和 Get请求的基础封装和对返回json解析的封装,具体代码如下:
/**
* 带json的post请求
*
* @param apiPath api地址
* @param json 请求json
* @return api返回的Response
*/
public static Response post(String apiPath, String json) {
// 开始发起post 请求
String path = Parameters.BOSEHOST + apiPath;
Response response = given().
contentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8").
headers("header1", "value1").
cookies("cookies1", "value1").
body(json).
when().log().all().post(path.trim());
log.info(response.statusCode());
log.info("reponse:");
response.getBody().prettyPrint();
return response;
}
/**
* get 请求
*
* @param apiPath api路径
* @return api的response
*/
public static Response get(String apiPath) {
// 开始发起GET 请求
String path = Parameters.BOSEHOST + apiPath;
Response response = given().
contentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8").
headers("headers1", "value1").
cookie("cookie1", "value1").
when().log().all().get(path.trim());
log.info(response.statusCode());
log.info("reponse:");
response.getBody().prettyPrint();
return response;
}
/**
* 获取json中某个key值
* @param response 接口返回
* @param jsonPath jsonpath, 例如 a.b.c a.b[1].c a
* @return
*/
public static String getJsonPathValue(Response response, String jsonPath) {
String reponseJson = String.valueOf(response.jsonPath().get(jsonPath));
// String jsonValue = String.valueOf(from(reponseJson).get(jsonPath));
return reponseJson;
}
3.新建个Steps 类,完成常用step的封装,具体代码如下:
import com.jayway.restassured.response.Response;
import com.tools.apitools.ApiTools;
import com.tools.apitools.MyAssert;
import com.tools.filetools.ReadTxtFile;
import cucumber.api.java.en.Then;
import cucumber.api.java.en.When;
import static net.javacrumbs.jsonunit.JsonAssert.assertJsonEquals;
/**
* Created by MeYoung on 8/1/2016.
*
* Steps 集合
*/
public class Steps {
Response response = null;
@When("^I send a GET request to \"(.*?)\"$")
public void getRequest(String path) {
response = ApiTools.get(path);
}
@When("^I send a POST request to \"(.*?)\"$")
public void postRequest(String apiPath) throws Throwable {
response = ApiTools.post(apiPath);
}
@When("^I send a POST request to \"(.*?)\" and request json:$")
public void postRequestWithJson(String apiPath, String json) {
response = ApiTools.post(apiPath, json);
}
@When("^I use a \"(.*?)\" file to send a POST request to \"(.*?)\"$")
public void postRequestWihtFile(String fileName, String path) {
String json = ReadTxtFile.readTxtFile(fileName);
response = ApiTools.post(path, json);
}
@Then("^the JSON response equals$")
public void assertResponseJson(String expected) {
String responseJson = response.body().asString();
assertJsonEquals(responseJson, expected);
}
@Then("^the JSON response equals json file \"(.*?)\"$")
public void theJSONResponseEqualsJsonFile(String fileName) {
String responseJson = response.body().asString();
String fileJson = ReadTxtFile.readTxtFile(fileName);
assertJsonEquals(responseJson, fileJson);
}
@Then("^the response status should be \"(\\d{3})\"$")
public void assertStatusCode(int statusCode) {
Object jsonResponse = response.getStatusCode();
MyAssert.assertEquals(jsonResponse, statusCode);
}
@Then("^the JSON response \"(.*?)\" equals \"(.*?)\"$")
public void assertEquals(String str, String expected) {
String jsonValue = ApiTools.getJsonPathValue(response, str);
MyAssert.assertEquals(jsonValue, expected);
}
@Then("^the JSON response \"(.*?)\" type should be \"(.*?)\"$")
public void assertMatch(String str, String match) {
String jsonValue = ApiTools.getJsonPathValue(response, str);
MyAssert.assertMatch(jsonValue, match);
}
@Then("^the JSON response \"(.*?)\" should be not null$")
public void assertNotNull(String str) {
String jsonValue = ApiTools.getJsonPathValue(response, str);
MyAssert.assertNotNull(jsonValue);
}
@Then("^the JSON response \"(.*?)\" start with \"(.*?)\"$")
public void assertStartWith(String str, String start) {
String jsonValue = ApiTools.getJsonPathValue(response, str);
MyAssert.assertStartWith(jsonValue, start);
}
@Then("^the JSON response \"(.*?)\" end with \"(.*?)\"$")
public void assertEndWith(String str, String end) {
String jsonValue = ApiTools.getJsonPathValue(response, str);
MyAssert.assertEndWith(jsonValue, end);
}
@Then("^the JSON response \"(.*?)\" include \"(.*?)\"$")
public void assertInclude(String str, String include) {
String jsonValue = ApiTools.getJsonPathValue(response, str);
MyAssert.assertInclude(jsonValue, include);
}
}
当然上面代码还涉及到一些Asssert的封装,这里就不列出来,个人喜好不同,更具自己熟悉的情况去引入自己熟悉的jar包。
ok,最后我们愉快的写两个case,看看效果:
@get
Scenario Outline: use examples
When I send a GET request to "apiurl"
Then the response status should be "200"
Then the JSON response "" equals ""
Examples:
| jsonPath | value |
| genericPlan | false |
| ehiCarrierId | 90121100 |
| carrierName | Anthem Blue Cross |
@post
Scenario: test post request
When I send a POST request to "apiurl"
Then the response status should be "200"
And the JSON response "message" equals "success"
# 校验放回值是否是某种类型
And the JSON response "sessionId" type should be "^\d{6}$"
# 校验返回值不为空
And the JSON response "url" should be not null
# 校验是否以XX开头
Then the JSON response "message" start with "su"
# 校验是否以XX开头
Then the JSON response "message" end with "ss"
# 校验是否以XX开头
Then the JSON response "message" include "ss"
# 校验返回json是否为XXX,对整个返回json的校验
Then the JSON response equals
"""
{
"result":"success"
}
"""
通过Junit 运行feature.
- 在Pom.xml 文件添加junit相关包:
info.cukes
cucumber-junit
1.2.4
test
junit
junit
4.12
test
- 在feature 同级目录下新建个运行类,代码例子如下:
import cucumber.api.CucumberOptions;
import cucumber.api.junit.Cucumber;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
@RunWith(Cucumber.class)
@CucumberOptions(
strict = true,
monochrome = true,
plugin = {"pretty", "html:target/cucumber", "json:target/cucumber.json"},
features = {"src/test/java/bosev2"},
glue = {"com.bose.step"},
tags = {"~@unimplemented"})
public class RunnerBoseTest {
}
@RunWith(Cucumber.class) : 注解表示通过Cucumber的Junit 方式运行脚本
@CucumberOptions () :注解用于配置运行信息,其中代码中的plugin 表示测试报告输出的路径和格式, feature 表示被运行的feature文件的包路径, glue中配置steps的包路径地址,tags中配置要运行的用例的tags名,其实~符号表示除了这个tags的所有tags.
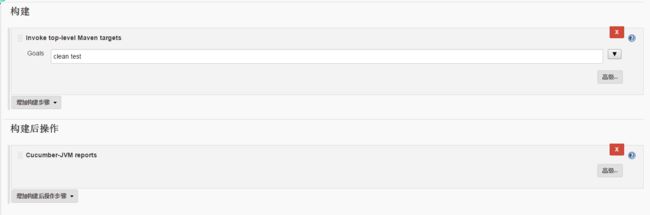
通过Jenkins 执行
- 在Pom.xml 文件里面添加运行插件,如下:
org.apache.maven.plugins
maven-compiler-plugin
3.3
true
1.7
1.7
UTF-8
org.apache.maven.plugins
maven-surefire-plugin
2.18.1
false
- 在Jenkins 中添加Cucumber-JVM reports插件。
- 新建Maven job,配置maven构建方式和构建后的测试报告展示。
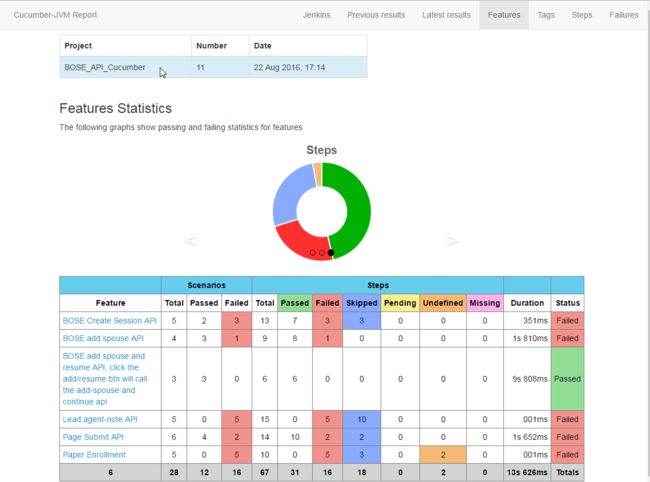
Cucumber-JVM reports 提供了非常漂亮的report,如下:
最后附上项目地址:https://github.com/MeYoung/cucumber_restassured