GRUB(Boot Loader):
grub: GRand Unified Bootloader
grub 0.x: grub legacy
grub 1.x: grub2
grub legacy:
stage1: mbr
stage1_5: mbr之后的扇区,让stage1中的bootloader能识别stage2所在的分区上的文件系统;
stage2:磁盘分区(/boot/grub/)
stage2及内核等通常放置于一个基本磁盘分区;
配置文件:/boot/grub/grub.conf <-- /etc/grub.conf
功用:
(1) 提供菜单、并提供交互式接口
e: 编辑模式,用于编辑菜单;
c: 命令模式,交互式接口;
(2) 加载用户选择的内核或操作系统
允许传递参数给内核
可隐藏此菜单
(3) 为菜单提供了保护机制
为编辑菜单进行认证
为启用内核或操作系统进行认证
grub如何识别设备:
(hd#,#)
hd#: 磁盘编号,用数字表示;从0开始编号
#: 分区编号,用数字表示; 从0开始编号
grub的命令行接口
help: 获取帮助列表
help KEYWORD: 详细帮助信息
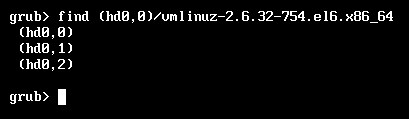
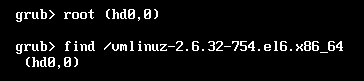
find (hd#,#)/PATH/TO/SOMEFILE
root (hd#,#)
kernel /PATH/TO/KERNEL_FILE: 设定本次启动时用到的内核文件;额外还可以添加许多内核支持使用的cmdline参数
例如:init=/path/to/init, selinux=0
initrd /PATH/TO/INITRAMFS_FILE: 设定为选定的内核提供额外文件的ramdisk
boot: 引导启动选定的内核
手动在grub命令行接口启动系统:
grub> root (hd#,#)
grub> kernel /vmlinuz-VERSION-RELEASE ro root=/dev/DEVICE
grub> initrd /initramfs-VERSION-RELEASE.img
grub> boot
配置文件:/boot/grub/grub.conf
[root@promote ~]# cat /etc/grub/grub.conf
cat: /etc/grub/grub.conf: No such file or directory
[root@promote ~]# cat /boot/grub/grub.conf
# grub.conf generated by anaconda
#
# Note that you do not have to rerun grub after making changes to this file
# NOTICE: You have a /boot partition. This means that
# all kernel and initrd paths are relative to /boot/, eg.
# root (hd0,0)
# kernel /vmlinuz-version ro root=/dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_root
# initrd /initrd-[generic-]version.img
#boot=/dev/sda
default=0
timeout=5
splashimage=(hd0,0)/grub/splash.xpm.gz
hiddenmenu
title CentOS 6 (2.6.32-573.el6.x86_64)
root (hd0,0)
kernel /vmlinuz-2.6.32-573.el6.x86_64 ro root=/dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_root rd_NO_LUKS LANG=en_US.UTF-8 rd_NO_MD rd_LVM_LV=VolGroup/lv_swap SYSFONT=latarcyrheb-sun16 crashkernel=auto rd_LVM_LV=VolGroup/lv_root KEYBOARDTYPE=pc KEYTABLE=us rd_NO_DM rhgb quiet
initrd /initramfs-2.6.32-573.el6.x86_64.img
配置项:
default=#: 设定默认启动的菜单项;落单项(title)编号从0开始;
timeout=#:指定菜单项等待选项选择的时长;
splashimage=(hd#,#)/PATH/TO/XPM_PIC_FILE:指明菜单背景图片文件路径;
hiddenmenu:隐藏菜单;
password [--md5] STRING: 菜单编辑认证;
title TITLE:定义菜单项“标题”, 可出现多次;
root (hd#,#):grub查找stage2及kernel文件所在设备分区;为grub的“根”;
kernel /PATH/TO/VMLINUZ_FILE [PARAMETERS]:启动的内核
initrd /PATH/TO/INITRAMFS_FILE: 内核匹配的ramfs文件;
password [--md5] STRING: 启动选定的内核或操作系统时进行认证;
grub-md5-crypt命令
[root@promote ~]# grub-md5-crypt
Password:
Retype password:
$1$H0XYM0$3ASdzIM3vfC3gh/ywCDkz1
进入单用户模式:
(1) 编辑grub菜单(选定要编辑的title,而后使用e命令);
(2) 在选定的kernel后附加
1, s, S或single都可以;
(3) 在kernel所在行,键入“b”命令;
安装grub:
(1) grub-install
grub-install --root-directory=ROOT /dev/DISK(2) grub命令
grub> root (hd#,#)
grub> setup (hd#)
ldd命令:
print shared library dependencies 打印应用程序依赖的库文件
ldd [OPTION]... FILE...
[root@promote ~]# ldd /bin/ls
linux-vdso.so.1 => (0x00007ffdecb65000)
libselinux.so.1 => /lib64/libselinux.so.1 (0x0000003456600000)
librt.so.1 => /lib64/librt.so.1 (0x0000003455600000)
libcap.so.2 => /lib64/libcap.so.2 (0x0000003461200000)
libacl.so.1 => /lib64/libacl.so.1 (0x000000345fe00000)
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x0000003454e00000)
libdl.so.2 => /lib64/libdl.so.2 (0x0000003454a00000)
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x0000003454600000)
libpthread.so.0 => /lib64/libpthread.so.0 (0x0000003455200000)
libattr.so.1 => /lib64/libattr.so.1 (0x0000003464a00000)
应用
1.在虚拟机中添加一块20G硬盘,装入grub
2.可以看出新硬盘sdb没有分区,先对其进行分区,一个操作系统正常来说应该有三个分区,即boot,swap和根
[root@promote ~]# fdisk -l /dev/sd[a-z]
Disk /dev/sda: 214.7 GB, 214748364800 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 26108 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00090dc2
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 1 64 512000 83 Linux
Partition 1 does not end on cylinder boundary.
/dev/sda2 64 26109 209202176 8e Linux LVM
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00000000
[root@promote ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb
Device contains neither a valid DOS partition table, nor Sun, SGI or OSF disklabel
Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x966f2c82.
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
After that, of course, the previous content won't be recoverable.
Warning: invalid flag 0x0000 of partition table 4 will be corrected by w(rite)
WARNING: DOS-compatible mode is deprecated. It's strongly recommended to
switch off the mode (command 'c') and change display units to
sectors (command 'u').
Command (m for help): n
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
p
Partition number (1-4): 1
First cylinder (1-2610, default 1):
Using default value 1
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (1-2610, default 2610): +100M
Command (m for help): n
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
p
Partition number (1-4): 2
First cylinder (15-2610, default 15):
Using default value 15
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (15-2610, default 2610): +2G
Command (m for help): t
Partition number (1-4): 2
Hex code (type L to list codes): 82
Changed system type of partition 2 to 82 (Linux swap / Solaris)
Command (m for help): n
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
p
Partition number (1-4): 3
First cylinder (277-2610, default 277):
Using default value 277
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (277-2610, default 2610): +5G
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x966f2c82
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 14 112423+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 15 276 2104515 82 Linux swap / Solaris
/dev/sdb3 277 930 5253255 83 Linux
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
[root@promote ~]# partx -a /dev/sdb
BLKPG: Device or resource busy
error adding partition 1
BLKPG: Device or resource busy
error adding partition 2
BLKPG: Device or resource busy
error adding partition 3
[root@promote ~]# cat /proc/partitions
major minor #blocks name
8 0 209715200 sda
8 1 512000 sda1
8 2 209202176 sda2
8 16 20971520 sdb
8 17 112423 sdb1
8 18 2104515 sdb2
8 19 5253255 sdb3
253 0 52428800 dm-0
253 1 2031616 dm-1
253 2 154738688 dm-2
[root@promote ~]# mke2fs -t ext4 /dev/sdb1
mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=1024 (log=0)
Fragment size=1024 (log=0)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
28112 inodes, 112420 blocks
5621 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=1
Maximum filesystem blocks=67371008
14 block groups
8192 blocks per group, 8192 fragments per group
2008 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
8193, 24577, 40961, 57345, 73729
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (4096 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
This filesystem will be automatically checked every 24 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
[root@promote ~]# mke2fs -t ext4 /dev/sdb3
mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2)
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
328656 inodes, 1313313 blocks
65665 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=1346371584
41 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
8016 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (32768 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
This filesystem will be automatically checked every 31 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
[root@promote ~]# mkswap /dev/sdb2
Setting up swapspace version 1, size = 2104508 KiB
no label, UUID=c5312464-50ea-45d6-8ecc-493c346c1e49
3.在/mnt下创建一个boot目录,把新硬盘的第一个分区,挂载到刚创建的目录
[root@promote ~]# mkdir /mnt/boot
[root@promote ~]# mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/boot/
[root@promote ~]# ls /mnt/boot
lost+found
4.安装grub并验证
[root@promote ~]# grub-install --root-directory=/mnt /dev/sdb
Probing devices to guess BIOS drives. This may take a long time.
Installation finished. No error reported.
This is the contents of the device map /mnt/boot/grub/device.map.
Check if this is correct or not. If any of the lines is incorrect,
fix it and re-run the script `grub-install'.
(fd0) /dev/fd0
(hd0) /dev/sda
(hd1) /dev/sdb
[root@promote ~]# ls /mnt/boot/
grub lost+found
[root@promote ~]# ls /mnt/boot/grub/
device.map fat_stage1_5 iso9660_stage1_5 minix_stage1_5 stage1 ufs2_stage1_5 xfs_stage1_5
e2fs_stage1_5 ffs_stage1_5 jfs_stage1_5 reiserfs_stage1_5 stage2 vstafs_stage1_5
5.没有配置文件,所以要自己写一个,也没有内核和initrd,所以需要复制本机的内核和initrd到新硬盘下
[root@promote ~]# cp /boot/vmlinuz-2.6.32-573.el6.x86_64 /mnt/boot/vmlinuz
[root@promote ~]# cp /boot/initramfs-2.6.32-573.el6.x86_64.img /mnt/boot/initramfs.img
[root@promote ~]# vim /mnt/boot/grub/grub.conf
default=0
timeout=5
title CentOS (Exprrss)
root (hd0,0)
kernel /vmlinuz ro root=/dev/sda3
initrd /initramfs.img
6.我们把根文件系统指向了/dev/sdb3,但是里面没有文件包,所以我们要把根文件系统里的文件在/dev/sdb3中创建
[root@promote ~]# mkdir /mnt/sysroot
[root@promote ~]# mount /dev/sdb3 /mnt/sysroot
[root@promote ~]# cd /mnt/sysroot/
[root@promote sysroot]# ls
lost+found
[root@promote sysroot]# mkdir -pv bin sbin lib lib64 dev proc sys tmp var usr home root mnt media
mkdir: created directory `bin'
mkdir: created directory `sbin'
mkdir: created directory `lib'
mkdir: created directory `lib64'
mkdir: created directory `dev'
mkdir: created directory `proc'
mkdir: created directory `sys'
mkdir: created directory `tmp'
mkdir: created directory `var'
mkdir: created directory `usr'
mkdir: created directory `home'
mkdir: created directory `root'
mkdir: created directory `mnt'
mkdir: created directory `media'
7.这里面并没有文件,我们复制一个bash到新硬盘下,并且要把依赖到的文件也复制过去,等下开机时,可以直接启动bash
注:任何命令或程序在运行时如果基于动态编译是要以来共享库的,通过ldd查看依赖文件
[root@promote sysroot]# cp /bin/bash /mnt/sysroot/bin/
[root@promote sysroot]# ldd /bin/bash
linux-vdso.so.1 => (0x00007ffcfbf32000)
libtinfo.so.5 => /lib64/libtinfo.so.5 (0x000000345d600000)
libdl.so.2 => /lib64/libdl.so.2 (0x0000003454a00000)
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x0000003454e00000)
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x0000003454600000)
[root@promote sysroot]# cp /lib64/libtinfo.so.5 /mnt/sysroot/lib64/
[root@promote sysroot]# cp /lib64/libdl.so.2 //mnt/sysroot/lib64/
[root@promote sysroot]# cp /lib64/libc.so.6 /mnt/sysroot/lib64/
[root@promote sysroot]# cp /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 /mnt/sysroot/lib64/
切换根,测试是否能启动
[root@promote sysroot]# cd
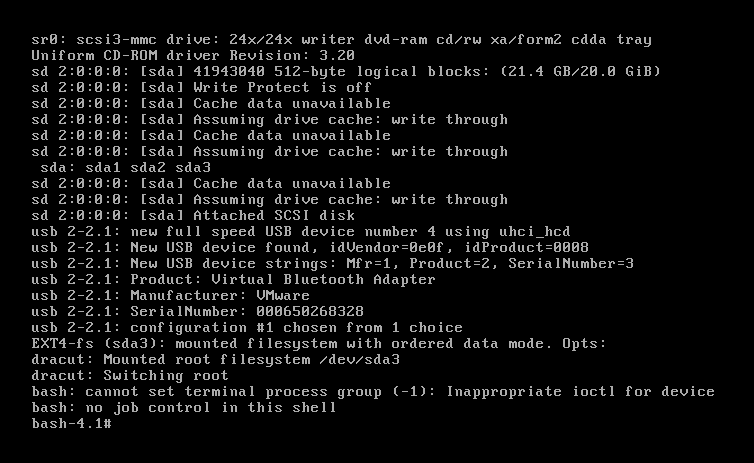
[root@promote ~]# chroot /mnt/sysroot/
bash-4.1#
bash-4.1#
8.限定系统的init程序,如果不指定,就会自动启动/sbin/init,因为我们这个硬盘里没有
default=0
timeout=5
title CentOS (Exprrss)
root (hd0,0)
kernel /vmlinuz ro root=/dev/sda3 init=/bin/bash
initrd /initramfs.img
[root@promote ~]# sync
9.使用vm创建一个新虚拟机,其他都一样,然后在选择磁盘的时候,选择使用现有的磁盘位置
10.直接启动,出现grub菜单,然后使用‘e’键,然后在kernel这一行,加入参数selinux=0,这个参数要加在init前面,然后回车回到kernel这一行,然后使用‘b’启动就可以了
11.把自己系统的mbr弄坏,然后使用光盘的grup进行引导修复
[root@promote ~]# dd if=/dev/sda of=/root/mbr.bak count=1 bs=512
1+0 records in
1+0 records out
512 bytes (512 B) copied, 0.00324258 s, 158 kB/s
[root@promote ~]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sda bs=200 count=1
1+0 records in
1+0 records out
200 bytes (200 B) copied, 0.000763293 s, 262 kB/s
[root@promote ~]# sync
此时grub的第一阶段给弄坏了,sync用来同步磁盘
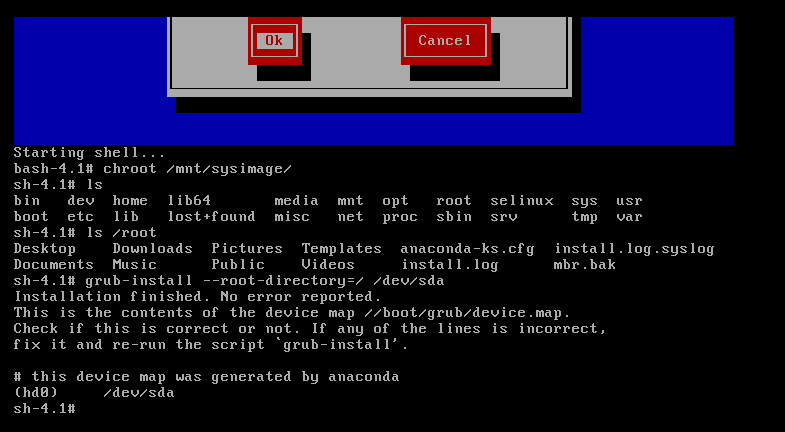
如果这个时候你的系统是开机状态,直接使用命令grub-install --root-directory=/ /dev/sda就可以直接修复了
[root@promote ~]# grub-install --root-directory=/ /dev/sda
Installation finished. No error reported.
This is the contents of the device map //boot/grub/device.map.
Check if this is correct or not. If any of the lines is incorrect,
fix it and re-run the script `grub-install'.
# this device map was generated by anaconda
(hd0) /dev/sda
[root@promote ~]# sync
然后sync同步以后,在重启就没有问题了
也可以使用grup然后回车进入命令行模式进行修复
[root@promote ~]# grub
Probing devices to guess BIOS drives. This may take a long time.
GNU GRUB version 0.97 (640K lower / 3072K upper memory)
[ Minimal BASH-like line editing is supported. For the first word, TAB
lists possible command completions. Anywhere else TAB lists the possible
completions of a device/filename.]
grub> root (hd0,0)
root (hd0,0)
Filesystem type is ext2fs, partition type 0x83
grub> setup (hd0)
setup (hd0)
Checking if "/boot/grub/stage1" exists... no
Checking if "/grub/stage1" exists... yes
Checking if "/grub/stage2" exists... yes
Checking if "/grub/e2fs_stage1_5" exists... yes
Running "embed /grub/e2fs_stage1_5 (hd0)"... 27 sectors are embedded.
succeeded
Running "install /grub/stage1 (hd0) (hd0)1+27 p (hd0,0)/grub/stage2 /grub/grub.conf"... succeeded
Done.
如果你的系统是关机,再启动就不行了,只能使用紧急救援模式进行修复
再把mbr弄坏,然后使用救援模式进行修复
弄坏之后进行重启,然后把光盘镜像挂载上,然后重启
然后选择第三项,即Rescue installed system 然后回车
或者摁‘ESC’输入linux rescus回车就可以了
然后exit回到救援模式的bash下重启就行了(光盘卸掉)