目录:
- if
- guard
- switch
- 控制转移语句
- 带标签语句
- 检测API可用性
1. if
同OC一样,只不过条件体不需要括号括起来
let a = 0
if a > 0 {
} else if a == 0 {
} else {
}
2. guard
此语法最好的地儿就是''提前退出''
一个guard语句总有一个else从句,如果条件不为真,则执行else从句代码.若条件为真,则执行guard大括号后面的代码
注意:
如果条件不被满足,在else分支上的代码就会被执行。这个分支必须转移控制以退出guard语句出现的代码段。它可以用控制转移语句如return,break,continue或者throw做这件事,或者调用一个不返回的方法或函数,例如fatalError()
class ViewController: UIViewController {
enum Sections: Int {
case student = 0
case teacher
case dog
}
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
let section = 2
guard Sections.dog.rawValue == section else {
print("条件不为真,走这里了")
return
}
print("条件为真,走这里了")
}
}
按需使用guard,会提高我们代码的可读性,所以,要巧用
class ViewController: UIViewController {
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
buy(product: ["name":"衣服"])
/*输出
我想买: 衣服
在什么位置买买买
*/
buy(product: ["name":"衣服","location" : "南京西路"])
/*输出
我想买: 衣服
我去 南京西路 买 衣服
*/
}
private func buy(product:[String : String]) {
guard let name = product["name"] else {
return
}
print("我想买:",name)
guard let location = product["location"] else {
print("在什么位置买买买")
return
}
print("我去",location,"买",name)
}
}
3. switch
当有可能有较多时,我们用switch语句。通常与枚举关联较多,我们可以把条件作为枚举值,然后用switch进行判断,这样可读性很高.
- Swift 与Int型枚举值结合使用演示
class ViewController: UIViewController {
enum Sections: Int {
case student
case teacher
}
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// 不存在隐士贯穿,所以不需要在case 后加break
let section = 0
switch section {
case Sections.student.rawValue:
print("嘿,student,section = ", Sections.student.rawValue)
case Sections.teacher.rawValue:
print("嘿,eacher,section = ", Sections.teacher.rawValue)
default: break
}
/* 输出
嘿,tudent,section = 0
*/
}
}
- 复合匹配
Swift与Int型枚举值结合使用演示(将两个值组合成一个匹配),就是在两个case间加一个,即可
class ViewController: UIViewController {
enum Sections: Int {
case student = 0
case teacher
case dog
}
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
let section = 2
switch section {
case Sections.student.rawValue, Sections.dog.rawValue:
if Sections.student.rawValue == section {
print("嘿,Student,section = ",Sections.student.rawValue)
} else {
print("嘿,Dog,section = ",Sections.dog.rawValue)
}
case Sections.teacher.rawValue:
print("嘿,teacher,section = ",Sections.teacher.rawValue)
default: break
}
/* 输出
嘿,Dog,section = 2
*/
}
}
- 牛点来了啊,Swift与元祖结合使用.列害了world哥
// 视频需要Id,直播不需要
enum Type {
case video(id: Int)
case live
}
class TwoViewController: UIViewController {
convenience init(type: Type) {
self.init()
switch type {
case Type.video(id: let videoId):
print("当类型为视频,做些视频该做的事儿",videoId)
case Type.live:
print("当=类型为直播,做些直播该做的事儿")
}
}
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
}
}
- 记得适当的时候我们也可以用
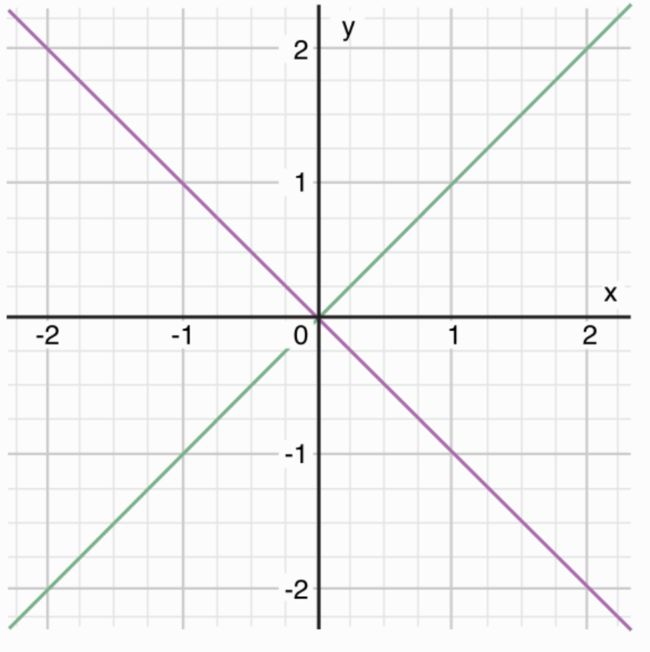
where(结合坐标图,看代码)
let yetAnotherPoint = (1, -1)
switch yetAnotherPoint {
case let (x, y) where x == y:
print("(\(x), \(y)) is on the line x == y")
case let (x, y) where x == -y:
print("(\(x), \(y)) is on the line x == -y")
case let (x, y):
print("(\(x), \(y)) is just some arbitrary point")
}
// 输出 "(1, -1) is on the line x == -y
4.控制转移语句
- continue
停止本次循环,立即执行下次循环 - break
立刻结束整个控制流的执行。当在循环体中时,执行跳出循环体,停止循环。当在switch语句中时,执行跳出switch条件判断。 - fallthrough
fallthrough,让 case 之后的语句会按顺序继续运行,且不论条件是否满足都会执行。 - return
终断代码继续往下执行,这个函数会立刻返回. - throw
throw来抛出一个错误并使用throws来表示一个可以抛出错误的函数。如果在函数中抛出一个错误,这个函数会立刻返回并且调用该函数的代码会进行错误处理(我会自Swift-错误处理中介绍)
5.带标签语句
label name: while condition { statements }
while循环有一个标签名"gameLoop"代表游戏循环的主循环
gameLoop: while square != finalSquare {
diceRoll += 1
if diceRoll == 7 { diceRoll = 1 }
switch square + diceRoll {
case finalSquare:
// 骰子数刚好使玩家移动到最终的方格里,游戏结束。
break gameLoop
case let newSquare where newSquare > finalSquare:
// 骰子数将会使玩家的移动超出最后的方格,那么这种移动是不合法的,玩家需要重新掷骰子
continue gameLoop
default:
// 合法移动,做正常的处理
square += diceRoll
square += board[square]
}
}
6.检测API可用性
最后一个参数,*,是必须的,用于指定在所有其它平台中,如果版本号高于你的设备指定的最低版本,if语句的代码块将会运行。
if #available(platform name version, ..., *) {
APIs 可用,语句将执行
} else { APIs 不可用,语句将不执行
}
```swift
if #available(iOS 10, macOS 10.12, *) {
// 在 iOS 使用 iOS 10 的 API, 在 macOS 使用 macOS 10.12 的 API
} else {
// 使用先前版本的 iOS 和 macOS 的 API
}