Caffe学习笔记(六):mnist手写数字识别训练实例
转载请注明作者和出处:http://blog.csdn.net/c406495762
Python版本: Python2.7
运行平台: Ubuntu14.04
一、前言
深度学习的一个简单实例就是mnist手写数字识别,只要这个例子弄明白,其它的内容就可以举一反三了。之前的内容如有遗忘,可以进行回顾。
- 使用pycaffe生成train.protxt、test.prototxt
- 使用pycaffe生成solver.prototxt
- 数据层、视觉层、激活层等知识点回顾
二、准备数据
数据集可以直接从我的github下载,包括数据集和代码,使用如下指令:
git clone https://github.com/Jack-Cherish/DeepLearning/tree/master/mnist如果github网速过慢,也可以从百度云下载:
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1_FarKhi9herjAYPdHIWZsg 密码: 2cme
获取的数据是zip格式的,在linux下可以使用如下指令进行解压(已安装unzip,没有安装使用指令unzip):
unzip mnist.zip数据分成了训练集(60000张共10类)和测试集(共10000张10类),每个类别放在一个单独的文件夹里。并且将所有的图片,都生成了txt列表清单(train.txt和test.txt)。下载下来后,直接解压到当前用户根目录下即可。
三、开始训练
之前讲解的训练方法是,将原始图片转换成db(leveldb/lmdb)文件,并计算图像均值。然后在网络的第一层数据层Data中指定db文件和均值文件的位置,创建数据层的方法还有几种,另一种常见的方法是把原始图片做成一个列表清单txt文件(一行一张图),则省去了图片格式转化和图片均值计算的过程,提供的数据集中已经包括了txt列表清单文件,因此也省却了我们手动生成的步骤,直接使用即可。因此我们可以使用ImageData作为数据源输入。训练步骤如下:
- 获取数据集
- 生成txt列表清单文件(已有)
- 生成train.prototxt、test.prototxt、solver.prototxt文件
- 训练数据,生成模型
1.编写代码
在my-caffe-project根目录下解压文件后,即可创建mnist.py文件,编写如下代码:
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import caffe #导入caffe包
def create_net(img_list, batch_size, include_acc=False):
#网络规范
net = caffe.NetSpec()
#ImageData数据层
net.data, net.labels = caffe.layers.ImageData(batch_size = batch_size,
source = img_list,
transform_param = dict(scale = 1./255),
ntop = 2)
#卷积层
net.conv1 = caffe.layers.Convolution(net.data, kernel_size = 5, num_output = 20,
weight_filler = dict(type = 'xavier'))
#池化层
net.pool1 = caffe.layers.Pooling(net.conv1, kernel_size = 2, stride = 2,
pool = caffe.params.Pooling.MAX)
#卷积层
net.conv2 = caffe.layers.Convolution(net.pool1, kernel_size = 5, num_output = 50,
weight_filler = dict(type = 'xavier'))
#池化层
net.pool2 = caffe.layers.Pooling(net.conv2, kernel_size = 2, stride = 2,
pool = caffe.params.Pooling.MAX)
#全连层
net.fc1 = caffe.layers.InnerProduct(net.pool2, num_output = 500,
weight_filler = dict(type = 'xavier'))
#激活函数层
net.relu1 = caffe.layers.ReLU(net.fc1, in_place = True)
#全连层
net.score = caffe.layers.InnerProduct(net.relu1, num_output = 10,
weight_filler = dict(type = 'xavier'))
#softmax层
net.loss = caffe.layers.SoftmaxWithLoss(net.score, net.labels)
if include_acc:
net.acc = caffe.layers.Accuracy(net.score, net.labels)
return net.to_proto()
return net.to_proto()
def write_net(train_proto, train_list, test_proto, test_list):
#写入prototxt文件
with open(train_proto, 'w') as f:
f.write(str(create_net(train_list, batch_size = 64)))
#写入prototxt文件
with open(test_proto, 'w') as f:
f.write(str(create_net(test_list, batch_size = 100, include_acc = True)))
def write_sovler(my_project_root, solver_proto, train_proto, test_proto):
sovler_string = caffe.proto.caffe_pb2.SolverParameter() #sovler存储
sovler_string.train_net = train_proto #train.prototxt位置指定
sovler_string.test_net.append(test_proto) #test.prototxt位置指定
sovler_string.test_iter.append(100) #10000/100 测试迭代次数
sovler_string.test_interval = 938 #60000/64 每训练迭代test_interval次进行一次测试
sovler_string.base_lr = 0.01 #基础学习率
sovler_string.momentum = 0.9 #动量
sovler_string.weight_decay = 5e-4 #权重衰减
sovler_string.lr_policy = 'step' #学习策略
sovler_string.stepsize = 3000 #学习率变化频率
sovler_string.gamma = 0.1 #学习率变化指数
sovler_string.display = 20 #每迭代display次显示结果
sovler_string.max_iter = 9380 #10 epoch 938*10 最大迭代数
sovler_string.snapshot = 938 #保存临时模型的迭代数
sovler_string.snapshot_prefix = my_project_root + 'mnist' #模型前缀
sovler_string.solver_mode = caffe.proto.caffe_pb2.SolverParameter.GPU #优化模式
with open(solver_proto, 'w') as f:
f.write(str(sovler_string))
def train(solver_proto):
caffe.set_device(1)
caffe.set_mode_gpu()
solver = caffe.SGDSolver(solver_proto)
solver.solve()
if __name__ == '__main__':
my_project_root = "/home/Jack-Cui/caffe-master/my-caffe-project/" #my-caffe-project目录
train_list = my_project_root + "mnist/train/train.txt" #train.txt文件的位置
test_list = my_project_root + "mnist/test/test.txt" #test.txt文件的位置
train_proto = my_project_root + "mnist/train.prototxt" #保存train.prototxt文件的位置
test_proto = my_project_root + "mnist/test.prototxt" #保存test.prototxt文件的位置
solver_proto = my_project_root + "mnist/solver.prototxt" #保存solver.prototxt文件的位置
write_net(train_proto, train_list, test_proto, test_list)
print "生成train.prototxt test.prototxt成功"
write_sovler(my_project_root, solver_proto, train_proto, test_proto)
print "生成solver.prototxt成功"
train(solver_proto)
print "训练完成"
由于以上内容在之前已经进行详细讲解,如有遗忘请回顾之前笔记。
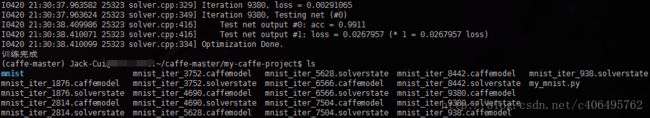
2.运行结果:
3.总结
从运行结果可以看出,训练准确率高达99.11%。训练生成的mnist_iter_9380.caffemodel即为最终训练得到的模型,下篇笔记将继续讲解,如何使用这个训练好的模型做预测。