OpenGL ES之十一——绘制3D图形
概述
这是一个系列的Android平台下OpenGl ES介绍,从最基本的使用最终到VR图的展示的实现,属于基础篇。(后面针对VR视频会再有几篇文章,属于进阶篇)
OpenGL ES之一——概念扫盲
OpenGL ES之二——Android中的OpenGL ES概述
OpenGL ES之三——绘制纯色背景
OpenGL ES之四——绘制点,线,三角形
OpenGL ES之五——相机和投影,绘制等腰三角形
OpenGL ES之六——绘制矩形和圆形
OpenGL ES之七——着色器语言GLSL
OpenGL ES之八——GLES20类和Matrix类
OpenGL ES之九——相机和投影
OpenGL ES之十——纹理贴图(展示一张图片)
OpenGL ES之十一——绘制3D图形
OpenGL ES之十二——地球仪和VR图
本篇概述
经过前面的铺垫,我们对OpenGLES了解了不少了,是时候绘制立体图像了。
一 圆锥
拆分原理:
在之前的文章中我们绘制过圆形,圆锥可以看成是圆心顶点坐标z不为0的圆形,绘制的方法和绘制一个圆是一样的,将圆锥的侧面切分为一个个三角形。如下:
着色器文件
顶点着色器
#version 300 es
layout (location = 0) in vec4 vPosition;
layout (location = 1) in vec4 aColor;
uniform mat4 u_Matrix;
out vec4 vColor;
void main() {
gl_Position = u_Matrix*vPosition;
gl_PointSize = 10.0;
vColor = aColor;
}
片段着色器
#version 300 es
precision mediump float;
in vec4 vColor;
out vec4 fragColor;
void main() {
fragColor = vColor;
}
渲染器
public class ConeRenderer implements GLSurfaceView.Renderer {
private static final int BYTES_PER_FLOAT = 4;
//顶点位置缓存
private final FloatBuffer vertexBuffer;
//顶点颜色缓存
private final FloatBuffer colorBuffer;
//渲染程序
private int mProgram;
//相机矩阵
private final float[] mViewMatrix = new float[16];
//投影矩阵
private final float[] mProjectMatrix = new float[16];
//最终变换矩阵
private final float[] mMVPMatrix = new float[16];
//返回属性变量的位置
//变换矩阵
private int uMatrixLocation;
//位置
private int aPositionLocation;
//颜色
private int aColorLocation;
//圆形顶点位置
private float circularCoords[];
//顶点的颜色
private float color[];
public ConeRenderer() {
createPositions(0.5f,60);
//顶点位置相关
//分配本地内存空间,每个浮点型占4字节空间;将坐标数据转换为FloatBuffer,用以传入给OpenGL ES程序
vertexBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(circularCoords.length * BYTES_PER_FLOAT)
.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder())
.asFloatBuffer();
vertexBuffer.put(circularCoords);
vertexBuffer.position(0);
//顶点颜色相关
colorBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(color.length * BYTES_PER_FLOAT)
.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder())
.asFloatBuffer();
colorBuffer.put(color);
colorBuffer.position(0);
}
private void createPositions(float radius, int n){
ArrayList data=new ArrayList<>();
data.add(0.0f); //设置圆锥顶点坐标
data.add(0.0f);
data.add(-0.5f);
float angDegSpan=360f/n;
for(float i=0;i<360+angDegSpan;i+=angDegSpan){
data.add((float) (radius*Math.sin(i*Math.PI/180f)));
data.add((float)(radius*Math.cos(i*Math.PI/180f)));
data.add(0.0f);
}
float[] f=new float[data.size()];
for (int i=0;i tempC = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList totalC = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList total0 = new ArrayList<>();
total0.add(0.5f);
total0.add(0.0f);
total0.add(0.0f);
total0.add(1.0f);
tempC.add(1.0f);
tempC.add(1.0f);
tempC.add(1.0f);
tempC.add(1.0f);
for (int i=0;i 上面唯一不同的就是相机的参数变了如下,如果认真看了之前关于相机和投影的知识这里很好理解。
//设置相机位置
Matrix.setLookAtM(mViewMatrix, 0, 6, 0, -1f, 0f, 0f, 0f, 0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
效果图

我们发现它不是个实体圆锥而是一个侧面。那么为了得到一个有底的圆锥,我们就再绘制一个圆就是了。
完整的渲染器
public class ConeRenderer implements GLSurfaceView.Renderer{
//一个Float占用4Byte
private static final int BYTES_PER_FLOAT = 4;
//顶点位置缓存(圆锥侧面)
private final FloatBuffer vertexBuffer;
//顶点位置缓存(圆锥底面)
private FloatBuffer vertexBuffer1;
//顶点颜色缓存
private final FloatBuffer colorBuffer;
//渲染程序
private int mProgram;
//相机矩阵
private final float[] mViewMatrix = new float[16];
//投影矩阵
private final float[] mProjectMatrix = new float[16];
//最终变换矩阵
private final float[] mMVPMatrix = new float[16];
//返回属性变量的位置
//变换矩阵
private int uMatrixLocation;
//位置
private int aPositionLocation;
//颜色
private int aColorLocation;
//圆锥顶点位置(侧面)
private float coneCoords[];
//圆锥顶点位置(圆底面)
private float coneCoords1[];
//顶点的颜色
private float color[];
public ConeRenderer() {
//圆锥的侧面数据
createPositions(0.5f,60);
//圆锥的圆形底面数据
createCircularPositions();
//顶点位置相关(圆锥侧面)
//分配本地内存空间,每个浮点型占4字节空间;将坐标数据转换为FloatBuffer,用以传入给OpenGL ES程序
vertexBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(coneCoords.length * BYTES_PER_FLOAT)
.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder())
.asFloatBuffer();
vertexBuffer.put(coneCoords);
vertexBuffer.position(0);
//顶点颜色相关
colorBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(color.length * BYTES_PER_FLOAT)
.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder())
.asFloatBuffer();
colorBuffer.put(color);
colorBuffer.position(0);
//顶点位置相关(圆锥底面)
vertexBuffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(coneCoords1.length * BYTES_PER_FLOAT)
.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder())
.asFloatBuffer();
vertexBuffer1.put(coneCoords1);
vertexBuffer1.position(0);
}
private void createCircularPositions() {
coneCoords1 = new float[coneCoords.length];
for (int i=0;i data=new ArrayList<>();
data.add(0.0f);//设置锥心坐标
data.add(0.0f);
data.add(-0.5f);
float angDegSpan=360f/n;
for(float i=0;i<360+angDegSpan;i+=angDegSpan){
data.add((float) (radius*Math.sin(i*Math.PI/180f)));
data.add((float)(radius*Math.cos(i*Math.PI/180f)));
data.add(0.0f);
}
float[] f=new float[data.size()];
for (int i=0;i tempC = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList totalC = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList totalCForColor = new ArrayList<>();
tempC.add(0.8f);
tempC.add(0.8f);
tempC.add(0.8f);
tempC.add(1.0f);
ArrayList zeroIndexC = new ArrayList<>();
zeroIndexC.add(1.0f);
zeroIndexC.add(0.0f);
zeroIndexC.add(0.0f);
zeroIndexC.add(1.0f);
for (int i=0;i 二 圆柱
2.1 拆分原理
圆柱的与圆锥类似,我们可以把圆柱拆解成上下两个圆面,加上一个圆筒。圆筒我们之前也没画过,它怎么拆解成三角形呢?我们可以如同拆圆的思路来理解圆柱,想想正三菱柱、正八菱柱、正一百菱柱……菱越多,就越圆滑与圆柱越接近了,然后再把每个菱面(矩形)拆解成两个三角形就OK了。
2.2 完整的渲染器
public class CylinderRenderer implements GLSurfaceView.Renderer{
private static final int SEPARATE_COUNT = 120;
private static final float RADIUS = 0.5f;
private static final float HEIGHT = 1.0f;
//一个Float占用4Byte
private static final int BYTES_PER_FLOAT = 4;
//顶点位置缓存(圆柱侧面)
private final FloatBuffer vertexBuffer;
//顶点位置缓存(圆柱底面)
private FloatBuffer vertexBuffer1;
//顶点位置缓存(圆柱底面)
private FloatBuffer vertexBuffer2;
//渲染程序
private int mProgram;
//相机矩阵
private final float[] mViewMatrix = new float[16];
//投影矩阵
private final float[] mProjectMatrix = new float[16];
//最终变换矩阵
private final float[] mMVPMatrix = new float[16];
//返回属性变量的位置
//变换矩阵
private int uMatrixLocation;
//位置
private int aPositionLocation;
//圆柱顶点位置(侧面)
private float cylinderCoords[];
//圆柱顶点位置(圆底面)
private float cylinderCoords1[];
//圆柱顶点位置(圆底面)
private float cylinderCoords2[];
public CylinderRenderer() {
//侧面数据
createCylinderPositions();
//底面数据
createCircularPositions();
//顶点位置相关(圆柱侧面)
//分配本地内存空间,每个浮点型占4字节空间;将坐标数据转换为FloatBuffer,用以传入给OpenGL ES程序
vertexBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(cylinderCoords.length * BYTES_PER_FLOAT)
.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder())
.asFloatBuffer();
vertexBuffer.put(cylinderCoords);
vertexBuffer.position(0);
//顶点位置相关(圆柱底面)
vertexBuffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(cylinderCoords1.length * BYTES_PER_FLOAT)
.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder())
.asFloatBuffer();
vertexBuffer1.put(cylinderCoords1);
vertexBuffer1.position(0);
//顶点位置相关(圆柱底面)
vertexBuffer2 = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(cylinderCoords2.length * BYTES_PER_FLOAT)
.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder())
.asFloatBuffer();
vertexBuffer2.put(cylinderCoords2);
vertexBuffer2.position(0);
}
private void createCircularPositions() {
ArrayList data=new ArrayList<>();
data.add(0.0f);
data.add(0.0f);
data.add(HEIGHT);
ArrayList data1=new ArrayList<>();
data1.add(0.0f);
data1.add(0.0f);
data1.add(0.0f);
float angDegSpan=360f/SEPARATE_COUNT;
for(float i=0;i<360+angDegSpan;i+=angDegSpan){
data.add((float) (RADIUS*Math.sin(i*Math.PI/180f)));
data.add((float)(RADIUS*Math.cos(i*Math.PI/180f)));
data.add(HEIGHT);
data1.add((float) (RADIUS*Math.sin(i*Math.PI/180f)));
data1.add((float)(RADIUS*Math.cos(i*Math.PI/180f)));
data1.add(0.0f);
}
float[] f=new float[data.size()];
float[] f1=new float[data.size()];
for (int i=0;i pos=new ArrayList<>();
float angDegSpan=360f/SEPARATE_COUNT;
for(float i=0;i<360+angDegSpan;i+=angDegSpan){
pos.add((float) (RADIUS*Math.sin(i*Math.PI/180f)));
pos.add((float)(RADIUS*Math.cos(i*Math.PI/180f)));
pos.add(HEIGHT);
pos.add((float) (RADIUS*Math.sin(i*Math.PI/180f)));
pos.add((float)(RADIUS*Math.cos(i*Math.PI/180f)));
pos.add(0.0f);
}
float[] d=new float[pos.size()];
for (int i=0;i 2.3 顶点着色器
稍微有变化,这里不去特意处理颜色。
#version 300 es
layout (location = 0) in vec4 vPosition;
layout (location = 1) in vec4 aColor;
uniform mat4 u_Matrix;
out vec4 vColor;
void main() {
gl_Position=u_Matrix*vPosition;
if(vPosition.z!=0.0){
vColor=vec4(0.0,0.0,0.0,1.0);
}else{
vColor=vec4(0.8,0.8,0.8,1.0);
}
}
2.4 效果图
三 球
球的绘制这里只是一个铺垫为后面的绘制“地球仪”和后面的VR图做准备。
3.1 原理
相对于圆锥圆柱来说,球体的拆解就复杂了许多,比较常见的拆解方法是将按照经纬度拆解和按照正多面体拆解,下图分别为正多面体示意和经纬度拆解示意:
正多面体的方法拆解:
经纬度的方法拆解(每一个小块看做一个四边形形,再拆成三角形。):
球面上点的坐标
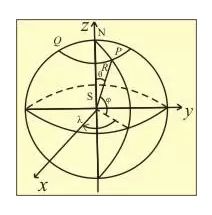
无论是按照经纬度拆还是按照多面体拆,都需要知道球上面点的坐标,这算是基本的几何知识了。以球的中心为坐标中心,球的半径为R的话,那么球上点的坐标则为:
(R∗cos(ψ)∗sin(λ),R∗sin(ψ),R∗cos(ψ)∗cos(λ))
其中,ψ为圆心到点的线段与xz平面的夹角,λ为圆心到点的线段在xz平面的投影与z轴的夹角。用图形表示如下:
按经纬度切分如下
先将球体以经度为准分为若干份,再在相应经度的一圈纬度上进行切分如下图(注意看下面获取顶点坐标时候的操作)。

3.2 绘制
顶点着色器
#version 300 es
in vec4 vPosition;
uniform mat4 u_Matrix;
out vec4 vColor;
void main(){
gl_Position=u_Matrix*vPosition;
float color;
if(vPosition.z>0.0){
color=vPosition.z;
}else{
color=-vPosition.z;
}
vColor=vec4(color,color,color,1.0);
}
片段着色器
#version 300 es
precision mediump float;
in vec4 vColor;
out vec4 fragColor;
void main() {
fragColor = vColor;
}
渲染器
public class BallRenderer implements GLSurfaceView.Renderer {
private static final int BYTES_PER_FLOAT = 4;
//顶点位置缓存
private final FloatBuffer vertexBuffer;
//渲染程序
private int mProgram;
//相机矩阵
private final float[] mViewMatrix = new float[16];
//投影矩阵
private final float[] mProjectMatrix = new float[16];
//最终变换矩阵
private final float[] mMVPMatrix = new float[16];
//返回属性变量的位置
//变换矩阵
private int uMatrixLocation;
//位置
private int aPositionLocation;
private float[] ballCoords;
public BallRenderer() {
createVertexPos();
//顶点位置相关
//分配本地内存空间,每个浮点型占4字节空间;将坐标数据转换为FloatBuffer,用以传入给OpenGL ES程序
vertexBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(ballCoords.length * BYTES_PER_FLOAT)
.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder())
.asFloatBuffer();
vertexBuffer.put(ballCoords);
vertexBuffer.position(0);
}
private void createVertexPos() {
float radius = 1.0f; // 球的半径
double angleSpan = Math.PI / 90f; // 将球进行单位切分的角度
ArrayList alVertix = new ArrayList<>();
for (double vAngle = 0; vAngle < Math.PI; vAngle = vAngle + angleSpan){
for (double hAngle = 0; hAngle < 2*Math.PI; hAngle = hAngle + angleSpan){
//获取一个四边形的四个顶点
float x0 = (float) (radius* Math.sin(vAngle) * Math.cos(hAngle));
float y0 = (float) (radius* Math.sin(vAngle) * Math.sin(hAngle));
float z0 = (float) (radius * Math.cos((vAngle)));
float x1 = (float) (radius* Math.sin(vAngle) * Math.cos(hAngle + angleSpan));
float y1 = (float) (radius* Math.sin(vAngle) * Math.sin(hAngle + angleSpan));
float z1 = (float) (radius * Math.cos(vAngle));
float x2 = (float) (radius* Math.sin(vAngle + angleSpan) * Math.cos(hAngle + angleSpan));
float y2 = (float) (radius* Math.sin(vAngle + angleSpan) * Math.sin(hAngle + angleSpan));
float z2 = (float) (radius * Math.cos(vAngle + angleSpan));
float x3 = (float) (radius* Math.sin(vAngle + angleSpan) * Math.cos(hAngle));
float y3 = (float) (radius* Math.sin(vAngle + angleSpan) * Math.sin(hAngle));
float z3 = (float) (radius * Math.cos(vAngle + angleSpan));
//将四个点拆分为两个三角形
alVertix.add(x1);
alVertix.add(y1);
alVertix.add(z1);
alVertix.add(x0);
alVertix.add(y0);
alVertix.add(z0);
alVertix.add(x3);
alVertix.add(y3);
alVertix.add(z3);
alVertix.add(x1);
alVertix.add(y1);
alVertix.add(z1);
alVertix.add(x3);
alVertix.add(y3);
alVertix.add(z3);
alVertix.add(x2);
alVertix.add(y2);
alVertix.add(z2);
}
}
int size = alVertix.size();
ballCoords = new float[size];
for (int i=0;i 里面最重要的是获取球面上顶点位置也就是方法createVertexPos()。




