常见算法面试题
文章目录
- 数组类问题
- 查找表相关问题
- 链表相关问题
- 栈和队列相关问题
- 二叉树和递归
- 递归和回溯法
- 动态规划
- 贪心算法
数组类问题
二分查找
template<typename T>
int binary_search(T arr[], int n, T target) {
int l = 0, r = n - 1;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2; // ☆
if (arr[mid] = target) return mid;
if (target > arr[mid]) l = mid + 1;
else r = mid - 1;
}
return -1;
}
☆ 处,如果写成 int mid = (r + l) / 2,在某些特殊情况下会导致整型溢出。比如,r和l都足够大的时候,r+l会超过整型的最大值。
数组相关例题
1. 移动零(LeetCode)
原题链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/move-zeroes/description/
给定一个数组 nums,编写一个函数将所有 0 移动到数组的末尾,同时保持非零元素的相对顺序。
示例:
Input:
[0,1,0,3,12]
Output:
[1,3,12,0,0]
说明:
- 必须在原数组上操作,不能拷贝额外的数组。
- 尽量减少操作次数。
代码:
第一种
class Solution {
public:
void moveZeroes(vector<int> &nums) {
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i)
if (nums[i])nums[k++] = nums[i];
for (int j = k; j < nums.size(); ++j)
nums[j] = 0;
}
};
第二种
class Solution {
public:
void moveZeroes(vector<int> &nums) {
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i)
if (nums[i])
if (i != k) // ★
swap(nums[k++], nums[i]);
else k++;
}
};
★处是为了防止数组中全是非0元素,而造成两个非0元素进行交换。
2. 删除排序数组中的重复项
原题链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array/description/
给定一个排序数组,你需要在原地删除重复出现的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次,返回移除后数组的新长度。
不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须在原地修改输入数组并在使用 O(1) 额外空间的条件下完成。
示例 1:
给定数组 nums = [1,1,2],
函数应该返回新的长度 2, 并且原数组 nums 的前两个元素被修改为 1, 2。
你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
示例 2:
给定 nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4],
函数应该返回新的长度 5, 并且原数组 nums 的前五个元素被修改为 0, 1, 2, 3, 4。
你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
说明:
为什么返回数值是整数,但输出的答案是数组呢?
请注意,输入数组是以“引用”方式传递的,这意味着在函数里修改输入数组对于调用者是可见的。
你可以想象内部操作如下:
// nums 是以“引用”方式传递的。也就是说,不对实参做任何拷贝
int len = removeDuplicates(nums);
// 在函数里修改输入数组对于调用者是可见的。
// 根据你的函数返回的长度, 它会打印出数组中该长度范围内的所有元素。
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
print(nums[i]);
}
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int removeDuplicates(vector<int> &nums) {
int k = 0;
if (nums.size() == 0) return 0;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); ++i)
if (nums[i] != nums[k])
nums[++k] = nums[i];
return k + 1;
}
};
3. 移除元素
原题链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-element/description/
给定一个数组 nums 和一个值 val,你需要原地移除所有数值等于 val 的元素,返回移除后数组的新长度。
不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须在原地修改输入数组并在使用 O(1) 额外空间的条件下完成。
元素的顺序可以改变。你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
示例 1:
给定 nums = [3,2,2,3], val = 3,
函数应该返回新的长度 2, 并且 nums 中的前两个元素均为 2。
你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
示例 2:
给定 nums = [0,1,2,2,3,0,4,2], val = 2,
函数应该返回新的长度 5, 并且 nums 中的前五个元素为 0, 1, 3, 0, 4。
注意这五个元素可为任意顺序。
你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
class Solution {
public:
int removeElement(vector<int> &nums, int val) {
if (!nums.size()) return 0;
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
if (nums[i] != val)
nums[k++] = nums[i];
}
return k;
}
};
4. 删除排序数组中的重复项 II
原题链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array-ii/description/
给定一个排序数组,你需要在原地删除重复出现的元素,使得每个元素最多出现两次,返回移除后数组的新长度。
不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须在原地修改输入数组并在使用 O(1) 额外空间的条件下完成。
示例 1:
给定 nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3],
函数应返回新长度 length = 5, 并且原数组的前五个元素被修改为 1, 1, 2, 2, 3 。
你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
示例 2:
给定 nums = [0,0,1,1,1,1,2,3,3],
函数应返回新长度 length = 7, 并且原数组的前五个元素被修改为 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 3 。
你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
代码
class Solution {
public:
int removeDuplicates(vector<int> &nums) {
if (nums.size() == 0) return 0;
int k = 0;
int current = nums[0];
int count = 1;
unsigned long len = nums.size();
for (int i = 1; i < len; ++i) {
if (nums[i] == current)
count++;
else {
current = nums[i];
count = 1;
}
if (k + 1 != i)
nums[k + 1] = nums[i];
if (count <= 2)k++;
}
return k + 1;
}
};
5. 颜色分类
原题链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-colors/description/
给定一个包含红色、白色和蓝色,一共 n 个元素的数组,原地对它们进行排序,使得相同颜色的元素相邻,并按照红色、白色、蓝色顺序排列。
此题中,我们使用整数 0、 1 和 2 分别表示红色、白色和蓝色。
注意:
不能使用代码库中的排序函数来解决这道题。
示例:
输入: [2,0,2,1,1,0]
输出: [0,0,1,1,2,2]
进阶:
- 一个直观的解决方案是使用计数排序的两趟扫描算法。
首先,迭代计算出0、1 和 2 元素的个数,然后按照0、1、2的排序,重写当前数组。 - 你能想出一个仅使用常数空间的一趟扫描算法吗?
代码:
class Solution {
public:
void sortColors(vector<int> &nums) {
int zero = -1;
int two = nums.size();
for (int i = 0; i < two;)
if (nums[i] == 1)
i++;
else if (nums[i] == 2)
swap(nums[i], nums[--two]);
else
swap(nums[++zero], nums[i++]);
}
};
6. 合并两个有序数组
原题链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-sorted-array/description/
给定两个有序整数数组 nums1 和 nums2,将 nums2 合并到 nums1 中,使得 num1 成为一个有序数组。
说明:
- 初始化 nums1 和 nums2 的元素数量分别为 m 和 n。
- 你可以假设 nums1 有足够的空间(空间大小大于或等于 m + n)来保存 nums2 中的元素。
示例:
输入:
nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3
nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
输出:[1,2,2,3,5,6]
代码:
class Solution {
public:
void merge(vector<int> &nums1, int m, vector<int> &nums2, int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int e = nums2[i];
int j;
// j是最终插入的位置
for (j = m++; j > 0 && nums1[j - 1] > e; --j)
nums1[j] = nums1[j - 1];
nums1[j] = e;
}
}
};
7. 数组中的第K个最大元素
原题链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/kth-largest-element-in-an-array/description/
在未排序的数组中找到第 k 个最大的元素。请注意,你需要找的是数组排序后的第 k 个最大的元素,而不是第 k 个不同的元素。
示例 1:
输入: [3,2,1,5,6,4] 和 k = 2
输出: 5
示例 2:
输入: [3,2,3,1,2,4,5,5,6] 和 k = 4
输出: 4
说明:
你可以假设 k 总是有效的,且 1 ≤ k ≤ 数组的长度。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int findKthLargest(vector<int> &nums, int k) {
srand((unsigned int) time(NULL));
return findKthLargest(nums, k - 1, 0, nums.size() - 1);
}
private:
int findKthLargest(vector<int> &nums, int k, int l, int r) {
if (l >= r) return nums[l];
int p = partition(nums, l, r);
if (k == p) return nums[p];
else if (k > p)
return findKthLargest(nums, k, p + 1, r);
else
return findKthLargest(nums, k, l, p - 1);
}
int partition(vector<int> &nums, int l, int r) {
swap(nums[l], nums[rand() % (r - l + 1) + l]);
int v = nums[l];
int j = l;
for (int i = l + 1; i <= r; ++i)
if (nums[i] > v)
swap(nums[i], nums[++j]);
swap(nums[j], nums[l]);
return j;
}
};
8. 两数之和 II - 输入有序数组
原题链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum-ii-input-array-is-sorted/description/
给定一个已按照升序排列 的有序数组,找到两个数使得它们相加之和等于目标数。
函数应该返回这两个下标值 index1 和 index2,其中 index1 必须小于 index2。
说明:
返回的下标值(index1 和 index2)不是从零开始的。
你可以假设每个输入只对应唯一的答案,而且你不可以重复使用相同的元素。
示例:
输入:numbers = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9
输出: [1,2]
解释: 2 与 7 之和等于目标数 9 。因此index1 = 1, index2 = 2 。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int> &numbers, int target) {
int i = 0, j = numbers.size() - 1;
while (i < j) {
if (numbers[i] + numbers[j] == target)
return vector<int>{i + 1, j + 1};
else if (numbers[i] + numbers[j] > target)
j--;
else
i++;
}
}
};
9. 验证回文串
原题链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-palindrome/description/
给定一个字符串,验证它是否是回文串,只考虑字母和数字字符,可以忽略字母的大小写。
说明: 本题中,我们将空字符串定义为有效的回文串。
示例 1:
输入: "A man, a plan, a canal: Panama"
输出: true
示例 2:
输入: "race a car"
输出: false
代码
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(string s) {
string str;
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i) {
char c = (char) tolower(s[i]);
if (check(c))str += c;
}
int i = 0, j = str.size() - 1;
while (i <= j) {
if (str[i++] != str[j--]) return false;
}
return true;
}
bool check(char c) {
return isalpha(c) || isdigit(c);
}
};
10. 反转字符串
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-string/description/
编写一个函数,其作用是将输入的字符串反转过来。
示例 1:
输入: "hello"
输出: "olleh"
示例 2:
输入: "A man, a plan, a canal: Panama"
输出: "amanaP :lanac a ,nalp a ,nam A"
代码:
class Solution {
public:
string reverseString(string s) {
int i = 0, j = s.size() - 1;
while (i <= j)
swap(s[i++], s[j--]);
return s;
}
};
11. 反转字符串中的元音字母
原题链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-vowels-of-a-string/description/
编写一个函数,以字符串作为输入,反转该字符串中的元音字母。
示例 1:
输入: "hello"
输出: "holle"
示例 2:
输入: "leetcode"
输出: "leotcede"
说明:
元音字母不包含字母"y"。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
string reverseVowels(string s) {
int i = 0, j = s.size() - 1;
int l = -1, r = -1;
while (i <= j) {
if (isVowel(s[i])) l = i;
if (isVowel(s[j])) r = j;
if (l < 0)i++;
if (r < 0)j--;
if (l >= 0 && r >= 0) {
swap(s[l], s[r]);
l = -1;
r = -1;
i++;
j--;
}
}
return s;
}
bool isVowel(char c) {
char vowels[] = "aeiouAEIOU";
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
if (vowels[i] == c) return true;
return false;
}
};
12. 盛最多水的容器
原题链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/container-with-most-water/description/
给定 n 个非负整数 a1,a2,…,an,每个数代表坐标中的一个点 (i, ai) 。在坐标内画 n 条垂直线,垂直线 i 的两个端点分别为 (i, ai) 和 (i, 0)。找出其中的两条线,使得它们与 x 轴共同构成的容器可以容纳最多的水。
示例:
输入: [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
输出: 49
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int maxArea(vector<int> &height) {
int volume = 0, w, h, v;
int i = 0, j = height.size() - 1;
while (i < j) {
w = j - i;
h = min(height[i], height[j]);
v = w * h;
if (v > volume) volume = v;
height[i] < height[j] ? i++ : j--;
}
return volume;
}
};
13. 长度最小的子数组
原题链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-size-subarray-sum/description/
给定一个含有 n 个正整数的数组和一个正整数 s ,找出该数组中满足其和 ≥ s 的长度最小的连续子数组。如果不存在符合条件的连续子数组,返回 0。
示例:
输入: s = 7, nums = [2,3,1,2,4,3]
输出: 2
解释: 子数组 [4,3] 是该条件下的长度最小的连续子数组。
进阶:
如果你已经完成了O(n) 时间复杂度的解法, 请尝试 O(n log n) 时间复杂度的解法。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int minSubArrayLen(int s, vector<int> &nums) {
int l = 0, r = -1;
int ans = nums.size() + 1;
int sum = 0;
while (l < nums.size()) {
if (r + 1 < nums.size() && sum < s)
sum += nums[++r];
else
sum -= nums[l++];
if (sum >= s)
ans = min(ans, r - l + 1);
}
if (ans == nums.size() + 1)
return 0;
return ans;
}
};
14. 无重复字符的最长子串
原题链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-substring-without-repeating-characters/description/
给定一个字符串,找出不含有重复字符的最长子串的长度。
示例 1:
输入: "abcabcbb"
输出: 3
解释: 无重复字符的最长子串是 "abc",其长度为 3。
示例 2:
输入: "bbbbb"
输出: 1
解释: 无重复字符的最长子串是 "b",其长度为 1。
示例 3:
输入: "pwwkew"
输出: 3
解释: 无重复字符的最长子串是 "wke",其长度为 3。
请注意,答案必须是一个子串,"pwke" 是一个子序列 而不是子串。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
int freq[256] = {0};
int l = 0, r = -1;
int res = 0;
while (l < s.size()) {
if (r + 1 < s.size() && freq[s[r + 1]] == 0)
freq[s[++r]]++;
else
freq[s[l++]]--;
res = max(res, r - l + 1);
}
return res;
}
};
15. 找到字符串中所有字母异位词
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-all-anagrams-in-a-string/description/
给定一个字符串 s 和一个非空字符串 p,找到 s 中所有是 p 的字母异位词的子串,返回这些子串的起始索引。
字符串只包含小写英文字母,并且字符串 s 和 p 的长度都不超过 20100。
说明:
字母异位词指字母相同,但排列不同的字符串。
不考虑答案输出的顺序。
示例 1:
输入:
s: "cbaebabacd" p: "abc"
输出:
[0, 6]
解释:
起始索引等于 0 的子串是 "cba", 它是 "abc" 的字母异位词。
起始索引等于 6 的子串是 "bac", 它是 "abc" 的字母异位词。
示例 2:
输入:
s: "abab" p: "ab"
输出:
[0, 1, 2]
解释:
起始索引等于 0 的子串是 "ab", 它是 "ab" 的字母异位词。
起始索引等于 1 的子串是 "ba", 它是 "ab" 的字母异位词。
起始索引等于 2 的子串是 "ab", 它是 "ab" 的字母异位词。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findAnagrams(string s, string p) {
if (s.size() < p.size())
return vector<int>{};
int freqS[26] = {0};
int freqQ[26] = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < p.size(); ++i) {
freqQ[p[i] - 'a']++;
freqS[s[i] - 'a']++;
}
vector<int> res;
int l = 0, r = p.size() - 1;
while (r < s.size()) {
if (isAnagram(freqS, freqQ))
res.push_back(l);
if (r + 1 >= s.size())
break;
freqS[s[++r] - 'a']++;
freqS[s[l++] - 'a']--;
}
return res;
}
private:
bool isAnagram(int s[], int p[]) {
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i)
if (s[i] != p[i]) return false;
return true;
}
};
16. 最小覆盖子串
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-window-substring/description/
给定一个字符串 S 和一个字符串 T,请在 S 中找出包含 T 所有字母的最小子串。
示例:
输入: S = "ADOBECODEBANC", T = "ABC"
输出: "BANC"
说明:
如果 S 中不存这样的子串,则返回空字符串 ""。
如果 S 中存在这样的子串,我们保证它是唯一的答案。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
string minWindow(string s, string t) {
int begin = 0, len = s.size();
int l = 0, r = -1;
bool isContain = false;
int alphaT[128] = {0}, alphaS[128] = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < t.size(); ++i) {
alphaT[t[i]]++;
}
while (l < s.size()) {
// 先判断当前窗口是否包含t中所有字母
if (containT(alphaS, alphaT)) {
isContain = true;
if (r - l + 1 < len) {
begin = l;
len = r - l + 1;
}
alphaS[s[l++]]--;
} else {
if (r + 1 >= s.size())
break;
alphaS[s[++r]]++;
}
}
if (!isContain)
return "";
string res(s, begin, len);
return res;
}
private:
bool containT(int alphaS[], int alphaT[]) {
for (int i = 'a'; i <= 'Z'; ++i)
if (alphaS[i] < alphaT[i])return false;
return true;
}
};
查找表相关问题
set和map相关例题
1. 两个数组的交集
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-arrays/description/
给定两个数组,编写一个函数来计算它们的交集。
示例 1:
输入: nums1 = [1,2,2,1], nums2 = [2,2]
输出: [2]
示例 2:
输入: nums1 = [4,9,5], nums2 = [9,4,9,8,4]
输出: [9,4]
说明:
输出结果中的每个元素一定是唯一的。
我们可以不考虑输出结果的顺序。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> intersection(vector<int> &nums1, vector<int> &nums2) {
set<int> set1(nums1.begin(), nums1.end());
set<int> intersect;
for (int i = 0; i < nums2.size(); ++i)
if (set1.find(nums2[i]) != set1.end())
intersect.insert(nums2[i]);
return vector<int>(intersect.begin(), intersect.end());
}
};
2. 两个数组的交集 II
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-arrays-ii/description/
给定两个数组,编写一个函数来计算它们的交集。
示例 1:
输入: nums1 = [1,2,2,1], nums2 = [2,2]
输出: [2,2]
示例 2:
输入: nums1 = [4,9,5], nums2 = [9,4,9,8,4]
输出: [4,9]
说明:
输出结果中每个元素出现的次数,应与元素在两个数组中出现的次数一致。
我们可以不考虑输出结果的顺序。
进阶:
如果给定的数组已经排好序呢?你将如何优化你的算法?
如果 nums1 的大小比 nums2 小很多,哪种方法更优?
如果 nums2 的元素存储在磁盘上,磁盘内存是有限的,并且你不能一次加载所有的元素到内存中,你该怎么办?
代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> intersect(vector<int> &nums1, vector<int> &nums2) {
unordered_map<int, int> map1;
for (int i = 0; i < nums1.size(); ++i)
map1[nums1[i]]++;
vector<int> res;
for (int j = 0; j < nums2.size(); ++j)
if (map1[nums2[j]] > 0) {
res.push_back(nums2[j]);
map1[nums2[j]]--;
}
return res;
}
};
3. 有效的字母异位词
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-anagram/description/
给定两个字符串 s 和 t ,编写一个函数来判断 t 是否是 s 的一个字母异位词。
示例 1:
输入: s = "anagram", t = "nagaram"
输出: true
示例 2:
输入: s = "rat", t = "car"
输出: false
说明:
你可以假设字符串只包含小写字母。
进阶:
如果输入字符串包含 unicode 字符怎么办?你能否调整你的解法来应对这种情况?
代码:
class Solution {
public:
bool isAnagram(string s, string t) {
unordered_map<int, int> S;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i)
S[s[i]]++;
int key;
for (int j = 0; j < t.size(); ++j) {
key = t[j];
if (S[key] > 0) {
S[key]--;
if (S[key] == 0)S.erase(key);
} else
return false;
}
return S.size() == 0;
}
};
4. 快乐数
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/happy-number/description/
编写一个算法来判断一个数是不是“快乐数”。
一个“快乐数”定义为:对于一个正整数,每一次将该数替换为它每个位置上的数字的平方和,然后重复这个过程直到这个数变为 1,也可能是无限循环但始终变不到 1。如果可以变为 1,那么这个数就是快乐数。
示例:
输入: 19
输出: true
解释:
1 2 + 9 2 = 82 1^2 + 9^2 = 82 12+92=82
8 2 + 2 2 = 68 8^2 + 2^2 = 68 82+22=68
6 2 + 8 2 = 100 6^2 + 8^2 = 100 62+82=100
1 2 + 0 2 + 0 2 = 1 1^2 + 0^2 + 0^2 = 1 12+02+02=1
代码:
class Solution {
public:
bool isHappy(int n) {
unordered_map<int, int> N;
int sum, remain;
while (n != 1 && N.find(n) == N.end()) {
N[n]++;
sum = 0;
while (n) {
remain = n % 10;
sum += remain * remain;
n /= 10;
}
n = sum;
}
return n == 1;
}
};
5. 单词模式
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/word-pattern/description/
给定一种 pattern(模式) 和一个字符串 str ,判断 str 是否遵循相同的模式。
这里的遵循指完全匹配,例如, pattern 里的每个字母和字符串 str 中的每个非空单词之间存在着双向连接的对应模式。
示例1:
输入: pattern = "abba", str = "dog cat cat dog"
输出: true
示例 2:
输入: pattern = "abba", str = "dog cat cat fish"
输出: false
示例 3:
输入: pattern = "aaaa", str = "dog cat cat dog"
输出: false
示例 4:
输入: pattern = "abba", str = "dog dog dog dog"
输出: false
说明:
你可以假设 pattern 只包含小写字母, str 包含了由单个空格分隔的小写字母。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
bool wordPattern(string pattern, string str) {
vector<string> words;
unordered_map<int, string> p2sMap; // p2sMap:pattern映射到str
unordered_map<string, int> s2pMap; //s2pMap:str映射到pattern
string s;
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); ++i)
if (str[i] == ' ') {
if (s.size()) {
words.push_back(s);
}
s = "";
} else {
s += str[i];
}
if (s.size())
words.push_back(s);
if (pattern.size() != words.size()) return false;
int len = pattern.size();
for (int j = 0; j < len; ++j) {
if (p2sMap.find(pattern[j]) == p2sMap.end() && s2pMap.find(words[j]) == s2pMap.end()) {
p2sMap[pattern[j]] = words[j];
s2pMap[words[j]] = pattern[j];
} else {
if (p2sMap[pattern[j]] != words[j])return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
6. 同构字符串
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/isomorphic-strings/description/
给定两个字符串 s 和 t,判断它们是否是同构的。
如果 s 中的字符可以被替换得到 t ,那么这两个字符串是同构的。
所有出现的字符都必须用另一个字符替换,同时保留字符的顺序。两个字符不能映射到同一个字符上,但字符可以映射自己本身。
示例 1:
输入: s = "egg", t = "add"
输出: true
示例 2:
输入: s = "foo", t = "bar"
输出: false
示例 3:
输入: s = "paper", t = "title"
输出: true
说明:
你可以假设 s 和 t 具有相同的长度。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
bool isIsomorphic(string s, string t) {
if (s.size() != t.size())return false;
unordered_map<int, int> s2tMap, t2sMap;
int len = s.size();
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
if (s2tMap.find(s[i]) == s2tMap.end() && t2sMap.find(t[i]) == t2sMap.end()) {
s2tMap[s[i]] = t[i];
t2sMap[t[i]] = s[i];
} else {
if (s2tMap[s[i]] != t[i]) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
7. 根据字符出现频率排序
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-characters-by-frequency/description/
给定一个字符串,请将字符串里的字符按照出现的频率降序排列。
示例 1:
输入:
"tree"
输出:
"eert"
解释:
'e'出现两次,'r'和't'都只出现一次。
因此'e'必须出现在'r'和't'之前。此外,"eetr"也是一个有效的答案。
示例 2:
输入:
"cccaaa"
输出:
"cccaaa"
解释:
'c'和'a'都出现三次。此外,"aaaccc"也是有效的答案。
注意"cacaca"是不正确的,因为相同的字母必须放在一起。
示例 3:
输入:
"Aabb"
输出:
"bbAa"
解释:
此外,"bbaA"也是一个有效的答案,但"Aabb"是不正确的。
注意'A'和'a'被认为是两种不同的字符。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
string frequencySort(string s) {
string res;
unordered_map<int, int> count;
int len = s.size();
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i)
count[s[i]]++;
while (count.size()) {
int ch;
int max = 0;
for (auto &item: count)
if (item.second > max) {
max = item.second;
ch = item.first;
}
for (int i = 0; i < max; ++i)
res += (char) ch;
count.erase(ch);
}
return res;
}
};
8. 两数之和
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum/description/
给定一个整数数组和一个目标值,找出数组中和为目标值的两个数。
你可以假设每个输入只对应一种答案,且同样的元素不能被重复利用。
示例:
给定 nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9
因为 nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9
所以返回 [0, 1]
代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int> &nums, int target) {
unordered_map<int, int> record;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
int k = target - nums[i];
if (record.find(k) != record.end())
return vector<int>{i, record[k]};
record[nums[i]] = i;
}
return vector<int>{};
}
};
9. 三数之和
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/3sum/description/
给定一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?找出所有满足条件且不重复的三元组。
注意: 答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
例如, 给定数组 nums = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4],
满足要求的三元组集合为:
[
[-1, 0, 1],
[-1, -1, 2]
]
代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int> &nums) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
if (nums.size() < 3) return res;
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
size_t i = 0;
while (i < nums.size() - 2) {
int target = -nums[i];
size_t l = i + 1, r = nums.size() - 1;
while (l < r) {
int sum = nums[l] + nums[r];
if (sum == target) {
vector<int> tri{nums[i], nums[l], nums[r]};
res.push_back(tri);
while (l < r && nums[l] == tri[1])
l++;
while (l < r && nums[r] == tri[2])
r--;
} else if (sum > target)
r--;
else
l++;
}
int curNum = nums[i];
while (i < nums.size() - 2 && nums[i] == curNum)
i++;
}
return res;
}
};
10. 四数之和
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/4sum/description/
给定一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums 和一个目标值 target,判断 nums 中是否存在四个元素 a,b,c 和 d ,使得 a + b + c + d 的值与 target 相等?找出所有满足条件且不重复的四元组。
注意:
答案中不可以包含重复的四元组。
示例:
给定数组 nums = [1, 0, -1, 0, -2, 2],和 target = 0。
满足要求的四元组集合为:
[
[-1, 0, 0, 1],
[-2, -1, 1, 2],
[-2, 0, 0, 2]
]
代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> fourSum(vector<int> &nums, int target) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
set<vector<int>> resultSet;
if (nums.size() < 4)
return res;
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
int i = 0;
while (i < nums.size() - 3) {
int j = i + 3;
while (j < nums.size()) {
int l = i + 1;
int r = j - 1;
int t = target - nums[i] - nums[j];
while (l < r) {
int sum = nums[l] + nums[r];
if (sum > t)
r--;
else if (sum < t)
l++;
else {
vector<int> solution{nums[i], nums[l], nums[r], nums[j]};
resultSet.insert(solution);
while (l < r && nums[l] == solution[1])l++;
while (l < r && nums[r] == solution[2])r--;
}
}
j++;
}
i++;
}
res = vector<vector<int>>(resultSet.begin(), resultSet.end());
return res;
}
};
11. 最接近的三数之和
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/3sum-closest/description/
给定一个包括 n 个整数的数组 nums 和 一个目标值 target。找出 nums 中的三个整数,使得它们的和与 target 最接近。返回这三个数的和。假定每组输入只存在唯一答案。
例如,给定数组 nums = [-1,2,1,-4], 和 target = 1.
与 target 最接近的三个数的和为 2. (-1 + 2 + 1 = 2).
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int threeSumClosest(vector<int> &nums, int target) {
if (nums.size() < 3) return 0;
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
int minDis = abs(nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2] - target);
int res = nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2];
size_t i = 0;
while (i < nums.size() - 2) {
int TARGET = target - nums[i];
size_t l = i + 1;
size_t r = nums.size() - 1;
while (l < r) {
int sum2 = nums[l] + nums[r];
if (sum2 > TARGET)
r--;
else if (sum2 < TARGET)
l++;
else
return target;
int sum3 = nums[i] + sum2;
int dis = abs(sum3 - target);
if (dis < minDis) {
minDis = dis;
res = sum3;
}
}
i++;
}
return res;
}
};
12. 四数相加 II
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/4sum-ii/description/
给定四个包含整数的数组列表 A , B , C , D ,计算有多少个元组 (i, j, k, l) ,使得 A[i] + B[j] + C[k] + D[l] = 0。
为了使问题简单化,所有的 A, B, C, D 具有相同的长度 N,且 0 ≤ N ≤ 500 。所有整数的范围在 -228 到 228 - 1 之间,最终结果不会超过 231 - 1 。
例如:
输入:
A = [ 1, 2]
B = [-2,-1]
C = [-1, 2]
D = [ 0, 2]
输出:
2
解释:
两个元组如下:
(0, 0, 0, 1) -> A[0] + B[0] + C[0] + D[1] = 1 + (-2) + (-1) + 2 = 0(1, 1, 0, 0) -> A[1] + B[1] + C[0] + D[0] = 2 + (-1) + (-1) + 0 = 0
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int fourSumCount(vector<int> &A, vector<int> &B, vector<int> &C, vector<int> &D) {
unordered_map<int, int> record;
for (int i = 0; i < C.size(); ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < D.size(); ++j)
record[C[i] + D[j]]++;
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < A.size(); ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < B.size(); ++j)
if (record.find(0 - A[i] - B[j]) != record.end())
res += record[0 - A[i] - B[j]];
return res;
}
};
13. 字母异位词分组
给定一个字符串数组,将字母异位词组合在一起。字母异位词指字母相同,但排列不同的字符串。
示例:
输入: ["eat", "tea", "tan", "ate", "nat", "bat"],
输出:
[
["ate","eat","tea"],
["nat","tan"],
["bat"]
]
说明:
- 所有输入均为小写字母。
- 不考虑答案输出的顺序。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<string>> groupAnagrams(vector<string> &strs) {
unordered_map<string, vector<string>> record;
for (auto str: strs) {
string s = str;
sort(s.begin(), s.end());
record[s].push_back(str);
}
vector<vector<string>> res;
for (auto anagram: record)
res.push_back(anagram.second);
return res;
}
};
14. 回旋镖的数量
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/number-of-boomerangs/description/
给定平面上 n 对不同的点,“回旋镖” 是由点表示的元组 (i, j, k) ,其中 i 和 j 之间的距离和 i 和 k 之间的距离相等(需要考虑元组的顺序)。
找到所有回旋镖的数量。你可以假设 n 最大为 500,所有点的坐标在闭区间 [-10000, 10000] 中。
示例:
输入:
[[0,0],[1,0],[2,0]]
输出:
2
解释:
两个回旋镖为 [[1,0],[0,0],[2,0]] 和 [[1,0],[2,0],[0,0]]
代码:
class Solution {
typedef pair<int, int> POINT;
typedef long long LL;
public:
int numberOfBoomerangs(vector<pair<int, int>> &points) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); ++i) {
map<int, int> record;
for (int j = 0; j < points.size(); ++j) {
if (i != j)
record[dis2(points[i], points[j])]++;
}
for (auto dis: record)
if (dis.second >= 2)
res += dis.second * (dis.second - 1);
}
return res;
}
LL dis2(POINT point1, POINT point2) {
return (point2.first - point1.first) * (point2.first - point1.first) +
(point2.second - point1.second) * (point2.second - point1.second);
}
};
15. 直线上最多的点数
给定一个二维平面,平面上有 n 个点,求最多有多少个点在同一条直线上。
示例 1:
输入: [[1,1],[2,2],[3,3]]
输出: 3
解释:
^
|
| o
| o
| o
+------------->
0 1 2 3 4
示例 2:
输入: [[1,1],[3,2],[5,3],[4,1],[2,3],[1,4]]
输出: 4
解释:
^
|
| o
| o o
| o
| o o
+------------------->
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
代码:
/**
* Definition for a point.
* struct Point {
* int x;
* int y;
* Point() : x(0), y(0) {}
* Point(int a, int b) : x(a), y(b) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
typedef pair<int, int> Slope;
public:
int maxPoints(vector<Point> &points) {
if (points.size() <= 2) return (int) points.size();
int res = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); ++i) {
Point point = points[i];
map<Slope, int> record;
int equal = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < points.size(); ++j)
if (i != j) {
if (isEqualPoint(point, points[j]))
equal++;
record[getSlope(points[j], point)]++;
}
for (auto &item: record) {
Slope slope = item.first;
if (slope.first && slope.second)
item.second += equal;
if (item.second > res)
res = item.second;
}
}
return res + 1;
}
Slope getSlope(Point a, Point b) {
int DX = a.x - b.x, DY = a.y - b.y;
int dy = 0, dx = 0;
if (DX != 0 && DY != 0) {
int g = gcd(a.y - b.y, a.x - b.x);
dy = (a.y - b.y) / g;
dx = (a.x - b.x) / g;
} else if (DX == 0 && DY != 0) {
dy = 1;
dx = 0;
} else if (DX != 0 && DY == 0) {
dy = 0;
dx = 1;
}
return make_pair(dy, dx);
}
bool isEqualPoint(Point a, Point b) {
return a.x == b.x && a.y == b.y;
}
int gcd(int a, int b) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a % b);
}
};
16. 存在重复元素 II
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/contains-duplicate-ii/description/
给定一个整数数组和一个整数 k,判断数组中是否存在两个不同的索引 i 和 j,使得 nums [i] = nums [j],并且 i 和 j 的差的绝对值最大为 k。
示例 1:
输入: nums = [1,2,3,1], k = 3
输出: true
示例 2:
输入: nums = [1,0,1,1], k = 1
输出: true
示例 3:
输入: nums = [1,2,3,1,2,3], k = 2
输出: false
代码:
class Solution {
public:
bool containsNearbyDuplicate(vector<int> &nums, int k) {
unordered_set<int> record;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
if (record.find(nums[i]) != record.end())
return true;
record.insert(nums[i]);
if (record.size() == k + 1)
record.erase(nums[i - k]);
}
return false;
}
};
17. 存在重复元素 III
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/contains-duplicate-iii/description/
给定一个整数数组,判断数组中是否有两个不同的索引 i 和 j,使得 nums [i] 和 nums [j] 的差的绝对值最大为 t,并且 i 和 j 之间的差的绝对值最大为 ķ。
示例 1:
输入: nums = [1,2,3,1], k = 3, t = 0
输出: true
示例 2:
输入: nums = [1,0,1,1], k = 1, t = 2
输出: true
示例 3:
输入: nums = [1,5,9,1,5,9], k = 2, t = 3
输出: false
代码:
class Solution {
typedef long long LL;
public:
bool containsNearbyAlmostDuplicate(vector<int> &nums, int k, int t) {
set<LL> record;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
if (record.lower_bound((LL) nums[i] - (LL) t) != record.end()
&& *record.lower_bound((LL) nums[i] - (LL) t) <= (LL) nums[i] + (LL) t)
return true;
record.insert((LL) nums[i]);
if (record.size() == k + 1)
record.erase(nums[i - k]);
}
return false;
}
};
18. 存在重复元素
给定一个整数数组,判断是否存在重复元素。
如果任何值在数组中出现至少两次,函数返回 true。如果数组中每个元素都不相同,则返回 false。
示例 1:
输入: [1,2,3,1]
输出: true
示例 2:
输入: [1,2,3,4]
输出: false
示例 3:
输入: [1,1,1,3,3,4,3,2,4,2]
输出: true
代码:
class Solution {
public:
bool containsDuplicate(vector<int> &nums) {
unordered_set<int> record;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i)
if (record.find(nums[i]) != record.end())
return true;
else
record.insert(nums[i]);
return false;
}
};
链表相关问题
1. 反转链表
反转一个单链表。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
进阶:
你可以迭代或递归地反转链表。你能否用两种方法解决这道题?
代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *reverseList(ListNode *head) {
if (head == NULL)return NULL;
ListNode *pre = NULL;
ListNode *cur = head;
ListNode *next;
while (cur != NULL) {
next = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
};
2. 反转链表 II
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii/description/
反转从位置 m 到 n 的链表。请使用一趟扫描完成反转。
说明:
1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ 链表长度。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2, n = 4
输出: 1->4->3->2->5->NULL
代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *reverseBetween(ListNode *head, int m, int n) {
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL || m == n)return head;
ListNode *START = head;
ListNode *PRE = NULL;
int i;
for (i = 1; i < m; ++i) {
PRE = START;
START = START->next;
}
ListNode *cur = START;
ListNode *pre = NULL;
for (i = m; i <= n && cur != NULL; ++i) {
ListNode *next = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
if (m == 1) {
START->next = cur;
return pre;
}
START->next = cur;
PRE->next = pre;
return head;
}
};
3. 两数相加
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/add-two-numbers/
给定两个非空链表来表示两个非负整数。位数按照逆序方式存储,它们的每个节点只存储单个数字。将两数相加返回一个新的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数字都不会以零开头。
示例:
输入: (2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
输出: 7 -> 0 -> 8
原因: 342 + 465 = 807
代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *addTwoNumbers(ListNode *l1, ListNode *l2) {
if (!l1 && !l2)return NULL;
if (!l1) return l2;
if (!l2) return l1;
ListNode *p1 = l1;
ListNode *p2 = l2;
ListNode *l3 = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode *p3 = l3;
ListNode *pre = p3;
int carry = 0; // 进位
while (p1 || p2) {
int sum = 0;
if (p1 && p2) {
sum = p1->val + p2->val + carry;
p1 = p1->next;
p2 = p2->next;
} else if (p1 && !p2) {
sum = p1->val + carry;
p1 = p1->next;
} else {
sum = p2->val + carry;
p2 = p2->next;
}
if (sum >= 10) {
carry = 1;
sum %= 10;
} else {
carry = 0;
}
p3->val = sum;
ListNode *newNode = new ListNode(-1);
p3->next = newNode;
pre = p3;
p3 = newNode;
}
if (carry) {
p3->val = 1;
} else {
pre->next = p3->next;
delete p3;
}
return l3;
}
};
4. 删除排序链表中的重复元素
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list/
给定一个排序链表,删除所有重复的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次。
示例 1:
输入: 1->1->2
输出: 1->2
示例 2:
输入: 1->1->2->3->3
输出: 1->2->3
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *deleteDuplicates(ListNode *head) {
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return head;
ListNode *pre = head;
ListNode *p = head->next;
while (p) {
if (p->val == pre->val) {
ListNode *delNode = p;
pre->next = p->next;
p = p->next;
delete delNode;
} else {
pre = p;
p = p->next;
}
}
return head;
}
};
5.分隔链表
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/partition-list/description/
给定一个链表和一个特定值 x,对链表进行分隔,使得所有小于 x 的节点都在大于或等于 x 的节点之前。
你应当保留两个分区中每个节点的初始相对位置。
示例:
输入: head = 1->4->3->2->5->2, x = 3
输出: 1->2->2->4->3->5
代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *partition(ListNode *head, int x) {
ListNode *dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode *p = dummyHead;
ListNode *tail = dummyHead;
int len = 0;
while (tail->next != NULL) {
len++;
tail = tail->next;
}
int i = 0;
ListNode *q = p->next;
while (i < len && q != tail) {
if (q->val >= x) {
p->next = q->next;
tail->next = q;
tail = q;
} else
p = p->next;
q = p->next;
i++;
}
tail->next = NULL;
head = dummyHead->next;
delete dummyHead;
return head;
}
};
6. 奇偶链表
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/odd-even-linked-list/
给定一个单链表,把所有的奇数节点和偶数节点分别排在一起。请注意,这里的奇数节点和偶数节点指的是节点编号的奇偶性,而不是节点的值的奇偶性。
请尝试使用原地算法完成。你的算法的空间复杂度应为 O(1),时间复杂度应为 O(nodes),nodes 为节点总数。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 1->3->5->2->4->NULL
示例 2:
输入: 2->1->3->5->6->4->7->NULL
输出: 2->3->6->7->1->5->4->NULL
说明:
应当保持奇数节点和偶数节点的相对顺序。
链表的第一个节点视为奇数节点,第二个节点视为偶数节点,以此类推。
代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *oddEvenList(ListNode *head) {
ListNode *dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode *p = dummyHead;
ListNode *tail = dummyHead;
int len = 0;
while (tail->next != NULL) {
len++;
tail = tail->next;
}
int i = 1;
ListNode *q = p->next;
while (i <= len && q != tail) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
p->next = q->next;
tail->next = q;
tail = q;
} else
p = p->next;
q = p->next;
i++;
}
tail->next = NULL;
head = dummyHead->next;
delete dummyHead;
return head;
}
};
7. 两数相加 II
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/add-two-numbers-ii/
给定两个非空链表来代表两个非负整数。数字最高位位于链表开始位置。它们的每个节点只存储单个数字。将这两数相加会返回一个新的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数字都不会以零开头。
进阶:
如果输入链表不能修改该如何处理?换句话说,你不能对列表中的节点进行翻转。
示例:
输入: (7 -> 2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
输出: 7 -> 8 -> 0 -> 7
代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *addTwoNumbers(ListNode *l1, ListNode *l2) {
vector<int> num1;
vector<int> num2;
ListNode *p1 = l1;
ListNode *p2 = l2;
while (p1) {
num1.push_back(p1->val);
p1 = p1->next;
}
while (p2) {
num2.push_back(p2->val);
p2 = p2->next;
}
if (num1.size() < num2.size()) {
vector<int> tmp = num1;
num1 = num2;
num2 = tmp;
}
int carry = 0;
int j = (int) (num2.size() - 1);
for (int i = (int) (num1.size() - 1); i >= 0; --i) {
int digit;
if (j < 0)
digit = num1[i] + carry;
else
digit = num1[i] + num2[j--] + carry;
if (digit >= 10) {
carry = 1;
digit %= 10;
} else
carry = 0;
num1[i] = digit;
}
if (carry > 0)
num1.insert(num1.begin(), 1);
ListNode *head = new ListNode(num1[0]);
ListNode *cur = head;
for (int i = 1; i < num1.size(); ++i) {
cur->next = new ListNode(num1[i]);
cur = cur->next;
}
return head;
}
};
8. 删除链表中的节点
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/
删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。
示例:
输入: 1->2->6->3->4->5->6, val = 6
输出: 1->2->3->4->5
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *removeElements(ListNode *head, int val) {
ListNode *dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode *p = dummyHead;
ListNode *q = p->next;
while (q) {
if (q->val == val) {
ListNode *delNode = q;
q = q->next;
p->next = q;
delete delNode;
} else {
p = q;
q = p->next;
}
}
head = dummyHead->next;
delete dummyHead;
return head;
}
};
9. 合并两个有序链表
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/
将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例:
输入: 1->2->4, 1->3->4
输出: 1->1->2->3->4->4
代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *mergeTwoLists(ListNode *l1, ListNode *l2) {
if (!l1)return l2;
if (!l2) return l1;
ListNode *dummyHead1 = new ListNode(-1);
dummyHead1->next = l1;
ListNode *dummyHead2 = new ListNode(-1);
dummyHead2->next = l2;
ListNode *p1 = l1;
ListNode *p2 = l2;
ListNode *p = dummyHead1;
while (p1 && p2) {
if (p1->val < p2->val) {
p->next = p1;
p = p1;
p1 = p1->next;
} else {
p->next = p2;
p = p2;
p2 = p2->next;
}
}
if (p1)
p->next = p1;
if (p2)
p->next = p2;
return dummyHead1->next;
}
};
10. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list-ii/
给定一个排序链表,删除所有含有重复数字的节点,只保留原始链表中 没有重复出现 的数字。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2->3->3->4->4->5
输出: 1->2->5
示例 2:
输入: 1->1->1->2->3
输出: 2->3
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *deleteDuplicates(ListNode *head) {
if (head == NULL) return NULL;
ListNode *dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode *PRE = dummyHead;
ListNode *p = head;
ListNode *q = p->next;
ListNode *dup = NULL;
while (q) {
if (q->val == p->val) {
dup = p;
ListNode *delNode = q;
q = q->next;
p->next = q;
delete delNode;
} else {
if (dup) {
p = q;
q = p->next;
PRE->next = p;
delete dup;
dup = NULL;
} else {
PRE = p;
p = q;
q = p->next;
}
}
}
if (dup) {
PRE->next = dup->next;
delete dup;
}
head = dummyHead->next;
delete dummyHead;
return head;
}
};
11. 两两交换链表中的节点
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/
给定一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后的链表。
示例:
给定 1->2->3->4, 你应该返回 2->1->4->3.
说明:
- 你的算法只能使用常数的额外空间。
- 你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *swapPairs(ListNode *head) {
ListNode *dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode *pre = dummyHead;
ListNode *oddNode;
ListNode *evenNode;
ListNode *next;
while (pre->next && pre->next->next) {
oddNode = pre->next;
evenNode = oddNode->next;
next = evenNode->next;
evenNode->next = oddNode;
oddNode->next = next;
pre->next = evenNode;
pre = oddNode;
}
head = dummyHead->next;
delete dummyHead;
return head;
}
};
12. k个一组翻转链表
给出一个链表,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,并返回翻转后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么将最后剩余节点保持原有顺序。
示例 :
给定这个链表:1->2->3->4->5
当 k = 2 时,应当返回: 2->1->4->3->5
当 k = 3 时,应当返回: 3->2->1->4->5
说明 :
- 你的算法只能使用常数的额外空间。
- 你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *reverseKGroup(ListNode *head, int k) {
ListNode *dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode *h = dummyHead;
ListNode *T = dummyHead;
for (int i = 1; T->next != NULL; ++i) {
T = T->next;
if (i % k == 0) {
ListNode *TNext = T->next;
ListNode *p = h->next;
ListNode *q = p->next;
while (q != TNext) {
p->next = q->next;
q->next = h->next;
h->next = q;
q = p->next;
}
T = p;
h = T;
}
}
head = dummyHead->next;
delete dummyHead;
return head;
}
};
13. 对链表进行插入排序
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/insertion-sort-list/
对链表进行插入排序。
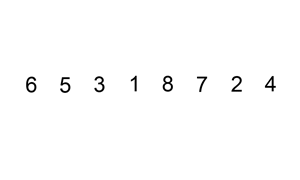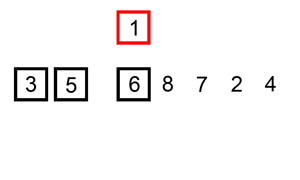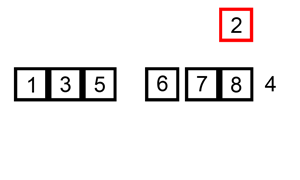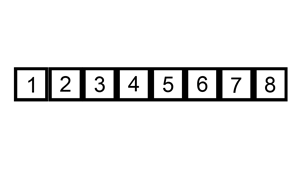
插入排序的动画演示如上。从第一个元素开始,该链表可以被认为已经部分排序(用黑色表示)。
每次迭代时,从输入数据中移除一个元素(用红色表示),并原地将其插入到已排好序的链表中。
插入排序算法:
- 插入排序是迭代的,每次只移动一个元素,直到所有元素可以形成一个有序的输出列表。
- 每次迭代中,插入排序只从输入数据中移除一个待排序的元素,找到它在序列中适当的位置,并将其插入。
- 重复直到所有输入数据插入完为止。
示例 1:
输入: 4->2->1->3
输出: 1->2->3->4
示例 2:
输入: -1->5->3->4->0
输出: -1->0->3->4->5
代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *insertionSortList(ListNode *head) {
if (head == NULL) return NULL;
ListNode *dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode *p1 = head->next;
ListNode *pre1 = head;
ListNode *p2, *pre2, *next;
while (p1 != NULL) {
p2 = dummyHead->next;
pre2 = dummyHead;
next = p1->next;
while (p1->val > p2->val) {
pre2 = p2;
p2 = p2->next;
}
if (p2 != p1) {
pre1->next = next;
p1->next = p2;
pre2->next = p1;
} else
pre1 = p1;
p1 = next;
}
head = dummyHead->next;
delete dummyHead;
return head;
}
};
14. 排序链表
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-list/description/
在 O(n log n) 时间复杂度和常数级空间复杂度下,对链表进行排序。
示例 1:
输入: 4->2->1->3
输出: 1->2->3->4
示例 2:
输入: -1->5->3->4->0
输出: -1->0->3->4->5
代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *sortList(ListNode *head) {
return mergeSort(head);
}
ListNode *mergeSort(ListNode *head) {
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return head;
ListNode *dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode *slow = dummyHead;
ListNode *fast = dummyHead;
while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
ListNode *mid = slow->next;
slow->next = NULL;
delete dummyHead;
ListNode *p1 = mergeSort(head);
ListNode *p2 = mergeSort(mid);
return merge(p1, p2);
}
ListNode *merge(ListNode *l1, ListNode *l2) {
ListNode *dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
dummyHead->next = l1;
ListNode *p1 = l1;
ListNode *pre1 = dummyHead;
ListNode *p2 = l2;
while (p1 && p2) {
if (p1->val < p2->val) {
pre1 = p1;
p1 = p1->next;
} else {
ListNode *tmp = p2;
p2 = p2->next;
pre1->next = tmp;
tmp->next = p1;
pre1 = tmp;
}
}
if (p1 == NULL) {
pre1->next = p2;
}
ListNode *retNode = dummyHead->next;
delete dummyHead;
return retNode;
}
};
15. 删除链表中的节点
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/delete-node-in-a-linked-list/
请编写一个函数,使其可以删除某个链表中给定的(非末尾)节点,你将只被给定要求被删除的节点。
现有一个链表 – head = [4,5,1,9],它可以表示为:
4 -> 5 -> 1 -> 9
示例 1:
输入: head = [4,5,1,9], node = 5
输出: [4,1,9]
解释: 给定你链表中值为 5 的第二个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 1 -> 9.
示例 2:
输入: head = [4,5,1,9], node = 1
输出: [4,5,9]
解释: 给定你链表中值为 1 的第三个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 5 -> 9.
说明:
- 链表至少包含两个节点。
- 链表中所有节点的值都是唯一的。
- 给定的节点为非末尾节点并且一定是链表中的一个有效节点。
- 不要从你的函数中返回任何结果。
代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void deleteNode(ListNode *node) {
if (node == NULL) return;
if (node->next == NULL) {
delete node;
node = NULL;
return;
}
ListNode *next = node->next;
node->val = next->val;
node->next = next->next;
delete next;
return;
}
};
16. 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/
给定一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个节点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例:
给定一个链表: 1->2->3->4->5, 和 n = 2.
当删除了倒数第二个节点后,链表变为 1->2->3->5.
说明:
给定的 n 保证是有效的。
进阶:
你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?
代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *removeNthFromEnd(ListNode *head, int n) {
if (head == NULL)return NULL;
ListNode *dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode *p = dummyHead;
ListNode *q = dummyHead;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i)
q = q->next;
while (q != NULL) {
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
}
ListNode *delNode = p->next;
p->next = delNode->next;
delete delNode;
head = dummyHead->next;
delete dummyHead;
return head;
}
};
17.回文链表
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-linked-list/description/
请判断一个链表是否为回文链表。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2
输出: false
示例 2:
输入: 1->2->2->1
输出: true
进阶:
你能否用 O(n) 时间复杂度和 O(1) 空间复杂度解决此题?
代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(ListNode *head) {
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return true;
ListNode *dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode *mid = dummyHead;
ListNode *q = dummyHead;
while (q != NULL && q->next != NULL) {
mid = mid->next;
q = q->next->next;
}
ListNode *pre = mid->next;
ListNode *p = pre->next;
while (p != NULL) {
pre->next = p->next;
p->next = mid->next;
mid->next = p;
p = pre->next;
}
p = dummyHead->next;
q = mid->next;
while (q != NULL) {
if (p->val != q->val)
return false;
else {
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
}
}
return true;
}
};
18. 重排链表
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reorder-list/
给定一个单链表 L:L0→L1→…→Ln-1→Ln ,
将其重新排列后变为: L0→Ln→L1→Ln-1→L2→Ln-2→…
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
示例 1:
给定链表 1->2->3->4, 重新排列为 1->4->2->3.
示例 2:
给定链表 1->2->3->4->5, 重新排列为 1->5->2->4->3.
代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void reorderList(ListNode *head) {
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return;
ListNode *dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode *mid = dummyHead;
ListNode *q = dummyHead;
while (q != NULL && q->next != NULL) {
mid = mid->next;
q = q->next->next;
}
ListNode *pre = mid->next;
ListNode *p = pre->next;
while (p != NULL) {
pre->next = p->next;
p->next = mid->next;
mid->next = p;
p = pre->next;
}
p = dummyHead->next;
q = mid->next;
while (q != NULL && p != mid) {
mid->next = q->next;
q->next = p->next;
p->next = q;
p = q->next;
q = mid->next;
}
}
};
19. 旋转链表
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/rotate-list/
给定一个链表,旋转链表,将链表每个节点向右移动 k 个位置,其中 k 是非负数。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, k = 2
输出: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
解释:
向右旋转 1 步: 5->1->2->3->4->NULL
向右旋转 2 步: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
示例 2:
输入: 0->1->2->NULL, k = 4
输出: 2->0->1->NULL
解释:
向右旋转 1 步: 2->0->1->NULL
向右旋转 2 步: 1->2->0->NULL
向右旋转 3 步: 0->1->2->NULL
向右旋转 4 步: 2->0->1->NULL
代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *rotateRight(ListNode *head, int k) {
if (head == NULL) return head;
ListNode *dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode *tail = dummyHead->next;
int len;
for (len = 1; tail->next != NULL; ++len)
tail = tail->next;
k %= len;
ListNode *breakPoint = dummyHead;
for (int i = 0; i < len - k; ++i)
breakPoint = breakPoint->next;
tail->next = dummyHead->next;
dummyHead->next = breakPoint->next;
breakPoint->next = NULL;
head = dummyHead->next;
delete dummyHead;
return head;
}
};
栈和队列相关问题
1. 有效的括号
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-parentheses/
给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
- 左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
- 左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
注意空字符串可被认为是有效字符串。
示例 1:
输入: "()"
输出: true
示例 2:
输入: "()[]{}"
输出: true
示例 3:
输入: "(]"
输出: false
示例 4:
输入: "([)]"
输出: false
示例 5:
输入: "{[]}"
输出: true
代码:
class Solution {
public:
bool isValid(string s) {
stack<char> stack;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i) {
char c = s[i];
if (isLeftParen(c))
stack.push(c);
else {
if (stack.empty())
return false;
char top = stack.top();
stack.pop();
if (!isMatch(top, c))
return false;
}
}
return stack.empty();
}
bool isLeftParen(char c) {
switch (c) {
case '(':
case '{':
case '[':
return true;
default:
return false;
}
}
bool isMatch(char leftParen, char rightParen) {
switch (leftParen) {
case '(':
return rightParen == ')';
case '{':
return rightParen == '}';
case '[':
return rightParen == ']';
default:
return false;
}
}
};
2. 简化路径
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/simplify-path/
给定一个文档 (Unix-style) 的完全路径,请进行路径简化。
例如,
path = "/home/", => "/home"
path = "/a/./b/../../c/", => "/c"
边界情况:
- 你是否考虑了 路径 =
"/../"的情况?
在这种情况下,你需返回"/"。 - 此外,路径中也可能包含多个斜杠
'/',如"/home//foo/"。
在这种情况下,你可忽略多余的斜杠,返回"/home/foo"。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
string simplifyPath(string path) {
stack<string> pathStack;
string dir;
int dirLen = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < path.size(); ++i) {
char c = path[i];
if (c == '/') {
if (dirLen != 0) {
if (dir == "..") {
if (!pathStack.empty())
pathStack.pop();
} else if (dir != ".") {
pathStack.push(dir);
}
dirLen = 0;
dir = "";
}
} else {
dirLen++;
dir += c;
}
}
if (dirLen) {
if (dir == "..") {
if (!pathStack.empty())
pathStack.pop();
} else if (dir != ".") {
pathStack.push(dir);
}
}
stack<string> retStack = reverseStack(pathStack);
string res;
while (!retStack.empty()) {
string s = (basic_string<char, char_traits<char>, allocator<char>> &&) retStack.top();
res += "/" + s;
retStack.pop();
}
if (res == "")res = "/";
return res;
}
stack<string> reverseStack(stack<string> oldStack) {
stack<string> retStack;
while (!oldStack.empty()) {
string s = (basic_string<char, char_traits<char>, allocator<char>> &&) oldStack.top();
retStack.push(s);
oldStack.pop();
}
return retStack;
}
};
3. 逆波兰表达式求值
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/evaluate-reverse-polish-notation/
根据逆波兰表示法,求表达式的值。
有效的运算符包括 +, -, *, / 。每个运算对象可以是整数,也可以是另一个逆波兰表达式。
说明:
整数除法只保留整数部分。
给定逆波兰表达式总是有效的。换句话说,表达式总会得出有效数值且不存在除数为 0 的情况。
示例 1:
输入: ["2", "1", "+", "3", "*"]
输出: 9
解释: ((2 + 1) * 3) = 9
示例 2:
输入: ["4", "13", "5", "/", "+"]
输出: 6
解释: (4 + (13 / 5)) = 6
示例 3:
输入: ["10", "6", "9", "3", "+", "-11", "*", "/", "*", "17", "+", "5", "+"]
输出: 22
解释:
((10 * (6 / ((9 + 3) * -11))) + 17) + 5
= ((10 * (6 / (12 * -11))) + 17) + 5
= ((10 * (6 / -132)) + 17) + 5
= ((10 * 0) + 17) + 5
= (0 + 17) + 5
= 17 + 5
= 22
代码:
class Solution {
private:
bool isOperator(string s) {
char c;
if (s.size() == 1)
c = s[0];
else
return false;
switch (c) {
case '+':
case '-':
case '*':
case '/':
return true;
default:
return false;
}
}
public:
int evalRPN(vector<string> &tokens) {
stack<int> stack;
for (string token:tokens)
if (isOperator(token)) {
int op2 = stack.top();
stack.pop();
int op1 = stack.top();
stack.pop();
int res = 1;
switch (token[0]) {
case '+':
res = op1 + op2;
break;
case '-':
res = op1 - op2;
break;
case '*':
res = op1 * op2;
break;
case '/':
res = op1 / op2;
break;
default:
break;
}
stack.push(res);
} else
stack.push(stoi(token));
int res = stack.top();
stack.pop();
return res;
}
};
4. 二叉树的前序遍历
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-preorder-traversal/
给定一个二叉树,返回它的 前序 遍历。
示例:
输入: [1,null,2,3]
1
\
2
/
3
输出: [1,2,3]
进阶: 递归算法很简单,你可以通过迭代算法完成吗?
代码1:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
enum OperateType {
GO, VISIT
};
struct Command {
OperateType type;
TreeNode *node;
Command(OperateType type, TreeNode *node) : type(type), node(node) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode *root) {
vector<int> res;
if (root == NULL) {
return res;
}
stack<Command> stack;
stack.push(Command(GO, root));
while (!stack.empty()) {
Command command = stack.top();
stack.pop();
if (command.type == VISIT) {
res.push_back(command.node->val);
} else {
TreeNode *node = command.node;
if (node->right)
stack.push(Command(GO, node->right));
if (node->left)
stack.push(Command(GO, node->left));
stack.push(Command(VISIT, node));
}
}
return res;
}
};
代码2:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode *root) {
vector<int> res;
if (root == NULL) {
return res;
}
stack<TreeNode *> stack;
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.empty()) {
TreeNode *node = stack.top();
res.push_back(node->val);
stack.pop();
if (node->right)
stack.push(node->right);
if (node->left)
stack.push(node->left);
}
return res;
}
};
5. 二叉树的中序遍历
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/
给定一个二叉树,返回它的中序 遍历。
示例:
输入: [1,null,2,3]
1
\
2
/
3
输出: [1,3,2]
进阶: 递归算法很简单,你可以通过迭代算法完成吗?
代码1:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
enum OperateType {
GO, VISIT
};
struct Command {
OperateType type;
TreeNode *node;
Command(OperateType type, TreeNode *node) : type(type), node(node) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode *root) {
vector<int> res;
if (root == NULL)
return res;
stack<Command> stack;
stack.push(Command(GO, root));
while (!stack.empty()) {
Command command = stack.top();
stack.pop();
TreeNode *node = command.node;
if (command.type == VISIT)
res.push_back(node->val);
else {
if (node->right)
stack.push(Command(GO, node->right));
stack.push(Command(VISIT, node));
if (node->left)
stack.push(Command(GO, node->left));
}
}
return res;
}
};
代码2:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
if(root == NULL)
return res;
stack<TreeNode *> stack;
TreeNode *p = root;
while(p || !stack.empty()){
if(p){
stack.push(p);
p = p->left;
}else{
p = stack.top();
stack.pop();
res.push_back(p->val);
p = p->right;
}
}
return res;
}
};
6. 二叉树的后序遍历
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-postorder-traversal/
给定一个二叉树,返回它的 后序 遍历。
示例:
输入: [1,null,2,3]
1
\
2
/
3
输出: [3,2,1]
进阶: 递归算法很简单,你可以通过迭代算法完成吗?
代码1:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
enum OperateType {
GO, VISIT
};
struct Command {
OperateType type;
TreeNode *node;
Command(OperateType type, TreeNode *node) :
type(type), node(node) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode *root) {
vector<int> res;
if (root == NULL) return res;
stack<Command> stack;
stack.push(Command(GO, root));
while (!stack.empty()) {
Command command = stack.top();
stack.pop();
if (command.type == VISIT)
res.push_back(command.node->val);
else {
TreeNode *node = command.node;
stack.push(Command(VISIT, node));
if (node->right)
stack.push(Command(GO, node->right));
if (node->left)
stack.push(Command(GO, node->left));
}
}
return res;
}
};
代码2:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode *root) {
vector<int> res;
if (root == NULL)
return res;
stack<TreeNode *> stack;
TreeNode *p = root;
TreeNode *r = NULL;
while (p || !stack.empty())
if (p) {
stack.push(p);
p = p->left;
} else {
p = stack.top();
if (p->right && p->right != r) {
p = p->right;
stack.push(p);
p = p->left;
} else {
stack.pop();
res.push_back(p->val);
r = p;
p = NULL;
}
}
return res;
}
};
7. 扁平化嵌套列表迭代器
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/flatten-nested-list-iterator/
给定一个嵌套的整型列表。设计一个迭代器,使其能够遍历这个整型列表中的所有整数。
列表中的项或者为一个整数,或者是另一个列表。
示例 1:
输入: [[1,1],2,[1,1]]
输出: [1,1,2,1,1]
解释: 通过重复调用 next 直到 hasNext 返回false,next 返回的元素的顺序应该是: [1,1,2,1,1]。
示例 2:
输入: [1,[4,[6]]]
输出: [1,4,6]
解释: 通过重复调用 next 直到 hasNext 返回false,next 返回的元素的顺序应该是: [1,4,6]。
代码:
/*
// This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists.
// You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
class NestedInteger {
public:
// Return true if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list.
bool isInteger() const;
// Return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer
// The result is undefined if this NestedInteger holds a nested list
int getInteger() const;
// Return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list
// The result is undefined if this NestedInteger holds a single integer
const vector &getList() const;
};
*/
class NestedIterator {
private:
stack<int> integerStack;
vector<int> res;
int currentIndex;
void inflateStack(vector<NestedInteger> &nestedList) {
for (auto nestedInteger:nestedList)
if (nestedInteger.isInteger())
integerStack.push(nestedInteger.getInteger());
else
inflateStack((vector<NestedInteger, allocator<NestedInteger>> &) nestedInteger.getList());
}
public:
NestedIterator(vector<NestedInteger> &nestedList) {
currentIndex = 0;
inflateStack(nestedList);
while (!integerStack.empty()) {
res.insert(res.begin(), (int &&) integerStack.top());
integerStack.pop();
}
}
int next() {
return res[currentIndex++];
}
bool hasNext() {
return currentIndex < res.size();
}
};
/**
* Your NestedIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* NestedIterator i(nestedList);
* while (i.hasNext()) cout << i.next();
*/
8. 二叉树的层次遍历
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/
给定一个二叉树,返回其按层次遍历的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
例如:
给定二叉树: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回其层次遍历结果:
[
[3],
[9,20],
[15,7]
]
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode *root) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
if (root == NULL)
return res;
queue<pair<TreeNode *, int>> q;
q.push(make_pair(root, 0));
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode *node = q.front().first;
int level = q.front().second;
q.pop();
if (level == res.size())
res.push_back(vector<int>());
res[level].push_back(node->val);
if (node->left)
q.push(make_pair(node->left, level + 1));
if (node->right)
q.push(make_pair(node->right, level + 1));
}
return res;
}
};
9. 二叉树的层次遍历 II
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal-ii/
给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值自底向上的层次遍历。 (即按从叶子节点所在层到根节点所在的层,逐层从左向右遍历)
例如:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回其自底向上的层次遍历为:
[
[15,7],
[9,20],
[3]
]
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode *root) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
if (root == NULL)
return res;
queue<pair<TreeNode *, int>> q;
q.push(make_pair(root, 0));
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode *node = q.front().first;
int level = q.front().second;
q.pop();
if (level == res.size())
res.push_back(vector<int>());
res[level].push_back(node->val);
if (node->left)
q.push(make_pair(node->left, level + 1));
if (node->right)
q.push(make_pair(node->right, level + 1));
}
reverse(res.begin(), res.end());
return res;
}
};
10. 二叉树的锯齿形层次遍历
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-zigzag-level-order-traversal/
给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值的锯齿形层次遍历。(即先从左往右,再从右往左进行下一层遍历,以此类推,层与层之间交替进行)。
例如:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回锯齿形层次遍历如下:
[
[3],
[20,9],
[15,7]
]
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode *root) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
if (root == NULL)
return res;
queue<pair<TreeNode *, int>> q;
q.push(make_pair(root, 0));
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode *node = q.front().first;
int level = q.front().second;
q.pop();
if (level == res.size())
res.push_back(vector<int>());
res[level].push_back(node->val);
if (node->left)
q.push(make_pair(node->left, level + 1));
if (node->right)
q.push(make_pair(node->right, level + 1));
}
for (int i = 1; i < res.size(); i += 2)
reverse(res[i].begin(), res[i].end());
return res;
}
};
11. 二叉树的右视图
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/
给定一棵二叉树,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。
示例:
输入: [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
输出: [1, 3, 4]
解释:
1 <---
/ \
2 3 <---
\ \
5 4 <---
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode *root) {
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder;
vector<int> res;
if (root == NULL)
return res;
queue<pair<TreeNode *, int>> q;
q.push(make_pair(root, 0));
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode *node = q.front().first;
int level = q.front().second;
q.pop();
if (level == levelOrder.size())
levelOrder.push_back(vector<int>());
levelOrder[level].push_back(node->val);
if (node->left)
q.push(make_pair(node->left, level + 1));
if (node->right)
q.push(make_pair(node->right, level + 1));
}
for (auto curLevel :levelOrder) {
res.push_back(curLevel[curLevel.size() - 1]);
}
return res;
}
};
12.完全平方数
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/perfect-squares/
给定正整数 n,找到若干个完全平方数(比如 1, 4, 9, 16, …)使得它们的和等于 n。你需要让组成和的完全平方数的个数最少。
示例 1:
输入: n = 12
输出: 3
解释: 12 = 4 + 4 + 4.
示例 2:
输入: n = 13
输出: 2
解释: 13 = 4 + 9.
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int numSquares(int n) {
assert(n > 0);
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push(make_pair(n, 0));
vector<bool> visited((unsigned) (n + 1), false);
visited[n] = true;
while (!q.empty()) {
int num = q.front().first;
int step = q.front().second;
q.pop();
for (int i = 1;; ++i) {
int a = num - i * i;
if (a < 0)
break;
if (a == 0)
return step + 1;
if (!visited[a]) {
q.push(make_pair(a, step + 1));
visited[a] = true;
}
}
}
throw invalid_argument("No Solution");
}
};
13.单词接龙
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/word-ladder/
给定两个单词(beginWord 和 endWord)和一个字典,找到从 beginWord 到 endWord 的最短转换序列的长度。转换需遵循如下规则:
- 每次转换只能改变一个字母。
- 转换过程中的中间单词必须是字典中的单词。
说明:
- 如果不存在这样的转换序列,返回 0。
- 所有单词具有相同的长度。
- 所有单词只由小写字母组成。
- 字典中不存在重复的单词。
- 你可以假设 beginWord 和 endWord 是非空的,且二者不相同。
示例 1:
输入:
beginWord = "hit",
endWord = "cog",
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log","cog"]
输出: 5
解释: 一个最短转换序列是 “hit” -> “hot” -> “dot” -> “dog” -> “cog”,
返回它的长度 5。
示例 2:
输入:
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
输出: 0
解释: endWord “cog” 不在字典中,所以无法进行转换。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int ladderLength(string beginWord, string endWord, vector<string> &wordList) {
bool possible = false;
for (int i = 0; i < wordList.size(); ++i)
if (endWord == wordList[i]) {
possible = true;
break;
}
// endWord不在列表中
if (!possible)
return 0;
queue<pair<string, int>> q;
q.push(make_pair(beginWord, 1));
vector<bool> visited(wordList.size(), false);
while (!q.empty()) {
string word = q.front().first;
int step = q.front().second;
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < wordList.size(); ++i) {
string item = wordList[i];
if (!visited[i] && isClose(word, item)) {
if (item == endWord)
return step + 1;
q.push(make_pair(item, step + 1));
visited[i] = true;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
bool isClose(string a, string b) {
int different = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.size() && different < 2; ++i)
if (a[i] != b[i])
different++;
return different == 1;
}
};
14.前K个高频元素
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/top-k-frequent-elements/
给定一个非空的整数数组,返回其中出现频率前 k 高的元素。
示例 1:
输入: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2
输出: [1,2]
示例 2:
输入: nums = [1], k = 1
输出: [1]
说明:
- 你可以假设给定的 k 总是合理的,且 1 ≤ k ≤ 数组中不相同的元素的个数。
- 你的算法的时间复杂度必须优于 O(n log n) , n 是数组的大小。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> topKFrequent(vector<int> &nums, int k) {
// <数据, 频率>
unordered_map<int, int> freq;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i)
freq[nums[i]]++;
// pair 对应<频率, 数据>
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>> pq;
for (auto &record: freq) {
if (pq.size() == k) {
if (record.second > pq.top().first) {
pq.pop();
pq.push(make_pair(record.second, record.first));
}
} else {
pq.push(make_pair(record.second, record.first));
}
}
vector<int> res;
while (!pq.empty()) {
res.push_back(pq.top().second);
pq.pop();
}
return res;
}
};
15.合并K个排序链表
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/
合并 k 个排序链表,返回合并后的排序链表。请分析和描述算法的复杂度。
示例:
输入:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
输出: 1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
bool compare(ListNode *p1, ListNode *p2) {
return p1->val > p2->val;
}
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *mergeKLists(vector<ListNode *> &lists) {
if (lists.size() == 0) return NULL;
priority_queue<ListNode *, vector<ListNode *>, function<bool(ListNode *, ListNode *)>> pq(compare);
for (int i = 0; i < lists.size(); ++i)
if (lists[i])
pq.push(lists[i]);
ListNode *dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode *p = dummyHead;
while (!pq.empty()) {
ListNode *node = pq.top();
pq.pop();
p->next = node;
p = node;
if (node->next)
pq.push(node->next);
}
p->next = NULL;
ListNode *head = dummyHead->next;
delete dummyHead;
return head;
}
};
二叉树和递归
1.二叉树的最大深度
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回它的最大深度 3 。
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode *root) {
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
return max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
};
2.二叉树的最小深度
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回它的最小深度 2.
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode *root) {
if (root == NULL)return 0;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return 1;
if (root->left == NULL)
return minDepth(root->right) + 1;
if (root->right == NULL)
return minDepth(root->left) + 1;
return min(minDepth(root->left), minDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
};
3.翻转二叉树
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/invert-binary-tree/
翻转一棵二叉树。
示例:
输入:
4
/ \
2 7
/ \ / \
1 3 6 9
输出:
4
/ \
7 2
/ \ / \
9 6 3 1
备注:
这个问题是受到 Max Howell 的 原问题 启发的 :
谷歌:我们90%的工程师使用您编写的软件(Homebrew),但是您却无法在面试时在白板上写出翻转二叉树这道题,这太糟糕了。
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode *invertTree(TreeNode *root) {
if (root == NULL)
return root;
swap(root->left, root->right);
invertTree(root->left);
invertTree(root->right);
return root;
}
};
4.相同的树
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/same-tree/
给定两个二叉树,编写一个函数来检验它们是否相同。
如果两个树在结构上相同,并且节点具有相同的值,则认为它们是相同的。
示例 1:
输入:
1 1
/ \ / \
2 3 2 3
[1,2,3], [1,2,3]
输出: true
示例 2:
输入:
1 1
/ \
2 2
[1,2], [1,null,2]
输出: false
示例 3:
输入:
1 1
/ \ / \
2 1 1 2
[1,2,1], [1,1,2]
输出: false
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSameTree(TreeNode *p, TreeNode *q) {
if (!p && !q)
return true;
if (p && q) {
return p->val == q->val &&
isSameTree(p->left, q->left) &&
isSameTree(p->right, q->right);
} else
return false;
}
};
5.对称二叉树
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/symmetric-tree/
给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。
例如,二叉树 [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] 是对称的。
1
/ \
2 2
/ \ / \
3 4 4 3
但是下面这个 [1,2,2,null,3,null,3] 则不是镜像对称的:
1
/ \
2 2
\ \
3 3
说明:
如果你可以运用递归和迭代两种方法解决这个问题,会很加分。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode *root) {
if (root == NULL)
return true;
return symmetric(root->left, root->right);
}
bool symmetric(TreeNode *p, TreeNode *q) {
if (!p && !q)
return true;
if (p && q) {
return p->val == q->val &&
symmetric(p->left, q->right) &&
symmetric(p->right, q->left);
}
return false;
}
};
6.完全二叉树的节点个数
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/count-complete-tree-nodes/
给出一个完全二叉树,求出该树的节点个数。
说明:
完全二叉树的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2 h 2^h 2h 个节点。
示例:
输入:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ /
4 5 6
输出: 6
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode *root) {
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int leftDepth = 0;
int rightDepth = 0;
TreeNode *p, *q;
p = root;
q = root;
while (p || q) {
if (p) {
leftDepth++;
p = p->left;
}
if (q) {
rightDepth++;
q = q->right;
}
}
if (leftDepth == rightDepth)
return (int) pow(2, leftDepth) - 1;
else
return countNodes(root->left) + countNodes(root->right) + 1;
}
};
7.平衡二叉树
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/balanced-binary-tree/
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:
一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1。
示例 1:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回 true 。
示例 2:
给定二叉树 [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4]
1
/ \
2 2
/ \
3 3
/ \
4 4
返回 false 。
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isBalanced(TreeNode *root) {
if (root == NULL)
return true;
int leftHeight = depth(root->left);
int rightHeight = depth(root->right);
return abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) <= 1 &&
isBalanced(root->left) &&
isBalanced(root->right);
}
int depth(TreeNode *root) {
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
return max(depth(root->left), depth(root->right)) + 1;
}
};
8.路径总和
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/path-sum/
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,判断该树中是否存在根节点到叶子节点的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22,
5
/ \
4 8
/ / \
11 13 4
/ \ \
7 2 1
返回 true, 因为存在目标和为 22 的根节点到叶子节点的路径 5->4->11->2。
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode *root, int sum) {
if (root == NULL)
return false;
if (!root->left && !root->right && root->val == sum)
return true;
return hasPathSum(root->left, sum - root->val) || hasPathSum(root->right, sum - root->val);
}
};
9.左叶子之和
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sum-of-left-leaves/
计算给定二叉树的所有左叶子之和。
示例:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
在这个二叉树中,有两个左叶子,分别是 9 和 15,所以返回 24
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode *root) {
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (isLeaf(root->left))
return root->left->val + sumOfLeftLeaves(root->right);
else
return sumOfLeftLeaves(root->left) + sumOfLeftLeaves(root->right);
}
bool isLeaf(TreeNode *node) {
if (node == NULL)
return false;
return !node->left && !node->right;
}
};
9.二叉树的所有路径
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-paths/
给定一个二叉树,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
输入:
1
/ \
2 3
\
5
输出: ["1->2->5", "1->3"]
解释: 所有根节点到叶子节点的路径为: 1->2->5, 1->3
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode *root) {
vector<string> res;
if (root == NULL)
return res;
if (!root->left && !root->right) {
res.push_back(to_string(root->val));
return res;
}
vector<string> leftStrs = binaryTreePaths(root->left);
for (int i = 0; i < leftStrs.size(); ++i)
res.push_back(to_string(root->val) + "->" + leftStrs[i]);
vector<string> rightStrs = binaryTreePaths(root->right);
for (int i = 0; i < rightStrs.size(); ++i)
res.push_back(to_string(root->val) + "->" + rightStrs[i]);
return res;
}
};
10.路径总和 II
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/path-sum-ii/
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,找到所有从根节点到叶子节点路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定如下二叉树,以及目标和sum = 22`,
5
/ \
4 8
/ / \
11 13 4
/ \ / \
7 2 5 1
返回:
[
[5,4,11,2],
[5,8,4,5]
]
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode *root, int sum) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
if (root == NULL)
return res;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
if (root->val == sum)
res.push_back(vector<int>{root->val});
else
return res;
vector<vector<int>> leftPath = pathSum(root->left, sum - root->val);
for (int i = 0; i < leftPath.size(); ++i) {
leftPath[i].insert(leftPath[i].begin(), root->val);
res.push_back(leftPath[i]);
}
vector<vector<int>> rightPath = pathSum(root->right, sum - root->val);
for (int i = 0; i < rightPath.size(); ++i) {
rightPath[i].insert(rightPath[i].begin(), root->val);
res.push_back(rightPath[i]);
}
return res;
}
};
11.求根到叶子节点数字之和
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sum-root-to-leaf-numbers/
给定一个二叉树,它的每个结点都存放一个 0-9 的数字,每条从根到叶子节点的路径都代表一个数字。
例如,从根到叶子节点路径 1->2->3 代表数字 123。
计算从根到叶子节点生成的所有数字之和。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
输入: [1,2,3]
1
/ \
2 3
输出: 25
解释:
从根到叶子节点路径 1->2 代表数字 12.
从根到叶子节点路径 1->3 代表数字 13.
因此,数字总和 = 12 + 13 = 25.
示例 2:
输入: [4,9,0,5,1]
4
/ \
9 0
/ \
5 1
输出: 1026
解释:
从根到叶子节点路径 4->9->5 代表数字 495.
从根到叶子节点路径 4->9->1 代表数字 491.
从根到叶子节点路径 4->0 代表数字 40.
因此,数字总和 = 495 + 491 + 40 = 1026.
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int sumNumbers(TreeNode *root) {
vector<vector<int>> paths = getPath(root);
int res = 0;
for (auto &path:paths) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = (int) path.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i)
sum += path[path.size() - 1 - i] * pow(10, i);
res += sum;
}
return res;
}
vector<vector<int>> getPath(TreeNode *root) {
vector<vector<int>> paths;
if (root == NULL)
return paths;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
paths.push_back(vector<int>{root->val});
vector<vector<int>> leftPaths = getPath(root->left);
for (int i = 0; i < leftPaths.size(); ++i) {
leftPaths[i].insert(leftPaths[i].begin(), root->val);
paths.push_back(leftPaths[i]);
}
vector<vector<int>> rightPaths = getPath(root->right);
for (int i = 0; i < rightPaths.size(); ++i) {
rightPaths[i].insert(rightPaths[i].begin(), root->val);
paths.push_back(rightPaths[i]);
}
return paths;
}
};
12.路径总和 III
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/path-sum-iii/
给定一个二叉树,它的每个结点都存放着一个整数值。
找出路径和等于给定数值的路径总数。
路径不需要从根节点开始,也不需要在叶子节点结束,但是路径方向必须是向下的(只能从父节点到子节点)。
二叉树不超过1000个节点,且节点数值范围是 [-1000000,1000000] 的整数。
示例:
root = [10,5,-3,3,2,null,11,3,-2,null,1], sum = 8
10
/ \
5 -3
/ \ \
3 2 11
/ \ \
3 -2 1
返回 3。和等于 8 的路径有:
- 5 -> 3
- 5 -> 2 -> 1
- -3 -> 11
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
// 在以root为根节点的二叉树中,寻找和为sum的路径,返回这样路径个数
int pathSum(TreeNode *root, int sum) {
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int res = findPath(root, sum);
res += pathSum(root->left, sum);
res += pathSum(root->right, sum);
return res;
}
private:
// 在以node为根节点的二叉树中,寻找包含node的路径,和为sum
// 返回这样的路径个数
int findPath(TreeNode *node, int sum) {
if (node == NULL)
return 0;
int res = 0;
if (node->val == sum)
res += 1;
res += findPath(node->left, sum - node->val);
res += findPath(node->right, sum - node->val);
return res;
}
};
13.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree/
给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
例如,给定如下二叉搜索树: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5]
_______6______
/ \
___2__ ___8__
/ \ / \
0 _4 7 9
/ \
3 5
示例 1:
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8
输出: 6
解释: 节点 2 和节点 8 的最近公共祖先是 6。
示例 2:
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4
输出: 2
解释: 节点 2 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是 2, 因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
说明:
所有节点的值都是唯一的。
p、q 为不同节点且均存在于给定的二叉搜索树中。
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode *lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode *root, TreeNode *p, TreeNode *q) {
if (root == NULL)
return nullptr;
if (p->val < root->val && q->val < root->val)
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
if (p->val > root->val && q->val > root->val)
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
return root;
}
};
14.验证二叉搜索树
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/validate-binary-search-tree/
给定一个二叉树,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
假设一个二叉搜索树具有如下特征:
- 节点的左子树只包含小于当前节点的数。
- 节点的右子树只包含大于当前节点的数。
- 所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
示例 1:
输入:
2
/ \
1 3
输出: true
示例 2:
输入:
5
/ \
1 4
/ \
3 6
输出: false
解释: 输入为: [5,1,4,null,null,3,6]。
根节点的值为 5 ,但是其右子节点值为 4 。
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidBST(TreeNode *root) {
return isBST(root, LONG_MIN, LONG_MAX);
}
bool isBST(TreeNode *root, long lower, long upper) {
if (root == NULL)
return true;
if (root->val <= lower || root->val >= upper)
return false;
return isBST(root->left, lower, root->val) && isBST(root->right, root->val, upper);
}
};
15.删除二叉搜索树中的节点
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/delete-node-in-a-bst/
给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root 和一个值 key,删除二叉搜索树中的 key 对应的节点,并保证二叉搜索树的性质不变。返回二叉搜索树(有可能被更新)的根节点的引用。
一般来说,删除节点可分为两个步骤:
- 首先找到需要删除的节点;
- 如果找到了,删除它。
说明: 要求算法时间复杂度为 O(h),h 为树的高度。
示例:
root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7]
key = 3
5
/ \
3 6
/ \ \
2 4 7
给定需要删除的节点值是 3,所以我们首先找到 3 这个节点,然后删除它。
一个正确的答案是 [5,4,6,2,null,null,7], 如下图所示。
5
/ \
4 6
/ \
2 7
另一个正确答案是 [5,2,6,null,4,null,7]。
5
/ \
2 6
\ \
4 7
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode *deleteNode(TreeNode *root, int key) {
if(root == NULL)
return NULL;
if(key < root->val){
root->left = deleteNode(root->left, key);
return root;
}else if(key > root->val){
root->right = deleteNode(root->right, key);
return root;
}else{
// key == root->val
if(root->left == NULL){
TreeNode *rightNode = root->right;
delete root;
return rightNode;
}
if(root->right == NULL){
TreeNode *leftNode = root->left;
delete root;
return leftNode;
}
TreeNode *successor = new TreeNode(minimum(root->right)->val);
successor->right = deleteMinNode(root->right);
successor->left = root->left;
delete root;
return successor;
}
}
TreeNode *minimum(TreeNode *root){
if(root == NULL || root->left == NULL)
return root;
return minimum(root->left);
}
TreeNode *deleteMinNode(TreeNode *root){
if(root == NULL)
return NULL;
if(root->left == NULL){
TreeNode *rightNode = root->right;
delete root;
return rightNode;
}
root->left = deleteMinNode(root->left);
return root;
}
};
16.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/convert-sorted-array-to-binary-search-tree/
将一个按照升序排列的有序数组,转换为一棵高度平衡二叉搜索树。
本题中,一个高度平衡二叉树是指一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1。
示例:
给定有序数组: [-10,-3,0,5,9],
一个可能的答案是:[0,-3,9,-10,null,5],它可以表示下面这个高度平衡二叉搜索树:
0
/ \
-3 9
/ /
-10 5
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode *sortedArrayToBST(vector<int> &nums) {
if (nums.size() == 0)
return NULL;
return sortedArrayToBST(nums, 0, (int) nums.size() - 1);
}
private:
TreeNode *sortedArrayToBST(vector<int> &nums, int begin, int end) {
if (begin > end)
return NULL;
if (begin == end)
return new TreeNode(nums[begin]);
int mid = (begin + end) / 2;
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root->left = sortedArrayToBST(nums, begin, mid - 1);
root->right = sortedArrayToBST(nums, mid + 1, end);
return root;
}
};
17.二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-bst/
给定一个二叉搜索树,编写一个函数 kthSmallest 来查找其中第 k 个最小的元素。
说明:
你可以假设 k 总是有效的,1 ≤ k ≤ 二叉搜索树元素个数。
示例 1:
输入: root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1
3
/ \
1 4
\
2
输出: 1
示例 2:
输入: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3
5
/ \
3 6
/ \
2 4
/
1
输出: 3
进阶:
如果二叉搜索树经常被修改(插入/删除操作)并且你需要频繁地查找第 k 小的值,你将如何优化 kthSmallest 函数?
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
private:
int k;
int count;
int res;
public:
int kthSmallest(TreeNode *root, int k) {
this->k = k;
this->count = 0;
this->res = 0;
inorder(root);
return res;
}
void inorder(TreeNode *root) {
if (root) {
inorder(root->left);
this->count++;
if (this->count == k) {
this->res = root->val;
return;
}
inorder(root->right);
}
}
};
18.二叉树的最近公共祖先
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
例如,给定如下二叉树: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
_______3______
/ \
___5__ ___1__
/ \ / \
6 _2 0 8
/ \
7 4
示例 1:
输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
输出: 3
解释: 节点 5 和节点 1 的最近公共祖先是节点 3。
示例 2:
输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4
输出: 5
解释: 节点 5 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是节点 5。因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
说明:
- 所有节点的值都是唯一的。
- p、q 为不同节点且均存在于给定的二叉树中。
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root == NULL || root == p || root == q)
return root;
TreeNode *left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
TreeNode *right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
if(left && right)
return root;
return left ?: right;
}
};
递归和回溯法
1. 电话号码的字母组合
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/letter-combinations-of-a-phone-number/
给定一个仅包含数字 2-9 的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。
给出数字到字母的映射如下(与电话按键相同)。注意 1 不对应任何字母。
示例:
输入:"23"
输出:["ad", "ae", "af", "bd", "be", "bf", "cd", "ce", "cf"].
说明:
尽管上面的答案是按字典序排列的,但是你可以任意选择答案输出的顺序。
代码:
class Solution {
private:
vector<string> res;
string letter[10] = {
"", // 0
"", // 1
"abc", // 2
"def", // 3
"ghi", // 4
"jkl", // 5
"mno", // 6
"pqrs", // 7
"tuv", // 8
"wxyz" //9
};
void findCombinations(const string &digits, int index, const string &s) {
if (index == digits.size()) {
res.push_back(s);
return;
}
char c = digits[index];
string letters = letter[c - '0'];
for (int i = 0; i < letters.size(); ++i)
findCombinations(digits, index + 1, s + letters[i]);
}
public:
vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) {
if (digits == "")
return res;
findCombinations(digits, 0, "");
return res;
}
};
2.复原IP地址
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/restore-ip-addresses/
给定一个只包含数字的字符串,复原它并返回所有可能的 IP 地址格式。
示例:
输入: "25525511135"
输出: ["255.255.11.135", "255.255.111.35"]
代码:
class Solution {
private:
vector<string> res;
string s;
public:
vector<string> restoreIpAddresses(string s) {
if (s.size() < 4 || s.size() > 12)
return res;
this->s = s;
dfs(0, "", 0);
return res;
}
// index : s从开始到末尾
// str : 当前暂存的字符,一旦符合ip规则,则存入res中
// order : 表示当前考虑的是ip中的第几个字段
void dfs(int index, string str, int order) {
if (order > 4)
return;
if (order == 4 && index == s.size()) {
res.push_back(str);
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i < 4; ++i) {
if (index + i > s.size())
return;
string field = s.substr((unsigned) index, (unsigned) i);
if (field[0] == '0' && field.size() > 1 || field.size() == 3 && stoi(field) > 255)
continue;
dfs(index + i, str + field + (order == 3 ? "" : "."), order + 1);
}
}
};
3.分割回文串
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-partitioning/
给定一个字符串 s,将 s 分割成一些子串,使每个子串都是回文串。
返回 s 所有可能的分割方案。
示例:
输入: "aab"
输出:
[
["aa","b"],
["a","a","b"]
]
代码:
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<string>> res;
bool isPalindrome(string s) {
int i = 0, j = (int) s.size() - 1;
while (i < j) {
if (s[i] != s[j])
return false;
i++;
j--;
}
return true;
}
void dfs(string s, int index, vector<string> &palindrome) {
if (index == s.size()) {
res.push_back(palindrome);
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < s.size(); i++) {
string str = s.substr((unsigned) index, (unsigned) i - index + 1);
if (isPalindrome(str)) {
palindrome.push_back(str);
dfs(s, i + 1, palindrome);
palindrome.pop_back();
}
}
}
public:
vector<vector<string>> partition(string s) {
vector<string> palindrome;
dfs(s, 0, palindrome);
return res;
}
};
4.全排列
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/permutations/
给定一个没有重复数字的序列,返回其所有可能的全排列。
示例:
输入: [1,2,3]
输出:
[
[1,2,3],
[1,3,2],
[2,1,3],
[2,3,1],
[3,1,2],
[3,2,1]
]
代码:
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<bool> used;
public:
vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int> &nums) {
used = vector<bool>(nums.size(), false);
vector<int> permutation;
generatePermutation(nums, 0, permutation);
return res;
}
void generatePermutation(const vector<int> &nums, int index, vector<int> &permutation) {
if (index == nums.size()) {
res.push_back(permutation);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
if (!used[i]) {
permutation.push_back(nums[i]);
used[i] = true;
generatePermutation(nums, index + 1, permutation);
permutation.pop_back();
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
};
5.全排列 II
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/permutations-ii/
给定一个可包含重复数字的序列,返回所有不重复的全排列。
示例:
输入: [1,1,2]
输出:
[
[1,1,2],
[1,2,1],
[2,1,1]
]
代码:
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<bool> used;
public:
vector<vector<int>> permuteUnique(vector<int> &nums) {
used = vector<bool>(nums.size(), false);
vector<int> permutation;
generatePermutation(nums, 0, permutation);
return res;
}
void generatePermutation(const vector<int> &nums, int index, vector<int> &permutation) {
if (index == nums.size()) {
res.push_back(permutation);
return;
}
unordered_set<int> numsUnique;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i)
if (!used[i])
numsUnique.insert(nums[i]);
for (auto &num : numsUnique) {
permutation.push_back(num);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i)
if (nums[i] == num && !used[i]) {
used[i] = true;
break;
}
generatePermutation(nums, index + 1, permutation);
permutation.pop_back();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i)
if (nums[i] == num && used[i]) {
used[i] = false;
break;
}
}
}
};
6. 组合
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combinations/
给定两个整数 n 和 k,返回 1 … n 中所有可能的 k 个数的组合。
示例:
输入: n = 4, k = 2
输出:
[
[2,4],
[3,4],
[2,3],
[1,2],
[1,3],
[1,4],
]
代码:
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<int>> res;
void generateCombination(int n, int k, int start, vector<int> &combination) {
if (combination.size() == k) {
res.push_back(combination);
return;
}
// 还有k-combination.size()个空位,所以,[i...n]中至少要有k-combination.size()个元素
// i最多为n-(k-combination.size())+1
for (int i = start; i <= n - (k - combination.size()) + 1; ++i) {
combination.push_back(i);
generateCombination(n, k, i + 1, combination);
combination.pop_back();
}
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> combine(int n, int k) {
if (k > n || n <= 0 || k <= 0)
return res;
vector<int> combination;
generateCombination(n, k, 1, combination);
return res;
}
};
7.组合总和
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum/
给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
说明:
所有数字(包括 target)都是正整数。
解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
输入: candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7`,
所求解集为:
[
[7],
[2,2,3]
]
示例 2:
输入: candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8`,
所求解集为:
[
[2,2,2,2],
[2,3,3],
[3,5]
]
代码:
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<int>> res;
void generateCombination(vector<int> &candidates, int target, int index, vector<int> &combination) {
if (target < 0)
return;
if (target == 0) {
res.push_back(combination);
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < candidates.size(); ++i) {
if (candidates[i] > target)
continue;
combination.push_back(candidates[i]);
generateCombination(candidates, target - candidates[i], i, combination);
combination.pop_back();
}
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum(vector<int> &candidates, int target) {
if (candidates.size() == 0)
return res;
vector<int> combination;
generateCombination(candidates, target, 0, combination);
return res;
}
};
8.组合总和 II
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum-ii/
给定一个数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。
说明:
所有数字(包括目标数)都是正整数。
解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
输入: candidates = [10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target = 8,
所求解集为:
[
[1, 7],
[1, 2, 5],
[2, 6],
[1, 1, 6]
]
示例 2:
输入: candidates = [2,5,2,1,2], target = 5,
所求解集为:
[
[1,2,2],
[5]
]
代码:
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<int>> res;
void generateCombination(vector<int> &candidates, int target, int index, vector<int> &combination) {
if (target < 0)
return;
if (target == 0) {
res.push_back(combination);
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < candidates.size(); ++i) {
if (i - 1 >= index && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1])
continue;
if (candidates[i] > target)
continue;
combination.push_back(candidates[i]);
generateCombination(candidates, target - candidates[i], i + 1, combination);
combination.pop_back();
}
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum2(vector<int> &candidates, int target) {
if (candidates.size() == 0 || target < 0)
return res;
vector<int> combination;
sort(candidates.begin(), candidates.end());
generateCombination(candidates, target, 0, combination);
return res;
}
};
9.子集
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/subsets/
给定一组不含重复元素的整数数组 nums,返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
说明: 解集不能包含重复的子集。
示例:
输入: nums = [1,2,3]
输出:
[
[3],
[1],
[2],
[1,2,3],
[1,3],
[2,3],
[1,2],
[]
]
代码:
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<int>> res;
void generateSubsets(vector<int> &nums, int index, vector<int> &subset) {
if (subset.size() == nums.size() - 1)
return;
for (int i = index; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
subset.push_back(nums[i]);
res.push_back(subset);
generateSubsets(nums, i + 1, subset);
subset.pop_back();
}
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> subsets(vector<int> &nums) {
res.push_back(vector<int>());
if (nums.size() == 0)
return res;
res.push_back(nums);
vector<int> subset;
generateSubsets(nums, 0, subset);
return res;
}
};
10.子集 II
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/subsets-ii/
给定一个可能包含重复元素的整数数组 nums,返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
说明: 解集不能包含重复的子集。
示例:
输入: [1,2,2]
输出:
[
[2],
[1],
[1,2,2],
[2,2],
[1,2],
[]
]
代码:
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<int>> res;
void generateSubsets(vector<int> &nums, int index, vector<int> &subset) {
if (subset.size() == nums.size() - 1)
return;
for (int i = index; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (i - 1 >= index && nums[i] == nums[i - 1])
continue;
subset.push_back(nums[i]);
res.push_back(subset);
generateSubsets(nums, i + 1, subset);
subset.pop_back();
}
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> subsetsWithDup(vector<int> &nums) {
res.push_back(vector<int>());
if (nums.size() == 0)
return res;
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
res.push_back(nums);
vector<int> subset;
generateSubsets(nums, 0, subset);
return res;
}
};
11.组合总和 III
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum-iii/
找出所有相加之和为 n 的 k 个数的组合。组合中只允许含有 1 - 9 的正整数,并且每种组合中不存在重复的数字。
说明:
- 所有数字都是正整数。
- 解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
输入: k = 3, n = 7
输出: [[1,2,4]]
示例 2:
输入: k = 3, n = 9
输出: [[1,2,6], [1,3,5], [2,3,4]]
代码:
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<int>> res;
void generateCombinationSum(int k, int n, int index, vector<int> &combination) {
if (n < 0)
return;
if (combination.size() == k && n == 0) {
res.push_back(combination);
return;
}
for (int i = index; i <= 9; ++i) {
if (i > n)
continue;
combination.push_back(i);
generateCombinationSum(k, n - i, i + 1, combination);
combination.pop_back();
}
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {
if (n <= 0 || k == 0)
return res;
vector<int> combination;
generateCombinationSum(k, n, 1, combination);
return res;
}
};
12.二进制手表
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-watch/
二进制手表顶部有 4 个 LED 代表小时(0-11),底部的 6 个 LED 代表分钟(0-59)。
例如,上面的二进制手表读取 “3:25”。
给定一个非负整数 n 代表当前 LED 亮着的数量,返回所有可能的时间。
案例:
输入: n = 1
返回: ["1:00", "2:00", "4:00", "8:00", "0:01", "0:02", "0:04", "0:08", "0:16", "0:32"]
注意事项:
- 输出的顺序没有要求。
- 小时不会以零开头,比如 “01:00” 是不允许的,应为 “1:00”。
- 分钟必须由两位数组成,可能会以零开头,比如 “10:2” 是无效的,应为 “10:02”。
代码:
class Solution {
private:
void generateSum(vector<int> &nums, int n, int index, vector<int> &combination, set<int> &set) {
if (n == 0) {
set.insert(0);
return;
}
if (combination.size() == n) {
int sum = 0;
for (auto &num:combination)
sum += num;
set.insert(sum);
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
combination.push_back(nums[i]);
generateSum(nums, n, i + 1, combination, set);
combination.pop_back();
}
}
public:
vector<string> readBinaryWatch(int num) {
vector<string> res;
vector<int> HOUR = {1, 2, 4, 8};
vector<int> MINUTE = {1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32};
for (int h = 0; h <= num; ++h) {
vector<int> hourCombination;
set<int> hourSet;
generateSum(HOUR, h, 0, hourCombination, hourSet);
int m = num - h;
vector<int> minuteCombination;
set<int> minuteSet;
generateSum(MINUTE, m, 0, minuteCombination, minuteSet);
for (auto hour:hourSet) {
if (hour > 11)
continue;
string hStr = to_string(hour);
for (auto minute:minuteSet) {
if (minute > 59)
continue;
string mStr = to_string(minute);
if (mStr.size() == 1)
mStr.insert(0, "0");
string time = hStr + ":" + mStr;
res.push_back(time);
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
13.单词搜索
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/word-search/
给定一个二维网格和一个单词,找出该单词是否存在于网格中。
单词必须按照字母顺序,通过相邻的单元格内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母不允许被重复使用。
示例:
board =
[
['A','B','C','E'],
['S','F','C','S'],
['A','D','E','E']
]
给定 word = “ABCCED”, 返回 true.
给定 word = “SEE”, 返回 true.
给定 word = “ABCB”, 返回 false.
代码:
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<int>> d = {{-1, 0},
{0, 1},
{1, 0},
{0, -1}};
int m, n;
vector<vector<bool>> visited;
bool inArea(int x, int y) {
return x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n;
}
bool searchWord(vector<vector<char>> &board, string word, int index, int startX, int startY) {
if (index == word.size() - 1)
return word[index] == board[startX][startY];
if (word[index] == board[startX][startY]) {
visited[startX][startY] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
vector<int> dir = d[i];
int newX = startX + dir[0];
int newY = startY + dir[1];
if (inArea(newX, newY) && !visited[newX][newY])
if (searchWord(board, word, index + 1, newX, newY))
return true;
}
visited[startX][startY] = false;
}
return false;
}
public:
bool exist(vector<vector<char>> &board, string word) {
m = (int) board.size();
n = (int) board[0].size();
visited = vector<vector<bool>>(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
if (searchWord(board, word, 0, i, j))
return true;
return false;
}
};
14.岛屿的个数
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/number-of-islands/
给定一个由 ‘1’(陆地)和 ‘0’(水)组成的的二维网格,计算岛屿的数量。一个岛被水包围,并且它是通过水平方向或垂直方向上相邻的陆地连接而成的。你可以假设网格的四个边均被水包围。
示例 1:
输入:
11110
11010
11000
00000
输出: 1
示例 2:
输入:
11000
11000
00100
00011
输出: 3
代码:
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<bool>> visited;
int m, n;
vector<vector<int>> d = {{-1, 0},
{0, 1},
{1, 0},
{0, -1}};
bool inArea(int x, int y) {
return x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n;
}
void dfs(vector<vector<char>> &grid, int x, int y) {
visited[x][y] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
vector<int> dir = d[i];
int newX = x + dir[0];
int newY = y + dir[1];
if (inArea(newX, newY) && grid[newX][newY] == '1' && !visited[newX][newY])
dfs(grid, newX, newY);
}
}
public:
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>> &grid) {
m = grid.size();
if (m == 0)
return 0;
n = grid[0].size();
int res = 0;
visited = vector<vector<bool>>(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
if (grid[i][j] == '1' && !visited[i][j]) {
res++;
dfs(grid, i, j);
}
return res;
}
};
15.被围绕的区域
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/surrounded-regions/
给定一个二维的矩阵,包含 ‘X’ 和 ‘O’(字母 O)。
找到所有被 ‘X’ 围绕的区域,并将这些区域里所有的 ‘O’ 用 ‘X’ 填充。
示例:
X X X X
X O O X
X X O X
X O X X
运行你的函数后,矩阵变为:
X X X X
X X X X
X X X X
X O X X
解释:
被围绕的区间不会存在于边界上,换句话说,任何边界上的 ‘O’ 都不会被填充为 ‘X’。 任何不在边界上,或不与边界上的 ‘O’ 相连的 ‘O’ 最终都会被填充为 ‘X’。如果两个元素在水平或垂直方向相邻,则称它们是“相连”的。
代码:
class Solution {
private:
int m, n;
vector<vector<bool>> visited;
vector<vector<int>> d = {{-1, 0},
{0, 1},
{1, 0},
{0, -1}};
bool inArea(int x, int y) {
return x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n;
}
void dfs(vector<vector<char>> &board, int x, int y) {
visited[x][y] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
vector<int> dir = d[i];
int newX = x + dir[0];
int newY = y + dir[1];
if (inArea(newX, newY) && board[newX][newY] == 'O' && !visited[newX][newY])
dfs(board, newX, newY);
}
}
public:
void solve(vector<vector<char>> &board) {
m = board.size();
if (m <= 2)
return;
n = board[0].size();
if (n <= 2)
return;
visited = vector<vector<bool>>(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (board[0][i] == 'O') {
dfs(board, 0, i);
}
if (board[m - 1][i] == 'O') {
dfs(board, m - 1, i);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < m - 1; ++i) {
if (board[i][0] == 'O') {
dfs(board, i, 0);
}
if (board[i][n - 1] == 'O') {
dfs(board, i, n - 1);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < m - 1; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j < n - 1; ++j) {
if (board[i][j] == 'O' && !visited[i][j])
board[i][j] = 'X';
}
}
}
};
16.太平洋大西洋水流问题
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/pacific-atlantic-water-flow/
给定一个 m x n 的非负整数矩阵来表示一片大陆上各个单元格的高度。“太平洋”处于大陆的左边界和上边界,而“大西洋”处于大陆的右边界和下边界。
规定水流只能按照上、下、左、右四个方向流动,且只能从高到低或者在同等高度上流动。
请找出那些水流既可以流动到“太平洋”,又能流动到“大西洋”的陆地单元的坐标。
提示:
- 输出坐标的顺序不重要
- m 和 n 都小于150
示例:
给定下面的 5x5 矩阵:
太平洋 ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
~ 1 2 2 3 (5) *
~ 3 2 3 (4) (4) *
~ 2 4 (5) 3 1 *
~ (6) (7) 1 4 5 *
~ (5) 1 1 2 4 *
* * * * * 大西洋
返回:
[[0, 4], [1, 3], [1, 4], [2, 2], [3, 0], [3, 1], [4, 0]] (上图中带括号的单元).
代码:
class Solution {
private:
int m, n;
vector<vector<int>> d = {{-1, 0},
{0, 1},
{1, 0},
{0, -1}};
vector<vector<bool>> flowPacific;
vector<vector<bool>> flowAtlantic;
bool inArea(int x, int y) {
return x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n;
}
void dfs(vector<vector<int>> &matrix, vector<vector<bool>> &flowOcean, int x, int y) {
flowOcean[x][y] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
vector<int> dir = d[i];
int newX = x + dir[0];
int newY = y + dir[1];
if (inArea(newX, newY) && !flowOcean[newX][newY] && matrix[newX][newY] >= matrix[x][y])
dfs(matrix, flowOcean, newX, newY);
}
}
public:
vector<pair<int, int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>> &matrix) {
vector<pair<int, int>> res;
m = matrix.size();
if (m == 0)
return res;
n = matrix[0].size();
flowPacific = vector<vector<bool>>(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
flowAtlantic = vector<vector<bool>>(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
// 太平洋
if (!flowPacific[0][i])
dfs(matrix, flowPacific, 0, i);
// 大西洋
if (!flowAtlantic[m - 1][i])
dfs(matrix, flowAtlantic, m - 1, i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
// 太平洋
if (!flowPacific[i][0])
dfs(matrix, flowPacific, i, 0);
// 大西洋
if (!flowAtlantic[i][n - 1])
dfs(matrix, flowAtlantic, i, n - 1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
if (flowPacific[i][j] && flowAtlantic[i][j])
res.push_back(make_pair(i, j));
return res;
}
};
17.N皇后
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/n-queens/
n 皇后问题研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。
上图为 8 皇后问题的一种解法。
给定一个整数 n,返回所有不同的 n 皇后问题的解决方案。
每一种解法包含一个明确的 n 皇后问题的棋子放置方案,该方案中 ‘Q’ 和 ‘.’ 分别代表了皇后和空位。
示例:
输入: 4
输出:
[
[".Q..", // 解法 1
"...Q",
"Q...",
"..Q."],
["..Q.", // 解法 2
"Q...",
"...Q",
".Q.."]
]
解释: 4 皇后问题存在两个不同的解法。
代码:
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<string>> res;
vector<bool> col;
vector<bool> dia1;
vector<bool> dia2;
vector<string> generateBoard(vector<int> &row) {
vector<string> board;
int n = row.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
string line(n, '.');
line[row[i]] = 'Q';
board.push_back(line);
}
return board;
}
void putQueen(int n, int index, vector<int> &row) {
if (index == n) {
res.push_back(generateBoard(row));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (!col[i] && !dia1[index + i] && !dia2[index - i + n - 1]) {
row[index] = i;
col[i] = true;
dia1[index + i] = true;
dia2[index - i + n - 1] = true;
putQueen(n, index + 1, row);
col[i] = false;
dia1[index + i] = false;
dia2[index - i + n - 1] = false;
}
}
}
public:
vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n) {
col = vector<bool>(n, false);
dia1 = vector<bool>(2 * n - 1, false);
dia2 = vector<bool>(2 * n - 1, false);
vector<int> row(n, 0);
putQueen(n, 0, row);
return res;
}
};
18.N皇后 II
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/n-queens-ii/
n 皇后问题研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。
上图为 8 皇后问题的一种解法。
给定一个整数 n,返回 n 皇后不同的解决方案的数量。
示例:
输入: 4
输出: 2
解释: 4 皇后问题存在如下两个不同的解法。
[
[".Q..", // 解法 1
"...Q",
"Q...",
"..Q."],
["..Q.", // 解法 2
"Q...",
"...Q",
".Q.."]
]
代码:
class Solution {
private:
int count;
vector<bool> col;
vector<bool> dia1;
vector<bool> dia2;
void putQueen(int n, int index) {
if (index == n) {
count++;
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (!col[i] && !dia1[index + i] && !dia2[index - i + n - 1]) {
col[i] = true;
dia1[index + i] = true;
dia2[index - i + n - 1] = true;
putQueen(n, index + 1);
col[i] = false;
dia1[index + i] = false;
dia2[index - i + n - 1] = false;
}
}
}
public:
int totalNQueens(int n) {
count = 0;
col = vector<bool>(n, false);
dia1 = vector<bool>(n, false);
dia2 = vector<bool>(n, false);
putQueen(n, 0);
return count;
}
};
19.解数独
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sudoku-solver/
编写一个程序,通过已填充的空格来解决数独问题。
一个数独的解法需遵循如下规则:
- 数字
1-9在每一行只能出现一次。 - 数字
1-9在每一列只能出现一次。 - 数字
1-9在每一个以粗实线分隔的3x3宫内只能出现一次。
空白格用'.'表示。
一个数独。
答案被标成红色。
Note:
- 给定的数独序列只包含数字 1-9 和字符 ‘.’ 。
- 你可以假设给定的数独只有唯一解。
- 给定数独永远是 9x9 形式的。
代码:
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<bool>> row;
vector<vector<bool>> col;
vector<vector<bool>> grid;
bool putNum(vector<vector<char>> &board, int index) {
while (index < 81 && board[index / 9][index % 9] != '.')index++;
if (index == 81)
return true;
int x = index / 9;
int y = index % 9;
for (int k = 0; k < 9; ++k) {
if (!row[x][k] && !col[y][k] && !grid[x / 3 * 3 + y / 3][k]) {
board[x][y] = (char) (k + 1 + '0');
row[x][k] = true;
col[y][k] = true;
grid[x / 3 * 3 + y / 3][k] = true;
if (putNum(board, index + 1))
return true;
board[x][y] = '.';
row[x][k] = false;
col[y][k] = false;
grid[x / 3 * 3 + y / 3][k] = false;
}
}
return false;
}
public:
void solveSudoku(vector<vector<char>> &board) {
row = vector<vector<bool>>(9, vector<bool>(9, false));
col = vector<vector<bool>>(9, vector<bool>(9, false));
grid = vector<vector<bool>>(9, vector<bool>(9, false));
for (int i = 0; i < 9; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < 9; ++j) {
char c = board[i][j];
if (c != '.') {
int num = c - '1';
row[i][num] = true;
col[j][num] = true;
grid[i / 3 * 3 + j / 3][num] = true;
}
}
putNum(board, 0);
}
};
动态规划
1.爬楼梯
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/climbing-stairs/
假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。
每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?
注意: 给定 n 是一个正整数。
示例 1:
输入: 2
输出: 2
解释: 有两种方法可以爬到楼顶。
- 1 阶 + 1 阶
- 2 阶
示例 2:
输入: 3
输出: 3
解释: 有三种方法可以爬到楼顶。
- 1 阶 + 1 阶 + 1 阶
- 1 阶 + 2 阶
- 2 阶 + 1 阶
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int climbStairs(int n) {
vector<int> stairs(n + 1);
stairs[0] = 0;
stairs[1] = 1;
stairs[2] = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; ++i) {
stairs[i] = stairs[i - 1] + stairs[i - 2];
}
return stairs[n];
}
};
2.最小路径和
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-path-sum/
给定一个包含非负整数的 m x n 网格,请找出一条从左上角到右下角的路径,使得路径上的数字总和为最小。
说明: 每次只能向下或者向右移动一步。
示例:
输入:
[
[1,3,1],
[1,5,1],
[4,2,1]
]
输出: 7
解释: 因为路径 1→3→1→1→1 的总和最小。
代码:
class Solution {
private:
public:
int minPathSum(vector<vector<int>> &grid) {
int m = grid.size();
if (m == 0)
return 0;
int n = grid[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> minPath = vector<vector<int>>(m, vector<int>(n, -1));
minPath[0][0] = grid[0][0];
for (int i = 1; i < m; ++i)
minPath[i][0] = minPath[i - 1][0] + grid[i][0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
minPath[0][i] = minPath[0][i - 1] + grid[0][i];
for (int i = 1; i < m; ++i)
for (int j = 1; j < n; ++j)
minPath[i][j] = min(minPath[i - 1][j], minPath[i][j - 1]) + grid[i][j];
return minPath[m - 1][n - 1];
}
};
3.三角形最小路径和
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/triangle/submissions/
给定一个三角形,找出自顶向下的最小路径和。每一步只能移动到下一行中相邻的结点上。
例如,给定三角形:
[
[2],
[3,4],
[6,5,7],
[4,1,8,3]
]
自顶向下的最小路径和为 11(即,2 + 3 + 5 + 1 = 11)。
说明:
如果你可以只使用 O(n) 的额外空间(n 为三角形的总行数)来解决这个问题,那么你的算法会很加分。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int minimumTotal(vector<vector<int>> &triangle) {
int m = triangle.size();
if (m == 0)
return 0;
vector<vector<int>> minTotal = vector<vector<int>>();
for (auto &level:triangle) {
int n = level.size();
minTotal.push_back(vector<int>(n, 0));
}
minTotal[0][0] = triangle[0][0];
for (int i = 1; i < m; ++i)
minTotal[i][0] = minTotal[i - 1][0] + triangle[i][0];
for (int i = 1; i < m; ++i)
minTotal[i][triangle[i].size() - 1] =
minTotal[i - 1][triangle[i - 1].size() - 1] + triangle[i][triangle[i].size() - 1];
for (int i = 2; i < m; ++i)
for (int j = 1; j < triangle[i].size() - 1; ++j)
minTotal[i][j] = min(minTotal[i - 1][j - 1], minTotal[i - 1][j]) + triangle[i][j];
int minimumTotal = minTotal[m - 1][0];
for (int i = 1; i < triangle[m - 1].size(); ++i)
if (minTotal[m - 1][i] < minimumTotal)
minimumTotal = minTotal[m - 1][i];
return minimumTotal;
}
};
3.整数拆分
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/integer-break/
给定一个正整数 n,将其拆分为至少两个正整数的和,并使这些整数的乘积最大化。 返回你可以获得的最大乘积。
示例 1:
输入: 2
输出: 1
解释: 2 = 1 + 1, 1 × 1 = 1。
示例 2:
输入: 10
输出: 36
解释: 10 = 3 + 3 + 4, 3 × 3 × 4 = 36。
说明: 你可以假设 n 不小于 2 且不大于 58。
代码:
class Solution {
private:
int max3(int a, int b, int c) {
return max(a, max(b, c));
}
public:
int integerBreak(int n) {
if (n <= 1)
return 0;
vector<int> memo = vector<int>(n + 1, -1);
memo[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i)
for (int j = 1; j <= i - 1; ++j)
memo[i] = max3(memo[i], j * (i - j), j * memo[i - j]);
return memo[n];
}
};
4.完全平方数
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/perfect-squares/
给定正整数 n,找到若干个完全平方数(比如 1, 4, 9, 16, ...)使得它们的和等于 n。你需要让组成和的完全平方数的个数最少。
示例 1:
输入: n = 12
输出: 3
解释: 12 = 4 + 4 + 4.
示例 2:
输入: n = 13
输出: 2
解释: 13 = 4 + 9.
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int numSquares(int n) {
vector<int> memo = vector<int>(n + 1, n);
memo[0] = 0;
memo[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i)
for (int j = 1; j <= sqrt(i); ++j)
memo[i] = min(memo[i], 1 + memo[i - j * j]);
return memo[n];
}
};
5.不同路径
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-paths/
一个机器人位于一个 m x n 网格的左上角 (起始点在下图中标记为“Start” )。
机器人每次只能向下或者向右移动一步。机器人试图达到网格的右下角(在下图中标记为“Finish”)。
问总共有多少条不同的路径?
例如,上图是一个7 x 3 的网格。有多少可能的路径?
说明: m 和 n 的值均不超过 100。
示例 1:
输入: m = 3, n = 2
输出: 3
解释:
从左上角开始,总共有 3 条路径可以到达右下角。
- 向右 -> 向右 -> 向下
- 向右 -> 向下 -> 向右
- 向下 -> 向右 -> 向右
示例 2:
输入: m = 7, n = 3
输出: 28
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
vector<vector<int>> memo = vector<vector<int>>(m, vector<int>(n, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
memo[i][0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
memo[0][i] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < m; ++i)
for (int j = 1; j < n; ++j)
memo[i][j] = memo[i - 1][j] + memo[i][j - 1];
return memo[m - 1][n - 1];
}
};
6.不同路径 II
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-paths-ii/
一个机器人位于一个 m x n 网格的左上角 (起始点在下图中标记为“Start” )。
机器人每次只能向下或者向右移动一步。机器人试图达到网格的右下角(在下图中标记为“Finish”)。
现在考虑网格中有障碍物。那么从左上角到右下角将会有多少条不同的路径?
网格中的障碍物和空位置分别用 1 和 0 来表示。
说明: m 和 n 的值均不超过 100。
示例 1:
输入:
[
[0,0,0],
[0,1,0],
[0,0,0]
]
输出: 2
解释:
3x3 网格的正中间有一个障碍物。
从左上角到右下角一共有 2 条不同的路径:
- 向右 -> 向右 -> 向下 -> 向下
- 向下 -> 向下 -> 向右 -> 向右
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int uniquePathsWithObstacles(vector<vector<int>> &obstacleGrid) {
int m = obstacleGrid.size();
if (m == 0)
return 0;
int n = obstacleGrid[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> memo = vector<vector<int>>(m, vector<int>(n, -1));
int k;
for (k = 0; k < m && obstacleGrid[k][0] != 1; ++k)
memo[k][0] = 1;
while (k < m)
memo[k++][0] = 0;
for (k = 0; k < n && obstacleGrid[0][k] != 1; ++k)
memo[0][k] = 1;
while (k < n)
memo[0][k++] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < m; ++i)
for (int j = 1; j < n; ++j)
if (obstacleGrid[i][j] == 1)
memo[i][j] = 0;
else
memo[i][j] = memo[i - 1][j] + memo[i][j - 1];
return memo[m - 1][n - 1];
}
};
7.解码方法
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/decode-ways/
一条包含字母 A-Z 的消息通过以下方式进行了编码:
‘A’ -> 1
‘B’ -> 2
…
‘Z’ -> 26
给定一个只包含数字的非空字符串,请计算解码方法的总数。
示例 1:
输入: "12"
输出: 2
解释: 它可以解码为 “AB”(1 2)或者 “L”(12)。
示例 2:
输入: "226"
输出: 3
解释: 它可以解码为 “BZ” (2 26), “VF” (22 6), 或者 “BBF” (2 2 6) 。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int numDecodings(string s) {
if (s.size() == 0)
return 0;
vector<int> decodeNum = vector<int>(s.size() + 1, 0);
decodeNum[0] = 1;
decodeNum[1] = s[0] == '0' ? 0 : 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= s.size(); ++i) {
if (s[i - 1] != '0')
decodeNum[i] = decodeNum[i - 1];
int num = stoi(s.substr(i - 2, 2));
if (num >= 10 && num <= 26)
decodeNum[i] += decodeNum[i - 2];
}
return decodeNum[s.size()];
}
};
8.打家劫舍
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/house-robber/
你是一个专业的小偷,计划偷窃沿街的房屋。每间房内都藏有一定的现金,影响你偷窃的唯一制约因素就是相邻的房屋装有相互连通的防盗系统,如果两间相邻的房屋在同一晚上被小偷闯入,系统会自动报警。
给定一个代表每个房屋存放金额的非负整数数组,计算你在不触动警报装置的情况下,能够偷窃到的最高金额。
示例 1:
输入: [1,2,3,1]
输出: 4
解释: 偷窃 1 号房屋 (金额 = 1) ,然后偷窃 3 号房屋 (金额 = 3)。
偷窃到的最高金额 = 1 + 3 = 4 。
示例 2:
输入: [2,7,9,3,1]
输出: 12
解释: 偷窃 1 号房屋 (金额 = 2), 偷窃 3 号房屋 (金额 = 9),接着偷窃 5 号房屋 (金额 = 1)。
偷窃到的最高金额 = 2 + 9 + 1 = 12 。
代码:
记忆化搜索:
class Solution {
private:
vector<int> memo;
int tryRob(vector<int> &nums, int index){
if(index >= nums.size())
return 0;
if(memo[index] != -1)
return memo[index];
int res = 0;
for(int i = index; i < nums.size(); i++)
res = max(res, nums[i] + tryRob(nums, i + 2));
memo[index] = res;
return res;
}
public:
int rob(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.size()==0)
return 0;
memo = vector<int>(nums.size(), -1);
return tryRob(nums, 0);
}
};
动态规划:
class Solution {
public:
int rob(vector<int> &nums) {
int n = nums.size();
if (n == 0)
return 0;
vector<int> memo(n, -1);
memo[n - 1] = nums[n - 1];
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
for (int j = i; j < n; j++)
memo[i] = max(memo[i], nums[j] + (j + 2 < n ? memo[j + 2] : 0));
return memo[0];
}
};
9.打家劫舍 II
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/house-robber-ii/
你是一个专业的小偷,计划偷窃沿街的房屋,每间房内都藏有一定的现金。这个地方所有的房屋都围成一圈,这意味着第一个房屋和最后一个房屋是紧挨着的。同时,相邻的房屋装有相互连通的防盗系统,如果两间相邻的房屋在同一晚上被小偷闯入,系统会自动报警。
给定一个代表每个房屋存放金额的非负整数数组,计算你在不触动警报装置的情况下,能够偷窃到的最高金额。
示例 1:
输入: [2,3,2]
输出: 3
解释: 你不能先偷窃 1 号房屋(金额 = 2),然后偷窃 3 号房屋(金额 = 2), 因为他们是相邻的。
示例 2:
输入: [1,2,3,1]
输出: 4
解释: 你可以先偷窃 1 号房屋(金额 = 1),然后偷窃 3 号房屋(金额 = 3)。
偷窃到的最高金额 = 1 + 3 = 4 。
代码:
记忆化搜索:
class Solution {
private:
int tryRob(vector<int> &nums, int index, int end, vector<int> &memo) {
int n = (int) nums.size();
if (index > end)
return 0;
if (memo[index] != -1)
return memo[index];
int res = 0;
for (int i = index; i <= end; ++i)
res = max(res, nums[i] + tryRob(nums, i + 2, end, memo));
memo[index] = res;
return res;
}
public:
int rob(vector<int> &nums) {
int n = (int) nums.size();
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n == 1)
return nums[0];
vector<int> memo1 = vector<int>(nums.size(), -1);
int num0 = tryRob(nums, 0, n - 2, memo1);
vector<int> memo2 = vector<int>(nums.size(), -1);
int num1 = tryRob(nums, 1, n - 1, memo2);
return max(num0, num1);
}
};
动态规划:
class Solution {
public:
int rob(vector<int> &nums) {
int n = (int) nums.size();
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n == 1)
return nums[0];
vector<int> memo1 = vector<int>(n, 0);
// 包含最后一个
memo1[n - 1] = nums[n - 1];
for (int i = n - 2; i > 0; --i)
for (int j = i; j < n; ++j)
memo1[i] = max(memo1[i], nums[j] + (j + 2 < n ? memo1[j + 2] : 0));
int res1 = memo1[1];
vector<int> memo2 = vector<int>(n, 0);
// 不包含最后一个
memo2[n - 1] = 0;
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; --i)
for (int j = i; j < n - 1; ++j)
memo2[i] = max(memo2[i], nums[j] + (j + 2 < n - 1 ? memo2[j + 2] : 0));
int res2 = memo2[0];
return max(res1, res2);
}
};
10.打家劫舍 III
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/house-robber-iii/
在上次打劫完一条街道之后和一圈房屋后,小偷又发现了一个新的可行窃的地区。这个地区只有一个入口,我们称之为“根”。 除了“根”之外,每栋房子有且只有一个“父“房子与之相连。一番侦察之后,聪明的小偷意识到“这个地方的所有房屋的排列类似于一棵二叉树”。 如果两个直接相连的房子在同一天晚上被打劫,房屋将自动报警。
计算在不触动警报的情况下,小偷一晚能够盗取的最高金额。
示例 1:
输入: [3,2,3,null,3,null,1]
3
/ \
2 3
\ \
3 1
输出: 7
解释: 小偷一晚能够盗取的最高金额 = 3 + 3 + 1 = 7.
示例 2:
输入: [3,4,5,1,3,null,1]
3
/ \
4 5
/ \ \
1 3 1
输出: 9
解释: 小偷一晚能够盗取的最高金额 = 4 + 5 = 9.
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
private:
int tryRob(TreeNode *root) {
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return root->val;
if (root->left == NULL)
return max(root->val + tryRob(root->right->left) + tryRob(root->right->right), tryRob(root->right));
if (root->right == NULL)
return max(root->val + tryRob(root->left->left) + tryRob(root->left->right), tryRob(root->left));
// 左右子树都不为空
// 加上根的值
int res1 = root->val + tryRob(root->left->left) + tryRob(root->left->right) +
tryRob(root->right->left) + tryRob(root->right->right);
// 不加上根的值
int res2 = tryRob(root->left) + tryRob(root->right);
return max(res1, res2);
}
public:
int rob(TreeNode *root) {
return tryRob(root);
}
};
11.最佳买卖股票时机含冷冻期
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-with-cooldown/
给定一个整数数组,其中第 i 个元素代表了第 i 天的股票价格 。
设计一个算法计算出最大利润。在满足以下约束条件下,你可以尽可能地完成更多的交易(多次买卖一支股票):
- 你不能同时参与多笔交易(你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票)。
- 卖出股票后,你无法在第二天买入股票 (即冷冻期为 1 天)。
示例:
输入: [1,2,3,0,2]
输出: 3
解释: 对应的交易状态为: [买入, 卖出, 冷冻期, 买入, 卖出]
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int> &prices) {
int n = (int) prices.size();
if (n <= 1)
return 0;
vector<int> have(n, 0);
vector<int> nohave(n, 0);
have[0] = -prices[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
// 今天有:①昨天有 ②今天买
have[i] = max(have[i - 1], (i - 2 >= 0 ? nohave[i - 2] : 0) - prices[i]);
// 今天没有:①昨天没有 ②今天卖
nohave[i] = max(nohave[i - 1], have[i - 1] + prices[i]);
}
return max(have[n - 1], nohave[n - 1]);
}
};
12. 01背包问题
代码:
记忆化搜索
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<int>> memo;
int bestValue(const vector<int> &w, const vector<int> &v, int index, int c) {
if (index < 0 || c <= 0)
return 0;
if (memo[index][c] != -1)
return memo[index][c];
int res = bestValue(w, v, index - 1, c);
if (c >= w[index])
res = max(res, v[index] + bestValue(w, v, index - 1, c - w[index]));
memo[index][c] = res;
return res;
}
public:
int knapsack01(const vector<int> &w, const vector<int> &v, int C) {
int n = (int) w.size();
memo = vector<vector<int>>(n, vector<int>(C + 1, -1));
return bestValue(w, v, n - 1, C);
}
};
动态规划:
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<int>> memo;
public:
int knapsack01(const vector<int> &w, const vector<int> &v, int C) {
int n = (int) w.size();
if (n == 0)
return 0;
memo = vector<vector<int>>(n, vector<int>(C + 1, -1));
for (int j = 0; j <= C; ++j)
memo[0][j] = (j >= w[0] ? v[0] : 0);
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j <= C; ++j) {
memo[i][j] = memo[i - 1][j];
if (j >= w[i])
memo[i][j] = max(memo[i - 1][j], v[i] + memo[i - 1][j - w[i]]);
}
return memo[n - 1][C];
}
};
动态规划优化1:
class Solution {
private:
public:
int knapsack01(const vector<int> &w, const vector<int> &v, int C) {
int n = (int) w.size();
if (n == 0)
return 0;
vector<vector<int>> memo = vector<vector<int>>(2, vector<int>(C + 1, -1));
for (int j = 0; j <= C; ++j)
memo[0][j] = (j >= w[0] ? v[0] : 0);
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j <= C; ++j) {
memo[i % 2][j] = memo[(i - 1) % 2][j];
if (j >= w[i])
memo[i % 2][j] = max(memo[(i - 1) % 2][j], v[i] + memo[(i - 1) % 2][j - w[i]]);
}
return memo[(n - 1) % 2][C];
}
};
动态规划优化2:
class Solution {
public:
int knapsack01(const vector<int> &w, const vector<int> &v, int C) {
int n = (int) w.size();
if (n == 0)
return 0;
vector<int> memo(C + 1, -1);
for (int j = 0; j <= C; ++j)
memo[j] = (j >= v[0] ? v[0] : 0);
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
for (int j = C; j >= w[i]; --j)
memo[j] = max(memo[j], v[i] + memo[j - w[i]]);
return memo[C];
}
};
13.分割等和子集
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/partition-equal-subset-sum/
给定一个只包含正整数的非空数组。是否可以将这个数组分割成两个子集,使得两个子集的元素和相等。
注意:
- 每个数组中的元素不会超过 100
- 数组的大小不会超过 200
示例 1:
输入: [1, 5, 11, 5]
输出: true
解释: 数组可以分割成 [1, 5, 5] 和 [11].
示例 2:
输入: [1, 2, 3, 5]
输出: false
解释: 数组不能分割成两个元素和相等的子集.
代码:
记忆化搜索:
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<int>> memo;
bool tryPartition(const vector<int> &nums, int index, int sum) {
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (index < 0 || sum < 0)
return false;
if (memo[index][sum] != -1)
return memo[index][sum] == 1;
memo[index][sum] =
tryPartition(nums, index - 1, sum) || tryPartition(nums, index - 1, sum - nums[index]) ? 1 : 0;
return memo[index][sum] == 1;
}
public:
bool canPartition(vector<int> &nums) {
int n = (int) nums.size();
if (n <= 1)
return false;
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i)
sum += nums[i];
if (sum % 2 == 1)
return false;
int C = sum / 2;
memo = vector<vector<int>>(n, vector<int>(C + 1, -1));
return tryPartition(nums, n - 1, C);
}
};
动态规划:
class Solution {
public:
bool canPartition(vector<int> &nums) {
int n = (int) nums.size();
if (n <= 1)
return false;
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i)
sum += nums[i];
if (sum % 2)
return false;
int C = sum / 2;
vector<vector<int>> memo = vector<vector<int>>(2, vector<int>(C + 1, -1));
for (int j = 0; j <= C; ++j)
memo[0][j] = (j == nums[0] ? 1 : 0);
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j <= C; ++j) {
memo[i % 2][j] = memo[(i - 1) % 2][j];
if (j >= nums[i])
memo[i % 2][j] = memo[(i - 1) % 2][j] || memo[(i - 1) % 2][j - nums[i]];
}
return memo[(n - 1) % 2][C] == 1;
}
};
动态规划优化:
class Solution {
public:
bool canPartition(vector<int> &nums) {
int n = (int) nums.size();
if (n <= 1)
return false;
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
sum += nums[i];
if (sum % 2)
return false;
int C = sum / 2;
vector<bool> memo(C + 1, false);
for (int i = 0; i <= C; ++i)
memo[i] = i == nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
for (int j = C; j >= nums[i]; --j)
memo[j] = memo[j] || memo[j - nums[i]];
return memo[C];
}
};
14.单词拆分
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/word-break/
给定一个非空字符串 s 和一个包含非空单词列表的字典 wordDict,判定 s 是否可以被空格拆分为一个或多个在字典中出现的单词。
说明:
拆分时可以重复使用字典中的单词。
你可以假设字典中没有重复的单词。
示例 1:
输入: s = "leetcode", wordDict = ["leet", "code"]
输出: true
解释: 返回 true 因为 "leetcode" 可以被拆分成 "leet code"。
示例 2:
输入: s = "applepenapple", wordDict = ["apple", "pen"]
输出: true
解释: 返回 true 因为 "applepenapple" 可以被拆分成 "apple pen apple"。
注意你可以重复使用字典中的单词。
示例 3:
输入: s = "catsandog", wordDict = ["cats", "dog", "sand", "and", "cat"]
输出: false
代码:
class Solution {
public:
bool wordBreak(string s, vector<string> &wordDict) {
int n = (int) s.size();
unordered_set<string> set(wordDict.begin(), wordDict.end());
vector<bool> memo(n + 1, false);
memo[0] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j)
if (memo[j] && set.find(s.substr(j, i - j)) != set.end()) {
memo[i] = true;
break;
}
return memo[n];
}
};
15. 零钱兑换
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/coin-change/
给定不同面额的硬币 coins 和一个总金额 amount。编写一个函数来计算可以凑成总金额所需的最少的硬币个数。如果没有任何一种硬币组合能组成总金额,返回 -1。
示例 1:
输入: coins = [1, 2, 5], amount = 11
输出: 3
解释: 11 = 5 + 5 + 1
示例 2:
输入: coins = [2], amount = 3
输出: -1
说明:
你可以认为每种硬币的数量是无限的。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int coinChange(vector<int> &coins, int amount) {
int n = (int) coins.size();
if (n == 0 || amount == 0)
return 0;
vector<int> memo(amount + 1, amount + 1);
memo[0] = 0;
sort(coins.begin(), coins.end());
for (int i = 1; i <= amount; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < n && i >= coins[j]; ++j)
memo[i] = min(memo[i], memo[i - coins[j]] + 1);
if (memo[amount] == amount + 1)
return -1;
return memo[amount];
}
};
16.组合总和 Ⅳ
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum-iv/
给定一个由正整数组成且不存在重复数字的数组,找出和为给定目标正整数的组合的个数。
示例:
nums = [1, 2, 3]
target = 4
所有可能的组合为:
(1, 1, 1, 1)
(1, 1, 2)
(1, 2, 1)
(1, 3)
(2, 1, 1)
(2, 2)
(3, 1)
请注意,顺序不同的序列被视作不同的组合。
因此输出为 7。
进阶:
如果给定的数组中含有负数会怎么样?
问题会产生什么变化?
我们需要在题目中添加什么限制来允许负数的出现?
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int combinationSum4(vector<int> &nums, int target) {
vector<int> memo(target + 1, 0);
memo[0] = 1;
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
for (int i = 1; i <= target; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < nums.size() && i >= nums[j]; ++j)
memo[i] += memo[i - nums[j]];
return memo[target];
}
};
17.一和零
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/ones-and-zeroes/
在计算机界中,我们总是追求用有限的资源获取最大的收益。
现在,假设你分别支配着 m 个 0 和 n 个 1。另外,还有一个仅包含 0 和 1 字符串的数组。
你的任务是使用给定的 m 个 0 和 n 个 1 ,找到能拼出存在于数组中的字符串的最大数量。每个 0 和 1 至多被使用一次。
注意:
- 给定 0 和 1 的数量都不会超过 100。
- 给定字符串数组的长度不会超过 600。
示例 1:
输入: Array = {"10", "0001", "111001", "1", "0"}, m = 5, n = 3
输出: 4
解释: 总共 4 个字符串可以通过 5 个 0 和 3 个 1 拼出,即 “10”,“0001”,“1”,“0” 。
示例 2:
输入: Array = {"10", "0", "1"}, m = 1, n = 1
输出: 2
解释: 你可以拼出 “10”,但之后就没有剩余数字了。更好的选择是拼出 “0” 和 “1” 。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int findMaxForm(vector<string>& strs, int m, int n) {
vector<vector<int>> dp(m+1, vector<int>(n+1, 0));
for(string &str:strs){
int len0 = 0, len1 = 0;
for(char &c:str)
if(c=='0')
len0++;
else
len1++;
for(int i = m;i>=len0;i--){
for(int j=n;j>=len1;j--){
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i-len0][j-len1]+1);
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
};
18.最长上升子序列
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-increasing-subsequence/
给定一个无序的整数数组,找到其中最长上升子序列的长度。
示例:
输入: [10,9,2,5,3,7,101,18]
输出: 4
解释: 最长的上升子序列是 [2,3,7,101],它的长度是 4。
说明:
- 可能会有多种最长上升子序列的组合,你只需要输出对应的长度即可。
- 你算法的时间复杂度应该为 O(n2) 。
进阶: 你能将算法的时间复杂度降低到 O(n log n) 吗?
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLIS(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
if(n == 0)
return 0;
vector<int> dp(n,1);
int res = 1;
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<i;j++)
if(nums[j]<nums[i]){
dp[i]=max(dp[i], dp[j]+1);
if(dp[i]>res)
res = dp[i];
}
return res;
}
};
19.摆动序列
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/wiggle-subsequence/
如果连续数字之间的差严格地在正数和负数之间交替,则数字序列称为摆动序列。第一个差(如果存在的话)可能是正数或负数。少于两个元素的序列也是摆动序列。
例如, [1,7,4,9,2,5] 是一个摆动序列,因为差值 (6,-3,5,-7,3) 是正负交替出现的。相反, [1,4,7,2,5] 和 [1,7,4,5,5] 不是摆动序列,第一个序列是因为它的前两个差值都是正数,第二个序列是因为它的最后一个差值为零。
给定一个整数序列,返回作为摆动序列的最长子序列的长度。 通过从原始序列中删除一些(也可以不删除)元素来获得子序列,剩下的元素保持其原始顺序。
示例 1:
输入: [1,7,4,9,2,5]
输出: 6
解释: 整个序列均为摆动序列。
示例 2:
输入: [1,17,5,10,13,15,10,5,16,8]
输出: 7
解释: 这个序列包含几个长度为 7 摆动序列,其中一个可为[1,17,10,13,10,16,8]。
示例 3:
输入: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
输出: 2
进阶:
你能否用 O(n) 时间复杂度完成此题?
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int wiggleMaxLength(vector<int> &nums) {
int n = (int) nums.size();
if (n == 0) return 0;
vector<pair<int, int>> memo(n, make_pair(1, 0));
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j)
if (nums[i] > nums[j] && memo[j].second != -1 && memo[j].first + 1 > memo[i].first)
memo[i] = make_pair(memo[j].first + 1, -1);
else if (nums[i] < nums[j] && memo[j].second != 1 && memo[j].first + 1 > memo[i].first)
memo[i] = make_pair(memo[j].first + 1, 1);
int res = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < memo.size(); ++i)
if (memo[i].first > res)
res = memo[i].first;
return res;
}
};
贪心算法
1.分发饼干
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/assign-cookies/
假设你是一位很棒的家长,想要给你的孩子们一些小饼干。但是,每个孩子最多只能给一块饼干。对每个孩子 i ,都有一个胃口值 gi ,这是能让孩子们满足胃口的饼干的最小尺寸;并且每块饼干 j ,都有一个尺寸 sj 。如果 sj >= gi ,我们可以将这个饼干 j 分配给孩子 i ,这个孩子会得到满足。你的目标是尽可能满足越多数量的孩子,并输出这个最大数值。
注意:
你可以假设胃口值为正。
一个小朋友最多只能拥有一块饼干。
示例 1:
输入: [1,2,3], [1,1]
输出: 1
**解释: **
你有三个孩子和两块小饼干,3个孩子的胃口值分别是:1,2,3。
虽然你有两块小饼干,由于他们的尺寸都是1,你只能让胃口值是1的孩子满足。
所以你应该输出1。
示例 2:
输入: [1,2], [1,2,3]
输出: 2
**解释: **
你有两个孩子和三块小饼干,2个孩子的胃口值分别是1,2。
你拥有的饼干数量和尺寸都足以让所有孩子满足。
所以你应该输出2.
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int findContentChildren(vector<int>& g, vector<int>& s) {
sort(g.begin(), g.end(), greater<int>());
sort(s.begin(), s.end(), greater<int>());
int res = 0;
int i = 0, j = 0;
while(i<s.size() && j<g.size()){
if(s[i]>=g[j]){
res++;
i++;
j++;
}else
j++;
}
return res;
}
};
2.判断子序列
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/is-subsequence/
给定字符串 s 和 t ,判断 s 是否为 t 的子序列。
你可以认为 s 和 t 中仅包含英文小写字母。字符串 t 可能会很长(长度 ~= 500,000),而 s 是个短字符串(长度 <=100)。
字符串的一个子序列是原始字符串删除一些(也可以不删除)字符而不改变剩余字符相对位置形成的新字符串。(例如,"ace"是"abcde"的一个子序列,而"aec"不是)。
示例 1:
s = "abc", t = "ahbgdc"
返回 true.
示例 2:
s = "axc", t = "ahbgdc"
返回 false.
后续挑战 :
如果有大量输入的 S,称作S1, S2, … , Sk 其中 k >= 10亿,你需要依次检查它们是否为 T 的子序列。在这种情况下,你会怎样改变代码?
代码:
class