TensorFlow笔记(11) GoolgeNet
TensorFlow笔记(11) GoolgeNet
- 1. Inception块
- 2. 数据读取
- 3. 构建模型
- 4. 训练模型
- 5. 评估模型
- 6. 模型预测
1. Inception块
根据 深度学习笔记(30) Inception网络 可以了解到
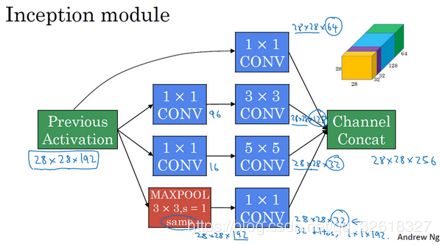
可以利用Inception块构建经典网络InceptionNet,也就是GoolgeNet

那么,以CIFAR-10 数据集的分类为例,采用GoolgeNet模型来解决问题
2. 数据读取
CIFAR-10 数据集的分类是机器学习中一个公开的基准测试问题
其任务是对一组32x32RGB的图像进行分类,这些图像涵盖了10个类别:
飞机, 汽车, 鸟, 猫, 鹿, 狗, 青蛙, 马, 船以及卡车

利用网上的 CIFAR-10 数据集 获取数据集压缩文件:

这里使用的是python版本 CIFAR-10 python version
-
载入数据集合:
import tensorflow as tf import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import os import urllib.request import tarfile import pickle as p from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder # 下载 cifar10 url = 'https://www.cs.toronto.edu/-kriz/cifar-10-python.tar.gz' filepath = '../data/cifar-10-python.tar.gz' if not os.path.isfile(filepath): result = urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, filepath) print('downloaded', result) else: print('Data file already exists.') # 解压 cifar10 if not os.path.exists("../data/cifar-10-batches-py"): tfile = tarfile.open("../data/cifar-10-python.tar.gz", 'r:gz') result = tfile.extractall("../data/") print('Extracted to ./../data/cifar-10-batches-py/') else: print('Directory already exists.') -
加载数据集
def load_CIFAR_batch(filename): """oad single batch of cifar""" with open(filename, 'rb')as f: # 一个样本由标签和图像数据组成 # <1 xlabel><3072 xpixel> (3072-32x32x3) data_dict = p.load(f, encoding='bytes') images = data_dict[b'data'] labels = data_dict[b'labels'] # 把原始数据结构调整为: BCWH images = images.reshape(10000, 3, 32, 32) # tensorflow处理图像数据的结构: BWHC # #把通道数据C移动到最后一个维度 images = images.transpose(0, 2, 3, 1) labels = np.array(labels) return images, labels def load_CIFAR_data(data_dir): """load CIFAR data""" images_train = [] labels_train = [] for i in range(5): f = os.path.join(data_dir, 'data_batch_{0}'.format(i + 1)) print('loading', f) # 调用loadCIFARbatch(获得批量的图像及其对应的标签 image_batch, label_batch = load_CIFAR_batch(f) images_train.append(image_batch) labels_train.append(label_batch) Xtrain = np.concatenate(images_train) Ytrain = np.concatenate(labels_train) del image_batch, label_batch Xtest, Ytest = load_CIFAR_batch(os.path.join(data_dir, 'test_batch')) print('finished loadding CIFAR-10 data') # 返回训练集的图象和标签,测试集的图像和标签 return Xtrain, Ytrain, Xtest, Ytest data_dir = '../data/cifar-10-batches-py/' Xtrain, Ytrain, Xtest, Ytest = load_CIFAR_data(data_dir) # loading ../data/cifar-10-batches-py/data_batch_1 # loading ../data/cifar-10-batches-py/data_batch_2 # loading ../data/cifar-10-batches-py/data_batch_3 # loading ../data/cifar-10-batches-py/data_batch_4 # loading ../data/cifar-10-batches-py/data_batch_5 # finished ../loadding CIFAR-10 data -
查看数据集数量
print('training data shape:', Xtrain.shape) print('training labels shape:', Ytrain.shape) print('test data shape:', Xtest.shape) print('test labels shape:', Ytest.shape) # training data shape: (50000, 32, 32, 3) # training labels shape: (50000,) # test data shape: (10000, 32, 32, 3) # test labels shape: (10000,)32x32 RGB3通道尺寸图片,训练图片50000张,测试图片10000张,
-
定义标签字典
对应类别信息查看:http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.htmllabel_dict = {0: "airplane", 1: "automobile", 2: "bird", 3: "cat", 4: "deer", 5: "dog", 6: "frog", 7: "horse", 8: "ship", 9: "truck"} -
查看第11张图片并查看对应的label
imshow_num = 10 plt.imshow(Xtrain[imshow_num]) plt.show() print("Xtrain[{0}] label:".format(imshow_num), label_dict[Ytrain[imshow_num]]) # Xtrain[10] label: deer -
图片进行数字标准化并对比数据
Xtrain_mean0 = np.mean(Xtrain.astype('float32')[:, :, :, 0]) Xtrain_mean1 = np.mean(Xtrain.astype('float32')[:, :, :, 1]) Xtrain_mean2 = np.mean(Xtrain.astype('float32')[:, :, :, 2]) Xtrain_mean = [Xtrain_mean0, Xtrain_mean1, Xtrain_mean2] Xtrain_std0 = np.std(Xtrain.astype('float32')[:, :, :, 0]) Xtrain_std1 = np.std(Xtrain.astype('float32')[:, :, :, 1]) Xtrain_std2 = np.std(Xtrain.astype('float32')[:, :, :, 2]) Xtrain_std = [Xtrain_std0, Xtrain_std1, Xtrain_std2] def data_norm(x, x_mean, x_std): x_norm = x.astype('float32') x_norm[:, :, :, 0] = (x_norm[:, :, :, 0] - x_mean[0]) / x_std[0] x_norm[:, :, :, 1] = (x_norm[:, :, :, 1] - x_mean[1]) / x_std[1] x_norm[:, :, :, 2] = (x_norm[:, :, :, 2] - x_mean[2]) / x_std[2] return x_norm Xtrain_norm = data_norm(Xtrain, Xtrain_mean, Xtrain_std) Xtest_norm = data_norm(Xtest, Xtrain_mean, Xtrain_std) # 对比图像数据 print("Xtrain[0][0][0] data:", Xtrain[0][0][0]) print("Xtrain_norm[0][0][0] data:", Xtrain_norm[0][0][0]) # Xtrain[0][0][0] data: [59 62 63] # Xtrain_normalize[0][0][0] data: [-1.0526042 -0.9816644 -0.7625441]现在标准化过的数据Xtrain_norm的对应的32x32x3个像素均值为0,标准差为1
测试集的标准化设置的均值和方差需以训练集为准
不然训练的模型对测试图片作用就没那么好了 -
标签数据处理并对比数据
encoder = OneHotEncoder(sparse=False, categories='auto') yy = [[0], [1], [2], [3], [4], [5], [6], [7], [8], [9]] encoder.fit(yy) Ytrain_reshape = Ytrain.reshape(-1, 1) Ytrain_onehot = encoder.transform(Ytrain_reshape) Ytest_reshape = Ytest.reshape(-1, 1) Ytest_onehot = encoder.transform(Ytest_reshape) print("Ytrain[10] data:", Ytrain[10]) print("Ytrain_onehot[10] data:", Ytrain_onehot[10]) # Ytrain[10] data: 4 # Ytrain_onehot[10] data: [0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]现在的标签数据Ytrain_onehot,Ytest_onehot 已采用独热编码形式
3. 构建模型
-
定义训练数据的占位符, x是32x32x3个像素点的特征值, y是10分类的标签值:
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 32, 32, 3], name="X") y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10], name="Y")shape中 None 表示行的数量未知
在实际训练时决定一次代入多少行样本 -
展开图片 x
为了使用卷积层,需把x变成一个4d向量
其第1维对应样本数, -1表示任意数量
其第2、第3维对应图片的宽、高,最后一维代表图片的颜色通道数x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 32, 32, 3]) -
定义权重初始化函数:
- 定义权重W 初始化函数 :从标准差0.1的截断正态分布中输出随机值
标准正态分布生生成的数据在负无穷到正无穷
但是截断式正态分布生成的数据在均值-2倍的标准差,均值+2倍的标准差这个范围内def weight_variable(shape): initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1) return tf.Variable(initial) - 定义权重b 初始化函数 :数值为0.1
def bias_variable(shape): initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape) return tf.Variable(initial) - 定义 卷积 函数:
TensorFow的卷积函数:# 定义1步长的 same卷积 def conv2d(x, W): return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') # 定义1步长的 valid卷积 def conv2d_v(x, W): return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='VALID') # 定义2步长的 same卷积 def conv2d_2(x, W): return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')tf.nn.conv2d()用法可在TensorFlow笔记(8) LeNet-5卷积神经网络中查看 - 定义 池化 函数:
TensorFow的池化函数:平均池化# 定义步长为1 大小3x3的 max pooling def max_pool_3x3(x): return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') # 定义步长为2 大小3x3的 max pooling def max_pool_3x3_2(x): return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME') # 定义步长为3 大小5x5的 avg pooling def avg_pool_5x5(x): return tf.nn.avg_pool(x, ksize=[1, 5, 5, 1], strides=[1, 3, 3, 1], padding='VALID') # 定义步长为1 大小7x7的 avg pooling def avg_pool_7x7(x): return tf.nn.avg_pool(x, ksize=[1, 7, 7, 1], strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='VALID')tf.nn.avg_pool()与最大池化tf.nn.max_pool()用法相似
同样可在TensorFlow笔记(8) LeNet-5卷积神经网络中查看
- 定义权重W 初始化函数 :从标准差0.1的截断正态分布中输出随机值
-
def inception(x, channel_in, filters_num): # 第一分支 conv 1x1+1s with tf.variable_scope("branch1"): branch1_w_conv1 = weight_variable([1, 1, channel_in, filters_num[0]]) branch1_b_conv1 = bias_variable([filters_num[0]]) branch1_h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x, branch1_w_conv1) + branch1_b_conv1) # 第二分支 conv 1x1+1s > conv 3x3+1s with tf.variable_scope("branch2"): branch2_w_conv1 = weight_variable([1, 1, channel_in, filters_num[1]]) branch2_b_conv1 = bias_variable([filters_num[1]]) branch2_h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x, branch2_w_conv1) + branch2_b_conv1) branch2_w_conv2 = weight_variable([3, 3, filters_num[1], filters_num[2]]) branch2_b_conv2 = bias_variable([filters_num[2]]) branch2_h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(branch2_h_conv1, branch2_w_conv2) + branch2_b_conv2) # 第三分支 conv 1x1+1s > conv 5x5+1s with tf.variable_scope("branch3"): branch3_w_conv1 = weight_variable([1, 1, channel_in, filters_num[3]]) branch3_b_conv1 = bias_variable([filters_num[3]]) branch3_h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x, branch3_w_conv1) + branch3_b_conv1) branch3_w_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, filters_num[3], filters_num[4]]) branch3_b_conv2 = bias_variable([filters_num[4]]) branch3_h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(branch3_h_conv1, branch3_w_conv2) + branch3_b_conv2) # 第四分支 max_pool 3x3+1s > conv 1x1+1s with tf.variable_scope("branch4"): branch4_pool1 = max_pool_3x3(x) branch4_w_conv1 = weight_variable([1, 1, channel_in, filters_num[5]]) branch4_b_conv1 = bias_variable([filters_num[5]]) branch4_h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(branch4_pool1, branch4_w_conv1) + branch4_b_conv1) # 输出叠加 with tf.variable_scope("depth_concat"): concat = tf.concat([branch1_h_conv1, branch2_h_conv2, branch3_h_conv2, branch4_h_conv1], axis=3) return concat -
第一二层:压缩图片
第一二层为什么混着来呢,因为其实作用都是调整和预处理图片
以确保第一次进入inception块时为28x28x192的尺寸

而cifar10图片尺寸较小,为配合后续的计算,调整一些原有结构压缩成28x28x192# 第一层 w_conv1 = weight_variable([3, 3, 3, 64]) b_conv1 = bias_variable([64]) h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d_v(x_image, w_conv1) + b_conv1) h_pool1 = max_pool_3x3(h_conv1) hh_lrn1 = tf.nn.lrn(h_pool1, 4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9.0, beta=0.75) # 第二层 w_conv2 = weight_variable([1, 1, 64, 64]) b_conv2 = bias_variable([64]) h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(hh_lrn1, w_conv2) + b_conv2) w_conv3 = weight_variable([3, 3, 64, 192]) b_conv3 = bias_variable([192]) h_conv3 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d_v(h_conv2, w_conv3) + b_conv3) h_lrn2 = tf.nn.lrn(h_conv3, 4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9.0, beta=0.75) h_pool2 = max_pool_3x3(h_lrn2)TensorFow的局部响应归一化函数:
tf.nn.lrn()的使用可在 TensorFlow笔记(9) ResNet 中查看 -
第三阶段 inception3

第三阶段的过程:Previous Activation > inception 3a > inception 3b > max_pool 3x3+2s# inception 3a:conv 1x1 64 + conv 1x1 96 > conv 3x3 128 + conv 1x1 16 > conv 3x3 32 + max_pool 3x3 > conv 3x3 32 filters_num_3a = [64, 96, 128, 16, 32, 32] # 设置inception 3a的通道数 inception_3a = inception(h_pool2, 192, filters_num_3a) # inception 3b:conv 1x1 128 + conv 1x1 128 > conv 3x3 192 + conv 1x1 32 > conv 3x3 96 + max_pool 3x3 > conv 3x3 64 filters_num_3b = [128, 128, 192, 32, 96, 64] inception_3b = inception(inception_3a, 256, filters_num_3b) h_pool3 = max_pool_3x3_2(inception_3b) -
第四阶段 inception4

第四阶段的过程:Previous Activation > inception 4a > inception 4b > inception 4c+(softmax0) > inception 4d > inception 4e+(softmax1) > max_pool 3x3+2s# inception 4a filters_num_4a = [192, 96, 208, 16, 48, 64] inception_4a = inception(h_pool3, 480, filters_num_4a) # inception 4b filters_num_4b = [160, 112, 224, 24, 64, 64] inception_4b = inception(inception_4a, 512, filters_num_4b) # softmax0 h_pool4 = avg_pool_5x5(inception_4a) # > conv 1x1 128 w_conv4 = weight_variable([1, 1, 512, 128]) b_conv4 = bias_variable([128]) h_conv4 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool4, w_conv4) + b_conv4) h_flat1 = tf.reshape(h_conv4, shape=[-1, 4 * 4 * 128]) # 重新展开 # > fc 1x1 1024 W_fc1 = weight_variable([4 * 4 * 128, 1024]) b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024]) h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_flat1, W_fc1) + b_fc1) # > fc 1x1 10 dropout_rate0 = tf.placeholder("float") h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, rate=dropout_rate0) W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024, 10]) b_fc2 = bias_variable([10]) h_fc2 = tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, W_fc2) + b_fc2 # > softmax0 pred0 = tf.nn.softmax(h_fc2) # inception 4c filters_num_4c = [128, 128, 256, 24, 64, 64] inception_4c = inception(inception_4b, 512, filters_num_4c) # inception 4d filters_num_4d = [112, 144, 288, 32, 64, 64] inception_4d = inception(inception_4c, 512, filters_num_4d) # inception 4e filters_num_4e = [256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128] inception_4e = inception(inception_4d, 528, filters_num_4e) h_pool5 = max_pool_3x3_2(inception_4e) # softmax1 h_pool6 = avg_pool_5x5(inception_4d) # > conv 1x1 128 w_conv5 = weight_variable([1, 1, 528, 128]) b_conv5 = bias_variable([128]) h_conv5 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool6, w_conv5) + b_conv5) h_flat2 = tf.reshape(h_conv5, shape=[-1, 4 * 4 * 128]) # 重新展开 # > fc 1x1 1024 W_fc3 = weight_variable([4 * 4 * 128, 1024]) b_fc3 = bias_variable([1024]) h_fc3 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_flat2, W_fc3) + b_fc3) # > fc 1x1 10 dropout_rate1 = tf.placeholder("float") h_fc3_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, rate=dropout_rate1) W_fc4 = weight_variable([1024, 10]) b_fc4 = bias_variable([10]) h_fc4 = tf.matmul(h_fc3_drop, W_fc4) + b_fc4 # > softmax1 pred1 = tf.nn.softmax(h_fc4)TensorFow的dropout 函数:
tf.nn.dropout()的使用可在TensorFlow笔记(9) ResNet中查看 -
第五阶段 最终输出

第五阶段的过程:inception 5a > inception 5b > avg_pool_7x7 > softmax2# inception 5a filters_num_5a = [256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128] inception_5a = inception(h_pool5, 832, filters_num_5a) # inception 5b filters_num_5b = [384, 192, 384, 48, 128, 128] inception_5b = inception(inception_5a, 832, filters_num_5b) # avg_pool_7x7 h_pool7 = avg_pool_7x7(inception_5b) h_flat3 = tf.reshape(h_pool7, shape=[-1, 1 * 1 * 1024]) # 重新展开 # softmax2 dropout_rate2 = tf.placeholder("float") h_pool7_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_flat3, rate=dropout_rate2) W_fc5 = weight_variable([1024, 10]) b_fc5 = bias_variable([10]) h_fc5 = tf.matmul(h_pool7_drop, W_fc5) + b_fc2 pred2 = tf.nn.softmax(h_fc5) -
整合softmax
forward = h_fc5 + h_fc4 * 0.3 + h_fc2 * 0.3 pred = pred2 + pred1 * 0.3 + pred0 * 0.3 -
定义损失函数
使用TensoFlow提供的结合Softmax的交叉熵损失函数定义方法:softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2
交叉熵损失函数其实就是逻辑回归损失函数的前半部 − y ∗ l o g ( p r e d ) - y * log(pred) −y∗log(pred)
忽略了 − ( 1 − y ) ∗ l o g ( 1 − p r e d ) -(1 - y) * log(1 - pred) −(1−y)∗log(1−pred)with tf.name_scope("LossFunction"): loss_function = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2(logits=forward, labels=y))
4. 训练模型
-
设置超参数:
train_epochs = 20 # 迭代次数 learning_rate = 0.001 # 学习率 -
定义Adam优化器,设置学习率和优化目标损失最小化:
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(loss_function) -
定义预测类别匹配情况
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1))tf.equal(A, B) :对比这两个矩阵或者向量的相等的元素,相等返回 True,相反返回 False
tf.argmax(input,axis) :根据axis取值的不同返回每行或者每列最大值的索引,axis 表示维度,0:第一维度(行),1:第二维度(列),-1:最后一个维度
其实,这里的最终求得的索引,恰好就表示图片上的数字 -
定义准确率,将布尔值转化成浮点数,再求平均值
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) -
读取模型与创建会话:
# 定义保存模型 saver = tf.train.Saver() save_dir = "../save_path/GoogleNet/" # 定义保存模型编号 save_step = 0 # 恢复保存模型 ckpt_dir = tf.train.latest_checkpoint(save_dir) sess = tf.Session() # 建立会话 if ckpt_dir != None: saver.restore(sess, ckpt_dir) print("Finished loading", ckpt_dir) save_step = int(input("Set the load save step:")) else: # 变量初始化 sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables()) print("Finished initialize")关于如何保存模型,可在TensorFlow笔记(10) CheckPoint中查看
如果是读取模型继续训练时,例如最近保存的是序号12的模型# Finished loading ../save_path/GoogleNet/model-12 Set the load save step:则输入现在加载的模型序号12,然后回车,之后的训练保存的模型就从13开始
Set the load save step:12 -
设置批次大小和数量:
如果在处理完整个5万个训练图片的训练集之后才进行一次训练
这样的处理速度相对缓慢
如果在处理完整个5万个训练图片的训练集之前先让梯度下降法处理一部分
算法速度会更快
可以把训练集分割为小一点的子集训练
如128张训练图片,然后就进行梯度下降法处理
这种梯度下降法处理方法称之为Mini-batch 梯度下降
具体可参考深度学习笔记(9) 优化算法(一)# 每个批次的大小,每次放入的大小,每次放入 128张图片 以矩阵的方式 batch_size = 128 # 计算一共有多少个批次,数量整除大小训练出有多少批次 n_batch = len(Ytrain_onehot) // batch_size # 定义显示训练过程中验证的间隔批量次数 display_test_num = n_batch // 10 # 定义显示训练过程.的间隔批量次数 display_train_num = display_test_num // 10 # 定义批次训练数据的占位符 x_batch = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 32, 32, 3], name="X_batch") # 随机上下翻转批次图片 Xtrain_batch_up = tf.image.random_flip_up_down(x_batch) # 随机左右翻转批次图片 Xtrain_batch_lf = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(Xtrain_batch_up) # 对角旋转批次图片 # Xtrain_batch_tp = tf.image.transpose_image(x_batch) # 定义训练集批次函数 def get_train_batch(num, size): Xtrain_batch = Xtrain_norm_shuffle[num * size:(num + 1) * size] Ytrain_batch = Ytrain_onehot_shuffle[num * size:(num + 1) * size] # 随机翻转数据 with tf.Session() as sess_batch: Xtrain_batch = sess_batch.run(Xtrain_batch_lf, feed_dict={x_batch: Xtrain_batch}) return Xtrain_batch, Ytrain_batch -
批次迭代训练,其中 dropout 随机丢弃的概率都为0.4,显示迭代过程中的信息:
for epoch in range(train_epochs): # 打乱训练数据集 index = [i for i in range(len(Ytrain_onehot))] random.shuffle(index) Xtrain_norm_shuffle = Xtrain_norm[index] Ytrain_onehot_shuffle = Ytrain_onehot[index] # 批次迭代训练 for batch in range(0, n_batch): xs, ys = get_train_batch(batch, batch_size) sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={x: xs, y: ys, dropout_rate0: 0.4, dropout_rate1: 0.4, dropout_rate2: 0.4}) if (batch + 1) % display_train_num == 0: print(".", end="") if (batch + 1) % display_test_num == 0: # 保存模型 save_step += 1 save_path = saver.save(sess, save_dir + "model", global_step=save_step) print("Complete save ", save_path) # 批次训练完成之后,使用测试数据计算误差与准确率 loss, acc = sess.run([loss_function, accuracy], feed_dict={x: Xtest_norm[0:512], y: Ytest_onehot[0:512], dropout_rate0: 0, dropout_rate1: 0, dropout_rate2: 0}) learning_rate = 0.95 * learning_rate # 学习率衰减 # ..........Complete save D:/save_path/GoogleNet/model-1 # TrainEpoch= 01 TrainBatch= 0039 Loss= 1.958486080 TestAccuracy= 0.1973 # ... # ..........Complete save D:/save_path/GoogleNet/model-10 # TrainEpoch= 01 TrainBatch= 0390 Loss= 1.628237653 TestAccuracy= 0.4268 # ... # ..........Complete save D:/save_path/GoogleNet/model-200 # TrainEpoch= 20 TrainBatch= 0390 Loss= 0.510145028 TestAccuracy= 0.8166数据训练量比较大,而设备有限,为了保护设备而断断续续的训练
过一遍数据,抽取测试集前512张图片分类的准确率到达42.68%
最后一共历遍训练集20次,抽取测试集前512张图片分类的准确率到达 81.66%
5. 评估模型
测试集上评估模型预测的准确率
test_total_batch = int(len(Xtest_norm) / batch_size)
test_acc_sum = 0.0
for i in range(test_total_batch):
test_image_batch = Xtest_norm[i * batch_size:(i + 1) * batch_size]
test_label_batch = Ytest_onehot[i * batch_size:(i + 1) * batch_size]
test_batch_acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: test_image_batch,
y: test_label_batch,
dropout_rate0: 0,
dropout_rate1: 0,
dropout_rate2: 0})
test_acc_sum += test_batch_acc
test_acc = float(test_acc_sum / test_total_batch)
print("Test accuracy:{:.6f}".format(test_acc))
# Test accuracy:0.807292
测试集的准确率达到80%
6. 模型预测
-
查看预测结果
# 转换第201-210张测试图片pred预测结果独热编码格式为数字0-9 prediction_result = sess.run(tf.argmax(pred, 1), feed_dict={x: Xtest_normalize[200:210], dropout_rate0: 0, dropout_rate1: 0, dropout_rate2: 0}) # 查看第201-210张测试图片的预测结果 print(prediction_result) # [5 1 8 7 1 3 0 5 7 9]但是这样没办法知道,预测的到底是不是正确的
-
预测结果可视化比对
定义可视化函数:def plot_images_labels_prediction(images, labels, prediction, idx, num=10): fig = plt.gcf() fig.set_size_inches(12, 6) if num > 10: num = 10 for i in range(0, num): ax = plt.subplot(2, 5, 1 + i) ax.imshow(images[idx], cmap="binary") title = str(i) + ',' + label_dict[labels[idx]] if len(prediction) > 0: title += '=>' + label_dict[prediction[i]] ax.set_title(title, fontsize=10) idx += 1 plt.show() -
可视化第201-210张测试图片的预测结果对比
plot_images_labels_prediction(Xtest, Ytest, rediction_result, 200, 10)这次的预测都判断正确,还行。
[1] python的代码地址:
https://github.com/JoveH-H/TensorFlow/blob/master/py/8.GoogleNet.py
[2] jupyter notebook的代码地址:
https://github.com/JoveH-H/TensorFlow/blob/master/ipynb/8.GoolgeNet.ipynb
[3] MNIST 数据集 t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html
相关推荐:
深度学习笔记(30) Inception网络
深度学习笔记(26) 卷积神经网络
TensorFlow笔记(10) CheckPoint
TensorFlow笔记(9) ResNet
TensorFlow笔记(8) LeNet-5卷积神经网络
谢谢!


