【C#】C#进阶笔记
文章目录
- 1. 特性(Attribute)
- 1.1 预定义特性
- 1.1.1 AttributeUsage
- 1.1.2 Conditional
- 1.1.3 Obsolete
- 1.2 自定义特性
- 2.反射(Reflection)
- 2.1 优缺点
- 2.2 反射的用途
- 2.3 使用反射来查看特性(attribute)信息
- 3. 属性(Property)
- 3.1 抽象属性
- 4. 索引器(Indexer)
接下来是C#的进阶教程了,仍然是杂七杂八并不全面的随笔。
1. 特性(Attribute)
特性(Attribute)是用于在运行时传递程序中各种元素(比如类、方法、结构、枚举、组件等)的行为信息的声明性标签。您可以通过使用特性向程序添加声明性信息。
特性(Attribute)用于添加元数据,如编译器指令和注释、描述、方法、类等其他信息。
1.1 预定义特性
1.1.1 AttributeUsage
描述了如何使用一个自定义特性类。它规定了特性可应用到的项目的类型。语法如下:
[AttributeUsage(
// 规定特性可被放置的语言元素。它是枚举器 AttributeTargets 的值的组合。默认值是 AttributeTargets.All。
validon,
// allowmultiple(可选的)为该特性的 AllowMultiple 属性(property)提供一个布尔值。如果为 true,则该特性是多用的。默认值是 false(单用的)。
AllowMultiple=allowmultiple,
//inherited(可选的)为该特性的 Inherited 属性(property)提供一个布尔值。如果为 true,则该特性可被派生类继承。默认值是 false(不被继承)。
Inherited=inherited
)]
1.1.2 Conditional
这个暂时不了解,等后面如果实际需要的时候再补上。。。
1.1.3 Obsolete
标记了不应被使用的程序实体。它可以让您通知编译器丢弃某个特定的目标元素。例如,当一个新方法被用在一个类中,但是您仍然想要保持类中的旧方法,您可以通过显示一个应该使用新方法,而不是旧方法的消息,来把它标记为 obsolete(过时的)。例如:
class Program
{
/*
* 参数 message,是一个字符串,描述项目为什么过时的原因以及该替代使用什么。
* 参数 iserror,是一个布尔值。如果该值为 true,编译器应把该项目的使用当作一个错误。默认值是 false(编译器生成一个警告)。
*/
[Obsolete("不要用旧方法啦",true)]
static void OldMethod() {
Console.WriteLine("这是一个旧方法");
}
static void NewMethod() {
Console.WriteLine("这是新的方法");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
OldMethod();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
因为iserror属性设置为了true,所以在main方法调用OldMethod方法时报错,
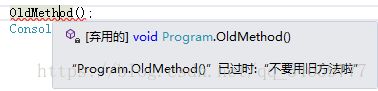
1.2 自定义特性
1、创建一个自定义特性:
// 描述如何使用一个自定义特性 SomethingAttribute
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.All, AllowMultiple = true, Inherited = true)]
//********自定义特性SomethingAttribute**************//
public class SomethingAttribute : Attribute {
private string name; // 名字
private string data; // 日期
public string Name {
get { return name; }
set { name = value; }
}
public string Data {
get { return data; }
set { data = value; }
}
public SomethingAttribute(string name) {
this.name = name;
this.name = name;
}
}
2、实例化自定义
[Something("Amy", Data = "2018-06-18")]
[Something("Jack", Data = "2018-06-18")]
class Test{}
3、获取自定义特性的中的变量
Type t = typeof(Test);
var something = t.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(SomethingAttribute),true);
foreach(SomethingAttribute each in something)
{
Console.WriteLine("Name:{0}", each.Name);
Console.WriteLine("Data:{0}",each.Data);
}
2.反射(Reflection)
反射指程序可以访问、检测和修改它本身状态或行为的一种能力。
2.1 优缺点
优点:
- 1、反射提高了程序的灵活性和扩展性。
- 2、降低耦合性,提高自适应能力。
- 3、它允许程序创建和控制任何类的对象,无需提前硬编码目标类。
缺点:
- 1、性能问题:使用反射基本上是一种解释操作,用于字段和方法接入时要远慢于直接代码。因此反射机制主要应用在对灵活性和拓展性要求很高的系统框架上,普通程序不建议使用。
- 2、使用反射会模糊程序内部逻辑;程序员希望在源代码中看到程序的逻辑,反射却绕过了源代码的技术,因而会带来维护的问题,反射代码比相应的直接代码更复杂。
2.2 反射的用途
- 它允许在运行时查看特性(attribute)信息。
- 它允许审查集合中的各种类型,以及实例化这些类型。
- 它允许延迟绑定的方法和属性(property)。
- 它允许在运行时创建新类型,然后使用这些类型执行一些任务。
2.3 使用反射来查看特性(attribute)信息
获取类和方法特性。
例如:
using System;
using System.Reflection;
namespace BugFixApplication
{
// 一个自定义特性 BugFix 被赋给类及其成员
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class |
AttributeTargets.Constructor |
AttributeTargets.Field |
AttributeTargets.Method |
AttributeTargets.Property,
AllowMultiple = true)]
public class DeBugInfo : System.Attribute
{
private int bugNo;
private string developer;
private string lastReview;
public string message;
public DeBugInfo(int bg, string dev, string d)
{
this.bugNo = bg;
this.developer = dev;
this.lastReview = d;
}
public int BugNo
{
get
{
return bugNo;
}
}
public string Developer
{
get
{
return developer;
}
}
public string LastReview
{
get
{
return lastReview;
}
}
public string Message
{
get
{
return message;
}
set
{
message = value;
}
}
}
[DeBugInfo(45, "Zara Ali", "12/8/2012",
Message = "Return type mismatch")]
[DeBugInfo(49, "Nuha Ali", "10/10/2012",
Message = "Unused variable")]
class Rectangle
{
// 成员变量
protected double length;
protected double width;
public Rectangle(double l, double w)
{
length = l;
width = w;
}
[DeBugInfo(55, "Zara Ali", "19/10/2012",
Message = "Return type mismatch")]
public double GetArea()
{
return length * width;
}
[DeBugInfo(56, "Zara Ali", "19/10/2012")]
public void Display()
{
Console.WriteLine("Length: {0}", length);
Console.WriteLine("Width: {0}", width);
Console.WriteLine("Area: {0}", GetArea());
}
}//end class Rectangle
class ExecuteRectangle
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Rectangle r = new Rectangle(4.5, 7.5);
r.Display();
Type type = typeof(Rectangle);
// 遍历 Rectangle 类的特性
foreach (Object attributes in type.GetCustomAttributes(false))
{
DeBugInfo dbi = (DeBugInfo)attributes;
if (null != dbi)
{
Console.WriteLine("Bug no: {0}", dbi.BugNo);
Console.WriteLine("Developer: {0}", dbi.Developer);
Console.WriteLine("Last Reviewed: {0}",
dbi.LastReview);
Console.WriteLine("Remarks: {0}", dbi.Message);
}
}
// 遍历方法特性
foreach (MethodInfo m in type.GetMethods())
{
foreach (Attribute a in m.GetCustomAttributes(true))
{
DeBugInfo dbi = (DeBugInfo)a;
if (null != dbi)
{
Console.WriteLine("Bug no: {0}, for Method: {1}",
dbi.BugNo, m.Name);
Console.WriteLine("Developer: {0}", dbi.Developer);
Console.WriteLine("Last Reviewed: {0}",
dbi.LastReview);
Console.WriteLine("Remarks: {0}", dbi.Message);
}
}
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
运行结果会显示附加到类 和方法上的自定义特性:
Length: 4.5
Width: 7.5
Area: 33.75
Bug No: 49
Developer: Nuha Ali
Last Reviewed: 10/10/2012
Remarks: Unused variable
Bug No: 45
Developer: Zara Ali
Last Reviewed: 12/8/2012
Remarks: Return type mismatch
Bug No: 55, for Method: GetArea
Developer: Zara Ali
Last Reviewed: 19/10/2012
Remarks: Return type mismatch
Bug No: 56, for Method: Display
Developer: Zara Ali
Last Reviewed: 19/10/2012
Remarks:
3. 属性(Property)
属性(Property) 是类(class)、结构(structure)和接口(interface)的命名(named)成员。类或结构中的成员变量或方法称为 域(Field)。属性(Property)是域(Field)的扩展,且可使用相同的语法来访问。它们使用 访问器(accessors) 让私有域的值可被读写或操作。
看起来很复杂,其实从下面这个例子就可以直观地了解到什么是属性啦:
// 声明类型为 string 的 Code 属性
public string Code
{
get
{
return code;
}
set
{
code = value;
}
}
在上面一个例子中,Code就是一个属性,get 、 set就是访问器。
3.1 抽象属性
抽象类可拥有抽象属性,这些属性应在派生类中被实现。
public abstract class Person
{
public abstract string Name
{
get;
set;
}
public abstract int Age
{
get;
set;
}
}
在派生类中:
class Student : Person
{
private string name = "N.A";
private int age = 0;
// 声明类型为 string 的 Name 属性
public override string Name
{
get
{
return name;
}
set
{
name = value;
}
}
// 声明类型为 int 的 Age 属性
public override int Age
{
get
{
return age;
}
set
{
age = value;
}
}
public override string ToString()
{
return "Name = " + Name + ", Age = " + Age;
}
}
4. 索引器(Indexer)
索引器(Indexer) 允许一个对象可以像数组一样被索引。当您为类定义一个索引器时,该类的行为就会像一个 虚拟数组(virtual array) 一样。您可以使用数组访问运算符([ ])来访问该类的实例。