解码Redis最易被忽视的CPU和内存占用高问题
我们在使用Redis时,总会碰到一些redis-server端CPU及内存占用比较高的问题。下面以几个实际案例为例,来讨论一下在使用Redis时容易忽视的几种情形。
一、短连接导致CPU高
某用户反映QPS不高,从监控看CPU确实偏高。既然QPS不高,那么redis-server自身很可能在做某些清理工作或者用户在执行复杂度较高的命令,经排查无没有进行key过期删除操作,没有执行复杂度高的命令。
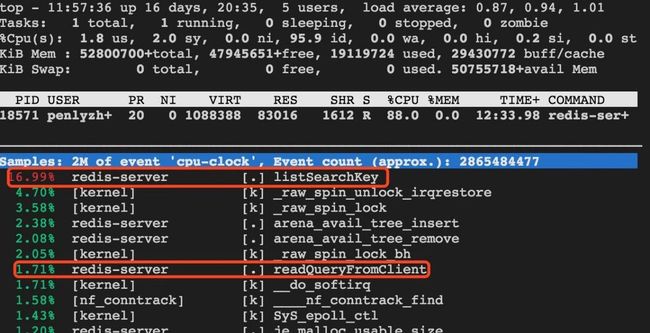
上机器对redis-server进行perf分析,发现函数listSearchKey占用CPU比较高,分析调用栈发现在释放连接时会频繁调用listSearchKey,且用户反馈说是使用的短连接,所以推断是频繁释放连接导致CPU占用有所升高。
1、对比实验
下面使用redis-benchmark工具分别使用长连接和短连接做一个对比实验,redis-server为社区版4.0.10。
1)长连接测试
使用10000个长连接向redis-server发送50w次ping命令:
./redis-benchmark -h host -p port -t ping -c 10000 -n 500000 -k
1(k=1表示使用长连接,k=0表示使用短连接)
最终QPS:
PING_INLINE: 92902.27 requests per second
PING_BULK: 93580.38 requests per second
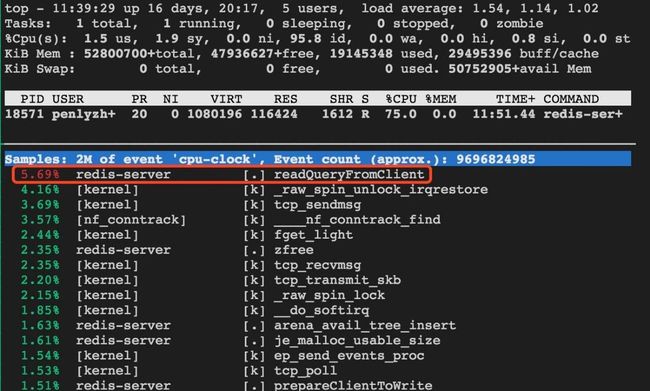
对redis-server分析,发现占用CPU最高的是readQueryFromClient,即主要是在处理来自用户端的请求。
2)短连接测试
使用10000个短连接向redis-server发送50w次ping命令:
./redis-benchmark -h host -p port -t ping -c 10000 -n 500000 -k 0
最终QPS:
PING_INLINE: 15187.18 requests per second
PING_BULK: 16471.75 requests per second
对redis-server分析,发现占用CPU最高的确实是listSearchKey,而readQueryFromClient所占CPU的比例比listSearchKey要低得多,也就是说CPU有点“不务正业”了,处理用户请求变成了副业,而搜索list却成为了主业。所以在同样的业务请求量下,使用短连接会增加CPU的负担。
从QPS上看,短连接与长连接差距比较大,原因来自两方面:
-
每次重新建连接引入的网络开销。
-
释放连接时,redis-server需消耗额外的CPU周期做清理工作。(这一点可以尝试从redis-server端做优化)
2、Redis连接释放
我们从代码层面来看下redis-server在用户端发起连接释放后都会做哪些事情,redis-server在收到用户端的断连请求时会直接进入到freeClient。
void freeClient(client *c) {
listNode *ln;
/* .........*/
/* Free the query buffer */
sdsfree(c->querybuf);
sdsfree(c->pending_querybuf);
c->querybuf = NULL;
/* Deallocate structures used to block on blocking ops. */
if (c->flags & CLIENT_BLOCKED) unblockClient(c);
dictRelease(c->bpop.keys);
/* UNWATCH all the keys */
unwatchAllKeys(c);
listRelease(c->watched_keys);
/* Unsubscribe from all the pubsub channels */
pubsubUnsubscribeAllChannels(c,0);
pubsubUnsubscribeAllPatterns(c,0);
dictRelease(c->pubsub_channels);
listRelease(c->pubsub_patterns);
/* Free data structures. */
listRelease(c->reply);
freeClientArgv(c);
/* Unlink the client: this will close the socket, remove the I/O
* handlers, and remove references of the client from different
* places where active clients may be referenced. */
/* redis-server维护了一个server.clients链表,当用户端建立连接后,新建一个client对象并追加到server.clients上,
当连接释放时,需求从server.clients上删除client对象 */
unlinkClient(c);
/* ...........*/
}
void unlinkClient(client *c) {
listNode *ln;
/* If this is marked as current client unset it. */
if (server.current_client == c) server.current_client = NULL;
/* Certain operations must be done only if the client has an active socket.
* If the client was already unlinked or if it's a "fake client" the
* fd is already set to -1\. */
if (c->fd != -1) {
/* 搜索server.clients链表,然后删除client节点对象,这里复杂为O(N) */
ln = listSearchKey(server.clients,c);
serverAssert(ln != NULL);
listDelNode(server.clients,ln);
/* Unregister async I/O handlers and close the socket. */
aeDeleteFileEvent(server.el,c->fd,AE_READABLE);
aeDeleteFileEvent(server.el,c->fd,AE_WRITABLE);
close(c->fd);
c->fd = -1;
}
/* ......... */
所以在每次连接断开时,都存在一个O(N)的运算。对于redis这样的内存数据库,我们应该尽量避开O(N)运算,特别是在连接数比较大的场景下,对性能影响比较明显。虽然用户只要不使用短连接就能避免,但在实际的场景中,用户端连接池被打满后,用户也可能会建立一些短连接。
3、优化
从上面的分析看,每次连接释放时都会进行O(N)的运算,那能不能降复杂度降到O(1)呢?
这个问题非常简单,server.clients是个双向链表,只要当client对象在创建时记住自己的内存地址,释放时就不需要遍历server.clients。接下来尝试优化下:
client *createClient(int fd) {
client *c = zmalloc(sizeof(client));
/* ........ */
listSetFreeMethod(c->pubsub_patterns,decrRefCountVoid);
listSetMatchMethod(c->pubsub_patterns,listMatchObjects);
if (fd != -1) {
/* client记录自身所在list的listNode地址 */
c->client_list_node = listAddNodeTailEx(server.clients,c);
}
initClientMultiState(c);
return c;
}
void unlinkClient(client *c) {
listNode *ln;
/* If this is marked as current client unset it. */
if (server.current_client == c) server.current_client = NULL;
/* Certain operations must be done only if the client has an active socket.
* If the client was already unlinked or if it's a "fake client" the
* fd is already set to -1\. */
if (c->fd != -1) {
/* 这时不再需求搜索server.clients链表 */
//ln = listSearchKey(server.clients,c);
//serverAssert(ln != NULL);
//listDelNode(server.clients,ln);
listDelNode(server.clients, c->client_list_node);
/* Unregister async I/O handlers and close the socket. */
aeDeleteFileEvent(server.el,c->fd,AE_READABLE);
aeDeleteFileEvent(server.el,c->fd,AE_WRITABLE);
close(c->fd);
c->fd = -1;
}
/* ......... */
优化后短连接测试
使用10000个短连接向redis-server发送50w次ping命令:
./redis-benchmark -h host -p port -t ping -c 10000 -n 500000 -k 0
最终QPS:
PING_INLINE: 21884.23 requests per second
PING_BULK: 21454.62 requests per second
与优化前相比,短连接性能能够提升30+%,所以能够保证存在短连接的情况下,性能不至于太差。
二、info命令导致CPU高
有用户通过定期执行info命令监视redis的状态,这会在一定程度上导致CPU占用偏高。频繁执行info时通过perf分析发现getClientsMaxBuffers、getClientOutputBufferMemoryUsage及getMemoryOverheadData这几个函数占用CPU比较高。
通过Info命令,可以拉取到redis-server端的如下一些状态信息(未列全):
client
connected_clients:1
client_longest_output_list:0 // redis-server端最长的outputbuffer列表长度
client_biggest_input_buf:0\. // redis-server端最长的inputbuffer字节长度
blocked_clients:0
Memory
used_memory:848392
used_memory_human:828.51K
used_memory_rss:3620864
used_memory_rss_human:3.45M
used_memory_peak:619108296
used_memory_peak_human:590.43M
used_memory_peak_perc:0.14%
used_memory_overhead:836182 // 除dataset外,redis-server为维护自身结构所额外占用的内存量
used_memory_startup:786552
used_memory_dataset:12210
used_memory_dataset_perc:19.74%
为了得到client_longest_output_list、client_longest_output_list状态,需要遍历redis-server端所有的client, 如getClientsMaxBuffers所示,可能看到这里也是存在同样的O(N)运算。
void getClientsMaxBuffers(unsigned long *longest_output_list,
unsigned long *biggest_input_buffer) {
client *c;
listNode *ln;
listIter li;
unsigned long lol = 0, bib = 0;
/* 遍历所有client, 复杂度O(N) */
listRewind(server.clients,&li);
while ((ln = listNext(&li)) != NULL) {
c = listNodeValue(ln);
if (listLength(c->reply) > lol) lol = listLength(c->reply);
if (sdslen(c->querybuf) > bib) bib = sdslen(c->querybuf);
}
*longest_output_list = lol;
*biggest_input_buffer = bib;
}
为了得到used_memory_overhead状态,同样也需要遍历所有client计算所有client的outputBuffer所占用的内存总量,如getMemoryOverheadData所示:
struct redisMemOverhead *getMemoryOverheadData(void) {
/* ......... */
mem = 0;
if (server.repl_backlog)
mem += zmalloc_size(server.repl_backlog);
mh->repl_backlog = mem;
mem_total += mem;
/* ...............*/
mem = 0;
if (listLength(server.clients)) {
listIter li;
listNode *ln;
/* 遍历所有的client, 计算所有client outputBuffer占用的内存总和,复杂度为O(N) */
listRewind(server.clients,&li);
while((ln = listNext(&li))) {
client *c = listNodeValue(ln);
if (c->flags & CLIENT_SLAVE)
continue;
mem += getClientOutputBufferMemoryUsage(c);
mem += sdsAllocSize(c->querybuf);
mem += sizeof(client);
}
}
mh->clients_normal = mem;
mem_total+=mem;
mem = 0;
if (server.aof_state != AOF_OFF) {
mem += sdslen(server.aof_buf);
mem += aofRewriteBufferSize();
}
mh->aof_buffer = mem;
mem_total+=mem;
/* ......... */
return mh;
}
#实验
从上面的分析知道,当连接数较高时(O(N)的N大),如果频率执行info命令,会占用较多CPU。
1)建立一个连接,不断执行info命令
func main() {
c, err := redis.Dial("tcp", addr)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Connect to redis error:", err)
return
}
for {
c.Do("info") } return
}
实验结果表明,CPU占用仅为20%左右。
2)建立9999个空闲连接,及一个连接不断执行info
func main() {
clients := []redis.Conn{}
for i := 0; i < 9999; i++ {
c, err := redis.Dial("tcp", addr)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Connect to redis error:", err)
return
}
clients = append(clients, c)
}
c, err := redis.Dial("tcp", addr)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Connect to redis error:", err)
return
}
for {
_, err = c.Do("info")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
return
}
实验结果表明CPU能够达到80%,所以在连接数较高时,尽量避免使用info命令。
3)pipeline导致内存占用高
有用户发现在使用pipeline做只读操作时,redis-server的内存容量偶尔也会出现明显的上涨, 这是对pipeline的使不当造成的。下面先以一个简单的例子来说明Redis的pipeline逻辑是怎样的。
下面通过golang语言实现以pipeline的方式从redis-server端读取key1、key2、key3。
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/garyburd/redigo/redis"
)
func main(){
c, err := redis.Dial("tcp", "127.0.0.1:6379")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
c.Send("get", "key1") //缓存到client端的buffer中
c.Send("get", "key2") //缓存到client端的buffer中
c.Send("get", "key3") //缓存到client端的buffer中
c.Flush() //将buffer中的内容以一特定的协议格式发送到redis-server端
fmt.Println(redis.String(c.Receive()))
fmt.Println(redis.String(c.Receive()))
fmt.Println(redis.String(c.Receive()))
}
而此时server端收到的内容为:
*2\r\n$3\r\nget\r\n$4\r\nkey1\r\n*2\r\n$3\r\nget\r\n$4\r\nkey2\r\n*2\r\n$3\r\nget\r\n$4\r\nkey3\r\n
下面是一段redis-server端非正式的代码处理逻辑,redis-server端从接收到的内容依次解析出命令、执行命令、将执行结果缓存到replyBuffer中,并将用户端标记为有内容需要写出。等到下次事件调度时再将replyBuffer中的内容通过socket发送到client,所以并不是处理完一条命令就将结果返回用户端。
readQueryFromClient(client* c) {
read(c->querybuf) // c->query="*2\r\n$3\r\nget\r\n$4\r\nkey1\r\n*2\r\n$3\r\nget\r\n$4\r\nkey2\r\n*2\r\n$3\r\nget\r\n$4\r\nkey3\r\n"
cmdsNum = parseCmdNum(c->querybuf) // cmdNum = 3
while(cmsNum--) {
cmd = parseCmd(c->querybuf) // cmd: get key1、get key2、get key3
reply = execCmd(cmd)
appendReplyBuffer(reply)
markClientPendingWrite(c)
}
}
考虑这样一种情况:
如果用户端程序处理比较慢,未能及时通过c.Receive()从TCP的接收buffer中读取内容或者因为某些BUG导致没有执行c.Receive(),当接收buffer满了后,server端的TCP滑动窗口为0,导致server端无法发送replyBuffer中的内容,所以replyBuffer由于迟迟得不到释放而占用额外的内存。当pipeline一次打包的命令数太多,以及包含如mget、hgetall、lrange等操作多个对象的命令时,问题会更突出。
小结
上面几种情况,都是非常简单的问题,没有复杂的逻辑,在大部分场景下都不算问题,但是在一些极端场景下要把Redis用好,开发者还是需要关注这些细节。建议:
- 尽量不要使用短连接;
- 尽量不要在连接数比较高的场景下频繁使用info;
- 使用pipeline时,要及时接收请求处理结果,且pipeline不宜一次打包太多请求。