Tomcat 初始化及启动过程
Tomcat中很多组件具有生命周期,如初始化、启动、关闭,这些组件的生命周期具有共性,因此Tomcat中将其抽象为接口Lifecycle,来控制组件的生命周期,它通过 事件机制 实现各个容器间的内部通讯。
Lifecycle接口的方法:

继承关系图:

Tomcat的类加载器架构
先是Bootstrap.initClassLoaders()设置类加载器:CommonClassLoader 、ServerClassLoader 、SharedClassLoader,
/common(存放Tomcat与所有Web应用程序共用的类库)、
/server(只Tomcat使用、而所有Web应用程序不可见的)、
/shared(Tomcat不可见、而所有Web应用程序共用)。
另外,在后面初始化每个Web应用程序解析web.xml时,会创建WebappClassLoader,只有对应的Web应用程序可见,加载对应Web应用程序的/WEB-INF/lib里的类库。
所以默认情况下,Tomcat类加载器架构如下:
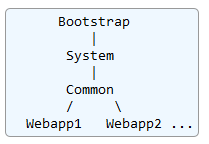
Bootstrap类加载器为Java虚拟机提供,包含JDK基本运行时类,
而System类加载器用于Tomcat启动初始化(通常忽略)
Tomcat类加载器架构是按照经典的”双亲委派模型”来实现的,即:当类加载器被要求加载特定的类或资源时,它首先将请求委托给父类加载器,然后只有当父类加载器找不到请求的类或资源时,它才在自己的存储库中查找。
Tomcat的类加载器架构的好处是可以按需要实现Tomcat与Web应用程序、以及不现Web应用程序之间的类库共享与隔离,如常用的Spring等类库可以放到共享目录,为多个Web应用程序共用;而”双亲委派模型”也是JDK类加载器的架构,可以有效组织类库的层次结构,避免一个类被不同加载器加载多次(注意,同一个类文件被不同加载器加载表示不同的类)。
简述:
整个启动加载过程的调用队列如下:
org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap#main
->org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap#init
->org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap#load
-->org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina#load
--->org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer#init
---->org.apache.catalina.core.StandardService#init
----->org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector#init
----->org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngine#init
->org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap#start
-->org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina#start 通过反射调用
--->org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer#start
---->org.apache.catalina.core.StandardService#start
----->org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngine#start
----->org.apache.catalina.Executor#start
----->org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector#start Tomca初始化
Catalina.load()中调用Server组件的初始化函数,Server.initInternal()又调用内部包含的Service组件的初始化…以此类推,按配置文件的组件结构顺序初始化
沿着Server—>Service->Container(Engine—>Host—>Context—>Wrapper—>Servlet)这一核心顺序一一总结Tomcat初始化的过程。
[1] StandardServer.initInternal():
(1)创建和注册(注册到MBeanServer)全局的StringCache;
(2)初始化GlobalNamingResources;
(3)初始化该Server包含的所有service组件(虽然通常都只有一个名为“Catalina”的service);
[2] StandardService.initInternal():
这一层其实包含了很多重要组件的初始化:Container,Executor,MapperListener,Connector;
(1)初始化容器,从容器的最外层(Engine)开始,一层层开始;
(2)如果定义了org.apache.catalina.Executor,初始化Executor。还是说明一下,它实现了J.U.C中的Executor,定义一个为所有Connector共享的线程池(因此在server.xml中Executor必须定义在Connector,因为前面提到了解析server.xml使用SAX的方式);
(3)初始化mapperListener,MapperListener是Tomcat中用来保存整个容器必要结构信息用于将请求URL映射到对应容器;
(4)初始化Connector,这个过程会初始化每个Connector包含的ProtocolHandldr等组件,让连接处理部分做好准备;
部分源代码如下:
//org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat#init
public void init() throws LifecycleException {
getServer();
getConnector();
server.init();
}
//org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat#getConnector
public Connector getConnector() {
getServer();
connector = new Connector("HTTP/1.1");
// connector = new Connector("org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11Protocol");
connector.setPort(port);
service.addConnector( connector );
return connector;
}
//org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat#getServer
public Server getServer() {
if (server != null) {
return server;
}
initBaseDir();
System.setProperty("catalina.useNaming", "false");
server = new StandardServer();
server.setPort( -1 );
service = new StandardService();
service.setName("Tomcat");
server.addService( service );
return server;
}
//org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer#initInternal
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
// Initialize our defined Services
for (int i = 0; i < services.length; i++) {
services[i].init();
}
}
//org.apache.catalina.core.StandardService#initInternal
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
if (container != null) {
container.init();
}
// Initialize any Executors
for (Executor executor : findExecutors()) {
executor.init();
}
// Initialize our defined Connectors
synchronized (connectors) {
for (Connector connector : connectors) {
connector.init();
}
}
}
//org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector#initInternal
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
// Initialize adapter
//该协议适配器会完成请求的真正处理
adapter = new CoyoteAdapter(this);
//对于不同的协议类型,会有不同的ProtocolHandler实现类,如:Http11Protocol用来处理HTTP请求
protocolHandler.setAdapter(adapter);
try {
// 初始化具体协议类型,如Http11Protocol协议
protocolHandler.init();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
// Initialize mapper listener
mapperListener.init();
}
//下一步,protocolHandler.init(); 调用的是abstractProtocol.init()
//1. 注册组件JIoEndPoint
//2. endpoint.init(),设置work threads的数量,默认为200,并创建serverSocket对象
//org.apache.coyote.AbstractProtocol#init
public void init() throws Exception {
try {
//调用JIoEndpoint的初始化方法
endpoint.init();
} catch (Exception ex) {}
}
//endpoint.init() 调用endpoint.bind()
//org.apache.tomcat.util.net.JIoEndpoint#bind
public void bind() throws Exception
// Initialize maxConnections
if (getMaxConnections() == 0) {
// User hasn't set a value - use the default
// 此值为server.xml的connector元素的属性MaxThreads值,默认200
setMaxConnections(getMaxThreadsInternal());
}
if (serverSocketFactory == null) {
if (isSSLEnabled()) {
serverSocketFactory = handler.getSslImplementation().getServerSocketFactory(this);
} else {
serverSocketFactory = new DefaultServerSocketFactory(this);
}
}
// 创建serverSocket对象
try {
if (getAddress() == null) {
serverSocket = serverSocketFactory.createSocket(getPort(), getBacklog());
}
} catch (BindException orig) { }
}
Tomca启动过程
[1] ContainerBase容器初始化
(1)Cluster服务启动;
(2)Realm服务启动;
(3)子容器的启动;
(4)Pipeline的启动(Pipeline进一步启动对应Valve链上所有的Valve);
(5)通知执行STARTING对应的Listener;
(6)后台任务共享线程的启动;
ContainerBase详情参照本人博客: https://blog.csdn.net/yangsnow_rain_wind/article/details/80053530
[2]StandardService.startInternal()
Executor,MapperListener,Connector都是接收请求直接相关的,其中Executor负责为Connector处理请求提供共用的线程池,MapperListener负责将请求映射到对应的容器中,Connector负责接收和解析请求,这里所有Connector启动完成后,Tomcat就准备好可以接受处理请求。
(1)启动Container,container.start();
(2)启动Executor;
(3)启动mapperListener;
(4)启动所有的Connector;
[3]StandardContext.startInternal()
(1)创建读取资源文件的对象:如果我们没有上面在初始化过程中提到的元素,将会创建一个默认的StandardRoot;
(2)创建ClassLoader对象,为了实现不同应用类的隔离,每个Context有自己的WebappLoader,创建对应的WebappClassLoader;
(3)设置应用的工作目录;
(4)启动相关辅助类:Logger,Cluster,Realm;
(5)创建会话管理器;
(6)通知ContextConfig读取和解析Web应用web.xml和注解
(7)启动子容器,也就是上一步创建的所有StandardWrapper;
(8)启动Pipeline;
(9)启动会话管理器Manager;
(10)获取ServletContext并设置必要的参数,ServletContext在Tomcat中的内部表示即ApplicationContext,返回到Servlet中的是它的门面对象ApplicationContextFacade;
(11)调用Initializer的onStartup;
(12)创建Context中配置的Listener;
(13)创建和初始化配置的Filter;
(14)创建和初始化loadOnStartup大于等于0的Servlet,StandardWrapper的门面类StandardWrapperFacade作为ServletConfig传入Servlet的init方法;
备注:
在StandardContext初始化完成后,会通知注册的LifecycleListener,其中包括ContextConfig,调用ContextConfig.init()解析/conf目录下的context.xml以及Context自身的配置文件,解析方式和前面servlet.xml一样,基于org.apache.tomcat.util.digester.Digester一边读取解析,一边构建对象网络。
部分源代码如下:
//org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat#start
public void start() throws LifecycleException {
getServer();
getConnector();
server.start();
}
//org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer#startInternal
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
for (int i = 0; i < services.length; i++) {
services[i].start();
}
}
//org.apache.catalina.core.StandardService#startInternal
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// 变更状态,发布事件
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
// Start our defined Container first
if (container != null) {
synchronized (container) {
// container:StandardEngine
// 逐一启动engine,host,context,warpper
container.start();
}
}
synchronized (executors) {
for (Executor executor: executors) {
executor.start();
}
}
// Start our defined Connectors second
synchronized (connectorsLock) {
for (Connector connector: connectors) {
try {
connector.start();
} catch (Exception e) {}
}
}
}
//容器启动
//org.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase#startInternal
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Start our subordinate components, if any
if ((loader != null) && (loader instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) loader).start();
logger = null;
getLogger();
if ((manager != null) && (manager instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) manager).start();
if ((cluster != null) && (cluster instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) cluster).start();
Realm realm = getRealmInternal();
if ((realm != null) && (realm instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) realm).start();
if ((resources != null) && (resources instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) resources).start();
// 异步请求所有子容器
Container children[] = findChildren();
List> results = new ArrayList>();
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
results.add(startStopExecutor.submit(new StartChild(children[i])));
}
boolean fail = false;
for (Future result : results) {
result.get();
}
// 启动管道
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle)
((Lifecycle) pipeline).start();
// 启动后台监控线程.
threadStart();
}
//Connector启动
//org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector#startInternal
try {
// 具体的协议类型类启动,如Http11Protocal启动
protocolHandler.start();
}
//org.apache.coyote.AbstractProtocol#start
endpoint.start();
JIoEndpoint监听创建过程
//org.apache.tomcat.util.net.JIoEndpoint#startInternal
public void startInternal() throws Exception {
if (!running) {
if (getExecutor() == null) {
// 根据MinSpareThreads、MaxThreads属性创建默认的ThreadPoolExecutor
createExecutor();
}
// 创建n个Acceptor用于接收客户端请求
startAcceptorThreads();
}
}
//1
public void createExecutor() {
internalExecutor = true;
TaskQueue taskqueue = new TaskQueue();
TaskThreadFactory tf = new TaskThreadFactory(getName() + "-exec-", daemon, getThreadPriority());
// MinSpareThreads、MaxThreads属性可在server.xml中Connector元素处配置
executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(getMinSpareThreads(), getMaxThreads(), 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,taskqueue, tf);
taskqueue.setParent( (ThreadPoolExecutor) executor);
}
//2
protected final void startAcceptorThreads() {
int count = getAcceptorThreadCount();
acceptors = new Acceptor[count];
// 创建count个Acceptor,每个对应一个线程thread,thread.start(),等待请求的到来
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
acceptors[i] = createAcceptor();
String threadName = getName() + "-Acceptor-" + i;
acceptors[i].setThreadName(threadName);
Thread t = new Thread(acceptors[i], threadName);
t.setPriority(getAcceptorThreadPriority());
t.setDaemon(getDaemon());
t.start();
}
}
1处: 可以看到创建一个线程池,为后续的Endpoint监听做准备.
2处,可以看到创建多个Acceptor. Acceptor 为JIoEndpoint的内部类, 该类监听TCP/IP请求,并将请求发送给合适的Processor
源码如下:
protected class Acceptor extends AbstractEndpoint.Acceptor {
@Override
public void run() {
// Loop until we receive a shutdown command
while (running) {
// block线程,等待请求的到来
socket = serverSocketFactory.acceptSocket(serverSocket);
//接受到请求之后处理请求
if (!processSocket(socket)) {
closeSocket(socket);
}
}
}
Tomcat初始化之后, 下一话题: Tomcat请求处理一个请求的过程,
参照本人博客: https://blog.csdn.net/yangsnow_rain_wind/article/details/80064945


