【tomcat路径匹配源码分析】搞懂tomcat中web.xml配置servlet的url-pattern为“/“和“/*“的区别
搞懂tomcat中web.xml配置servlet的url-pattern为"/"和"/*"的区别
- 前言
-
- 结论
- Servlet匹配规则(tomcat源码)
- 分析
- 举个例子
- 路径配置为`/`导致拦截静态资源问题的解决方案
- 总结
原文地址
前言
我在写原生javaWEB项目时,想通过注册一个servlet实现拦截所有请求由HandOutServlet统一分发,于是我就想到把urlPatterns设置为"/"

但是这个会出现一个问题就是这个也会把 静态资源(html,css,js等) 的请求也拦截了,导致前端无法获取到正确的页面资源(解决方法在下面会提到),也正好我在配置过滤器时使用到另一个形式的url就是"/*",所以我想弄清楚这两个的区别是什么?我于是开始了源码的调试和研究。。。。。。
结论
url-pattern为"/"时会覆盖tomcat中的default servlet(这个给是用于提供静态资源的),表示匹配所有没有注册的url-pattern的地址,就是web.xml里的其他的url-pattern都没有匹配时就会走这个地址。(比如index.html也会被匹配到因为没有注册html类型的mapping,而index.jsp就不会匹配因为jsp有注册了对应的servlet-mapping)
注意: 在tomcat的安装路径下也有一个web.xml(比如:“apache-tomcat-x.x.xx\conf\web.xml”),这个web.xml会和我们项目里的web.xml合并,该web.xml配置了默认的servlet和处理jsp的servlet
url-pattern为"/*"时,其实和/*的优先级比/高。在项目的servlet中如果配置了index.jsp,index.html,css,js啥的文件统统匹配到/*对应的servlet下,不过如果注册有更加清晰的路径比如\test\123之类的则是匹配到
Servlet匹配规则(tomcat源码)
private final void internalMapWrapper(ContextVersion contextVersion,
CharChunk path,
MappingData mappingData) throws IOException {
int pathOffset = path.getOffset();
int pathEnd = path.getEnd();
boolean noServletPath = false;
int length = contextVersion.path.length();
if (length == (pathEnd - pathOffset)) {
noServletPath = true;
}
int servletPath = pathOffset + length;
path.setOffset(servletPath);
// Rule 1 -- Exact Match
MappedWrapper[] exactWrappers = contextVersion.exactWrappers;
internalMapExactWrapper(exactWrappers, path, mappingData);
// Rule 2 -- Prefix Match
boolean checkJspWelcomeFiles = false;
MappedWrapper[] wildcardWrappers = contextVersion.wildcardWrappers;
if (mappingData.wrapper == null) {
internalMapWildcardWrapper(wildcardWrappers, contextVersion.nesting,
path, mappingData);
if (mappingData.wrapper != null && mappingData.jspWildCard) {
char[] buf = path.getBuffer();
if (buf[pathEnd - 1] == '/') {
/*
* Path ending in '/' was mapped to JSP servlet based on
* wildcard match (e.g., as specified in url-pattern of a
* jsp-property-group.
* Force the context's welcome files, which are interpreted
* as JSP files (since they match the url-pattern), to be
* considered. See Bugzilla 27664.
*/
mappingData.wrapper = null;
checkJspWelcomeFiles = true;
} else {
// See Bugzilla 27704
mappingData.wrapperPath.setChars(buf, path.getStart(),
path.getLength());
mappingData.pathInfo.recycle();
}
}
}
if(mappingData.wrapper == null && noServletPath &&
contextVersion.object.getMapperContextRootRedirectEnabled()) {
// The path is empty, redirect to "/"
path.append('/');
pathEnd = path.getEnd();
mappingData.redirectPath.setChars
(path.getBuffer(), pathOffset, pathEnd - pathOffset);
path.setEnd(pathEnd - 1);
return;
}
// Rule 3 -- Extension Match
MappedWrapper[] extensionWrappers = contextVersion.extensionWrappers;
if (mappingData.wrapper == null && !checkJspWelcomeFiles) {
internalMapExtensionWrapper(extensionWrappers, path, mappingData,
true);
}
// Rule 4 -- Welcome resources processing for servlets
if (mappingData.wrapper == null) {
boolean checkWelcomeFiles = checkJspWelcomeFiles;
if (!checkWelcomeFiles) {
char[] buf = path.getBuffer();
checkWelcomeFiles = (buf[pathEnd - 1] == '/');
}
if (checkWelcomeFiles) {
for (int i = 0; (i < contextVersion.welcomeResources.length)
&& (mappingData.wrapper == null); i++) {
path.setOffset(pathOffset);
path.setEnd(pathEnd);
path.append(contextVersion.welcomeResources[i], 0,
contextVersion.welcomeResources[i].length());
path.setOffset(servletPath);
// Rule 4a -- Welcome resources processing for exact macth
internalMapExactWrapper(exactWrappers, path, mappingData);
// Rule 4b -- Welcome resources processing for prefix match
if (mappingData.wrapper == null) {
internalMapWildcardWrapper
(wildcardWrappers, contextVersion.nesting,
path, mappingData);
}
// Rule 4c -- Welcome resources processing
// for physical folder
if (mappingData.wrapper == null
&& contextVersion.resources != null) {
String pathStr = path.toString();
WebResource file =
contextVersion.resources.getResource(pathStr);
if (file != null && file.isFile()) {
internalMapExtensionWrapper(extensionWrappers, path,
mappingData, true);
if (mappingData.wrapper == null
&& contextVersion.defaultWrapper != null) {
mappingData.wrapper =
contextVersion.defaultWrapper.object;
mappingData.requestPath.setChars
(path.getBuffer(), path.getStart(),
path.getLength());
mappingData.wrapperPath.setChars
(path.getBuffer(), path.getStart(),
path.getLength());
mappingData.requestPath.setString(pathStr);
mappingData.wrapperPath.setString(pathStr);
}
}
}
}
path.setOffset(servletPath);
path.setEnd(pathEnd);
}
}
/* welcome file processing - take 2
* Now that we have looked for welcome files with a physical
* backing, now look for an extension mapping listed
* but may not have a physical backing to it. This is for
* the case of index.jsf, index.do, etc.
* A watered down version of rule 4
*/
if (mappingData.wrapper == null) {
boolean checkWelcomeFiles = checkJspWelcomeFiles;
if (!checkWelcomeFiles) {
char[] buf = path.getBuffer();
checkWelcomeFiles = (buf[pathEnd - 1] == '/');
}
if (checkWelcomeFiles) {
for (int i = 0; (i < contextVersion.welcomeResources.length)
&& (mappingData.wrapper == null); i++) {
path.setOffset(pathOffset);
path.setEnd(pathEnd);
path.append(contextVersion.welcomeResources[i], 0,
contextVersion.welcomeResources[i].length());
path.setOffset(servletPath);
internalMapExtensionWrapper(extensionWrappers, path,
mappingData, false);
}
path.setOffset(servletPath);
path.setEnd(pathEnd);
}
}
// Rule 7 -- Default servlet
if (mappingData.wrapper == null && !checkJspWelcomeFiles) {
if (contextVersion.defaultWrapper != null) {
mappingData.wrapper = contextVersion.defaultWrapper.object;
mappingData.requestPath.setChars
(path.getBuffer(), path.getStart(), path.getLength());
mappingData.wrapperPath.setChars
(path.getBuffer(), path.getStart(), path.getLength());
mappingData.matchType = ApplicationMappingMatch.DEFAULT;
}
// Redirection to a folder
char[] buf = path.getBuffer();
if (contextVersion.resources != null && buf[pathEnd -1 ] != '/') {
String pathStr = path.toString();
// Note: Check redirect first to save unnecessary getResource()
// call. See BZ 62968.
if (contextVersion.object.getMapperDirectoryRedirectEnabled()) {
WebResource file;
// Handle context root
if (pathStr.length() == 0) {
file = contextVersion.resources.getResource("/");
} else {
file = contextVersion.resources.getResource(pathStr);
}
if (file != null && file.isDirectory()) {
// Note: this mutates the path: do not do any processing
// after this (since we set the redirectPath, there
// shouldn't be any)
path.setOffset(pathOffset);
path.append('/');
mappingData.redirectPath.setChars
(path.getBuffer(), path.getStart(), path.getLength());
} else {
mappingData.requestPath.setString(pathStr);
mappingData.wrapperPath.setString(pathStr);
}
} else {
mappingData.requestPath.setString(pathStr);
mappingData.wrapperPath.setString(pathStr);
}
}
}
path.setOffset(pathOffset);
path.setEnd(pathEnd);
}
分析
从源码结合注释可以看出servlet的匹配规则顺序是:
- 精确匹配:查找一个与请求路径匹配的 Servlet(比如:请求路径是
/test/login,如果配置有的servlet映射则会匹配该servlet,没有接着下一个规则即前缀路径匹配,下面的规则也是如此,没有匹配到就到下一个规则,直到默认的处理)/test/login - 前缀路径匹配:通配符匹配,匹配前缀最长的(比如
和/test1/test2/* ,请求路径假设是/test1/* /test/login/123则匹配的是,而不是/test1/test2/* )/test1/* - 扩展名匹配:如果请求路径最后一部分包含扩展名,就像 .html之类的,则尝试匹配注册有处理此扩展名请求的 Servlet(比如:
)*.html - 欢迎资源处理:查找是否有匹配的默认首页文件(在请求路径后加上欢迎文件列表比如请求的是
/test,则添加后就是/test/index.html,欢迎列表默认有[index.html,index.htm,index.jsp],这些都会依次尝试匹配)
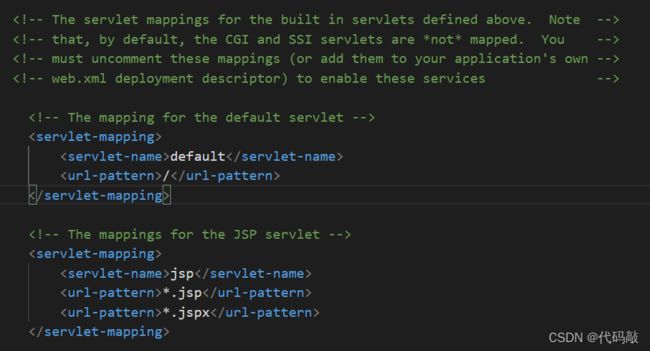
下图就是tomcat默认的欢迎列表:
- 默认匹配:前几个规则没有匹配成功,交由默认 Servlet处理,如果在自己项目的web.xml配置有
则这个就是默认的servlet,即它取代了tomcat默认的servlet/
举个例子
假设项目结构如下(故意加了一个index.jsp)
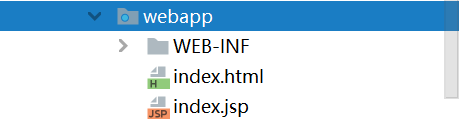
项目的上下文是/test

在浏览器访问localhost:8080/test
![]()
之后会被重定向到localhost:8080/test/
![]()
假设没有在项目的web.xml中配置任何servlet(但是不要忘记了还有tomcat默认的servlet)

当http://localhost:8080/test/这个请求进来,经过处理实际进行匹配的路径是/,然后开始第一个匹配规则精确匹配,这时候因为在web.xml中没有配置有明确路径的servlet,所以第一个匹配失败,接着尝试前缀匹配,和第一个规则一样,没有配置这类的servlet所以也失败了,然后是拓展名匹配,默认tomcat的web.xml配置有处理拓展名为jsp和jspx的servlet,但是这个也不符合/这个路径;接着下一个规则就是欢迎资源处理,这里会给路径加上欢迎列表中指定的文件。
默认的欢迎列表如下

即给路径/加上index.html变成/index.html,之后欢迎列表会按顺序依此在路径上添加后进行尝试匹配,首先开始尝试/index.html
- 一开始先进行精确匹配,和一开始一样,因为在
web.xml中没有配置有明确路径的servlet,所以匹配失败 - 之后开始前缀匹配,这个也和之前一样,没有配置这类的servlet所以也失败了
- 在尝试过加上欢迎列表后的精确匹配和前缀匹配后,如果还没找到对应的处理的serlvet,会判断项目物理上是否存在欢迎列表中指定的文件即
index.html如果物理上存在在且注册有对应的拓展名servlet映射,就会交给该servlet处理,如果没有对应的拓展名映射的servlet就会交给默认的servlet处理。显然index.html物理上是存在的,但是我们没有配置处理html拓展名的servlet,所以会交给默认的servlet处理,之后就不会继续尝试/index.htm和/index.jsp了。默认的servlet是处理静态资源的所以可以正确响应index.html文件。
路径配置为/导致拦截静态资源问题的解决方案
static包下放了css,js,image等资源
我的 web.xml 的部分配置
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>defaultservlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.htmlurl-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>defaultservlet-name>
<url-pattern>/static/*url-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
这样配置映射可以将html文件和static包下的其他的静态资源的请求交给tomcat默认的servlet处理
总结
以上就是我对servlet路径匹配的一些见解
喜欢这篇文章就点个赞呗!!!