vertx 异步编程指南 step7-保护和控制访问
保护和控制访问与Vert.x很容易。 在本节中,我们将:
从HTTP转移到HTTPS,以及
使用基于组的权限将用户身份验证添加到Web应用程序,以及
使用 JSON Web令牌 (JWT) 控制对Web API的访问 。
证书可以存储在Java KeyStore 文件中。 您可能需要 用于测试目的 的 自签名证书, 以下是如何在 server-keystore.jksKeyStore中 创建一个 密码为 secret:
keytool -genkey \
-alias test \
-keyalg RSA \
-keystore server-keystore.jks \
-keysize 2048 \
-validity 360 \
-dname CN =localhost \
-keypass secret \
-storepass secret然后,我们可以更改HTTP服务器创建,以传递一个 HttpServerOptions对象来指定我们需要SSL,并指向我们的KeyStore文件:
HttpServer server = vertx.createHttpServer(new HttpServerOptions ()
.setSsl(true new JksOptions ()
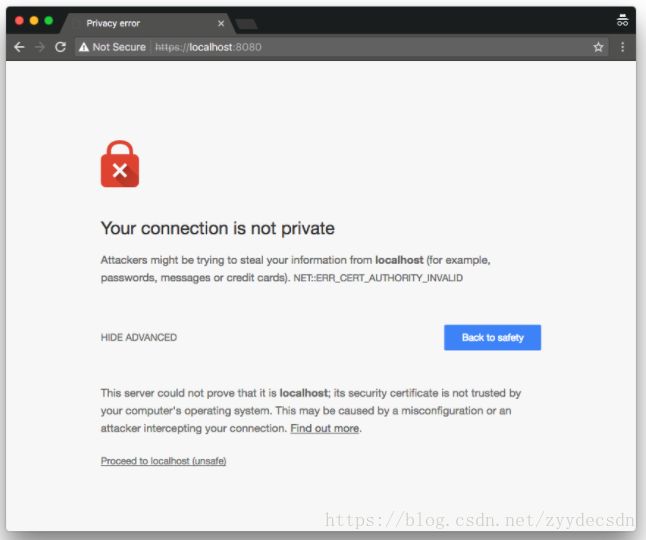
.setPath(" server-keystore.jks " " secret " 我们可以将浏览器指向 https:// localhost:8080 / ,但由于证书是自签名的,所以任何优秀的浏览器都会正确地产生安全警告:
最后但并非最不重要的是,我们需要更新测试用例, ApiTest因为原始代码是用于通过Web客户端发出HTTP请求的:
webClient = WebClient .create(vertx, new WebClientOptions ()
.setDefaultHost(" localhost " 8080 true (1 )
.setTrustOptions(new JksOptions ().setPath(" server-keystore.jks " " secret "
确保SSL。
由于证书是自签名的,我们需要明确信任它,否则Web客户端连接将失败,就像Web浏览器一样。
访问控制和认证
Vert.x为执行身份验证和授权提供了广泛的选项。 官方支持的模块涵盖了JDBC,MongoDB, Apache Shiro ,OAuth2以及众所周知的提供者和JWT(JSON Web令牌)。
虽然下一部分将介绍JWT,但本部分重点介绍如何使用Apache Shiro,这在验证必须由LDAP或Active Directory服务器支持时特别有用。 在我们的例子中,我们只是将凭据存储在属性文件中以保持简单,但对LDAP服务器的API使用保持不变。
目标是要求用户使用wiki进行身份验证,并拥有基于角色的权限:
没有角色只允许阅读页面,
具有 作家 角色允许编辑页面,
具有 编辑 角色允许创建,编辑和删除页面,
具有 管理 角色相当于具有所有可能的角色。
警告
由于Apache Shiro的内部运作,Vert.x Shiro集成有一些问题。 有些部分阻塞会影响性能,有些数据是使用线程本地状态存储的。 您不应该尝试滥用暴露的内部状态API。
将Apache Shiro身份验证添加到路由
第一步是将 vertx-auth-shiro模块 添加 到Maven依赖关系列表中:
我们使用的属性文件定义如下,位于 src/main/resources/wiki-users.properties:
user.root=w00t,admin
user.foo=bar,editor,writer
user.bar=baz,writer
user.baz=baz
role.admin=*
role.editor=create,delete ,update
role.writer=update
带 user前缀的条目是一个用户帐户,其中第一个值条目是密码可能跟随的角色。 在这个例子中,用户 bar有密码 baz,是一个 writer,并且 writer有 update权限。
回到 HttpServerVerticle课程代码,我们使用Apache Shiro创建认证提供者:
AuthProvider ShiroAuth .create(vertx, new ShiroAuthOptions ()
.setType(ShiroAuthRealmType .PROPERTIES )
.setConfig(new JsonObject ()
.put(" properties_path " " classpath:wiki-users.properties " 该 ShiroAuth对象实例然后用于处理服务器端用户会话:
Router router = Router .router(vertx);
router.route().handler(CookieHandler BodyHandler .create());
router.route().handler(SessionHandler .create(LocalSessionStore .create(vertx)));
router.route().handler(UserSessionHandler .create(auth)); (1 )
AuthHandler authHandler = RedirectAuthHandler .create(auth, " /login " (2 )
router.route(" / " (3 )
router.route(" /wiki/* " " /action/* " " / " this " /wiki/:page " this " /action/save " this " /action/create " this " /action/backup " this " /action/delete " this
我们为所有路由安装用户会话处理程序。
这会自动将请求重定向到 /login没有用户会话的请求时。
我们安装 authHandler了所有需要身份验证的路由。
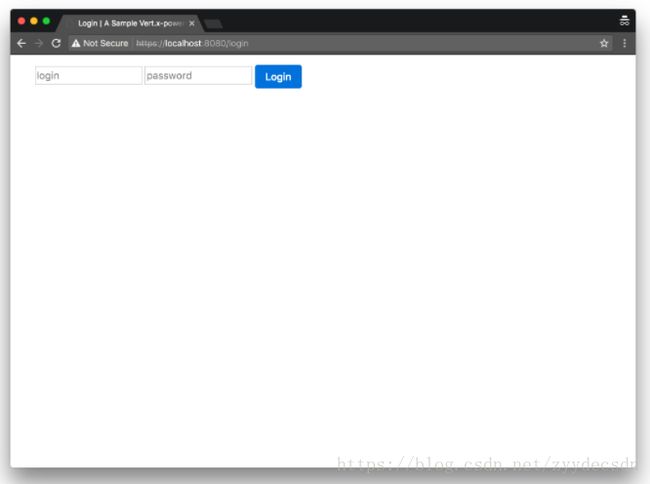
最后,我们需要创建3条路线来显示登录表单,处理登录表单提交和注销用户:
router.get(" /login " this : :loginHandler );
router.post(" /login-auth " FormLoginHandler .create(auth)); (1 )
router.get(" /logout " (2 )
context.response()
.setStatusCode(302 " Location " " / " end ();
});
FormLoginHandler是处理登录提交请求的助手。 默认情况下,它希望HTTP POST请求具有: username作为登录名, password密码以及 return_url成功时重定向到的URL。
注销用户很简单,就像从当前清除它一样 RoutingContext。
private void loginHandler (RoutingContext context) {
context.put(" title " " Login " " templates " " /login.ftl " if " Content-Type " " text/html " else HTML模板位于 src/main/resources/templates/login.ftl:
< #include "header.ftl" >
class = " row " >
class = " col-md-12 mt-1 " >
action =" /login-auth " method =" POST " >
class = " form-group " >
type = " text " name =" username " placeholder =" login " >
type = " password " name =" password " placeholder =" password " >
type = " hidden " name =" return_url " value =" / " >
type = " submit " class = " btn btn-primary " > Login
< #include
"footer.ftl" >
登录页面如下所示:
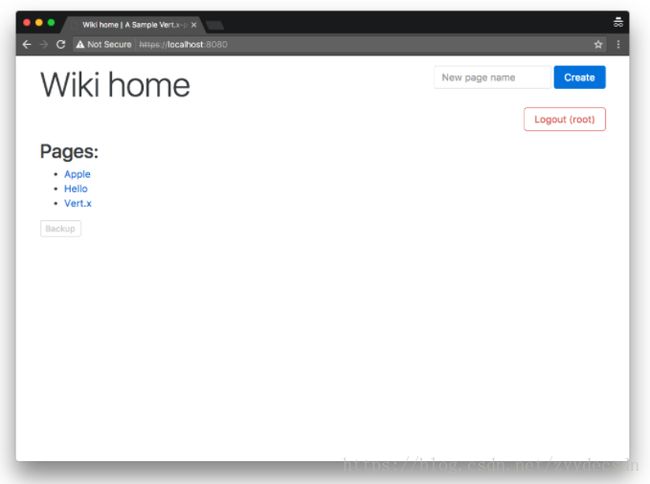
支持基于角色的功能
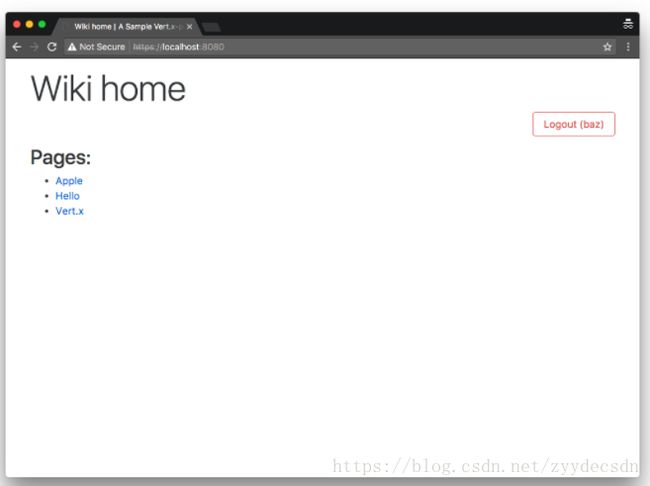
只有当用户拥有足够的权限时才能激活功能。 在以下屏幕截图中,管理员可以创建一个页面并执行备份:
相比之下,没有角色的用户不能执行这些操作:
为此,我们可以访问 RoutingContext用户参考,并查询权限。 以下是 indexHandler处理器方法的 实现 方式:
private void indexHandler (RoutingContext context) {
context.user().isAuthorised(" create " (1 )
boolean (2 )
dbService.fetchAllPages(reply -> {
if " title " " Wiki home " " pages " " canCreatePage " (3 )
context.put(" username " " username " (4 )
templateEngine.render(context, " templates " " /index.ftl " if " Content-Type " " text/html " else else
这是如何进行权限查询的。 请注意,这是一个异步操作。
我们使用结果...
...在HTML模板中利用它。
我们也可以访问用户登录。
模板代码已被修改为仅基于以下值来呈现特定片段 canCreatePage:
< #include "header.ftl" >
class = " row " >
class = " col-md-12 mt-1 " >
< #if context.canCreatePage>
class = " float-xs-right " >
class = " form-inline " action =" /action/create " method =" post " >
class = " form-group " >
type = " text " class = " form-control " id =" name " name =" name " placeholder =" New page name " >
type = " submit " class = " btn btn-primary " > Create
#if >
class = " display-4 " > ${context.title} class = " float-xs-right " >
class = " btn btn-outline-danger " href =" /logout " role =" button " aria-pressed =" true " > Logout (${context.username})
class = " col-md-12 mt-1 " >
< #list context.pages>
Pages :< #items as page>
href =" /wiki/${page} " > ${page}#items>
< #else >
The wiki is currently empty!#list>
< #if context.canCreatePage>
< #if context.backup_gist_url?has_content>
class = " alert alert-success " role =" alert " >
Successfully created a backup:
href =" ${context.backup_gist_url} " class = " alert-link " > ${context.backup_gist_url}
< #
else >
class = " btn btn-outline-secondary btn-sm " href =" /action/backup " role =" button " aria-pressed =" true " > Backup #if >
#if >
< #include
"footer.ftl" >
该代码类似于确保更新或删除页面仅限于某些角色,并可从指南Git存储库中获得。
确保检查也是在HTTP POST请求处理程序上完成,而不仅仅是在呈现HTML页面时进行。 事实上,恶意攻击者仍然可以制作请求并执行操作,而无需进行身份验证。 以下是如何通过将 pageDeletionHandler代码 包装在 最上面的权限检查中 来保护页面删除 :
private void pageDeletionHandler (RoutingContext context) {
context.user().isAuthorised(" delete " if Integer .valueOf(context.request().getParam(" id " if 303 " Location " " / " else else 403 使用JWT验证Web API请求
JSON Web Tokens ( RFC 7519 )是发布包含 声明的 JSON编码标记的标准,通常标识用户和权限,但声明可以是任何事情。
令牌由服务器发出,并使用服务器密钥进行签名。 客户端可以将令牌发送回以及随后的请求:客户端和服务器都可以检查令牌是否真实且未改变。
警告
JWT令牌签名时,其内容未加密。 它必须通过安全通道(例如HTTPS)进行传输,并且它不应该有敏感数据作为声明(例如,密码,私人API密钥等)。
添加JWT支持
我们首先将 vertx-auth-jwt模块 添加 到Maven依赖关系中:
我们将有一个JCEKS密钥库来保存我们测试的密钥。 以下是如何 keystore.jceks使用各种长度的适当键 生成一个文件 :
keytool -genseckey -keystore keystore.jceks -storetype jceks -storepass secret -keyalg HMacSHA256 -keysize 2048 -alias HS256 -keypass secret
keytool -genseckey -keystore keystore.jceks -storetype jceks -storepass secret -keyalg HMacSHA384 -keysize 2048 -alias HS384 -keypass secret
keytool -genseckey -keystore keystore.jceks -storetype jceks -storepass secret -keyalg HMacSHA512 -keysize 2048 -alias HS512 -keypass secret
keytool -genkey -keystore keystore.jceks -storetype jceks -storepass secret -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -alias RS256 -keypass secret -sigalg SHA256withRSA -dname "CN=,OU=,O=,L=,ST=,C=" -validity 360
keytool -genkey -keystore keystore.jceks -storetype jceks -storepass secret -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -alias RS384 -keypass secret -sigalg SHA384withRSA -dname "CN=,OU=,O=,L=,ST=,C=" -validity 360
keytool -genkey -keystore keystore.jceks -storetype jceks -storepass secret -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -alias RS512 -keypass secret -sigalg SHA512withRSA -dname "CN=,OU=,O=,L=,ST=,C=" -validity 360
keytool -genkeypair -keystore keystore.jceks -storetype jceks -storepass secret -keyalg EC -keysize 256 -alias ES256 -keypass secret -sigalg SHA256withECDSA -dname "CN=,OU=,O=,L=,ST=,C=" -validity 360
keytool -genkeypair -keystore keystore.jceks -storetype jceks -storepass secret -keyalg EC -keysize 256 -alias ES384 -keypass secret -sigalg SHA384withECDSA -dname "CN=,OU=,O=,L=,ST=,C=" -validity 360
keytool -genkeypair -keystore keystore.jceks -storetype jceks -storepass secret -keyalg EC -keysize 256 -alias ES512 -keypass secret -sigalg SHA512withECDSA -dname "CN=,OU=,O=,L=,ST=,C=" -validity 360 我们需要在API路由上安装JWT令牌处理程序:
Router apiRouter = Router .router(vertx);
JWTAuth jwtAuth = JWTAuth .create(vertx, new JsonObject ()
.put(" keyStore " new JsonObject ()
.put(" path " " keystore.jceks " " type " " jceks " " password " " secret " JWTAuthHandler .create(jwtAuth, " /api/token " 我们通过 /api/token作为 JWTAuthHandler对象创建 的参数 来指定该URL将被忽略。 的确,这个URL被用来生成新的JWT令牌:
apiRouter.get(" /token " new " username " " login " " password " " password " (1 )
if " create " (2 )
user.isAuthorised(" delete " " update " String (3 )
new " username " " login " " canCreate " " canDelete " " canUpdate " new " Wiki API " " Vert.x " " Content-Type " " text/plain " else 401
我们预计登录名和密码信息已通过HTTP请求标头传递,我们使用上一节的Apache Shiro身份验证提供程序进行身份验证。
一旦成功,我们可以查询角色。
我们生成令牌 username, canCreate, canDelete和 canUpdate索赔。
每个API处理程序方法现在可以查询当前的用户主体和声明。 这是如何 apiDeletePage做到的:
private void apiDeletePage (RoutingContext context) {
if " canDelete " false int Integer .valueOf(context.request().getParam(" id " else 401 使用JWT令牌
为了说明如何使用JWT令牌,让我们为 root用户 创建一个新的令牌 :
$ http --verbose --verify no GET https://localhost:8080/api/token login:root password:w00t
GET /api/token HTTP/1.1
Accept: */*
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Connection: keep-alive
Host: localhost:8080
User-Agent: HTTPie/0.9.8
login: root
password: w00t
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Length: 242
Content-Type: text/plain
Set-Cookie: vertx-web.session=8cbb38ac4ce96737bfe31cc0ceaae2b9; Path=/
eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJ1c2VybmFtZSI6InJvb3QiLCJjYW5DcmVhdGUiOnRydWUsImNhbkRlbGV0ZSI6dHJ1ZSwiY2FuVXBkYXRlIjp0cnVlLCJpYXQiOjE0ODk0NDE1OTAsImlzcyI6IlZlcnQueCIsInN1YiI6Ildpa2kgQVBJIn0=.RmtJb81QKVUFreXL-ajZ8ktLGasoKEqG8GSQncRWrN8=
我们可以检查执行不带令牌的API请求会导致拒绝访问:
$ http --verbose --verify no GET https://localhost:8080/api/pages
GET /api/pages HTTP/1.1
Accept: */*
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Connection: keep-alive
Host: localhost:8080
User-Agent: HTTPie/0.9.8
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
Content-Length: 12
Unauthorized
发送JWT令牌与请求一起使用 AuthorizationHTTP请求头,其值必须是 Bearer 。 以下是如何通过传递已发布给我们的JWT令牌来修复上面的API请求:
$ http --verbose --verify no GET https://localhost:8080/api/pages 'Authorization: Bearer eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJ1c2VybmFtZSI6InJvb3QiLCJjYW5DcmVhdGUiOnRydWUsImNhbkRlbGV0ZSI6dHJ1ZSwiY2FuVXBkYXRlIjp0cnVlLCJpYXQiOjE0ODk0NDE1OTAsImlzcyI6IlZlcnQueCIsInN1YiI6Ildpa2kgQVBJIn0=.RmtJb81QKVUFreXL-ajZ8ktLGasoKEqG8GSQncRWrN8='
GET /api/pages HTTP/1.1
Accept: */*
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Authorization: Bearer eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJ1c2VybmFtZSI6InJvb3QiLCJjYW5DcmVhdGUiOnRydWUsImNhbkRlbGV0ZSI6dHJ1ZSwiY2FuVXBkYXRlIjp0cnVlLCJpYXQiOjE0ODk0NDE1OTAsImlzcyI6IlZlcnQueCIsInN1YiI6Ildpa2kgQVBJIn0=.RmtJb81QKVUFreXL-ajZ8ktLGasoKEqG8GSQncRWrN8=
Connection: keep-alive
Host: localhost:8080
User-Agent: HTTPie/0.9.8
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Length: 99
Content-Type: application/json
Set-Cookie: vertx-web.session=0598697483371c7f3cb434fbe35f15e4; Path=/
{
"pages": [
{
"id": 0,
"name": "Hello"
},
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Apple"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Vert.x"
}
],
"success": true
}
调整API测试夹具
本 ApiTest类需要进行更新,以支持JWT令牌。
我们添加一个新字段来检索要在测试用例中使用的令牌值:
private String 我们添加第一步来检索经过身份验证的JTW令牌 foo:
@Test public void play_with_api (TestContext context) {
Async async = context.async();
Future <String > tokenRequest = Future .future();
webClient.get(" /api/token " " login " " foo " (1 )
.putHeader(" password " " bar " (2 )
.send(ar -> {
if (3 )
} else
凭证作为标题传递。
响应有效载荷是 text/plain类型的,因此我们将其用于身体解码编解码器。
一旦成功,我们 tokenRequest用令牌值 完成 未来。
Future postRequest = Future .future();
tokenRequest.compose(token -> {
jwtTokenHeaderValue = " Bearer " (1 )
webClient.post(" /api/pages " " Authorization " (2 )
.as (BodyCodec.jsonObject())
.sendJsonObject(page, ar -> {
if postResponse = ar.result();
postRequest.complete(postResponse.body());
} else Future getRequest = Future .future();
postRequest.compose(h -> {
webClient.get(" /api/pages " " Authorization " as (BodyCodec.jsonObject())
.send(ar -> {
if getResponse = ar.result();
getRequest.complete(getResponse.body());
} else
我们将带有 Bearer前缀 的令牌存储 在下一个请求的字段中。
我们将令牌作为头部传递。
你可能感兴趣的:(vertx)
python快速实现dbc转excel
大柠檬鲸
python 开发语言
步骤1-安装canmatrix包打开cmd输入:python-mpipinstallcanmatrix步骤2-打开要转换dbc所在的文件夹路径步骤3-在下图的路径框中输入cmd后直接按回车键步骤4-输入cmd在弹出的cmd中输入canconvertxxx.dbctarget.xlsx其中xxx.dbc为要转换的dbc,target.xlsx为输出的excel在当前路径下即生成转换后的excel
springboot与vertx异步并发对比
千寻_GHSA
springboot目前主要还是阻塞式响应,需要等到服务端计算完成,才会返回。vertx本身异步响应,客户端发出请求后,服务端计算完成后,通知返回。系统的处理能力会大大提升。针对同样的业务,做一个200并发的测试springbootspringboot的average在165秒vertxvertx的average在85秒从cpu的使用率对比vertx的CPU使用率较低;springboot的CPU
vertx添加后获取记录id
Levi_9d29
直接用户queryWithParams方法执行添加sql就可以了,如果是postgresql需要在sql语句最后加上returningid,其他数据库没试过
程序媛在公司的进修之路(三)
小芹菜_4d69
这次隔了两周,因为是双周任务和总结,学习任务如下:学习vertx框架,重点学习core、web、dataaccess三个组件。在这之前自己什么框架也没有学过,包括MVC,,,,所以完全不知道该如何入手。大体自己的学习思路如下:1、直接上官网:https://vertx.io/docs/#web看手册,了解相关的概念的知识,运行出第一个helloword(例子都是官网现成的)。这里英文不好的就去看中
使用 curl multi interface 编写的高性能封装类和示例
fishjam
HTTP Curl 性能优化 curl multi interface HTTP
CurlMultiDemo使用libCurl的MultiInterface的一个简单封装类,支持功能:单线程+纯异步的Get/Post支持极高的性能(使用POST上传600+文件,仅耗时4~6秒)使用方式:1.编译或下载libcurl库,我采用的是vcpkg2.搭建或找一个支持MultiPart上传文件的服务器,如没有,可以使用vertx-upload3.VisualStudio(2015)打开工
sklearn线性模型之Lasso回归
微小冷
# sklearn sklearn 回归 人工智能 Lasso python LassoCV
文章目录Lasso简介Lasso类LassoCVLasso简介Lasso,即TheLeastAbsoluteShrinkageandSelectionOperator,是用于拟合稀疏系数的线性模型,其最小化目标函数为minw12n∥Xw−y∥22+α∥w∥1\min_w\frac{1}{2n}\VertXw-y\Vert^2_2+\alpha\Vertw\Vert_1wmin2n1∥Xw−y∥2
sklearn岭回归
微小冷
# sklearn sklearn 回归 人工智能 python 岭回归
文章目录基本原理sklearn实现基本原理最小二乘法的判定条件是minw∥Xw−y∥22\min_w\VertXw-y\Vert_2^2wmin∥Xw−y∥22其中,minwF(w)\min_wF(w)minwF(w)表示F(w)F(w)F(w)最小时的www;www是拟合参数,x,yx,yx,y是变量。对于线性问题,可通过对www求导,得到F(w)F(w)F(w)极值处的www,具体表达式为
2019-01-19
喀喀喀580
gitreset--hardxxx,gitreset--softxxx与gitrevertxxx三者作用都是用来撤销某项操作,只是工作的领域和方式不同.gitreset--softxxximagegitreset--hardxxxhard(修改版本库,修改暂存区,修改工作区)imagegitrevertxxxrevert--gitrevert也是撤销命令,区别在于reset是指向原地或者向前移动指
vertx写sip服务器
帐篷Li
开源视频联动物联网平台 流媒体开发 服务器 运维
Vert.xSIP模块默认使用TCP协议进行通信。如果您需要支持UDP协议,您需要自定义SIP协议栈,并在其中实现UDP传输。以下是一个示例代码,演示如何在Vert.x中创建一个支持UDP的SIP服务器:importio.vertx.core.net.SocketAddress;importio.vertx.ext.SIP;importio.vertx.ext.SIP.Method;importi
vertx 写sip协议
帐篷Li
开源视频联动物联网平台 网络 服务器 运维
Vert.x是一个用于构建响应式系统的工具包,它支持多种协议,包括SIP。要在Vert.x中编写SIP协议,您需要使用Vert.xSIP模块。以下是在Vert.x中编写SIP协议的一般步骤:添加依赖项:在您的项目中添加Vert.xSIP模块的依赖项。创建SIP服务器:使用Vert.xSIP模块创建一个SIP服务器。您需要指定服务器的地址和端口号。创建SIP路由:在您的SIP服务器上创建SIP路由。
git reset --hard xxx , git reset --soft xxx , git revert xxx 的区别
这是余传书简书
gitreset--hardxxx,gitreset--softxxx,gitrevertxxxgitrevert三者区别三者作用都是用来撤销某项操作,只是工作的领域和方式不同。gitresetgitreset常用于代码回滚,是直接删除指定的commit,但是文件和修改会移动到workspace工作区。gitreset--softxxx从暂存区撤回。soft命令会让版本回到某次commit后的状态
实体、DataTable、json、xml互转
ylattx
C# .net core .net json xml c#
需要用到Newtonsoft.Json//////将xml转换datatabe/////////publicstaticDataTableConvertXMLToDataTable(stringxmlData){DataSetdsData=newDataSet();dsData.ReadXml(newXmlTextReader(newStringReader(xmlData)));DataTabl
vertx常用方法示例
wbkys
vertx restful 后端 java vertx
一、多个回调如何避免回调地域方法:使用compose与Future示例1:按顺序执行里面的回调方法//回调方法1privateFuturegetStatus1(Stringid){returnFuture.future(f->{f.complete(true);});}//回调方法2privateFuturegetStatus2(booleanid){returnFuture.future(f->
vertx学习
一户董
杂 学习
写在前面新公司用到了vertx,所以这里学习下。源码。1:vertx是啥?是个框架吗?不是。只是一个工具类,只不过提供的功能比较全面,如http,websocket,tcp,json处理,定时任务,文件IO等。2:Vert.xCore核心对象io.vertx.core.Vertx。2.1:定时器//使用vertx执行定时执行任务@TestpublicvoidtimerWithVertx()thro
vertx系列
一个带着思想做开发的人
分布式技术
vertx系列第一节1:谈下博主如何解除到vertx,目前大多公司用到的都是spring体系,但是博主在工作中,,感觉spring体系特别笨重,无论是国内,出的springalibaba等。不可否认,他们对java生态的分布式,做了很多。但是用起来还是特别重,性能比较低,有人说,用java就不要谈性能。java的性能不如go,很重要在于他的线程模型,后来,博主感觉,想自己去实现一套异步的分布式架构
[USACO2012-Mar-Silver] Flowerpot 题解(单调队列 c++)
上烟雨心上尘
题解 c++ 算法 开发语言
[USACO12MAR]FlowerpotS题解(单调队列c++)题目链接:[USACO2012-Mar-Silver]Flowerpot题意:给你n个点,每个点有对应的x,y确认是否存在两个点,在y1,y2y_1,y_2y1,y2满足要求的情况下,输出最小的∣x2−x1∣\lvertx_2-x_1\rvert∣x2−x1∣思路:如果暴力的话,我们就考虑对于每一个点,寻找其对应的∣y1−y2∣>=
vert.x学习心得笔记(一)
给我的名字加个鸡腿_
vert.x官方中文文档:https://vertxchina.github.io/vertx-translation-chinese/官方英文文档:一:背景介绍首先我们介绍vert.x,它是一种事件驱动,且异步的基于JVM的Java框架。由于近年来,移动网络、社交网络和电商的兴起,使各大服务提供商的客户端请求数量激增,传统服务器架构已不堪重负,致使基于事件和异步的解决方案备受追捧。而vert.x
Vert.x 3学习笔记---02
avastxa
vertx java vert.x nodejs
文档地址:http://vertx.io/docs/vertx-core/java/Verticlesverticles是一个很重要的概念。你可以将verticles当做是ActorModel(一种编程模型)中的actor。它是一段代码的集合—可以部署和被Vert.x运行。并且verticles能够被Vert.x支持的所有语言编写,并不仅限于java。一个应用可以包含不同语言编写的verticle
Vert.x 3学习笔记---03
avastxa
vertx vert.x nodejs java
TheEventBus概述本文介绍eventbus。TheeventbusisthenervoussystemofVert.x.每一个Vertx实例都只有一个eventbus实例,可以使用eventBus方法获取。eventbus容许你的应用程序的各个部分(相同或者不同语言编写的,相同或者不同的vertx或者vertx的其他部分)进行通讯。Theeventbusallowsdifferentpar
Vert.x 3学习笔记---06
avastxa
vertx vert.x server tcp java nodejs
WritingTCPserversandclients编写TCP服务端和客户端使用vertx可以很简单的编写出无阻塞的tcp服务端和客户端。下面逐一来介绍。CreatingaTCPserverNetServerserver=vertx.createNetServer();ConfiguringaTCPserver可以使用NetServerOptions来配置tcp服务端:NetServerOpti
GIT reset hard/soft/revert的区别
leo_luo
三个命令都是撤销gitreset--hardxxx撤销你没有提交的改动和将你本地库全部的操作退回到XXX。gitreset--softxxx是将XXX从暂存区中撤回gitrevertxxx将在编辑器内修改的内容撤回,撤销一个提交的同时会创建一个新的提交。
【Java】Vert.x Jackson 序列化后日期数据正常展示
kida_yuan
Java java 开发语言
有段时间没有更新了,年尾嘛大家都懂的。其实最近有个想法,想将自己的vtx_fw框架给开源了。但开源之前还是有很多收尾的工作需要做的(总不能让各位笑话吧o(╥﹏╥)o),这不今天就发现了一个问题,立刻就归纳一下给各位分享。这个问题就是Vert.x框架中日期类型数据在Jackson序列化下的展示问题。有玩过Vert.x的小伙伴都知道在vertx-core包中会默认依赖jackson-core包。如果实
博客git区别
不喝雪碧我怕透心凉_c7de
gitreset--hardxxxgitreset--softxxxgitrevertxxx的区别resertgitrevertxxx如果修改了某些内容,但是还没有push到远程仓库,可以用gitreset去撤销更改,除了在当前分支上操作,还可以通过传入标记来修改缓存区或者工作目录,这些标记限定了gitreset的作用域,常常跟HEAD作为参数一起使用gitreset--softxxx回退到某个版
Vert.x 学习笔记
wbkys
vertx java 开发语言 后端
一、概述Vert.x(http://vertx.io)是一个基于JVM、轻量级、高性能的应用平台,非常适用于最新的移动端后台、互联网、企业应用架构.Vert.x是基于大名鼎鼎netty的异步的工具集。可以简单理解成运行在JVM上的Node.js。拥有高性能的一个java框架,可以维持单服务器至少120万长连接的平台.特性:1、同时支持多种编程语言——目前已经支持了Java、Scala、JavaSc
27Vert.X框架学习笔记
林伢仔
01Java java 网络 分布式
vert.x框架学习笔记文章目录1Vert.x简明介绍1.1Vert.x能干什么1.2Vert.x快速体验1.3Vert.x的简单介绍1.4Vert.x的一些优势1.4.1异步非阻塞1.4.2Vertx支持多种编程语言1.4.3不依赖中间件1.4.4完善的生态1.4.5为服务而生1.5Vert.x的技术体系1.5.1核心模块1.5.2Web模块1.5.3数据访问模块1.5.4Reactive响应式
Vert.x学习笔记(二) Vert.x Web Client
乐百川
java vertx vert.x web 框架
本文参考自Vert.xWebClient官方文档。套用官网的话来说,Vert.xWebClient是一个异步的HTTP和HTTP/2网络客户端。相对来说,这是一个比较小的框架,而且功能也很直接,做一个方便好用的HTTP客户端。它具有以下功能:Jsonbody编码/解码request参数统一的错误处理表单提交需要注意,它和Vertx核心包中的HttpClient有很多联系。它继承了HttpClien
Vert.X使用笔记
小周今天code了吗
VertX java 开发语言
Vert.X使用笔记(一)一、开发环境二、官方文档三、vert.x概述1、vertx-core四、HelloWorld1、生成工程2、打开工程3、编写启动类4、启动项目5、另一种启动方法四、理解示例程序五、概念1、事件驱动2、非阻塞3、链式循环处理4、未来(future)5、verticle6、eventbus六、使用案例1、定时执行七、插曲ApacheIgnite一、开发环境-框架VERTX_V
Vert.x 3学习笔记---09
avastxa
vertx vert.x nodejs async-file
UsingthefilesystemwithVert.xvertx的FileSystem对象提供很多的便捷操作。每一个vertx的实例拥有一个FileSystem对象的实例。每一个操作都提供了阻塞和非阻塞的版本。非阻塞版本的操作使用一个handler来处理完成或者失败的结果。FileSystemfs=vertx.fileSystem();//Copyfilefromfoo.txttobar.txt
java html转换xml文件,使用Java在HTML中转换XML + XSL
weixin_39915267
java html转换xml文件
我们将数据作为XML使用,并且存在多种格式化XSL样式。在IE中它一直工作得很好。使用Java在HTML中转换XML+XSL然后,我们需要在Chrome中显示与HTML相同的内容。所以,我们在服务器端(Java)找到一个API来将XML+XSL转换为HTML。publicstaticStringconvertXMLXSL(Stringxml,Stringxsl)throwsSQLException
latex格式中的范数
狗狗狗大王
Latex latex 数学
latex格式中的范数$\Vertx\Vert$效果:∥x∥\Vertx\Vert∥x∥L1范数$\Vertx\Vert_1$效果:∥x∥1\Vertx\Vert_1∥x∥1L2范数$\Vertx\Vert_2$效果:∥x∥2\Vertx\Vert_2∥x∥2无穷范数$\Vertx\Vert_\infty$效果:∥x∥∞\Vertx\Vert_\infty∥x∥∞
算法 单链的创建与删除
换个号韩国红果果
c 算法
先创建结构体
struct student {
int data;
//int tag;//标记这是第几个
struct student *next;
};
// addone 用于将一个数插入已从小到大排好序的链中
struct student *addone(struct student *h,int x){
if(h==NULL) //??????
《大型网站系统与Java中间件实践》第2章读后感
白糖_
java中间件
断断续续花了两天时间试读了《大型网站系统与Java中间件实践》的第2章,这章总述了从一个小型单机构建的网站发展到大型网站的演化过程---整个过程会遇到很多困难,但每一个屏障都会有解决方案,最终就是依靠这些个解决方案汇聚到一起组成了一个健壮稳定高效的大型系统。
看完整章内容,
zeus持久层spring事务单元测试
deng520159
java DAO spring jdbc
今天把zeus事务单元测试放出来,让大家指出他的毛病,
1.ZeusTransactionTest.java 单元测试
package com.dengliang.zeus.webdemo.test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
import
Rss 订阅 开发
周凡杨
html xml 订阅 rss 规范
RSS是 Really Simple Syndication的缩写(对rss2.0而言,是这三个词的缩写,对rss1.0而言则是RDF Site Summary的缩写,1.0与2.0走的是两个体系)。
RSS
分页查询实现
g21121
分页查询
在查询列表时我们常常会用到分页,分页的好处就是减少数据交换,每次查询一定数量减少数据库压力等等。
按实现形式分前台分页和服务器分页:
前台分页就是一次查询出所有记录,在页面中用js进行虚拟分页,这种形式在数据量较小时优势比较明显,一次加载就不必再访问服务器了,但当数据量较大时会对页面造成压力,传输速度也会大幅下降。
服务器分页就是每次请求相同数量记录,按一定规则排序,每次取一定序号直接的数据
spring jms异步消息处理
510888780
jms
spring JMS对于异步消息处理基本上只需配置下就能进行高效的处理。其核心就是消息侦听器容器,常用的类就是DefaultMessageListenerContainer。该容器可配置侦听器的并发数量,以及配合MessageListenerAdapter使用消息驱动POJO进行消息处理。且消息驱动POJO是放入TaskExecutor中进行处理,进一步提高性能,减少侦听器的阻塞。具体配置如下:
highCharts柱状图
布衣凌宇
hightCharts 柱图
第一步:导入 exporting.js,grid.js,highcharts.js;第二步:写controller
@Controller@RequestMapping(value="${adminPath}/statistick")public class StatistickController { private UserServi
我的spring学习笔记2-IoC(反向控制 依赖注入)
aijuans
spring mvc Spring 教程 spring3 教程 Spring 入门
IoC(反向控制 依赖注入)这是Spring提出来了,这也是Spring一大特色。这里我不用多说,我们看Spring教程就可以了解。当然我们不用Spring也可以用IoC,下面我将介绍不用Spring的IoC。
IoC不是框架,她是java的技术,如今大多数轻量级的容器都会用到IoC技术。这里我就用一个例子来说明:
如:程序中有 Mysql.calss 、Oracle.class 、SqlSe
TLS java简单实现
antlove
java ssl keystore tls secure
1. SSLServer.java
package ssl;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.security.KeyStore;
import
Zip解压压缩文件
百合不是茶
Zip格式解压 Zip流的使用 文件解压
ZIP文件的解压缩实质上就是从输入流中读取数据。Java.util.zip包提供了类ZipInputStream来读取ZIP文件,下面的代码段创建了一个输入流来读取ZIP格式的文件;
ZipInputStream in = new ZipInputStream(new FileInputStream(zipFileName));
&n
underscore.js 学习(一)
bijian1013
JavaScript underscore
工作中需要用到underscore.js,发现这是一个包括了很多基本功能函数的js库,里面有很多实用的函数。而且它没有扩展 javascript的原生对象。主要涉及对Collection、Object、Array、Function的操作。 学
java jvm常用命令工具——jstatd命令(Java Statistics Monitoring Daemon)
bijian1013
java jvm jstatd
1.介绍
jstatd是一个基于RMI(Remove Method Invocation)的服务程序,它用于监控基于HotSpot的JVM中资源的创建及销毁,并且提供了一个远程接口允许远程的监控工具连接到本地的JVM执行命令。
jstatd是基于RMI的,所以在运行jstatd的服务
【Spring框架三】Spring常用注解之Transactional
bit1129
transactional
Spring可以通过注解@Transactional来为业务逻辑层的方法(调用DAO完成持久化动作)添加事务能力,如下是@Transactional注解的定义:
/*
* Copyright 2002-2010 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version
我(程序员)的前进方向
bitray
程序员
作为一个普通的程序员,我一直游走在java语言中,java也确实让我有了很多的体会.不过随着学习的深入,java语言的新技术产生的越来越多,从最初期的javase,我逐渐开始转变到ssh,ssi,这种主流的码农,.过了几天为了解决新问题,webservice的大旗也被我祭出来了,又过了些日子jms架构的activemq也开始必须学习了.再后来开始了一系列技术学习,osgi,restful.....
nginx lua开发经验总结
ronin47
使用nginx lua已经两三个月了,项目接开发完毕了,这几天准备上线并且跟高德地图对接。回顾下来lua在项目中占得必中还是比较大的,跟PHP的占比差不多持平了,因此在开发中遇到一些问题备忘一下 1:content_by_lua中代码容量有限制,一般不要写太多代码,正常编写代码一般在100行左右(具体容量没有细心测哈哈,在4kb左右),如果超出了则重启nginx的时候会报 too long pa
java-66-用递归颠倒一个栈。例如输入栈{1,2,3,4,5},1在栈顶。颠倒之后的栈为{5,4,3,2,1},5处在栈顶
bylijinnan
java
import java.util.Stack;
public class ReverseStackRecursive {
/**
* Q 66.颠倒栈。
* 题目:用递归颠倒一个栈。例如输入栈{1,2,3,4,5},1在栈顶。
* 颠倒之后的栈为{5,4,3,2,1},5处在栈顶。
*1. Pop the top element
*2. Revers
正确理解Linux内存占用过高的问题
cfyme
linux
Linux开机后,使用top命令查看,4G物理内存发现已使用的多大3.2G,占用率高达80%以上:
Mem: 3889836k total, 3341868k used, 547968k free, 286044k buffers
Swap: 6127608k total,&nb
[JWFD开源工作流]当前流程引擎设计的一个急需解决的问题
comsci
工作流
当我们的流程引擎进入IRC阶段的时候,当循环反馈模型出现之后,每次循环都会导致一大堆节点内存数据残留在系统内存中,循环的次数越多,这些残留数据将导致系统内存溢出,并使得引擎崩溃。。。。。。
而解决办法就是利用汇编语言或者其它系统编程语言,在引擎运行时,把这些残留数据清除掉。
自定义类的equals函数
dai_lm
equals
仅作笔记使用
public class VectorQueue {
private final Vector<VectorItem> queue;
private class VectorItem {
private final Object item;
private final int quantity;
public VectorI
Linux下安装R语言
datageek
R语言 linux
命令如下:sudo gedit /etc/apt/sources.list1、deb http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/CRAN/bin/linux/ubuntu/ precise/ 2、deb http://dk.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu hardy universesudo apt-key adv --keyserver ke
如何修改mysql 并发数(连接数)最大值
dcj3sjt126com
mysql
MySQL的连接数最大值跟MySQL没关系,主要看系统和业务逻辑了
方法一:进入MYSQL安装目录 打开MYSQL配置文件 my.ini 或 my.cnf查找 max_connections=100 修改为 max_connections=1000 服务里重起MYSQL即可
方法二:MySQL的最大连接数默认是100客户端登录:mysql -uusername -ppass
单一功能原则
dcj3sjt126com
面向对象的程序设计 软件设计 编程原则
单一功能原则[
编辑]
SOLID 原则
单一功能原则
开闭原则
Liskov代换原则
接口隔离原则
依赖反转原则
查
论
编
在面向对象编程领域中,单一功能原则(Single responsibility principle)规定每个类都应该有
POJO、VO和JavaBean区别和联系
fanmingxing
VO POJO javabean
POJO和JavaBean是我们常见的两个关键字,一般容易混淆,POJO全称是Plain Ordinary Java Object / Plain Old Java Object,中文可以翻译成:普通Java类,具有一部分getter/setter方法的那种类就可以称作POJO,但是JavaBean则比POJO复杂很多,JavaBean是一种组件技术,就好像你做了一个扳子,而这个扳子会在很多地方被
SpringSecurity3.X--LDAP:AD配置
hanqunfeng
SpringSecurity
前面介绍过基于本地数据库验证的方式,参考http://hanqunfeng.iteye.com/blog/1155226,这里说一下如何修改为使用AD进行身份验证【只对用户名和密码进行验证,权限依旧存储在本地数据库中】。
将配置文件中的如下部分删除:
<!-- 认证管理器,使用自定义的UserDetailsService,并对密码采用md5加密-->
mac mysql 修改密码
IXHONG
mysql
$ sudo /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld_safe –user=root & //启动MySQL(也可以通过偏好设置面板来启动)$ sudo /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqladmin -uroot password yourpassword //设置MySQL密码(注意,这是第一次MySQL密码为空的时候的设置命令,如果是修改密码,还需在-
设计模式--抽象工厂模式
kerryg
设计模式
抽象工厂模式:
工厂模式有一个问题就是,类的创建依赖于工厂类,也就是说,如果想要拓展程序,必须对工厂类进行修改,这违背了闭包原则。我们采用抽象工厂模式,创建多个工厂类,这样一旦需要增加新的功能,直接增加新的工厂类就可以了,不需要修改之前的代码。
总结:这个模式的好处就是,如果想增加一个功能,就需要做一个实现类,
评"高中女生军训期跳楼”
nannan408
首先,先抛出我的观点,各位看官少点砖头。那就是,中国的差异化教育必须做起来。
孔圣人有云:有教无类。不同类型的人,都应该有对应的教育方法。目前中国的一体化教育,不知道已经扼杀了多少创造性人才。我们出不了爱迪生,出不了爱因斯坦,很大原因,是我们的培养思路错了,我们是第一要“顺从”。如果不顺从,我们的学校,就会用各种方法,罚站,罚写作业,各种罚。军
scala如何读取和写入文件内容?
qindongliang1922
java jvm scala
直接看如下代码:
package file
import java.io.RandomAccessFile
import java.nio.charset.Charset
import scala.io.Source
import scala.reflect.io.{File, Path}
/**
* Created by qindongliang on 2015/
C语言算法之百元买百鸡
qiufeihu
c 算法
中国古代数学家张丘建在他的《算经》中提出了一个著名的“百钱买百鸡问题”,鸡翁一,值钱五,鸡母一,值钱三,鸡雏三,值钱一,百钱买百鸡,问翁,母,雏各几何?
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int cock,hen,chick; /*定义变量为基本整型*/
for(coc
Hadoop集群安全性:Hadoop中Namenode单点故障的解决方案及详细介绍AvatarNode
wyz2009107220
NameNode
正如大家所知,NameNode在Hadoop系统中存在单点故障问题,这个对于标榜高可用性的Hadoop来说一直是个软肋。本文讨论一下为了解决这个问题而存在的几个solution。
1. Secondary NameNode
原理:Secondary NN会定期的从NN中读取editlog,与自己存储的Image进行合并形成新的metadata image
优点:Hadoop较早的版本都自带,