分布式内存存储式元数据服务的构建
文章目录
- 前言
- 内存式元数据服务概述
- 通用的简单K-V内存存储的replicated server
- 内存式Replicated server的实现
- Client side的实现
- Server side的实现
- 引用
前言
在前面的文章里(基于状态机方法构建高容错性服务, Apache Ratis的Ratis Server主从同步机制),笔者谈论过如何利用状态机理论来构建replicated server的文章,以此做到服务的高可用性,可做到随时的动态切换。前面文章已经详细阐述里面replicated的原理细节内容,本文笔者打算谈论其中一类特殊的数据服务:纯内存式的replicated server,即In memory的replicated server。纯内存式的数据服务在读写性能上毫无疑问有着极快的响应时间,在实际用途中也有很多的适用场景。下面我们来聊聊这块的内容以及对此的一个简单代码实现。
内存式元数据服务概述
内存元数据服务,顾名思义,就是将系统的元数据信息全部加载到内存中进行访问。鉴于内存访问速度远远快于磁盘读写速度,因此内存元数据服务有着其固有的一大优势:数据读写快。但是它同样有着相比于磁盘做存储而言的一些劣势,
- 内存空间有限,不如磁盘空间大,论单节点而言,一个系统服务所在节点的可用内存大的会达到百GB级别,但是磁盘一个节点可达到TB级别。
- 内存数据转瞬即逝,需要有好的策略定期持久化内存数据出去。
不过回头来看,上百GB级别的内存空间用来做元数据的存储还是足够的,毕竟每个元数据单位空间占据不至于那么大。以HDFS NameNode为例,上100GB的NN内存使用可以容纳2亿级别的block元数据信息了。
通用的简单K-V内存存储的replicated server
如小标题所示,本文笔者想要阐述的是一种较为简单的,纯内存存储的K-V键值对的replicated server。这类replicated server将会提供以下基本的服务要求:
- 内存存储元数据数据,操作响应时间短
- K-V存储的使用方式,对用户友好,易于使用
- 对上层应用提供通用的元数据存储功能
- 具有replicated server属性,能做到高可用性,错误出现时能做到容灾切换
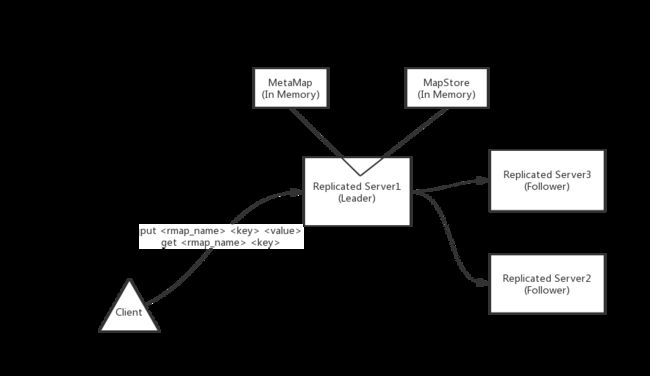
以下是内存存储replicated server的架构模式图:
在上图中,MapStore是实质存储KV键值的map存储数据结构,MetaMap是map store的元数据存储集。Client到Replicated Server1连线部分的文字即为Client实际操作的使用命令方式:
put操作 <目标操作map名称>
get操作 <目标操作map名称> <待取出的key名称>
了解完内存式的replicated server后,我们来了解对此server的一个简单实现,来自于Apache Ratis的JIRA: RATIS-40: Replicated Map。
内存式Replicated server的实现
在内存式Replicated server的整个模块实现中,可以进一步划分为client side和server side的实现。
Client side的实现
Client side端的实现相比较Server端要简化许多。在Client端,暴露给用户使用的CLI命令如下所示:
Usage: ratis rmap <command> [<args>]");
Commands:
create <rmap_name> <key_class> <value_class>
put <rmap_name> <key> <value>
get <rmap_name> <key>
这里的rmap即replicated map的意思,map为KV内存键值对存储map,以下是对应crete操作方法:
private int create(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, IOException {
if (args.length < 3) {
return printUsage();
}
// 1)构造replicated map的元信息
RMapInfo info = RMapInfo.newBuilder()
.withName(RMapName.valueOf(args[0]))
.withKeyClass(Class.forName(args[1]))
.withValueClass(Class.forName(args[2]))
.build();
// 2)获取admin接口创建Rmap
try (Client client = ClientFactory.getClient(new FileQuorumSupplier());
Admin admin = client.getAdmin()) {
info = admin.createRMap(info);
System.out.println("Created rmap:" + info);
}
return 0;
}
另外的put方法实现如下:
private int put(String[] args) throws IOException {
if (args.length < 3) {
return printUsage();
}
// 1)解析得到目标RMap id
long rmapId = Long.parseLong(args[0]);
try (Client client = ClientFactory.getClient(new FileQuorumSupplier());
RMap<String, String> rmap = client.getRMap(rmapId)) {
// 2)将解析得到的k,v值存入解析得到的RMap内
rmap.put(args[1], args[2]);
System.out.println("Put success rmap:" + rmapId + ", " + args[1] + "=" + args[2]);
}
return 0;
}
上述方法调用的rmap变量本质上为Client调用远端replicated server的API定义类,类接口定义如下:
/**
* Replicated in memory Map API定义
*/
public interface RMap<K, V> extends Closeable {
// put方法
void put(K key, V value) throws IOException;
// 根据键值,取value操作
V get(K key) throws IOException;
// scan扫描方法(scan操作在这里并没有暴露在CLI上)
Iterable<Entry<K, V>> scan(Scan<K> scan) throws IOException;
}
RMap实例实现如下:
public class RMapImpl<K, V> implements RMap<K, V> {
// 实质Client调用类
private final RaftClient raftClient;
// 目标操作的RMmap元信息
private final RMapInfo info;
// key值序列化类
private final Serde<K> keySerde;
// value值序列化类
private final Serde<V> valueSerde;
...
public void put(K key, V value) throws IOException {
// 1)根据key, value的序列化类进行K,V值的序列化操作
ByteString k = keySerde.serialize(key);
ByteString v = valueSerde.serialize(value);
// 2)构造包含K,V的put request请求
Request req = ProtobufConverter.buildMultiPutRequest(info.getId(), k, v);
// 3)调用Client发起请求
RaftClientReply reply = raftClient.send(req);
if (!reply.isSuccess()) {
throw new IOException("Request failed :" + reply);
}
Response resp = ProtobufConverter.parseResponseFrom(reply.getMessage().getContent());
MultiActionResponse multiActionResponse = resp.getMultiActionResponse();
assert multiActionResponse != null;
// nothing to check in the response
}
至此,client端的调用部分基本完成,下面我们来看看server端的处理过程。
Server side的实现
Server side的实现还是基于Raft server带上一个指定的StateMachine进行实现的。
private RMapServer(String id, QuorumSupplier quorumSupplier) throws IOException {
properties = new RaftProperties();
properties.setBoolean(RaftServerConfigKeys.RAFT_SERVER_USE_MEMORY_LOG_KEY, false);
...
raftServer = RaftServer.newBuilder()
.setServerId(myId)
.setPeers(peers)
.setProperties(properties)
// 新建RMapStateMachine作为状态机
.setStateMachine(new RMapStateMachine())
.build();
}
在RMapStateMachine中,维护了内存元数据存储结果RMapStore,
public class RMapStateMachine extends BaseStateMachine {
static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RMapStateMachine.class);
// RMap的元数据map
private final MetaMap metaMap;
private final SimpleStateMachineStorage storage;
// replicated map集
private final ConcurrentHashMap<Long, RMapStore> rmaps = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
...
client的rmap请求到StateMachine这边被转化为了transaction,然后再被进一步处理,
public TransactionContext applyTransactionSerial(TransactionContext trx) throws IOException {
ByteString data = trx.getSMLogEntry().get().getData();
WALEntry walEntry = WALEntry.parseFrom(data);
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("Applying WALEntry:{}", TextFormat.shortDebugString(walEntry)); // TODO: trace
}
// 1)从transaction中获取rmapId,然后借此得到RMap store.
long rmapId = walEntry.getRmapId();
RMapStore store = rmaps.get(rmapId);
if (store == null) {
throw new IOException("Cannot find RMap with id:" + rmapId + ", for transaction: " + trx);
}
// TODO: locks and all
// 根据WAL类型,进行RMap store的操作
switch (walEntry.getWALEntryTypeCase()) {
// 如果是CREATE RMAP请求,则进行create map操作
case CREATE_RMAP_ENTRY:
trx.setStateMachineContext(applyCreateRMap(trx, walEntry));
break;
case WALENTRYTYPE_NOT_SET: // Multi action
// 另外一种,则进行K,V信息的apply到RMap store内
trx.setStateMachineContext(applyToStore(walEntry, store));
break;
}
LOG.info(store.debugDump()); // TODO: remove
return super.applyTransactionSerial(trx);
}
...
/**
* 将WAL entry中的值apply到RMap store中
*/
private Response applyToStore(WALEntry walEntry, RMapStore store) {
// 遍历wal entry中的键值对,put到RMap store
for (Entry entry : walEntry.getEntryList()) {
ByteString key = entry.getKey();
ByteString value = entry.getValue();
store.put(key, value);
}
return ProtobufConverter.buildMultiPutResponse(Stream.of(walEntry));
}
最后我们来进入上述的实质存储结构RMapStore的实现,对于外界来说,它提供的接口其实很简单,就是标准的KV键值对存储。
首先我们来看其内部变量定义,
/**
* This is the in-memory implementation for a sorted map of K to V. The concurrency model
* is pretty simple for now, and does not pipeline the memory insertions with the WAL commits.
* @param the class for keys
* @param the class for values
*/
public class RMapStore<
K,
V,
KS extends Serde<K>,
VS extends Serde<V>,
KC extends Comparator<? super K>> {
// RMap的元数据信息
private final RMapInfo<K, V, KS, VS, KC> info;
// key的序列化类信息
private final Serde<K> keySerde;
// value值的反序列类信息
private final Serde<V> valueSerde;
// 用线程安全,排序map(可便于scan)做K,V值存储介质
private final ConcurrentSkipListMap<K, V> map;
...
因为要支持线程安全的排序map的属性,于是这里使用了ConcurrentSkipListMap而非TreeMap。二者结构在排序实现原理上并不相同,后者使用的是红黑树原理而前者则使用的是"跳跃表"的概念。
我们挑选其中的put方法,看看它的实现是如何的,
/**
* Put执行方法
*/
public void put(ByteString key, ByteString value) {
// 1)反序列化键值
K k = keySerde.deserialize(key);
V v = valueSerde.deserialize(value);
// 2)将反序列的键值放入排序map内
put(k,v);
}
public void put(K key, V value) {
map.put(key, value);
}
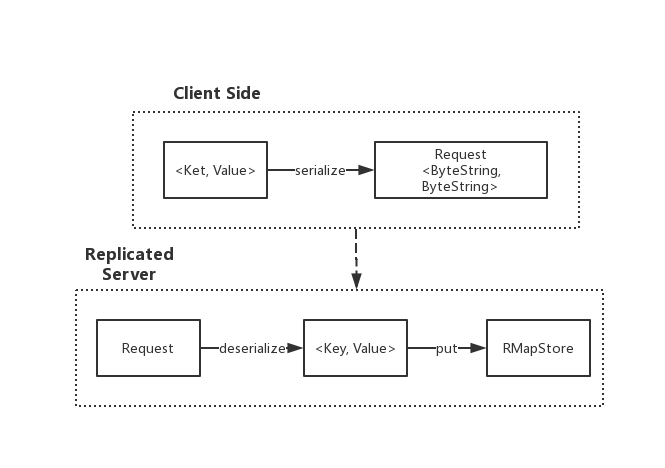
综上实现,将client和server端的实现完全串联起来,关系图如下所示:
以上就是本文所要阐述的纯内存式存储的元数据replicated server实现,在一定场合还是能够提供一种较为简单的数据服务能力的。
引用
[1].https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/RATIS-40 . Replicated Map
[2].https://blog.csdn.net/Androidlushangderen/article/details/97974228 . 基于状态机方法构建高容错性服务
[3]https://blog.csdn.net/Androidlushangderen/article/details/99663173 . Apache Ratis的Ratis Server主从同步机制