Spring源码分析总结(二)-Spring AOP 解析aop:aspectj-autoproxy
Spring AOP
当前分析的Spring 版本 5.0Spring 2.0开始采用@AspectJ注解对POJO标注,使用切点表达式语法进行切点定义.
Spring支持注解的AOP,需要在配置文件xml中配置
在Spring中自定义的注解和自定义的标签都会在Spring中找到 注册该注解或者标签的对应解析器。
一、注册解析器-init()追溯
在配置文件中配置了
public class AopNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
/**
* Register the {@link BeanDefinitionParser BeanDefinitionParsers} for the
* '{@code config}', '{@code spring-configured}', '{@code aspectj-autoproxy}'
* and '{@code scoped-proxy}' tags.
*/
@Override
public void init() {
// In 2.0 XSD as well as in 2.1 XSD.
registerBeanDefinitionParser("config", new ConfigBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("aspectj-autoproxy", new AspectJAutoProxyBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionDecorator("scoped-proxy", new ScopedProxyBeanDefinitionDecorator());
// Only in 2.0 XSD: moved to context namespace as of 2.1
registerBeanDefinitionParser("spring-configured", new SpringConfiguredBeanDefinitionParser());
}
}AopNamespaceHandler类init()方法
1、这里是 解析自定义元素节点 调用parseCustomElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBd)方法
从上图可知,追溯调用了
-->XmlBeanDefinitionReader类的 loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) 方法
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
}由上图可知,一步一步从refresh()方法,一步一步 调用了到XmlBeanDefinitionReader类的 loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) 方法 最后开始在AopNamespaceHandler类中注册了aspectj-autoproxy,
2、这里是对子标签下的自定义属性调用decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired方法进行解析 追溯到开始也调用了 loadBeanDefinitions方法 也就是开始解析xml文件的时候开始
二、注册解析器
所有的解析器,都实现了BeanDefinitionParser接口,入口都是从BeanDefinitionParser接口的方法parse()开始
AspectJAutoProxyBeanDefinitionParser类的parse方法如下:
@Override
@Nullable
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
AopNamespaceUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(parserContext, element);//注册AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
extendBeanDefinition(element, parserContext);//对于注解中子类的处理
return null;
}AspectJAutoProxyBeanDefinitionParser类的parse方法追溯如下,也是从loadBeanDefinitions()
-->loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource)
-->doLoadBeanDefinitions()
-->registerBeanDefinitions()
-->一步一步 最后到--》parse()方法
parse方法里面的registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary方法实现如下:
public static void registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(
ParserContext parserContext, Element sourceElement) {
//注册或升级AutoProxyCreator定义beanName为org.Springframework.aop.config.internalAutoProxyCreator的BeanDefinition
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(
parserContext.getRegistry(), parserContext.extractSource(sourceElement));
useClassProxyingIfNecessary(parserContext.getRegistry(), sourceElement); //对于proxy-target-class以及expose-proxy属性的处理
registerComponentIfNecessary(beanDefinition, parserContext);//注册组件并通知,便于监听器做进一步处理,其中beanDefinition的className是AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
}1、-->AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary
-->AopConfigUtils类的
@Nullable
private static BeanDefinition registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(Class cls, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry,
@Nullable Object source) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
//是否已经存在自动代理创建器
if (registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
BeanDefinition apcDefinition = registry.getBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME);
if (!cls.getName().equals(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName())) {//如果已经存在,根据优先级来判断采用那个创建器
int currentPriority = findPriorityForClass(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName());
int requiredPriority = findPriorityForClass(cls);
if (currentPriority < requiredPriority) {
apcDefinition.setBeanClassName(cls.getName()); //这里拿到已经创建的创建器,然后设置beanClassName
}
}
return null; //这里就不返回新的创建器了
}
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(cls);
beanDefinition.setSource(source);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("order", Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
beanDefinition.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
registry.registerBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME, beanDefinition);//注册自动代理创建器
return beanDefinition;
}2、--> AopNamespaceUtils类的registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary方法的
-》useClassProxyingIfNecessary(parserContext.getRegistry(), sourceElement);
useClassProxyingIfNecessary实现了 proxy-target-class属性和expose-proxy属性的处理
private static void useClassProxyingIfNecessary(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Element sourceElement) {
if (sourceElement != null) {//处理proxy-target-class属性
boolean proxyTargetClass = Boolean.parseBoolean(sourceElement.getAttribute(PROXY_TARGET_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE));
if (proxyTargetClass) {
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry);
}//下面是处理expose-proxy属性
boolean exposeProxy = Boolean.parseBoolean(sourceElement.getAttribute(EXPOSE_PROXY_ATTRIBUTE));
if (exposeProxy) {
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToExposeProxy(registry);
}
}
}AopConfigUtils类 处理proxy-target-class属性
public static void forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
if (registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
BeanDefinition definition = registry.getBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME);
definition.getPropertyValues().add("proxyTargetClass", Boolean.TRUE);
}
}public static void forceAutoProxyCreatorToExposeProxy(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
if (registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
BeanDefinition definition = registry.getBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME);
definition.getPropertyValues().add("exposeProxy", Boolean.TRUE);
}
}上面代码 registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME)
因为DefaultListableBeanFactory继承了BeanDefinitionRegistry 也就是查看容器里面是否包含了auto_proxy_creator_bean_name,也就是查看解析xml初始化的时候 beanDefinitionMap中是否有auto_proxy_creator_bean_name这个key。
proxy-target-class属性: Spring AOP使用JDK动态代理和CGLIB代理来为目标对象创建代理。(建议尽量使用JDK动态代理),
如果被代理的目标对象实现了至少一个接口,则会使用JDK动态代理,所有该目标类型实现的接口都将 被代理。 若该目标对象没有实现任何接口,则创建一个CGLIB代理.
如果想要强制使用CGLIB代理,需要将
如果需要使用CGLIB代理和@AspectJ自动代理支持,配置
expose-proxy属性:
public interface TestService{
public void a();
public void b();
}
@Service
public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService{
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void a(){
this.b();
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED_NEW)
public void b(){}
}
this.b();将不会执行b事务的切面,也就是不会执行事务的增强,因为b方法的事务定义是Propagation.REQUIRED_NEW
如果需要解决这个,需要 用到expose-proxy属性
然后修改b方法代码,改为 ((TestService)AopContext.currentProxy()).b()
二、创建代理
AopConfigUtils类
@Nullable
public static BeanDefinition registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry,
@Nullable Object source) {
return registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class, registry, source);
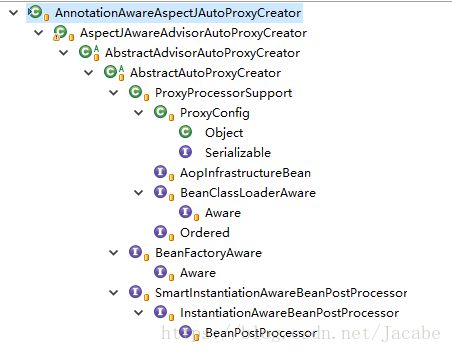
}从上面registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired方法 参数AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator类
由上图可知 AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator类实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,
当Spring加载这个bean的时候会在实例化前后分别调用postProcessBeforeInitialization和postProcessAfterInitialization方法。
在父类AbstractAutoProxyCreator的postProcessAfterInitialization方法
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
return bean;
}
/**
* Create a proxy with the configured interceptors if the bean is
* identified as one to proxy by the subclass.
* @see #getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean != null) {//构建出key,格式是 &beanName 或者 beanName
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) {
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}/**
* Wrap the given bean if necessary, i.e. if it is eligible for being proxied.
* @param bean the raw bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param cacheKey the cache key for metadata access
* @return a proxy wrapping the bean, or the raw bean instance as-is
*/
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {//如果已经处理了直接返回
return bean;
}
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {//如果在advisedBeans找不到对应的key直接返回
return bean;
}//如果指定的bean类是一个基础设施类(包括Advice,Pointcut,Advisor,AopInfrastructureBean)或者不需要自动代理跳过
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// Create proxy if we have advice.
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());return proxy;}this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);return bean;}真正 创建代理的代码从 getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean开始,如果存在advice就创建proxy
// Create proxy if we have advice.
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
1、getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean方法
AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator类
@Override
@Nullable
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(
Class beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource) {
List advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);
if (advisors.isEmpty()) {
return DO_NOT_PROXY;
}
return advisors.toArray();
}
@Override
protected List findCandidateAdvisors() {
// Add all the Spring advisors found according to superclass rules.
List advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors();//调用父类方法加载配置文件中的AOP声明
// Build Advisors for all AspectJ aspects in the bean factory.
if (this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder != null) {
advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors());
}
return advisors;
} this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors() //获取bean的注解增强
/**
* Look for AspectJ-annotated aspect beans in the current bean factory,
* and return to a list of Spring AOP Advisors representing them.
* Creates a Spring Advisor for each AspectJ advice method.
* @return the list of {@link org.springframework.aop.Advisor} beans
* @see #isEligibleBean
*/
public List buildAspectJAdvisors() {
List aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
synchronized (this) {
aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
List advisors = new LinkedList<>();
aspectNames = new LinkedList<>(); //1.获取所有的beanName
String[] beanNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Object.class, true, false);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {//2.循环所有的beanName,并找出声明AspectJ注解的类并进一步处理
if (!isEligibleBean(beanName)) {//检查aspect bean 是否合法合格 默认返回true
continue;
}
// We must be careful not to instantiate beans eagerly as in this case they
// would be cached by the Spring container but would not have been weaved.
Class beanType = this.beanFactory.getType(beanName);//获取对于的bean类型
if (beanType == null) {
continue;
}
if (this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)) {//如果是aspect 注解
aspectNames.add(beanName);
AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName);
if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON) {
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
//3.对标记AspectJ注解的类进行增强器的提取ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory类
@Override
public List getAdvisors(MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory) {
Class aspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();//标记为aspectJ的类
String aspectName = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectName();//get标记为aspectJ的名字
validate(aspectClass);
// We need to wrap the MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory with a decorator
// so that it will only instantiate once.
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory =
new LazySingletonAspectInstanceFactoryDecorator(aspectInstanceFactory);
List advisors = new LinkedList<>();
for (Method method : getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass)) {
Advisor advisor = getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, advisors.size(), aspectName);
if (advisor != null) {
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
// If it's a per target aspect, emit the dummy instantiating aspect.
if (!advisors.isEmpty() && lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated()) {
//如果寻找的增强器不为空又配置了增强延迟初始化,那就需要在首位加入同步实例化增强器----》 Advisor instantiationAdvisor = new SyntheticInstantiationAdvisor(lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory);
advisors.add(0, instantiationAdvisor);
}
// Find introduction fields.
for (Field field : aspectClass.getDeclaredFields()) {
Advisor advisor = getDeclareParentsAdvisor(field); //DeclareParent主要用于引介增强的注解形式的实现。
if (advisor != null) {
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
return advisors;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Advisor getAdvisor(Method candidateAdviceMethod, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory,
int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName) {
validate(aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
//获取切点信息pointcut
AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut = getPointcut(
candidateAdviceMethod, aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
if (expressionPointcut == null) {
return null;
}
//根据expressionPointcut获取增强器
return new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(expressionPointcut, candidateAdviceMethod,
this, aspectInstanceFactory, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName);
}1)、//pointcut //获取的是 指定注解的表达式信息的获取 ,@After("a()") 中的a()
@Nullable
private AspectJExpressionPointcut getPointcut(Method candidateAdviceMethod, Class candidateAspectClass) {
AspectJAnnotation aspectJAnnotation =
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (aspectJAnnotation == null) {
return null;
}
AspectJExpressionPointcut ajexp =
new AspectJExpressionPointcut(candidateAspectClass, new String[0], new Class[0]);
ajexp.setExpression(aspectJAnnotation.getPointcutExpression());
if (this.beanFactory != null) {
ajexp.setBeanFactory(this.beanFactory);
}
return ajexp;
}ajexp.setExpression(aspectJAnnotation.getPointcutExpression());提取得到的注解中的表达式如:@Pointcut("execution(* *.*test*(..))")中的execution(* *.*test*(..))
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory类的findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod方法
/**
* Find and return the first AspectJ annotation on the given method
* (there should only be one anyway...)
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Nullable
protected static AspectJAnnotation findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(Method method) {
Class[] classesToLookFor = new Class[] {
Before.class, Around.class, After.class, AfterReturning.class, AfterThrowing.class, Pointcut.class};
for (Class c : classesToLookFor) {
AspectJAnnotation foundAnnotation = findAnnotation(method, (Class) c);
if (foundAnnotation != null) {
return foundAnnotation;
}
}
return null;
}
2)、根据切点的信息 组成增强,所有的增强都由InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl统一封装。
public InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(AspectJExpressionPointcut declaredPointcut,
Method aspectJAdviceMethod, AspectJAdvisorFactory aspectJAdvisorFactory,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName)这个方法下面有一个this.instantiatedAdvice = instantiateAdvice(this.declaredPointcut);
instantiateAdvice 根据注解中的信息初始化对应的增强器
private Advice instantiateAdvice(AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut) {
Advice advice = this.aspectJAdvisorFactory.getAdvice(this.aspectJAdviceMethod, pointcut,
this.aspectInstanceFactory, this.declarationOrder, this.aspectName);
return (advice != null ? advice : EMPTY_ADVICE);
}ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory类中的
@Override
@Nullable
public Advice getAdvice(Method candidateAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) {
Class candidateAspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
validate(candidateAspectClass);
AspectJAnnotation aspectJAnnotation =
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (aspectJAnnotation == null) {
return null;
}
// If we get here, we know we have an AspectJ method.
// Check that it's an AspectJ-annotated class
if (!isAspect(candidateAspectClass)) {
throw new AopConfigException("Advice must be declared inside an aspect type: " +
"Offending method '" + candidateAdviceMethod + "' in class [" +
candidateAspectClass.getName() + "]");
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Found AspectJ method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);
}
AbstractAspectJAdvice springAdvice;
switch (aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotationType()) {
case AtBefore:
springAdvice = new AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfter:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfterReturning:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterReturningAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterReturning afterReturningAnnotation = (AfterReturning) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterReturningAnnotation.returning())) {
springAdvice.setReturningName(afterReturningAnnotation.returning());
}
break;
case AtAfterThrowing:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterThrowing afterThrowingAnnotation = (AfterThrowing) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing())) {
springAdvice.setThrowingName(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing());
}
break;
case AtAround:
springAdvice = new AspectJAroundAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtPointcut:
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Processing pointcut '" + candidateAdviceMethod.getName() + "'");
}
return null;
default:
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"Unsupported advice type on method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);
}
// Now to configure the advice...
springAdvice.setAspectName(aspectName);
springAdvice.setDeclarationOrder(declarationOrder);
String[] argNames = this.parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (argNames != null) {
springAdvice.setArgumentNamesFromStringArray(argNames);
}
springAdvice.calculateArgumentBindings();
return springAdvice;
}2、创建代理
AbstractAutoProxyCreator类的createProxy方法/**
* Create an AOP proxy for the given bean.
* @param beanClass the class of the bean
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param specificInterceptors the set of interceptors that is
* specific to this bean (may be empty, but not null)
* @param targetSource the TargetSource for the proxy,
* already pre-configured to access the bean
* @return the AOP proxy for the bean
* @see #buildAdvisors
*/
protected Object createProxy(Class beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);//获取当前类的相关属性
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {//检查proxyTargetClass属性
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {//添加代理接口
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);//设置要代理的类
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory); //定制代理
//用来控制代理工厂被配置之后,是否还允许修改通知。缺省值为false(在代理被配置之后,不允许修改代理的配置)
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());//获取代理
}1).AbstractAutoProxyCreator类的buildAdvisors方法
/**
* Determine the advisors for the given bean, including the specific interceptors
* as well as the common interceptor, all adapted to the Advisor interface.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param specificInterceptors the set of interceptors that is
* specific to this bean (may be empty, but not null)
* @return the list of Advisors for the given bean
*/
protected Advisor[] buildAdvisors(@Nullable String beanName, @Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors) {
// Handle prototypes correctly...
Advisor[] commonInterceptors = resolveInterceptorNames();
List2.proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());//获取代理
ProxyFactory类getProxy
/**
* Create a new proxy according to the settings in this factory.
* Can be called repeatedly. Effect will vary if we've added
* or removed interfaces. Can add and remove interceptors.
*
Uses a default class loader: Usually, the thread context class loader
* (if necessary for proxy creation).
* @return the proxy object
*/
public Object getProxy() {
return createAopProxy().getProxy();
}
ProxyCreatorSupport类
/**
* Subclasses should call this to get a new AOP proxy. They should not
* create an AOP proxy with {@code this} as an argument.
*/
protected final synchronized AopProxy createAopProxy() {
if (!this.active) {
activate();
}
return getAopProxyFactory().createAopProxy(this);
}@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class DefaultAopProxyFactory implements AopProxyFactory, Serializable {
@Override
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
Class targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
}
if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
}
else {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
}if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config))
optimize:用来控制CGLIB创建的代理是否使用激进的优化策略,除非很了解如何优化aop代理,否则不推荐使用,
目前这个属性仅仅用于CGLIB代理,对于jdk动态代理默认无效。
hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces:是否存在代理接口。
最后就是
createAopProxy().getProxy(); 获取对应的实例 CGLIB或者JDK版权声明:原创文章,如需转载需经过博主同意