Java--equals()、hashCode()作用、hash算法分析
本文主要阐述个人所学知识观点,技能水平有限,如有不足之处,望各位大哥给小弟点建议,蟹蟹啦啦啦,文章走起咯~
一、equals()、hashCode()使用说明
1、hashCode()、equals()方法都是Object类中定义的方法即所有引用数据类型均可调用该方法;
2、Object类中的hashCode()方法,默认实现是返回对象的内部地址转成的整数值,子类可重写该方法,并尽可能根据自身的属性制定规则来计算返回的hashCode值;
3、Object类中的equals()方法,默认实现是返回对象的内部地址比较结果,子类可重写该方法,并尽可能根据自身的属性制定规则进行比较并返回比较结果。
二、equals()、hashCode()作用
1、equals()用来判断两个对象是否相等,hashCode()方法用来提高散列结构集合的查找效率;
2、集合中判断对象是否存在,常规做法是循环遍历集合,一一对对象进行equals比较,比较结果为true表示集合已存在相等对象,fasle则表示不存在相等对象。常规做法效率比较低,因此引入了hash算法来提高效率。
(图)散列结构集合中判断是否存在相等对象A
result1:做存储操作时,直接添加对象A;
result2:做存储操作时,HashMap会替换已存在相等的对象为相同key的对象A,HashSet则直接舍弃对象A。
三、hash算法
hash算法是什么?
HashMap的数据结构是数组table[index])+ 链表(Entry
HashMap的底层源码使用到了hash算法,hash算法实现过程,首先根据每个对象hashCode值,再根据hashCode值计算到自己的哈希码(hash值),最后再根据hash值(位运算或者取模)计算对象被分配在哈希表中的table[index]即数组位置。
hash算法作用
HashMap、HashSet、HashTable等散列存储结构集合中,判断对象是否存在,采用hash算法,根据每个对象hashCode值,计算自己的哈希码(hash值),再根据hash值计算对象在哈希表中的table[index]即数组位置,只需要在该table[index]的链表中查找,效率大大提升。
HashMap的hash算法底层源码(JDK1.6)
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
static int hash(int h) {
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
} HashMap的hash算法底层源码(JDK1.8)
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}下面通过一个例子介绍hash算法是如何通过对象的hashCode方法,计算对象会被分配到哈希表中哪个table[index]数组位置?
测试代码
public class CalculateHashIndexTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap(16); //初始化容量initialCapacity=16,table.length=16
Student s1 = new Student("尹一",21);
Student s2 = new Student("小二",22);
Student s3 = new Student("张三",23);
Student s4 = new Student("李四",24);
Student s5 = new Student("王五",25);
Student s6 = new Student("赵六",26);
Student s7 = new Student("陈七",27);
Student s8 = new Student("王八",28);
Student s9 = new Student("陈九",29);
hashMap.put("s1",s1);
hashMap.put("s2",s2);
hashMap.put("s3",s3);
hashMap.put("s4",s4);
hashMap.put("s5",s5);
hashMap.put("s6",s6);
hashMap.put("s7",s7);
hashMap.put("s8",s8);
hashMap.put("s9",s9);
System.out.println("hashCode值====");
System.out.println("hashCode1=" + s1.hashCode());
System.out.println("hashCode2=" + s2.hashCode());
System.out.println("hashCode3=" + s3.hashCode());
System.out.println("hashCode4=" + s4.hashCode());
System.out.println("hashCode5=" + s5.hashCode());
System.out.println("hashCode6=" + s6.hashCode());
System.out.println("hashCode7=" + s7.hashCode());
System.out.println("hashCode8=" + s8.hashCode());
System.out.println("hashCode9=" + s9.hashCode());
System.out.println("=================================JDK1.8======================================");
System.out.println("====hash值====");
//int hash = hashCode ^ (hashCode >>> 16) JDK1.8 hash值算法
System.out.println("hash1=" + ((s1.hashCode()) ^ (s1.hashCode() >>> 16)));
System.out.println("hash2=" + ((s2.hashCode()) ^ (s2.hashCode() >>> 16)));
System.out.println("hash3=" + ((s3.hashCode()) ^ (s3.hashCode() >>> 16)));
System.out.println("hash4=" + ((s4.hashCode()) ^ (s4.hashCode() >>> 16)));
System.out.println("hash5=" + ((s5.hashCode()) ^ (s5.hashCode() >>> 16)));
System.out.println("hash6=" + ((s6.hashCode()) ^ (s6.hashCode() >>> 16)));
System.out.println("hash7=" + ((s7.hashCode()) ^ (s7.hashCode() >>> 16)));
System.out.println("hash8=" + ((s8.hashCode()) ^ (s8.hashCode() >>> 16)));
System.out.println("hash9=" + ((s9.hashCode()) ^ (s9.hashCode() >>> 16)));
System.out.println("====hash表table[index]的位置====");
//table[index]
//tab[i = (n - 1) & hash] JDK1.8源码中计算对象存放在哈希表中table[index]的位置
//index=(n - 1) & hash,n表示初始化容量initialCapacity,例子中initialCapacity=16
System.out.println(s1.getName()+ "在hash表table[" + ((15-1) & ((s1.hashCode()) ^ (s1.hashCode() >>> 16))) + "]位置");
System.out.println(s2.getName()+ "在hash表table[" + ((15-1) & ((s2.hashCode()) ^ (s2.hashCode() >>> 16))) + "]位置");
System.out.println(s3.getName()+ "在hash表table[" + ((15-1) & ((s3.hashCode()) ^ (s3.hashCode() >>> 16))) + "]位置");
System.out.println(s4.getName()+ "在hash表table[" + ((15-1) & ((s4.hashCode()) ^ (s4.hashCode() >>> 16))) + "]位置");
System.out.println(s5.getName()+ "在hash表table[" + ((15-1) & ((s5.hashCode()) ^ (s5.hashCode() >>> 16))) + "]位置");
System.out.println(s6.getName()+ "在hash表table[" + ((15-1) & ((s6.hashCode()) ^ (s6.hashCode() >>> 16))) + "]位置");
System.out.println(s7.getName()+ "在hash表table[" + ((15-1) & ((s7.hashCode()) ^ (s7.hashCode() >>> 16))) + "]位置");
System.out.println(s8.getName()+ "在hash表table[" + ((15-1) & ((s8.hashCode()) ^ (s8.hashCode() >>> 16))) + "]位置");
System.out.println(s9.getName()+ "在hash表table[" + ((15-1) & ((s9.hashCode()) ^ (s9.hashCode() >>> 16))) + "]位置");
System.out.println("=================================JDK1.6======================================");
System.out.println("====hash值====");
//int hash;
//hashCode ^= (hashCode >>> 20) ^ (hashCode >>> 12);
//hash = hashCode ^ (hashCode >>> 7) ^ (hashCode >>> 4); JDK1.6 hash值算法
int hashCode1 = s1.hashCode();
hashCode1 ^= (hashCode1 >>> 20) ^ (hashCode1 >>> 12);
int hash1 = hashCode1 ^ (hashCode1 >>> 7) ^ (hashCode1 >>> 4);
int hashCode2 = s2.hashCode();
hashCode2 ^= (hashCode2 >>> 20) ^ (hashCode2 >>> 12);
int hash2 = hashCode2 ^ (hashCode2 >>> 7) ^ (hashCode2 >>> 4);
int hashCode3 = s3.hashCode();
hashCode3 ^= (hashCode3 >>> 20) ^ (hashCode3 >>> 12);
int hash3 = hashCode3 ^ (hashCode3 >>> 7) ^ (hashCode3 >>> 4);
int hashCode4 = s4.hashCode();
hashCode4 ^= (hashCode4 >>> 20) ^ (hashCode4 >>> 12);
int hash4 = hashCode4 ^ (hashCode4 >>> 7) ^ (hashCode4 >>> 4);
int hashCode5 = s5.hashCode();
hashCode5 ^= (hashCode5 >>> 20) ^ (hashCode5 >>> 12);
int hash5 = hashCode5 ^ (hashCode5 >>> 7) ^ (hashCode5 >>> 4);
int hashCode6 = s6.hashCode();
hashCode6 ^= (hashCode6 >>> 20) ^ (hashCode6 >>> 12);
int hash6 = hashCode6 ^ (hashCode6 >>> 7) ^ (hashCode6 >>> 4);
int hashCode7 = s7.hashCode();
hashCode7 ^= (hashCode7 >>> 20) ^ (hashCode7 >>> 12);
int hash7 = hashCode7 ^ (hashCode7 >>> 7) ^ (hashCode7 >>> 4);
int hashCode8 = s8.hashCode();
hashCode8 ^= (hashCode8 >>> 20) ^ (hashCode8 >>> 12);
int hash8 = hashCode8 ^ (hashCode8 >>> 7) ^ (hashCode8 >>> 4);
int hashCode9 = s9.hashCode();
hashCode9 ^= (hashCode9 >>> 20) ^ (hashCode9 >>> 12);
int hash9 = hashCode9 ^ (hashCode9 >>> 7) ^ (hashCode9 >>> 4);
System.out.println("hash1=" + hash1);
System.out.println("hash2=" + hash2);
System.out.println("hash3=" + hash3);
System.out.println("hash4=" + hash4);
System.out.println("hash5=" + hash5);
System.out.println("hash6=" + hash6);
System.out.println("hash7=" + hash7);
System.out.println("hash8=" + hash8);
System.out.println("hash9=" + hash9);
System.out.println("table[index]的位置====");
//table[index]
//index = hash & (table.length-1),table.length表示数组大小,等于初始化容量initialCapacity大小,即table.length=16
System.out.println(s1.getName()+ "在hash表table[" + (hash1 & (16-1)) + "]位置");
System.out.println(s2.getName()+ "在hash表table[" + (hash2 & (16-1)) + "]位置");
System.out.println(s3.getName()+ "在hash表table[" + (hash3 & (16-1)) + "]位置");
System.out.println(s4.getName()+ "在hash表table[" + (hash4 & (16-1)) + "]位置");
System.out.println(s5.getName()+ "在hash表table[" + (hash5 & (16-1)) + "]位置");
System.out.println(s6.getName()+ "在hash表table[" + (hash6 & (16-1)) + "]位置");
System.out.println(s7.getName()+ "在hash表table[" + (hash7 & (16-1)) + "]位置");
System.out.println(s8.getName()+ "在hash表table[" + (hash9 & (16-1)) + "]位置");
System.out.println(s9.getName()+ "在hash表table[" + (hash9 & (16-1)) + "]位置");
} 输出结果>>>
hashCode值====
hashCode1=753459
hashCode2=752328
hashCode3=776563
hashCode4=843766
hashCode5=938801
hashCode6=1145215
hashCode7=1214401
hashCode8=939621
hashCode9=1214553
============JDK1.8=================
====hash值====
hash1=753464
hash2=752323
hash3=776568
hash4=843770
hash5=938815
hash6=1145198
hash7=1214419
hash8=939627
hash9=1214539
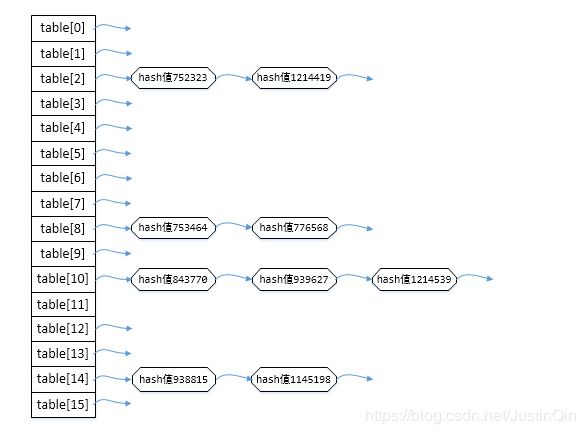
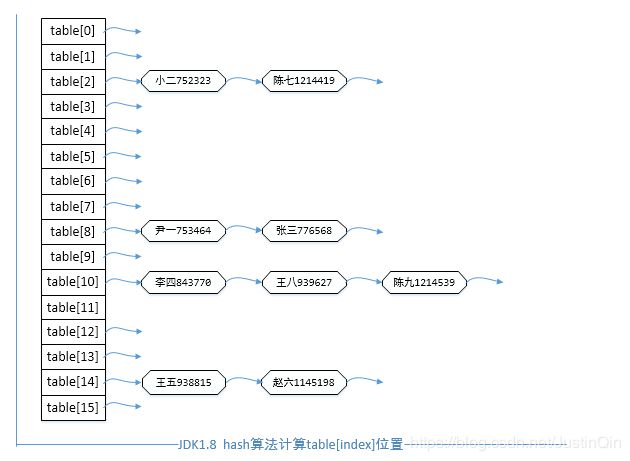
====hash表table[index]的位置====
尹一在hash表table[8]位置
小二在hash表table[2]位置
张三在hash表table[8]位置
李四在hash表table[10]位置
王五在hash表table[14]位置
赵六在hash表table[14]位置
陈七在hash表table[2]位置
王八在hash表table[10]位置
陈九在hash表table[10]位置
================JDK1.6=============
====hash值====
hash1=777859
hash2=777004
hash3=750561
hash4=789366
hash5=961102
hash6=1068319
hash7=1280907
hash8=962373
hash9=1279221
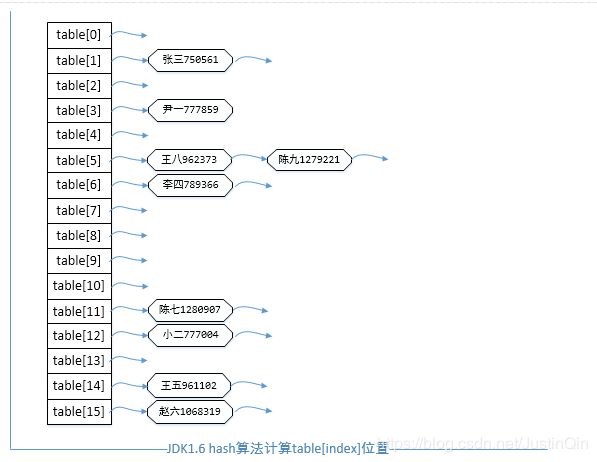
table[index]的位置====
尹一在hash表table[3]位置
小二在hash表table[12]位置
张三在hash表table[1]位置
李四在hash表table[6]位置
王五在hash表table[14]位置
赵六在hash表table[15]位置
陈七在hash表table[11]位置
王八在hash表table[5]位置
陈九在hash表table[5]位置
(图)测试结果>>>对象在哈希表分配状况(JDK1.8)
(图)测试结果>>>对象在哈希表分配状况(JDK1.6)
hash算法只在HashMap、HashSet、HashTable等散列存储结构集合中有效,List等线性列表集合中无效。
四、方法重写
1、hashCode()默认、equals()默认
例1
public class Student {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Student() {
super();
}
public Student(String name, Integer age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "name:" + name + ", age:" + age;
}
}public class TestHashSet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet>>>输出结果
name:张三, age:23
name:张三, age:23
name:李四, age:24
先进行hashCode值比较,hashCode()方法默认返回对象内部地址对应的整数值,两个不同对象的内部对象地址不同,hashCode值不同。此时jdk会认为s1和s2是不相等的对象,因此set会添加s2成功,违反Set集合元素唯一特性。
2、hashCode()重写、equals()默认
例2
public class Student {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Student() {
super();
}
public Student(String name, Integer age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
//set()...
//get()...
@Override
public String toString() {
return "name:" + name + ", age:" + age;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((age == null) ? 0 : age.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
}>>>输出结果
name:张三, age:23
name:张三, age:23
name:李四, age:24
hashCode()方法重写后,返回根据其自身属性计算得到对应的整数值,s1,s2属性相同,所以计算得到的hasdCode值相同,再进行equals比较,equals默认比较对象内部地址,s1,s2两个不同对象内部址不同,返回false,此时jdk会认为s2和s1是不相等的对象,因此set会添加s2,违反set集合元素唯一性。
3、hashCode()默认、equals()重写
例3
public class Student {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Student() {
super();
}
public Student(String name, Integer age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
//set()...
//get()...
@Override
public String toString() {
return "name:" + name + ", age:" + age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Student other = (Student) obj;
if (age == null) {
if (other.age != null)
return false;
} else if (!age.equals(other.age))
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;
}
>>>输出结果
name:张三, age:23
name:张三, age:23
name:李四, age:24
先进行hashCode值比较,hashCode()方法默认返回对象地址对应的整数值。s1,s2两个不同对象内部地址不同,hashCode值不同,此时jdk会认为s2和s1是不相等的对象,因此set.add(s2)成功,违反set集合元素唯一性。
4、hashCode()重写、equals()重写
例4
public class Student {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Student() {
super();
}
public Student(String name, Integer age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
//set()...
//get()...
@Override
public String toString() {
return "name:" + name + ", age:" + age;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((age == null) ? 0 : age.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Student other = (Student) obj;
if (age == null) {
if (other.age != null)
return false;
} else if (!age.equals(other.age))
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;
}
>>>输出结果
name:张三, age:23
name:李四, age:24
hashCode()方法重写后,返回根据其自身属性计算得到对应的整数值,s1,s2属性相同,所以计算得到的hasdCode值相同,再进行equals比较,equals()方法重写后,比较的是对象的自身属性是否一一相等,s1,s2两个对象的属性相等,因此equals比较结果为true,此时jdk会认为s2和s1是相等的对象,set.add(s2)时s2会被舍弃。
5、重写hashCode()、重写equals()方法,内存泄漏问题
例5
public class Student {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Student() {
super();
}
public Student(String name, Integer age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
//set()...
//get()...
@Override
public String toString() {
return "name:" + name + ", age:" + age;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((age == null) ? 0 : age.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Student other = (Student) obj;
if (age == null) {
if (other.age != null)
return false;
} else if (!age.equals(other.age))
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;
}
}
public class HashSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet<>();
Student s1 = new Student("张三",23);
Student s2 = new Student("李四",24);
hashSet.add(s1);
hashSet.add(s2);
s1.setAge(46);
hashSet.remove(s1);
Iterator iterator = hashSet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Student stu = (Student) iterator.next();
System.out.println(stu.toString());
}
}
}
>>>输出结果
name:张三, age:46
name:李四, age:24
set.add(s1)、set.add(s2),修改对象s1的属性,再set.remove(s1),s1不会被删除。
由于程序运行期间,修改了对象s1的属性,对应的hashCode值也会改变,当set.remove(s1)时会先判断set中是否存在s1,此时set中s1的hashCode还是修改属性前的值,但是remove(s1)的s1的由于属性被改变因此hashCode值也会改变,所以jdk认为Set集合中不存在对象s1,因此不会删除对象s1,但是用户认为对象s1已经删除,导致对象s1长时间不能被释放,导致内存泄露。
因此程序运行期间不允许修改计算hashCode值相关的对象属性值,如果需要修改对象属性值,则应先从集合中删除该对象。
五、文章小结
1、散列存储结构中要确保其唯一特性,必须同时重写equals()、hashCode()方法;
2、两个对象equals()比较结果为true,则hashCode()返回值一定相等;
3、两个对象hashCode()返回值相等,equals()比较结果不一定为true。
4、hash算法中,通过hashCode能够高效计算对象的存储地址;
5、hash算法只在散列存储结构中有效,在线性列表结构中无效;
6、程序运行期间,修改计算对象hashCode值相关的属性值,容易导致内存泄漏;
学习资料
https://blog.csdn.net/lijiecao0226/article/details/24609559
https://www.cnblogs.com/keyi/p/7119825.html
https://blog.csdn.net/fenglibing/article/details/8905007