Python3 --- BeautifulSoup4用法总结
一、BeautifulSoup4简介
BeautifulSoup4和 lxml 一样,Beautiful Soup 也是一个HTML/XML的解析器,主要的功能也是如何解析和提取 HTML/XML 数据。
官方文档:http://beautifulsoup.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/v4.4.0/
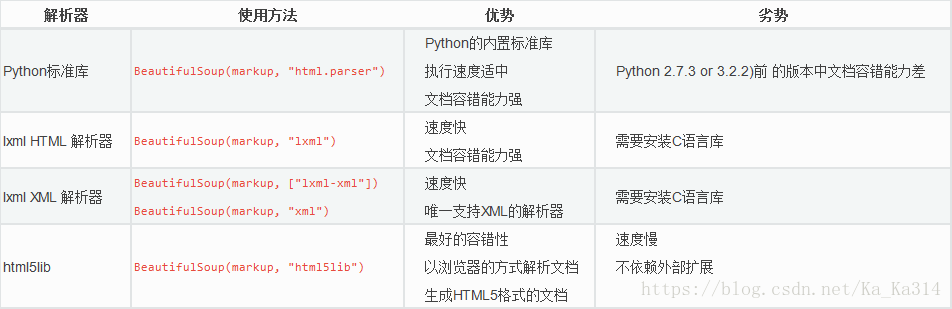
二、BeautifulSoup4主要解析器,以及优缺点:
三、BeautifulSoup4简单使用
假设有这样一个Html,具体内容如下:
html>
content="text/html;charset=utf-8" http-equiv="content-type"/>
content="IE=Edge" http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible"/>
content="always" name="referrer"/>
href="https://ss1.bdstatic.com/5eN1bjq8AAUYm2zgoY3K/r/www/cache/bdorz/baidu.min.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css"/>
</span><span style="color:#e8bf6a;"> </span>百度一下,你就知道
<span style="color:#e8bf6a;">
link="#0000cc">
id="wrapper">
id="head">
class="head_wrapper">
id="u1">
class="mnav" href="http://news.baidu.com" name="tj_trnews">
新闻
class="mnav" href="https://www.hao123.com" name="tj_trhao123">
hao123
class="mnav" href="http://map.baidu.com" name="tj_trmap">
地图
class="mnav" href="http://v.baidu.com" name="tj_trvideo">
视频
class="mnav" href="http://tieba.baidu.com" name="tj_trtieba">
贴吧
class="bri" href="//www.baidu.com/more/" name="tj_briicon" style="display: block;">
更多产品
创建beautifulsoup4对象:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup file = open('./aa.html', 'rb') html = file.read() bs = BeautifulSoup(html,"html.parser") # 缩进格式 print(bs.prettify()) # 获取title标签的所有内容 print(bs.title) # 获取title标签的名称 print(bs.title.name) # 获取title标签的文本内容 print(bs.title.string) # 获取head标签的所有内容 print(bs.head) # 获取第一个div标签中的所有内容 print(bs.div) # 获取第一个div标签的id的值 print(bs.div["id"]) # 获取第一个a标签中的所有内容 print(bs.a) # 获取所有的a标签中的所有内容 print(bs.find_all("a")) # 获取id="u1" print(bs.find(id="u1")) # 获取所有的a标签,并遍历打印a标签中的href的值 for item in bs.find_all("a"): print(item.get("href")) # 获取所有的a标签,并遍历打印a标签的文本值 for item in bs.find_all("a"): print(item.get_text())
四、BeautifulSoup4四大对象种类
BeautifulSoup4将复杂HTML文档转换成一个复杂的树形结构,每个节点都是Python对象,所有对象可以归纳为4种:
- Tag
- NavigableString
- BeautifulSoup
- Comment
4.1、Tag
Tag通俗点讲就是HTML中的一个个标签,例如:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup file = open('./aa.html', 'rb') html = file.read() bs = BeautifulSoup(html,"html.parser") # 获取title标签的所有内容 print(bs.title) # 获取head标签的所有内容 print(bs.head) # 获取第一个a标签的所有内容 print(bs.a) # 类型 print(type(bs.a))
我们可以利用 soup 加标签名轻松地获取这些标签的内容,这些对象的类型是bs4.element.Tag。但是注意,它查找的是在所有内容中的第一个符合要求的标签。
对于 Tag,它有两个重要的属性,是 name 和 attrs:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup file = open('./aa.html', 'rb') html = file.read() bs = BeautifulSoup(html,"html.parser") # [document] #bs 对象本身比较特殊,它的 name 即为 [document] print(bs.name) # head #对于其他内部标签,输出的值便为标签本身的名称 print(bs.head.name) # 在这里,我们把 a 标签的所有属性打印输出了出来,得到的类型是一个字典。 print(bs.a.attrs) #还可以利用get方法,传入属性的名称,二者是等价的 print(bs.a['class']) # bs.a.get('class') # 可以对这些属性和内容等等进行修改 bs.a['class'] = "newClass" print(bs.a) # 还可以对这个属性进行删除 del bs.a['class'] print(bs.a)
4.2、NavigableString
既然我们已经得到了标签的内容,那么问题来了,我们要想获取标签内部的文字怎么办呢?很简单,用 .string 即可,例如:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup file = open('./aa.html', 'rb') html = file.read() bs = BeautifulSoup(html,"html.parser") print(bs.title.string) print(type(bs.title.string))
4.3、BeautifulSoup
BeautifulSoup对象表示的是一个文档的内容。大部分时候,可以把它当作 Tag 对象,是一个特殊的 Tag,我们可以分别获取它的类型,名称,以及属性,例如:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup file = open('./aa.html', 'rb') html = file.read() bs = BeautifulSoup(html,"html.parser") print(type(bs.name)) print(bs.name) print(bs.attrs)
4.4、Comment
Comment 对象是一个特殊类型的 NavigableString 对象,其输出的内容不包括注释符号。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup file = open('./aa.html', 'rb') html = file.read() bs = BeautifulSoup(html,"html.parser") print(bs.a) # 此时不能出现空格和换行符,a标签如下: # print(bs.a.string) # 新闻 print(type(bs.a.string)) #
五、遍历文档树
5.1、.contents:获取Tag的所有子节点,返回一个list
# tag的.content 属性可以将tag的子节点以列表的方式输出 print(bs.head.contents) # 用列表索引来获取它的某一个元素 print(bs.head.contents[1])5.2、.children:获取Tag的所有子节点,返回一个生成器
for child in bs.body.children: print(child)5.3、.descendants:获取Tag的所有子孙节点
5.4、.strings:如果Tag包含多个字符串,即在子孙节点中有内容,可以用此获取,而后进行遍历
5.5、.stripped_strings:与strings用法一致,只不过可以去除掉那些多余的空白内容
5.6、.parent:获取Tag的父节点
5.7、.parents:递归得到父辈元素的所有节点,返回一个生成器
5.8、.previous_sibling:获取当前Tag的上一个节点,属性通常是字符串或空白,真实结果是当前标签与上一个标签之间的顿号和换行符
5.9、.next_sibling:获取当前Tag的下一个节点,属性通常是字符串或空白,真是结果是当前标签与下一个标签之间的顿号与换行符5.10、.previous_siblings:获取当前Tag的上面所有的兄弟节点,返回一个生成器
5.11、.next_siblings:获取当前Tag的下面所有的兄弟节点,返回一个生成器5.12、.previous_element:获取解析过程中上一个被解析的对象(字符串或tag),可能与previous_sibling相同,但通常是不一样的
5.13、.next_element:获取解析过程中下一个被解析的对象(字符串或tag),可能与next_sibling相同,但通常是不一样的5.14、.previous_elements:返回一个生成器,可以向前访问文档的解析内容
5.15、.next_elements:返回一个生成器,可以向后访问文档的解析内容
5.16、.has_attr:判断Tag是否包含属性六、搜索文档树
6.1、find_all(name, attrs, recursive, text, **kwargs)
在上面的栗子中我们简单介绍了find_all的使用,接下来介绍一下find_all的更多用法-过滤器。这些过滤器贯穿整个搜索API,过滤器可以被用在tag的name中,节点的属性等。
(1)name参数:
字符串过滤:会查找与字符串完全匹配的内容
a_list = bs.find_all("a") print(a_list)
正则表达式过滤:如果传入的是正则表达式,那么BeautifulSoup4会通过search()来匹配内容
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import re file = open('./aa.html', 'rb') html = file.read() bs = BeautifulSoup(html,"html.parser") t_list = bs.find_all(re.compile("a")) for item in t_list: print(item)
列表:如果传入一个列表,BeautifulSoup4将会与列表中的任一元素匹配到的节点返回
t_list = bs.find_all(["meta","link"]) for item in t_list: print(item)
方法:传入一个方法,根据方法来匹配
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup file = open('./aa.html', 'rb') html = file.read() bs = BeautifulSoup(html,"html.parser") def name_is_exists(tag): return tag.has_attr("name") t_list = bs.find_all(name_is_exists) for item in t_list: print(item)
(2)kwargs参数:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import re file = open('./aa.html', 'rb') html = file.read() bs = BeautifulSoup(html,"html.parser") # 查询id=head的Tag t_list = bs.find_all(id="head") print(t_list) # 查询href属性包含ss1.bdstatic.com的Tag t_list = bs.find_all(href=re.compile("http://news.baidu.com")) print(t_list) # 查询所有包含class的Tag(注意:class在Python中属于关键字,所以加_以示区别) t_list = bs.find_all(class_=True) for item in t_list: print(item)
(3)attrs参数:
并不是所有的属性都可以使用上面这种方式进行搜索,比如HTML的data-*属性:
t_list = bs.find_all(data-foo="value")
如果执行这段代码,将会报错。我们可以使用attrs参数,定义一个字典来搜索包含特殊属性的tag:
t_list = bs.find_all(attrs={"data-foo":"value"}) for item in t_list: print(item)
(4)text参数:
通过text参数可以搜索文档中的字符串内容,与name参数的可选值一样,text参数接受 字符串,正则表达式,列表
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import re file = open('./aa.html', 'rb') html = file.read() bs = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser") t_list = bs.find_all(attrs={"data-foo": "value"}) for item in t_list: print(item) t_list = bs.find_all(text="hao123") for item in t_list: print(item) t_list = bs.find_all(text=["hao123", "地图", "贴吧"]) for item in t_list: print(item) t_list = bs.find_all(text=re.compile("\d")) for item in t_list: print(item)当我们搜索text中的一些特殊属性时,同样也可以传入一个方法来达到我们的目的:
def length_is_two(text): return text and len(text) == 2 t_list = bs.find_all(text=length_is_two) for item in t_list: print(item)
(5)limit参数:
可以传入一个limit参数来限制返回的数量,当搜索出的数据量为5,而设置了limit=2时,此时只会返回前2个数据
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import re file = open('./aa.html', 'rb') html = file.read() bs = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser") t_list = bs.find_all("a",limit=2) for item in t_list: print(item)
find_all除了上面一些常规的写法,还可以对其进行一些简写:
# 两者是相等的 # t_list = bs.find_all("a") => t_list = bs("a") t_list = bs("a") # 两者是相等的 # t_list = bs.a.find_all(text="新闻") => t_list = bs.a(text="新闻") t_list = bs.a(text="新闻")
6.2、find()
find()将返回符合条件的第一个Tag,有时我们只需要或一个Tag时,我们就可以用到find()方法了。当然了,也可以使用find_all()方法,传入一个limit=1,然后再取出第一个值也是可以的,不过未免繁琐。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import re file = open('./aa.html', 'rb') html = file.read() bs = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser") # 返回只有一个结果的列表 t_list = bs.find_all("title",limit=1) print(t_list) # 返回唯一值 t = bs.find("title") print(t) # 如果没有找到,则返回None t = bs.find("abc") print(t)
从结果可以看出find_all,尽管传入了limit=1,但是返回值仍然为一个列表,当我们只需要取一个值时,远不如find方法方便。但
是如果未搜索到值时,将返回一个None
在上面介绍BeautifulSoup4的时候,我们知道可以通过bs.div来获取第一个div标签,如果我们需要获取第一个div下的第一个div,
我们可以这样:
t = bs.div.div # 等价于 t = bs.find("div").find("div")
七、CSS选择器
BeautifulSoup支持发部分的CSS选择器,在Tag获取BeautifulSoup对象的.select()方法中传入字符串参数,即可使用CSS选择器的语法找到Tag:
7.1、通过标签名查找
print(bs.select('title')) print(bs.select('a'))
7.2、通过类名查找
print(bs.select('.mnav'))
7.3、通过id查找
print(bs.select('#u1'))
7.4、组合查找
print(bs.select('div .bri'))
7.5、属性查找
print(bs.select('a[class="bri"]')) print(bs.select('a[href="http://tieba.baidu.com"]'))
7.6、直接子标签查找
t_list = bs.select("head > title") print(t_list)
7.7、兄弟节点标签查找
t_list = bs.select(".mnav ~ .bri") print(t_list)
7.8、获取内容
t_list = bs.select("title") print(bs.select('title')[0].get_text())