docker study --- containerd
上次写了个containerd的源码分析,不知道为什么CSDN给删掉了,难道是审核不通过?......
重新写一篇,希望这次顺利
Containerd 是一个控制 runC 的守护进程,主要是为了性能和密度。Containerd 提供一个命令行客户端和 API,在一个机器上管理容器。Containerd 使用 runC 来根据 OCI 规范运行容器 。
containerd 是docker “四大金刚”之一。 上接docker daemon,下连shim。它将docker daemon传过来的GRPC消息转化成实际要操作runc要执行的命令。
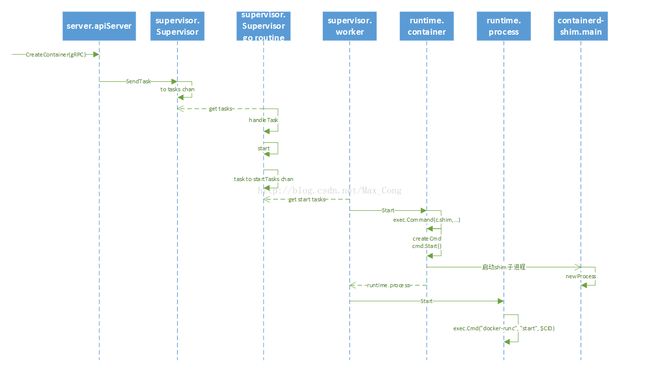
containerd 最重要的就是Supervisot中的两个go chan:Task 和startTask。
// Supervisor represents a container supervisor
type Supervisor struct {
// stateDir is the directory on the system to store container runtime state information.
stateDir string
// name of the OCI compatible runtime used to execute containers
runtime string
runtimeArgs []string
shim string
containers map[string]*containerInfo
startTasks chan *startTask
// we need a lock around the subscribers map only because additions and deletions from
// the map are via the API so we cannot really control the concurrency
subscriberLock sync.RWMutex
subscribers map[chan Event]struct{}
machine Machine
tasks chan Task
monitor *Monitor
eventLog []Event
eventLock sync.Mutex
timeout time.Duration
}还有三个重要的go协程。
1. api server协程,主要负责将Task放入Task chan
2. supervisor协程,主要将Task从Task chan中取出放入startTask chan
3. spuervisor worker协程(十个)主要负责从startTask chan中取出startTask,做相应的操作。
下边,以CreateContainer为例。
1. api server
当有个CreateContainer(GRPC)消息传入时会调用相应的函数
// Server API for API service
type APIServer interface {
GetServerVersion(context.Context, *GetServerVersionRequest) (*GetServerVersionResponse, error)
CreateContainer(context.Context, *CreateContainerRequest) (*CreateContainerResponse, error)
UpdateContainer(context.Context, *UpdateContainerRequest) (*UpdateContainerResponse, error)
Signal(context.Context, *SignalRequest) (*SignalResponse, error)
UpdateProcess(context.Context, *UpdateProcessRequest) (*UpdateProcessResponse, error)
AddProcess(context.Context, *AddProcessRequest) (*AddProcessResponse, error)
CreateCheckpoint(context.Context, *CreateCheckpointRequest) (*CreateCheckpointResponse, error)
DeleteCheckpoint(context.Context, *DeleteCheckpointRequest) (*DeleteCheckpointResponse, error)
ListCheckpoint(context.Context, *ListCheckpointRequest) (*ListCheckpointResponse, error)
State(context.Context, *StateRequest) (*StateResponse, error)
Events(*EventsRequest, API_EventsServer) error
Stats(context.Context, *StatsRequest) (*StatsResponse, error)
}func (s *apiServer) CreateContainer(ctx context.Context, c *types.CreateContainerRequest) (*types.CreateContainerResponse, error) {
if c.BundlePath == "" {
return nil, errors.New("empty bundle path")
}
// Maxx start tasks for create command
e := &supervisor.StartTask{}
e.ID = c.Id
e.BundlePath = c.BundlePath
e.Stdin = c.Stdin
e.Stdout = c.Stdout
e.Stderr = c.Stderr
e.Labels = c.Labels
e.NoPivotRoot = c.NoPivotRoot
e.Runtime = c.Runtime
e.RuntimeArgs = c.RuntimeArgs
e.StartResponse = make(chan supervisor.StartResponse, 1)
if c.Checkpoint != "" {
e.CheckpointDir = c.CheckpointDir
e.Checkpoint = &runtime.Checkpoint{
Name: c.Checkpoint,
}
}
// sendtask put task to task chan
// D:\study\go\containerd-docker-v1.12.x\supervisor\supervisor.go
s.sv.SendTask(e)
if err := <-e.ErrorCh(); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
r := <-e.StartResponse
apiC, err := createAPIContainer(r.Container, false)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &types.CreateContainerResponse{
Container: apiC,
}, nil
}// SendTask sends the provided event the the supervisors main event loop
func (s *Supervisor) SendTask(evt Task) {
TasksCounter.Inc(1)
s.tasks <- evt
}2. supervisor协程
这里要先说说containerd的开始流程。在containerd 的main函数中,start了supervisor和worker协程。
func main() {
logrus.SetFormatter(&logrus.TextFormatter{TimestampFormat: time.RFC3339Nano})
app := cli.NewApp()
app.Name = "containerd"
if containerd.GitCommit != "" {
app.Version = fmt.Sprintf("%s commit: %s", containerd.Version, containerd.GitCommit)
} else {
app.Version = containerd.Version
}
app.Usage = usage
app.Flags = daemonFlags
app.Before = func(context *cli.Context) error {
setupDumpStacksTrap()
if context.GlobalBool("debug") {
logrus.SetLevel(logrus.DebugLevel)
if context.GlobalDuration("metrics-interval") > 0 {
if err := debugMetrics(context.GlobalDuration("metrics-interval"), context.GlobalString("graphite-address")); err != nil {
return err
}
}
}
if p := context.GlobalString("pprof-address"); len(p) > 0 {
pprof.Enable(p)
}
if err := checkLimits(); err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
}
app.Action = func(context *cli.Context) {
// Maxx daemon
if err := daemon(context); err != nil {
logrus.Fatal(err)
}
}
if err := app.Run(os.Args); err != nil {
logrus.Fatal(err)
}
}
func daemon(context *cli.Context) error {
s := make(chan os.Signal, 2048)
signal.Notify(s, syscall.SIGTERM, syscall.SIGINT)
sv, err := supervisor.New(
context.String("state-dir"),
context.String("runtime"),
context.String("shim"),
context.StringSlice("runtime-args"),
context.Duration("start-timeout"),
context.Int("retain-count"))
if err != nil {
return err
}
// Maxx start 10 worker thread
wg := &sync.WaitGroup{}
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
wg.Add(1)
w := supervisor.NewWorker(sv, wg)
go w.Start()
}
// Maxx start GRPC server of containerd
if err := sv.Start(); err != nil {
return err
}
// Split the listen string of the form proto://addr
listenSpec := context.String("listen")
listenParts := strings.SplitN(listenSpec, "://", 2)
if len(listenParts) != 2 {
return fmt.Errorf("bad listen address format %s, expected proto://address", listenSpec)
}
// Maxx start Supervisor
// definition of supervisor is under D:\study\go\containerd-docker-v1.12.x\supervisor\supervisor.go
// start function
server, err := startServer(listenParts[0], listenParts[1], sv)
if err != nil {
return err
}
for ss := range s {
switch ss {
default:
logrus.Infof("stopping containerd after receiving %s", ss)
server.Stop()
os.Exit(0)
}
}
return nil
}上边函数调用了supervisor的Start函数。
// Start is a non-blocking call that runs the supervisor for monitoring contianer processes and
// executing new containers.
//
// This event loop is the only thing that is allowed to modify state of containers and processes
// therefore it is save to do operations in the handlers that modify state of the system or
// state of the Supervisor
func (s *Supervisor) Start() error {
logrus.WithFields(logrus.Fields{
"stateDir": s.stateDir,
"runtime": s.runtime,
"runtimeArgs": s.runtimeArgs,
"memory": s.machine.Memory,
"cpus": s.machine.Cpus,
}).Debug("containerd: supervisor running")
go func() {
for i := range s.tasks {
// Maxx xxx
s.handleTask(i)
}
}()
return nil
}func (s *Supervisor) handleTask(i Task) {
var err error
switch t := i.(type) {
case *AddProcessTask:
err = s.addProcess(t)
case *CreateCheckpointTask:
err = s.createCheckpoint(t)
case *DeleteCheckpointTask:
err = s.deleteCheckpoint(t)
case *StartTask:
// Maxx start come here
err = s.start(t)
case *DeleteTask:
err = s.delete(t)
case *ExitTask:
err = s.exit(t)
case *GetContainersTask:
err = s.getContainers(t)
case *SignalTask:
err = s.signal(t)
case *StatsTask:
err = s.stats(t)
case *UpdateTask:
err = s.updateContainer(t)
case *UpdateProcessTask:
err = s.updateProcess(t)
case *OOMTask:
err = s.oom(t)
default:
err = ErrUnknownTask
}
if err != errDeferredResponse {
i.ErrorCh() <- err
close(i.ErrorCh())
}
}func (s *Supervisor) start(t *StartTask) error {
start := time.Now()
rt := s.runtime
rtArgs := s.runtimeArgs
if t.Runtime != "" {
rt = t.Runtime
rtArgs = t.RuntimeArgs
}
container, err := runtime.New(runtime.ContainerOpts{
Root: s.stateDir,
ID: t.ID,
Bundle: t.BundlePath,
Runtime: rt,
RuntimeArgs: rtArgs,
Shim: s.shim,
Labels: t.Labels,
NoPivotRoot: t.NoPivotRoot,
Timeout: s.timeout,
})
if err != nil {
return err
}
s.containers[t.ID] = &containerInfo{
container: container,
}
ContainersCounter.Inc(1)
task := &startTask{
Err: t.ErrorCh(),
Container: container,
StartResponse: t.StartResponse,
Stdin: t.Stdin,
Stdout: t.Stdout,
Stderr: t.Stderr,
}
if t.Checkpoint != nil {
task.CheckpointPath = filepath.Join(t.CheckpointDir, t.Checkpoint.Name)
}
//Maxx 构造一个新的startTask,并传递给startTasks channel
// then go to D:\study\go\containerd-docker-v1.12.x\supervisor\worker.go
// Supervisor.worker的Start方法中,读取startTasks channel,并调用runtime.Container接口的Start方法
s.startTasks <- task
ContainerCreateTimer.UpdateSince(start)
return errDeferredResponse
}这里我们发现supervisor将Task转化后放入了startTask chan
3. spuervisor worker
上面在daemon函数中调用了
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
wg.Add(1)
w := supervisor.NewWorker(sv, wg)
go w.Start()
}// Start runs a loop in charge of starting new containers
func (w *worker) Start() {
defer w.wg.Done()
for t := range w.s.startTasks {
started := time.Now()
// Maxx start D:\study\go\containerd-docker-v1.12.x\runtime\container.go, also call the start below
process, err := t.Container.Start(t.CheckpointPath, runtime.NewStdio(t.Stdin, t.Stdout, t.Stderr))
......
if t.CheckpointPath == "" {
// Maxx call exec.cmd(docker-runc start $CID)
// D:\study\go\containerd-docker-v1.12.x\runtime\process.go
if err := process.Start(); err != nil {
......
}1. t.Container.Start
func (c *container) Start(checkpointPath string, s Stdio) (Process, error) {
processRoot := filepath.Join(c.root, c.id, InitProcessID)
if err := os.Mkdir(processRoot, 0755); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Maxx start shim process cmd
/*
docker-containerd-shim 817c43b3f5794d0e5dfdb92acf60fe7653b3efc33a4388733d357d00a8d8ae1a /var/run/docker/libcontainerd/817c43b3f5794d0e5dfdb92acf60fe7653b3efc33a4388733d357d00a8d8ae1a docker-runc*/
cmd := exec.Command(c.shim,
c.id, c.bundle, c.runtime,
)
cmd.Dir = processRoot
cmd.SysProcAttr = &syscall.SysProcAttr{
Setpgid: true,
}
spec, err := c.readSpec()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
config := &processConfig{
checkpoint: checkpointPath,
root: processRoot,
id: InitProcessID,
c: c,
stdio: s,
spec: spec,
processSpec: specs.ProcessSpec(spec.Process),
}
// Maxx
p, err := newProcess(config)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Max run the cmd, now containerd end, turn to runc
if err := c.createCmd(InitProcessID, cmd, p); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return p, nil
}createCmd() 调用cmd.Start()系统命令启动docker-containerd-shim进程。
func (c *container) createCmd(pid string, cmd *exec.Cmd, p *process) error {
p.cmd = cmd
// Maxx
if err := cmd.Start(); err != nil {
close(p.cmdDoneCh)
if exErr, ok := err.(*exec.Error); ok {
if exErr.Err == exec.ErrNotFound || exErr.Err == os.ErrNotExist {
return fmt.Errorf("%s not installed on system", c.shim)
}
}
return err
}
// We need the pid file to have been written to run
defer func() {
go func() {
err := p.cmd.Wait()
if err == nil {
p.cmdSuccess = true
}
if same, err := p.isSameProcess(); same && p.pid > 0 {
// The process changed its PR_SET_PDEATHSIG, so force
// kill it
logrus.Infof("containerd: %s:%s (pid %v) has become an orphan, killing it", p.container.id, p.id, p.pid)
err = unix.Kill(p.pid, syscall.SIGKILL)
if err != nil && err != syscall.ESRCH {
logrus.Errorf("containerd: unable to SIGKILL %s:%s (pid %v): %v", p.container.id, p.id, p.pid, err)
} else {
for {
err = unix.Kill(p.pid, 0)
if err != nil {
break
}
time.Sleep(5 * time.Millisecond)
}
}
}
close(p.cmdDoneCh)
}()
}()
if err := c.waitForCreate(p, cmd); err != nil {
return err
}
c.processes[pid] = p
return nil
}func (c *container) waitForCreate(p *process, cmd *exec.Cmd) error {
wc := make(chan error, 1)
go func() {
for {
if _, err := p.getPidFromFile(); err != nil {
if os.IsNotExist(err) || err == errInvalidPidInt {
alive, err := isAlive(cmd)
if err != nil {
wc <- err
return
}
if !alive {
// runc could have failed to run the container so lets get the error
// out of the logs or the shim could have encountered an error
messages, err := readLogMessages(filepath.Join(p.root, "shim-log.json"))
if err != nil {
wc <- err
return
}
for _, m := range messages {
if m.Level == "error" {
wc <- fmt.Errorf("shim error: %v", m.Msg)
return
}
}
// no errors reported back from shim, check for runc/runtime errors
messages, err = readLogMessages(filepath.Join(p.root, "log.json"))
if err != nil {
if os.IsNotExist(err) {
err = ErrContainerNotStarted
}
wc <- err
return
}
for _, m := range messages {
if m.Level == "error" {
wc <- fmt.Errorf("oci runtime error: %v", m.Msg)
return
}
}
wc <- ErrContainerNotStarted
return
}
time.Sleep(15 * time.Millisecond)
continue
}
wc <- err
return
}
// the pid file was read successfully
wc <- nil
return
}
}()
select {
case err := <-wc:
if err != nil {
return err
}
err = p.saveStartTime()
if err != nil {
logrus.Warnf("containerd: unable to save %s:%s starttime: %v", p.container.id, p.id, err)
}
return nil
case <-time.After(c.timeout):
cmd.Process.Kill()
cmd.Wait()
return ErrContainerStartTimeout
}
}
// Start starts the specified command but does not wait for it to complete.
//
// The Wait method will return the exit code and release associated resources
// once the command exits.
func (c *Cmd) Start() error {
if c.lookPathErr != nil {
c.closeDescriptors(c.closeAfterStart)
c.closeDescriptors(c.closeAfterWait)
return c.lookPathErr
}
if runtime.GOOS == "windows" {
lp, err := lookExtensions(c.Path, c.Dir)
if err != nil {
c.closeDescriptors(c.closeAfterStart)
c.closeDescriptors(c.closeAfterWait)
return err
}
c.Path = lp
}
if c.Process != nil {
return errors.New("exec: already started")
}
if c.ctx != nil {
select {
case <-c.ctx.Done():
c.closeDescriptors(c.closeAfterStart)
c.closeDescriptors(c.closeAfterWait)
return c.ctx.Err()
default:
}
}
type F func(*Cmd) (*os.File, error)
for _, setupFd := range []F{(*Cmd).stdin, (*Cmd).stdout, (*Cmd).stderr} {
fd, err := setupFd(c)
if err != nil {
c.closeDescriptors(c.closeAfterStart)
c.closeDescriptors(c.closeAfterWait)
return err
}
c.childFiles = append(c.childFiles, fd)
}
c.childFiles = append(c.childFiles, c.ExtraFiles...)
var err error
// Maxx start 容器中的物理进程init
// D:\study\go\runc-master\libcontainer\process_linux.go
c.Process, err = os.StartProcess(c.Path, c.argv(), &os.ProcAttr{
Dir: c.Dir,
Files: c.childFiles,
Env: c.envv(),
// Maxx SysProcAttr字段中则填充了各种runC所需启用的namespace等属性
Sys: c.SysProcAttr,
})
if err != nil {
c.closeDescriptors(c.closeAfterStart)
c.closeDescriptors(c.closeAfterWait)
return err
}
c.closeDescriptors(c.closeAfterStart)
c.errch = make(chan error, len(c.goroutine))
for _, fn := range c.goroutine {
go func(fn func() error) {
c.errch <- fn()
}(fn)
}
if c.ctx != nil {
c.waitDone = make(chan struct{})
go func() {
select {
case <-c.ctx.Done():
c.Process.Kill()
case <-c.waitDone:
}
}()
}
return nil
}
2. process.Start
// Start unblocks the associated container init process.
// This should only be called on the process with ID "init"
func (p *process) Start() error {
if p.ID() == InitProcessID {
var (
errC = make(chan error, 1)
args = append(p.container.runtimeArgs, "start", p.container.id)
cmd = exec.Command(p.container.runtime, args...)
)
go func() {
out, err := cmd.CombinedOutput()
if err != nil {
errC <- fmt.Errorf("%s: %q", err.Error(), out)
}
errC <- nil
}()
select {
case err := <-errC:
if err != nil {
return err
}
case <-p.cmdDoneCh:
if !p.cmdSuccess {
if cmd.Process != nil {
cmd.Process.Kill()
}
cmd.Wait()
return ErrShimExited
}
err := <-errC
if err != nil {
return err
}
}
}
return nil
}
图片源自网络