redis源码分析之对象系统源码分析-string, list链表,hash哈希,set集合,zset有序集合
=====================================================
redis源码学习系列文章:
redis源码分析之sha1算法分析
redis源码分析之字典源码分析
redis源码分析之内存编码分析intset, ziplist编码分析
redis源码分析之跳跃表
redis源码分析之内存淘汰策略的原理分析
redis源码分析之对象系统源码分析string, list链表,hash哈希,set集合,zset有序集合
=====================================================
在我的github上会持续更新Redis代码的中文分析,地址送出https://github.com/chensongpoixs/credis_source,共同学习进步
前言
在redis中使用八种数据结构都封装成对象系统
分析流程
- redis对象数据结构介绍和对应数据使用编码格式
- string 介绍
- list链表底层实现原理
- hash哈希底层实现原理
- set集合底层实现原理
- zset有序集合底层实现原理
正文
一, redis对象数据结构介绍和对应数据使用编码格式
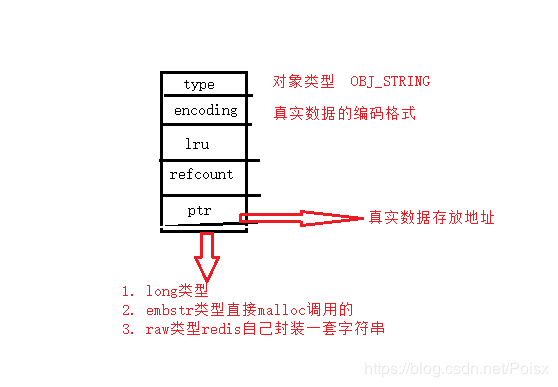
redis中对象的数据结构
typedef struct redisObject {
unsigned type:4; // 数据类型的对象
unsigned encoding:4; //数据编码压缩的格式
unsigned lru:LRU_BITS; /* LRU time (relative to global lru_clock) or
* LFU data (least significant 8 bits frequency
* and most significant 16 bits access time). */
int refcount; // 类似于java中的引用计数 --> shared
void *ptr; // 保存redis中的五种数据结构的指针
} robj;
- type 就是我们使用命令那些数据结构string, list, hash, set, zset
- encoding 是我们使用数据结构底层实现编码格式
- lru 这个涉及到redis的内存淘汰机制
- refcount 这个是引用计数,
- ptr 这是我们要保持数据的对象指针
1. type在redis中的对象类型
| redis中的对象 | 数据类型 |
|---|---|
| OBJ_STRING | 字符串 |
| OBJ_LIST | 链表 |
| OBJ_SET | 集合 |
| OBJ_ZSET | 有序集合 |
| OBJ_HASH | 哈希 |
2. 对象底层encoding编码分析
| redis数据类型 | 编码格式 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OBJ_STRING | OBJ_ENCODING_INT | long类型编码格式 | ||
| OBJ_STRING | OBJ_ENCODING_EMBSTR | 字符串小于44使用该编码格式 | ||
| OBJ_STRING | OBJ_ENCODING_RAW | 字符串大于44的使用该动态申请内存(sds) | ||
| OBJ_LIST | OBJ_ENCODING_QUICKLIST | 在内存中编码格式quick_list数据结构 | ||
| OBJ_LIST | OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST | 在保存落地文件的时候是以压缩编码ziplist格式保存文件中去的,在redis启动时候要报落地文件中list结构转换quick_list编码格式 | ||
| OBJ_HASH | OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST | 字符或者数字的长度小64时是要ziplist压缩编码 | ||
| OBJ_HASH | OBJ_ENCODING_HT | 字符或者数字的长度大于64时使用hashtable编码 | ||
| OBJ_SET | OBJ_ENCODING_HT | hashtable编码 | ||
| OBJ_SET | OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET | intset编码每个要插入字符都要检查, 字符过长就是要hashtable编码格式 | ||
| OBJ_ZSET | OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST | 有序集合子字符串小于64字节时使用ziplist编码格式,在zset中年使用ziplist是两个节点为一组数据即key-value | ||
| OBJ_ZSET | OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST | key是哈希表的插入的数字是使用跳跃表的进行排序的,跳跃表的 |
二, string 底层实现原理
string类型底层编码有三种格式分别是
- long类型
- embstr
- raw
需要注意的就是redis都命令操作append是基于raw的操作字符串操作
数据都是保持ptr指针这里的
string结构在内存结构图
三, list链表底层实现原理
list链表底层实现有两种数据的结构分别是
- quicklist (快速列表)
- ziplist (压缩编码列表)
list链表是应向有重复数据的这是和它底层实现有关
在redis5.0中内存中使用都是quicklist数据结构实现的,而异步存储是使用ziplist存储到落地文件的,读取落地文件读取ziplist后要转换quicklist数据结构
在创建没有任何适配ziplist数据结构
void pushGenericCommand(client *c, int where) {
int j, pushed = 0;
robj *lobj = lookupKeyWrite(c->db,c->argv[1]);
if (lobj && lobj->type != OBJ_LIST) {
addReply(c,shared.wrongtypeerr);
return;
}
for (j = 2; j < c->argc; j++) {
// 第一次时要插入redis的dict中的key即hash值之后都是使用quicktlist连接数据的
if (!lobj) {
// 把链表的数据结构
lobj = createQuicklistObject();
// 设置每个链表的可以存储数据的个数 只是在redis.conf的配置文件中配置的 默认配置的8kb的大小
quicklistSetOptions(lobj->ptr, server.list_max_ziplist_size,
server.list_compress_depth);
// 把hash值插入redis的dict中去
dbAdd(c->db, c->argv[1], lobj);
}
// 插入链表中的使用
listTypePush(lobj,c->argv[j],where);
pushed++;
}
addReplyLongLong(c, (lobj ? listTypeLength(lobj) : 0));
if (pushed) {
char *event = (where == LIST_HEAD) ? "lpush" : "rpush";
signalModifiedKey(c->db,c->argv[1]);
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_LIST,event,c->argv[1],c->db->id);
}
server.dirty += pushed;
}
读取文件
//读取落地文件时是ziplist转换为quicklist的数据结构
} else if (rdbtype == RDB_TYPE_LIST) {
/* Read list value */
if ((len = rdbLoadLen(rdb,NULL)) == RDB_LENERR) return NULL;
o = createQuicklistObject();
quicklistSetOptions(o->ptr, server.list_max_ziplist_size,
server.list_compress_depth);
/* Load every single element of the list */
while(len--) {
if ((ele = rdbLoadEncodedStringObject(rdb)) == NULL) return NULL;
dec = getDecodedObject(ele);
size_t len = sdslen(dec->ptr);
quicklistPushTail(o->ptr, dec->ptr, len);
decrRefCount(dec);
decrRefCount(ele);
}
存储文件
} else if (o->type == OBJ_LIST) {
/* Save a list value */
// list保存数据的是转换ziplist保存到落地文件
if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_QUICKLIST) {
quicklist *ql = o->ptr;
quicklistNode *node = ql->head;
if ((n = rdbSaveLen(rdb,ql->len)) == -1) return -1;
nwritten += n;
while(node) {
if (quicklistNodeIsCompressed(node)) {
void *data;
size_t compress_len = quicklistGetLzf(node, &data);
if ((n = rdbSaveLzfBlob(rdb,data,compress_len,node->sz)) == -1) return -1;
nwritten += n;
} else {
if ((n = rdbSaveRawString(rdb,node->zl,node->sz)) == -1) return -1;
nwritten += n;
}
node = node->next;
}
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown list encoding");
}
在redis内存布局
四, hash哈希底层实现原理
哈希表的底层实现有两种分别是
- ziplist压缩编码
- hashtable
在哈希表中每次插入数据或者修改都会检查当编码是ziplist时数据的长度是否大于配置表的hash-max-ziplist-value大于就使用hashtable表数据结构对象
在使用ziplist存储key-value时都是使用两个节点存储的,在查找和删除时都两个节点一迭代的key-value两个节点是想连接在一起的
int hashTypeSet(robj *o, sds field, sds value, int flags) {
int update = 0;
if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {
unsigned char *zl, *fptr, *vptr;
zl = o->ptr;
fptr = ziplistIndex(zl, ZIPLIST_HEAD);
if (fptr != NULL) {
fptr = ziplistFind(fptr, (unsigned char*)field, sdslen(field), 1);
if (fptr != NULL) {
/* Grab pointer to the value (fptr points to the field) */
vptr = ziplistNext(zl, fptr);
serverAssert(vptr != NULL);
update = 1;
/* Delete value */
zl = ziplistDelete(zl, &vptr);
/* Insert new value */
zl = ziplistInsert(zl, vptr, (unsigned char*)value,
sdslen(value));
}
}
if (!update) {
/* Push new field/value pair onto the tail of the ziplist */
zl = ziplistPush(zl, (unsigned char*)field, sdslen(field),
ZIPLIST_TAIL);
zl = ziplistPush(zl, (unsigned char*)value, sdslen(value),
ZIPLIST_TAIL);
}
o->ptr = zl;
/* Check if the ziplist needs to be converted to a hash table */
if (hashTypeLength(o) > server.hash_max_ziplist_entries)
hashTypeConvert(o, OBJ_ENCODING_HT);
1, ziplist 在内存布局
2,hashtable
中哈希碰撞时没有处理只是增加链表
哈希表没有什么好说的
五, set集合底层实现原理
set集合底层编码有两种分别是
- intset整数编码
- hashtable
整数
当前编码是intset每次都会检查要插入的数据是否可以转换longlong 不可以就转换编码格式hastble,还有插入后检查当前intset这一块数据是否大于配置表中set-max-intset-entries的值, 大于就要转换hashtable的编码格式
} else if (subject->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET) {
// 集合如果intset编码格式会对每一个要插入数据进行检查是否是转换longlong, 不可以就转换hashtable表的编码格式
if (isSdsRepresentableAsLongLong(value,&llval) == C_OK) {
uint8_t success = 0;
// 这个插入的有一个点讲究哦, 可能要转换编码格式哦
// intset中的整数编码四种格式
// 1. 一个字节
// 2. 二个字节
// 3. 四个字节
// 4. 八个字节
subject->ptr = intsetAdd(subject->ptr,llval,&success);
if (success) {
/* Convert to regular set when the intset contains
* too many entries. */
// intset 整数编码格式的长度是否大于配置表的中的大小如果大于就要的修改成hashtable的编码格式了
if (intsetLen(subject->ptr) > server.set_max_intset_entries)
setTypeConvert(subject,OBJ_ENCODING_HT);
return 1;
}
} else {
/* Failed to get integer from object, convert to regular set. */
setTypeConvert(subject,OBJ_ENCODING_HT);
/* The set *was* an intset and this value is not integer
* encodable, so dictAdd should always work. */
serverAssert(dictAdd(subject->ptr,sdsdup(value),NULL) == DICT_OK);
return 1;
}
在set集合中不应许有重复数据是因为intset在插入的时候就使用二分查找法定位数据的下标了
static uint8_t intsetSearch(intset *is, int64_t value, uint32_t *pos) {
int min = 0, max = intrev32ifbe(is->length)-1, mid = -1;
int64_t cur = -1;
/* The value can never be found when the set is empty */
if (intrev32ifbe(is->length) == 0) {
if (pos) *pos = 0;
return 0;
} else {
/* Check for the case where we know we cannot find the value,
* but do know the insert position. */
// 检查数据中最后一个和前一个和要插入的数据比较是否得到相对位置的下标的 -[相对位置的下标是0位置是否大于0或者小0的比较]
if (value > _intsetGet(is,intrev32ifbe(is->length)-1)) {
if (pos) *pos = intrev32ifbe(is->length);
return 0;
} else if (value < _intsetGet(is,0)) {
if (pos) *pos = 0;
return 0;
}
}
while(max >= min) {
// 二叉查找法 -> 中位置
mid = ((unsigned int)min + (unsigned int)max) >> 1;
cur = _intsetGet(is,mid);
if (value > cur) {
min = mid+1;
} else if (value < cur) {
max = mid-1;
} else {
break;
}
}
// 如果存在就不会在插入数据
if (value == cur) {
if (pos) *pos = mid;
return 1;
} else {
if (pos) *pos = min;
return 0;
}
}
intset在内存布局
hashtable中的value插入一个空值就可以了
六, zset有序集合底层实现原理
zset有序集合编码有两种分别是
- ziplist压缩编码
- skiplist跳跃表
key的值大于64字节就使用skiplist跳跃表编码格式
ziplist编码使用和hash种使用一样的但是有一个区别是在hash中ziplist插入key-value是没有顺序的在zset中是有序的所以zset在插入时想表ziplist中的score的值找到要插入的位置,修改的时候先是删除在重新查找要插入的位置
int zsetAdd(robj *zobj, double score, sds ele, int *flags, double *newscore) {
/* Turn options into simple to check vars. */
int incr = (*flags & ZADD_INCR) != 0;
int nx = (*flags & ZADD_NX) != 0;
int xx = (*flags & ZADD_XX) != 0;
*flags = 0; /* We'll return our response flags. */
double curscore;
/* NaN as input is an error regardless of all the other parameters. */
// 是否score数据是否符合要求
if (isnan(score)) {
*flags = ZADD_NAN;
return 0;
}
/* Update the sorted set according to its encoding. */
if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {
unsigned char *eptr;
// 查找key 这里里面已经修改 迭代器的指针两个节点一迭代
if ((eptr = zzlFind(zobj->ptr,ele,&curscore)) != NULL) {
/* NX? Return, same element already exists. */
if (nx) {
*flags |= ZADD_NOP;
return 1;
}
/* Prepare the score for the increment if needed. */
if (incr) {
score += curscore;
if (isnan(score)) {
*flags |= ZADD_NAN;
return 0;
}
if (newscore) *newscore = score;
}
/* Remove and re-insert when score changed. */
// score是否相同不相同就删除添加进入
// 1. 更新操作
if (score != curscore) {
// 删除两个节点数据的在zset有序集合中自己封装的删除节点
zobj->ptr = zzlDelete(zobj->ptr, eptr);
zobj->ptr = zzlInsert(zobj->ptr, ele, score);
*flags |= ZADD_UPDATED;
}
return 1;
} else if (!xx) {
/* Optimize: check if the element is too large or the list
* becomes too long *before* executing zzlInsert. */
// 2. 直接插入
zobj->ptr = zzlInsert(zobj->ptr,ele,score);
if (zzlLength(zobj->ptr) > server.zset_max_ziplist_entries)
zsetConvert(zobj,OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST);
if (sdslen(ele) > server.zset_max_ziplist_value)
zsetConvert(zobj,OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST);
if (newscore) *newscore = score;
*flags |= ZADD_ADDED;
return 1;
} else {
*flags |= ZADD_NOP;
return 1;
}
使用skiplist跳跃表和hashtable一起使用的查找比较快的下面的我就不说了
} else if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST) {
zset *zs = zobj->ptr;
zskiplistNode *znode;
dictEntry *de;
de = dictFind(zs->dict,ele);
if (de != NULL) {
/* NX? Return, same element already exists. */
if (nx) {
*flags |= ZADD_NOP;
return 1;
}
curscore = *(double*)dictGetVal(de);
/* Prepare the score for the increment if needed. */
if (incr) {
score += curscore;
if (isnan(score)) {
*flags |= ZADD_NAN;
return 0;
}
if (newscore) *newscore = score;
}
/* Remove and re-insert when score changes. */
if (score != curscore) {
znode = zslUpdateScore(zs->zsl,curscore,ele,score);
/* Note that we did not removed the original element from
* the hash table representing the sorted set, so we just
* update the score. */
dictGetVal(de) = &znode->score; /* Update score ptr. */
*flags |= ZADD_UPDATED;
}
return 1;
} else if (!xx) {
ele = sdsdup(ele);
znode = zslInsert(zs->zsl,score,ele);
serverAssert(dictAdd(zs->dict,ele,&znode->score) == DICT_OK);
*flags |= ZADD_ADDED;
if (newscore) *newscore = score;
return 1;
} else {
*flags |= ZADD_NOP;
return 1;
}
//----------------------------------------------
zskiplistNode *zslUpdateScore(zskiplist *zsl, double curscore, sds ele, double newscore) {
zskiplistNode *update[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL], *x;
int i;
/* We need to seek to element to update to start: this is useful anyway,
* we'll have to update or remove it. */
x = zsl->header;
// 找到跳跃表的节点指针 跳跃表中分等级的哦每个等级中的数据的个数可能相等哦
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {
// 遍历每个等级中的数据的于当前节点的数据的是要修改的节点数据的
while (x->level[i].forward &&
(x->level[i].forward->score < curscore ||
(x->level[i].forward->score == curscore &&
sdscmp(x->level[i].forward->ele,ele) < 0)))
{
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
update[i] = x;
}
/* Jump to our element: note that this function assumes that the
* element with the matching score exists. */
x = x->level[0].forward;
serverAssert(x && curscore == x->score && sdscmp(x->ele,ele) == 0);
/* If the node, after the score update, would be still exactly
* at the same position, we can just update the score without
* actually removing and re-inserting the element in the skiplist. */
// 判断节点判断保持数据的是否需要的修改位置 跳跃表中的数据的是从小到大的排序的
if ((x->backward == NULL || x->backward->score < newscore) &&
(x->level[0].forward == NULL || x->level[0].forward->score > newscore))
{
x->score = newscore;
return x;
}
/* No way to reuse the old node: we need to remove and insert a new
* one at a different place. */
// 说明要修改的数据的score大于当前的节点的score的值的所以需要的删除了当前节点从新插入的节点数据的
zslDeleteNode(zsl, x, update);
// 插入的跳跃表的节点
zskiplistNode *newnode = zslInsert(zsl,newscore,x->ele);
/* We reused the old node x->ele SDS string, free the node now
* since zslInsert created a new one. */
x->ele = NULL;
zslFreeNode(x);
return newnode;
}
结语
个人博客地址