Java使用Apache poi 操作Excel-基本概念与使用
1.添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poigroupId>
<artifactId>poiartifactId>
<version>3.14version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poigroupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxmlartifactId>
<version>3.14version>
dependency>2.POI的核心类及与Excel的对应关系
本人在使用poi使用的版本是3.14,而我所翻译的教程中使用的是3.9因此下面所列出的接口的实现了以翻译的教程对应的版本为准。此外部分内容为本人总结添加。
操作Excel主要包括
- 创建 :创建Excel文件,电子表格,行,单元格。
- 数据操作 :从单元格读取及写入内容。
- 设置:属性,样式等,打印语言,超链接等设置。
POI的Excel部分为我们提供了相对应的类完成这些操作。
2.1POI处理Excel的核心类
Workbook
Workbook是所有用来创建或维护excel文件的类所要实现的接口,这个接口在
org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel下。实现这个接口的类包括。
- HSSFWorkbook:这个类包含了读取或写入.xls格式文件的方法。能处理的版本包括 97-2003.
- XSSFWorkbook:这个类包含了读取或写入.xlsx或.xls文件格式的方法,能够处理2007及以后版本的文档。
这两个类用来创建Excel文件,因此对应于Excel文件。
HSSFWorkbook
这个是org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel包下的一个类,实现了Workbook接口,用来处理.xls格式的文件。HSSFWorkbook类包含许多方法,然而仅能处理xls格式的文档。
XSSFWorkbook
这个类即能处理低版本也能处理高版本Excel文件的格式。该类在org.apache.xssf.usemodel包下,并且实现了Workbook接口。
Sheet
Sheet是org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel包下的一个接口,该接口是所有用来创建指定名称电子表格的类所需要实现的接口。
两个实现类包括。
- XSSFSheet
- HSSFSheet
这两个类用来创建电子表格,当通过XSSFWorkbook创建好Excel文件后,需要使用XSSFSheet来创建电子表格,HSSFWorkbook创建的Excel文件则是通过HSSFSheet来创建电子表格。下面的行,单元格同理。
Row
这个接口在org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel包下,用来表示电子表单中的行,所有用来创建行对象的类都要实现这个接口。
实现类包括
- XSSFRow
- HSSFRow
Cell
这个接口在org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel包下。所以用来处理单元格的类都要实现该接口。单元格可以有不同的属性,如blank,numeric,date,error等。每个单元格都有一个编号。
实现类包括
- XSSFCell
- HSSFCell
上面这些接口及其实现是创建,读取Excel的核心接口与类。与Excel的对应关系如下图。

接下来的类主要是完成属性,样式等的设置。
XSSFCellStyle
这个类在org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel包下,提供了电子表单中与单元格内容格式相关的信息。
HSSFColor
这个类在org.apache.poi.hssf.util包下。用来处理颜色。
XSSFColor
这个类在org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel包下。用来描述XSSFWorkbook中单元格颜色。
XSSFFont
这个类在org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel包下。实现了Font接口,用来处理字体。
XSSFHyperlink
这个类在org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel包下。实现了Hyperlink接口,用来设置超链接。
XSSFPrintSetup
这个类在org.apache.poi.xsssf.usermodel包下。实现了PrintSetup接口。用来设置与打印相关的属性。
其它的不再赘述,使用时请查阅API文档即可。
3. workbook的创建与打开
这里workbook的含义是Excel文件。下面的代码创建了一个空的工作簿。
import java.io.*;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.*;
public class CreateWorkBook
{
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
{
//Create Blank workbook
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
//Create file system using specific name
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(
new File("D:\\createworkbook.xlsx"));
//write operation workbook using file out object
workbook.write(out);
out.close();
System.out.println("
createworkbook.xlsx written successfully");
}
}
//执行后会在D:\\下创建Excel文件名为createworkbook
//打开已存在的工作簿
import java.io.*;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.*;
public class OpenWorkBook
{
public static void main(String args[])throws Exception
{
File file = new File("D:\\workbook.xlsx");
FileInputStream fIP = new FileInputStream(file);
//Get the workbook instance for XLSX file
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(fIP);
if(file.isFile() && file.exists())
{
System.out.println(
"openworkbook.xlsx file open successfully.");
}
else
{
System.out.println(
"Error to open workbook.xlsx file.");
}
}
}
4.SpreadSheets(电子表格)的操作
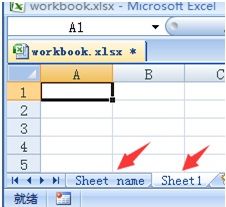
本节将演示如何通过Java创建电子表格。电子表格是Excel文件中的一个页面,并包含行以及列。下图的excel文件中包含两个Spreadsheet,名字分别为Sheet name与Sheet1。
创建字典表格
//创建空的工作簿
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
//创建空的电子表格
XSSFSheet spreadsheet = workbook.createSheet(“Sheet Name”);
电子表格中的行
电子表格采用的是网格布局。行与列是通过具体的名称来标识。列是通过字母标识行是通过数字标识。下面的代码在电子表单中创建了一行。
XSSFRow row = spreadsheet.createRow((short)1);
向电子表单中写入数据
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeMap;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
public class Writesheet
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
//Create blank workbook
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
//Create a blank sheet
XSSFSheet spreadsheet = workbook.createSheet(
" Employee Info ");
//Create row object
XSSFRow row;
//This data needs to be written (Object[])
Map < String, Object[] > empinfo =
new TreeMap < String, Object[] >();
empinfo.put( "1", new Object[] {
"EMP ID", "EMP NAME", "DESIGNATION" });
empinfo.put( "2", new Object[] {
"tp01", "Gopal", "Technical Manager" });
empinfo.put( "3", new Object[] {
"tp02", "Manisha", "Proof Reader" });
empinfo.put( "4", new Object[] {
"tp03", "Masthan", "Technical Writer" });
empinfo.put( "5", new Object[] {
"tp04", "Satish", "Technical Writer" });
empinfo.put( "6", new Object[] {
"tp05", "Krishna", "Technical Writer" });
//Iterate over data and write to sheet
Set < String > keyid = empinfo.keySet();
int rowid = 0;
for (String key : keyid)
{
row = spreadsheet.createRow(rowid++);
Object [] objectArr = empinfo.get(key);
int cellid = 0;
for (Object obj : objectArr)
{
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellid++);
cell.setCellValue((String)obj);
}
}
//Write the workbook in file system
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(
new File("Writesheet.xlsx"));
workbook.write(out);
out.close();
System.out.println(
"Writesheet.xlsx written successfully" );
}
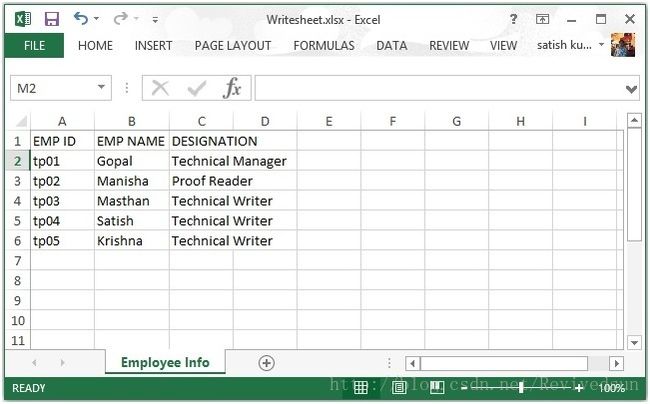
}执行后的数据写入Excel文件中。
注:可以看到,数据写入Excel中就是创建Excel文件(WorkBook),行(Row),单元格(Cell),最后将数据写入单元格。而这些对象Excel文件(WorkBook),行(Row),单元格(Cell)构成一个父子关系(树形结构)。每个对象通过父对象创建。而workbook是根,通过new操作符来创建。
从电子表格中读取数据
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.util.Iterator;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
public class Readsheet
{
static XSSFRow row;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(
new File("WriteSheet.xlsx"));
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(fis);
XSSFSheet spreadsheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
Iterator < Row > rowIterator = spreadsheet.iterator();
while (rowIterator.hasNext())
{
row = (XSSFRow) rowIterator.next();
Iterator < Cell > cellIterator = row.cellIterator();
while ( cellIterator.hasNext())
{
Cell cell = cellIterator.next();
switch (cell.getCellType())
{
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC:
System.out.print(
cell.getNumericCellValue() + " \t\t " );
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING:
System.out.print(
cell.getStringCellValue() + " \t\t " );
break;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
fis.close();
}
}
注:从Excel中读取数据,首先要打开Excel文件,然后获取对应的电子表格(可能有多个),遍历各个行,再从各个行的单元格中取出数据即可。
5.单元格的操作
数据在Excel中都是存储在单元格中的。通过行号与列号来定位到一个单元格。
下面是创建单元格。
//create new workbook
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
//create spreadsheet with a name
XSSFSheet spreadsheet = workbook.createSheet("new sheet");
//create first row on a created spreadsheet
XSSFRow row = spreadsheet.createRow(0);
//create first cell on created row
XSSFCell cell = row.createCell(0);
单元格的类型
单元格的类型指定了一个单元格是否能够包含字符串,数字,或公式。字符串单元格不能存放数字,同理数字单元格也不能存放字符串。
下面代码演示了在电子表格中创建不同类型的单元格。
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.util.Date;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFCell;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
public class TypesofCells
{
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
{
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
XSSFSheet spreadsheet = workbook.createSheet("cell types");
XSSFRow row = spreadsheet.createRow((short) 2);
row.createCell(0).setCellValue("Type of Cell");
row.createCell(1).setCellValue("cell value");
row = spreadsheet.createRow((short) 3);
row.createCell(0).setCellValue("set cell type BLANK");
row.createCell(1);
row = spreadsheet.createRow((short) 4);
row.createCell(0).setCellValue("set cell type BOOLEAN");
row.createCell(1).setCellValue(true);
row = spreadsheet.createRow((short) 5);
row.createCell(0).setCellValue("set cell type ERROR");
row.createCell(1).setCellValue(XSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_ERROR );
row = spreadsheet.createRow((short) 6);
row.createCell(0).setCellValue("set cell type date");
row.createCell(1).setCellValue(new Date());
row = spreadsheet.createRow((short) 7);
row.createCell(0).setCellValue("set cell type numeric" );
row.createCell(1).setCellValue(20 );
row = spreadsheet.createRow((short) 8);
row.createCell(0).setCellValue("set cell type string");
row.createCell(1).setCellValue("A String");
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(
new File("typesofcells.xlsx"));
workbook.write(out);
out.close();
System.out.println(
"typesofcells.xlsx written successfully");
}
}
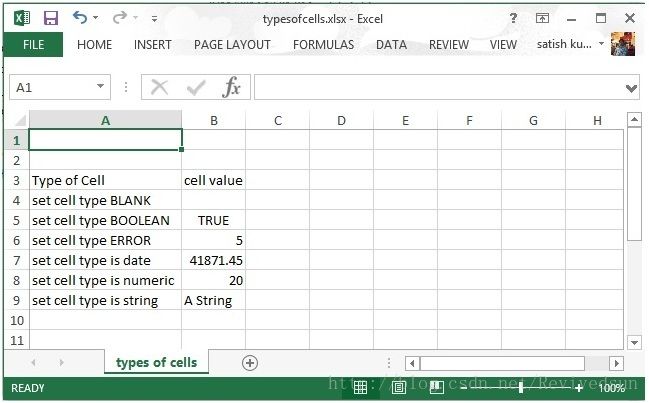
执行后生成的文件如下。
6.单元格样式设置
单元格样式处理包合并相邻单元格,添加边框,设置单元格对齐方式,颜色填充等。下面的代码演示了样式设置。
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.util.HSSFColor;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.IndexedColors;
import org.apache.poi.ss.util.CellRangeAddress;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFCell;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFCellStyle;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
public class CellStyle {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
{
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
XSSFSheet spreadsheet = workbook.createSheet("cellstyle");
XSSFRow row = spreadsheet.createRow((short) 1);
row.setHeight((short) 800);
XSSFCell cell = (XSSFCell) row.createCell((short) 1);
cell.setCellValue("test of merging");
//MEARGING CELLS
//this statement for merging cells
spreadsheet.addMergedRegion(new CellRangeAddress(
1, //first row (0-based)
1, //last row (0-based)
1, //first column (0-based)
4 //last column (0-based)
));
//CELL Alignment
row = spreadsheet.createRow(5);
cell = (XSSFCell) row.createCell(0);
row.setHeight((short) 800);
// Top Left alignment
XSSFCellStyle style1 = workbook.createCellStyle();
spreadsheet.setColumnWidth(0, 8000);
style1.setAlignment(XSSFCellStyle.ALIGN_LEFT);
style1.setVerticalAlignment(XSSFCellStyle.VERTICAL_TOP);
cell.setCellValue("Top Left");
cell.setCellStyle(style1);
row = spreadsheet.createRow(6);
cell = (XSSFCell) row.createCell(1);
row.setHeight((short) 800);
// Center Align Cell Contents
XSSFCellStyle style2 = workbook.createCellStyle();
style2.setAlignment(XSSFCellStyle.ALIGN_CENTER);
style2.setVerticalAlignment(
XSSFCellStyle.VERTICAL_CENTER);
cell.setCellValue("Center Aligned");
cell.setCellStyle(style2);
row = spreadsheet.createRow(7);
cell = (XSSFCell) row.createCell(2);
row.setHeight((short) 800);
// Bottom Right alignment
XSSFCellStyle style3 = workbook.createCellStyle();
style3.setAlignment(XSSFCellStyle.ALIGN_RIGHT);
style3.setVerticalAlignment(
XSSFCellStyle.VERTICAL_BOTTOM);
cell.setCellValue("Bottom Right");
cell.setCellStyle(style3);
row = spreadsheet.createRow(8);
cell = (XSSFCell) row.createCell(3);
// Justified Alignment
XSSFCellStyle style4 = workbook.createCellStyle();
style4.setAlignment(XSSFCellStyle.ALIGN_JUSTIFY);
style4.setVerticalAlignment(
XSSFCellStyle.VERTICAL_JUSTIFY);
cell.setCellValue("Contents are Justified in Alignment");
cell.setCellStyle(style4);
//CELL BORDER
row = spreadsheet.createRow((short) 10);
row.setHeight((short) 800);
cell = (XSSFCell) row.createCell((short) 1);
cell.setCellValue("BORDER");
XSSFCellStyle style5 = workbook.createCellStyle();
style5.setBorderBottom(XSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THICK);
style5.setBottomBorderColor(
IndexedColors.BLUE.getIndex());
style5.setBorderLeft(XSSFCellStyle.BORDER_DOUBLE);
style5.setLeftBorderColor(
IndexedColors.GREEN.getIndex());
style5.setBorderRight(XSSFCellStyle.BORDER_HAIR);
style5.setRightBorderColor(
IndexedColors.RED.getIndex());
style5.setBorderTop(XSSFCellStyle.BIG_SPOTS);
style5.setTopBorderColor(
IndexedColors.CORAL.getIndex());
cell.setCellStyle(style5);
//Fill Colors
//background color
row = spreadsheet.createRow((short) 10 );
cell = (XSSFCell) row.createCell((short) 1);
XSSFCellStyle style6 = workbook.createCellStyle();
style6.setFillBackgroundColor(
HSSFColor.LEMON_CHIFFON.index );
style6.setFillPattern(XSSFCellStyle.LESS_DOTS);
style6.setAlignment(XSSFCellStyle.ALIGN_FILL);
spreadsheet.setColumnWidth(1,8000);
cell.setCellValue("FILL BACKGROUNG/FILL PATTERN");
cell.setCellStyle(style6);
//Foreground color
row = spreadsheet.createRow((short) 12);
cell = (XSSFCell) row.createCell((short) 1);
XSSFCellStyle style7=workbook.createCellStyle();
style7.setFillForegroundColor(HSSFColor.BLUE.index);
style7.setFillPattern( XSSFCellStyle.LESS_DOTS);
style7.setAlignment(XSSFCellStyle.ALIGN_FILL);
cell.setCellValue("FILL FOREGROUND/FILL PATTERN");
cell.setCellStyle(style7);
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(
new File("D:\\cellstyle.xlsx"));
workbook.write(out);
out.close();
System.out.println("cellstyle.xlsx written successfully");
}
}
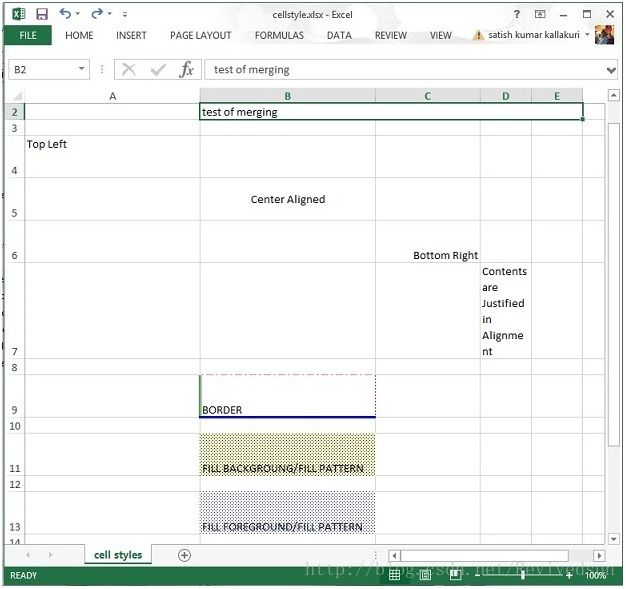
执行后效果如下。
7.字体设置
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.util.HSSFColor;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFCell;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFCellStyle;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFFont;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
public class FontStyle {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
{
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
XSSFSheet spreadsheet = workbook.createSheet("Fontstyle");
XSSFRow row = spreadsheet.createRow(2);
//Create a new font and alter it.
XSSFFont font = workbook.createFont();
font.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 30);
font.setFontName("IMPACT");
font.setItalic(true);
font.setColor(HSSFColor.BRIGHT_GREEN.index);
//Set font into style
XSSFCellStyle style = workbook.createCellStyle();
style.setFont(font);
// Create a cell with a value and set style to it.
XSSFCell cell = row.createCell(1);
cell.setCellValue("Font Style");
cell.setCellStyle(style);
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(
new File("D:\\fontstyle.xlsx"));
workbook.write(out);
out.close();
System.out.println(
"fontstyle.xlsx written successfully");
}
}
8.文本方向设置
单元格中的文本展示方向包括垂直,从左向右等。下面的代码展示了方向设置。
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFCell;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFCellStyle;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
public class TextDirection
{
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
{
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
XSSFSheet spreadsheet = workbook.createSheet(
"Text direction");
XSSFRow row = spreadsheet.createRow(2);
XSSFCellStyle myStyle = workbook.createCellStyle();
myStyle.setRotation((short) 0);
XSSFCell cell = row.createCell(1);
cell.setCellValue("0D angle");
cell.setCellStyle(myStyle);
//30 degrees
myStyle=workbook.createCellStyle();
myStyle.setRotation((short) 30);
cell = row.createCell(3);
cell.setCellValue("30D angle");
cell.setCellStyle(myStyle);
//90 degrees
myStyle=workbook.createCellStyle();
myStyle.setRotation((short) 90);
cell = row.createCell(5);
cell.setCellValue("90D angle");
cell.setCellStyle(myStyle);
//120 degrees
myStyle=workbook.createCellStyle();
myStyle.setRotation((short) 120);
cell = row.createCell(7);
cell.setCellValue("120D angle");
cell.setCellStyle(myStyle);
//270 degrees
myStyle = workbook.createCellStyle();
myStyle.setRotation((short) 270);
cell = row.createCell(9);
cell.setCellValue("270D angle");
cell.setCellStyle(myStyle);
//360 degrees
myStyle=workbook.createCellStyle();
myStyle.setRotation((short) 360);
cell = row.createCell(12);
cell.setCellValue("360D angle");
cell.setCellStyle(myStyle);
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(
new File("textdirection.xlsx"));
workbook.write(out);
out.close();
System.out.println(
"textdirection.xlsx written successfully");
}
}
9. 公式设置
在一个公式中,我们会传递一个数值。在执行公式时,将会得到期望结果,下标列出了一些在Excel中常用的公式。
下面的代码将公式添加到单元格中,并执行公式。
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFCell;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
public class Formula
{
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
{
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
XSSFSheet spreadsheet = workbook.createSheet("formula");
XSSFRow row = spreadsheet.createRow(1);
XSSFCell cell = row.createCell(1);
cell.setCellValue("A =" );
cell = row.createCell(2);
cell.setCellValue(2);
row = spreadsheet.createRow(2);
cell = row.createCell(1);
cell.setCellValue("B =");
cell = row.createCell(2);
cell.setCellValue(4);
row = spreadsheet.createRow(3);
cell = row.createCell(1);
cell.setCellValue("Total =");
cell = row.createCell(2);
// Create SUM formula
cell.setCellType(XSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA);
cell.setCellFormula("SUM(C2:C3)" );
cell = row.createCell(3);
cell.setCellValue("SUM(C2:C3)");
row = spreadsheet.createRow(4);
cell = row.createCell(1);
cell.setCellValue("POWER =");
cell=row.createCell(2);
// Create POWER formula
cell.setCellType(XSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA);
cell.setCellFormula("POWER(C2,C3)");
cell = row.createCell(3);
cell.setCellValue("POWER(C2,C3)");
row = spreadsheet.createRow(5);
cell = row.createCell(1);
cell.setCellValue("MAX =");
cell = row.createCell(2);
// Create MAX formula
cell.setCellType(XSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA);
cell.setCellFormula("MAX(C2,C3)");
cell = row.createCell(3);
cell.setCellValue("MAX(C2,C3)");
row = spreadsheet.createRow(6);
cell = row.createCell(1);
cell.setCellValue("FACT =");
cell = row.createCell(2);
// Create FACT formula
cell.setCellType(XSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA);
cell.setCellFormula("FACT(C3)");
cell = row.createCell(3);
cell.setCellValue("FACT(C3)");
row = spreadsheet.createRow(7);
cell = row.createCell(1);
cell.setCellValue("SQRT =");
cell = row.createCell(2);
// Create SQRT formula
cell.setCellType(XSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA);
cell.setCellFormula("SQRT(C5)");
cell = row.createCell(3);
cell.setCellValue("SQRT(C5)");
workbook.getCreationHelper()
.createFormulaEvaluator()
.evaluateAll();
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(
new File("formula.xlsx"));
workbook.write(out);
out.close();
System.out.println("fromula.xlsx written successfully");
}
}
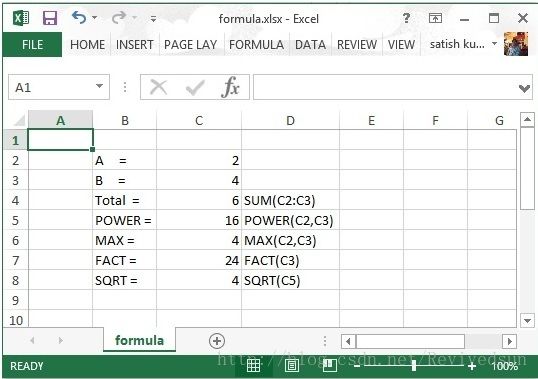
执行后结果下图所示。
10. 设置单元格超链接
本节展示给单元格内容添加超链接。通过XSSFHyperlink对象来完成。
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import org.apache.poi.common.usermodel.Hyperlink;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.util.HSSFColor;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.CreationHelper;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFCell;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFCellStyle;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFFont;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFHyperlink;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
public class HyperlinkEX
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
XSSFSheet spreadsheet = workbook
.createSheet("Hyperlinks");
XSSFCell cell;
CreationHelper createHelper = workbook
.getCreationHelper();
XSSFCellStyle hlinkstyle = workbook.createCellStyle();
XSSFFont hlinkfont = workbook.createFont();
hlinkfont.setUnderline(XSSFFont.U_SINGLE);
hlinkfont.setColor(HSSFColor.BLUE.index);
hlinkstyle.setFont(hlinkfont);
//URL Link
cell = spreadsheet.createRow(1)
.createCell((short) 1);
cell.setCellValue("URL Link");
XSSFHyperlink link = (XSSFHyperlink)createHelper
.createHyperlink(Hyperlink.LINK_URL);
link.setAddress("http://www.tutorialspoint.com/" );
cell.setHyperlink((XSSFHyperlink) link);
cell.setCellStyle(hlinkstyle);
//Hyperlink to a file in the current directory
cell = spreadsheet.createRow(2)
.createCell((short) 1);
cell.setCellValue("File Link");
link = (XSSFHyperlink)createHelper
.createHyperlink(Hyperlink.LINK_FILE);
link.setAddress("cellstyle.xlsx");
cell.setHyperlink(link);
cell.setCellStyle(hlinkstyle);
//e-mail link
cell = spreadsheet.createRow(3)
.createCell((short) 1);
cell.setCellValue("Email Link");
link = (XSSFHyperlink)createHelper
.createHyperlink(Hyperlink.LINK_EMAIL);
link.setAddress(
"mailto:[email protected]?"
+"subject=Hyperlink");
cell.setHyperlink(link);
cell.setCellStyle(hlinkstyle);
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(
new File("hyperlink.xlsx"));
workbook.write(out);
out.close();
System.out.println("hyperlink.xlsx written successfully");
}
}
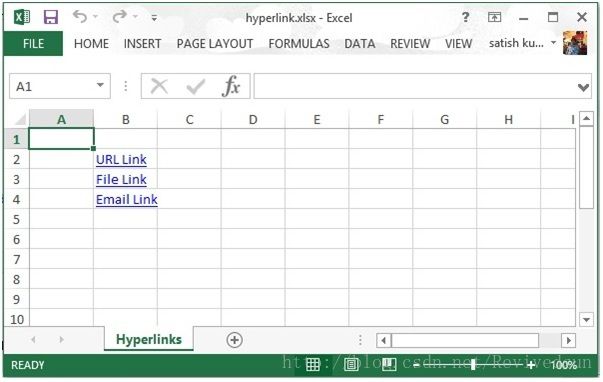
点击链接可以跳转到对应的网站。
11. 打印预览设置
本节演示打区域印属性的设置。通常打印区域是从左上到右下。打印区域是可以根据需求来设置,就是说,你可以打印整个电子表格的一个特定范围,定制页面大小等。
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFPrintSetup;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
public class PrintArea
{
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
{
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
XSSFSheet spreadsheet = workbook
.createSheet("Print Area");
//set print area with indexes
workbook.setPrintArea(
0, //sheet index
0, //start column
5, //end column
0, //start row
5 //end row
);
//set paper size
spreadsheet.getPrintSetup().setPaperSize(
XSSFPrintSetup.A4_PAPERSIZE);
//set display grid lines or not
spreadsheet.setDisplayGridlines(true);
//set print grid lines or not
spreadsheet.setPrintGridlines(true);
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(
new File("printarea.xlsx"));
workbook.write(out);
out.close();
System.out.println("printarea.xlsx written successfully");
}
}
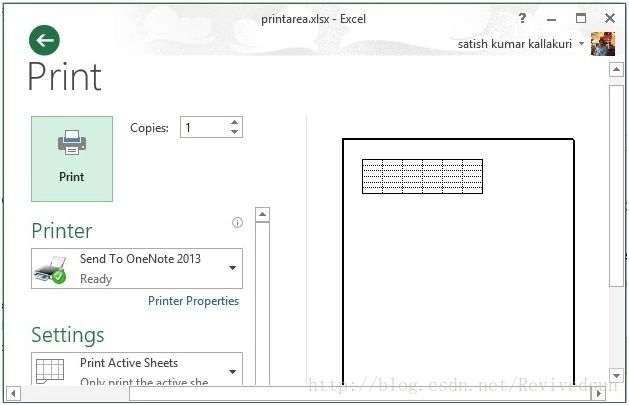
打开生成的文件,并通过打印预览可以看到如下的效果。
12.将数据库数据导入Excel
本节展示POI是如何与数据库交互的,通过JDBC可以从数据库中获取数据,并插入数据到电子表格中,下面以MySql数据库为例,将数据库中的数据写入Excel。
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFCell;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
public class ExcelDatabase
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection connect = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test" ,
"root" ,
"root"
);
Statement statement = connect.createStatement();
ResultSet resultSet = statement
.executeQuery("select * from emp_tbl");
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
XSSFSheet spreadsheet = workbook
.createSheet("employe db");
XSSFRow row=spreadsheet.createRow(1);
XSSFCell cell;
cell=row.createCell(1);
cell.setCellValue("EMP ID");
cell=row.createCell(2);
cell.setCellValue("EMP NAME");
cell=row.createCell(3);
cell.setCellValue("DEG");
cell=row.createCell(4);
cell.setCellValue("SALARY");
cell=row.createCell(5);
cell.setCellValue("DEPT");
int i=2;
while(resultSet.next())
{
row=spreadsheet.createRow(i);
cell=row.createCell(1);
cell.setCellValue(resultSet.getInt("eid"));
cell=row.createCell(2);
cell.setCellValue(resultSet.getString("ename"));
cell=row.createCell(3);
cell.setCellValue(resultSet.getString("deg"));
cell=row.createCell(4);
cell.setCellValue(resultSet.getString("salary"));
cell=row.createCell(5);
cell.setCellValue(resultSet.getString("dept"));
i++;
}
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(
new File("exceldatabase.xlsx"));
workbook.write(out);
out.close();
System.out.println(
"exceldatabase.xlsx written successfully");
}
}
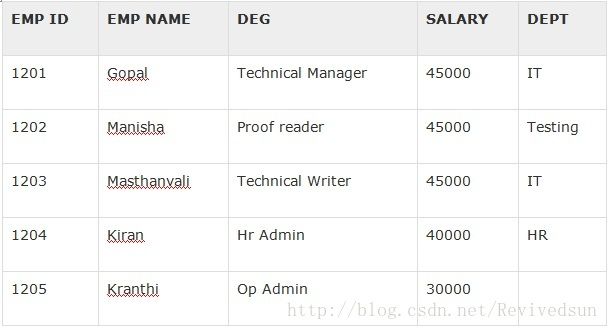
可以看到,从数据库中读数据并写入excel中还是那些步骤,即将数据库中对应列的数据写入excel的单元格,然后保存即可。执行后可以看到下面的效果。
13.总结
通过POI简化了EXCEL的操作,其中POI提供的WorkBook, spreadsheet,Row,Cell及其实现类来完成对Excel中对应部分(Excel文件,电子表格,行,单元格)的操作(读取,写入)。此外通过类型,样式,字体等类可以完成各种属性的操作。学习POI主要是搞清楚其核心类与Excel各个组件的对应关系,那么就很容易理解和使用了。
原文地址:https://www.tutorialspoint.com/apache_poi/index.htm