深浅拷贝——Java
一、深浅拷贝(对象)
protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
要想让对象具有拷贝的功能,必须要实现Cloneable接口(标识接口,表示此类允许被克隆),并且在类中自定义clone调用Object类提供的继承权限clone方法。
(只有接口名称,没有任何抽象方法,标识接口,给所有实现这个接口的类打上标识,表示它有什么样的能力)
只有子类实现了Cloneable接口后,才可以使用Object类提供的clone方法
Cloneable:CloneNotSupportedException,在没有实现Cloneable时(表示这个类有了clone能力),就抛出CloneNotSupportedException异常
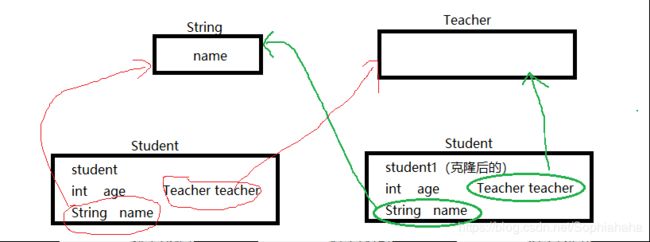
1、浅拷贝——值的拷贝 那个类用要clone,实现接口,类中的自定义类属性不用实现接口
对于浅拷贝而言,拷贝出来的对象仍然保留原对象的所有引用
问题:牵一发而动全身,只要任意一个拷贝对象或原对象中的引用大声改变,所有对象均会收到影响
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Teacher teacher = new Teacher("dage","run");
Student student = new Student("zhangsan",29,teacher);
Student student1 = student.clone();
System.out.println(teacher);
System.out.println(student+" "+student.getTeacher());
System.out.println(student1+" "+student1.getTeacher());
System.out.println(student.getName()==student1.getName());
}
}
class Teacher{
private String name;
private String hobby;
public Teacher(String name, String hobby) {
this.name = name;
this.hobby = hobby;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getHobby() {
return hobby;
}
public void setHobby(String hobby) {
this.hobby = hobby;
}
}
class Student implements Cloneable{
private String name;
private int age;
private Teacher teacher;
public Student(){}
public Student(String name, int age, Teacher teacher) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.teacher = teacher;
}
public Student clone(){
try {
return (Student)super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Teacher getTeacher() {
return teacher;
}
public void setTeacher(Teacher teacher) {
this.teacher = teacher;
}
}
程序运行结果:
jvm.Teacher@1540e19d
jvm.Student@677327b6 jvm.Teacher@1540e19d
jvm.Student@14ae5a5 jvm.Teacher@1540e19d
true
拷贝原理:
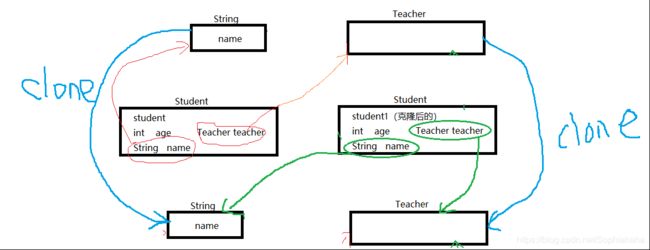
2、深拷贝:
拷贝出来的对象产生了所有引用的新的对象
特点:修改任意一个对象不会对其他对象产生影响
如何实现深拷贝:
1、包含的其他类(自定义类)继续实现Cloneable接口,并且调用clone方法,递归实现克隆
那个类用要clone,实现接口,类中的自定义类属性不用实现接口
问题:级联拷贝
2、使用序列化(常用,只能深拷贝):使用序列化实现深拷贝时,无需再实现Cloneable接口,只需要实现Serializable接口
所有类实现Serializable接口,用的类实现克隆方法
1、实现Cloneable接口
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Teacher teacher = new Teacher("dage","run");
Student student = new Student("zhangsan",29,teacher);
Student student1 = student.clone();
System.out.println(teacher);
System.out.println(student+" "+student.getTeacher());
System.out.println(student1+" "+student1.getTeacher());
System.out.println(student.getName()==student1.getName());
}
}
class Teacher implements Cloneable{
private String name;
private String hobby;
public Teacher(String name, String hobby) {
this.name = name;
this.hobby = hobby;
}
public Teacher clone(){
try {
return (Teacher)super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getHobby() {
return hobby;
}
public void setHobby(String hobby) {
this.hobby = hobby;
}
}
class Student implements Cloneable{
private String name;
private int age;
private Teacher teacher;
public Student(){}
public Student(String name, int age, Teacher teacher) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.teacher = teacher;
}
public Student clone(){
Student student = null;
try {
student = (Student)super.clone();
student.teacher = this.teacher.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return student;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Teacher getTeacher() {
return teacher;
}
public void setTeacher(Teacher teacher) {
this.teacher = teacher;
}
}
结果:
jvm.Teacher@1540e19d
jvm.Student@677327b6 jvm.Teacher@1540e19d
jvm.Student@14ae5a5 jvm.Teacher@7f31245a
true
拷贝原理
3、延迟拷贝:浅拷贝+深拷贝
先浅拷贝,读的时候不用管,修改的时候再深拷贝