1 Dubbo配置方式
- XML配置:基于 Spring 的 Schema 和 XML 扩展机制实现;
- 属性配置:加载 classpath 根目录下的 dubbo.properties;
- API 配置:通过硬编码方式配置(不推荐使用);
- 注解配置:通过注解方式配置(Dubbo-2.5.7及以上版本支持,不推荐使用);
1.1 属性配置
对于 属性配置 方式,可以通过 环境变量、-D 启动参数来指定 dubbo.properties 文件,加载文件顺序为:
- -D 启动参数;
- 环境变量;
- classpath 根目录;
属性配置 加载代码 ConfigUtils.java 如下:
public static final String DUBBO_PROPERTIES_KEY = "dubbo.properties.file";
public static final String DEFAULT_DUBBO_PROPERTIES = "dubbo.properties";
private static volatile Properties PROPERTIES;
/**
* 属性配置加载逻辑
*/
public static Properties getProperties() {
if (PROPERTIES == null) {
synchronized (ConfigUtils.class) {
if (PROPERTIES == null) {
// 1. -D 启动参数
String path = System.getProperty(Constants.DUBBO_PROPERTIES_KEY);
if (path == null || path.length() == 0) {
// 2. 环境变量
path = System.getenv(Constants.DUBBO_PROPERTIES_KEY);
if (path == null || path.length() == 0) {
// 3. classpath 根目录
path = Constants.DEFAULT_DUBBO_PROPERTIES;
}
}
PROPERTIES = ConfigUtils.loadProperties(path, false, true);
}
}
}
return PROPERTIES;
}
2 Dubbo的Schema扩展
文章开头已经提到,Dubbo XML配置方式是基于 Spring 的 Schema 和 XML 扩展机制实现的。通过该机制,我们可以编写自己的 Schema,并根据自定义的 Schema 自定义标签来配置 Bean。
使用 Spring 的 XML 扩展机制有以下几个步骤:
- 定义 Schema(编写 .xsd 文件);
- 定义 JavaBean;
- 编写 NamespaceHandler 和 BeanDefinitionParser 完成 Schema 解析;
- 编写 spring.handlers 和 spring.schemas 文件串联解析部件;
- 在 XML 文件中应用配置;
2.1 定义 Schema
Schema 的定义体现在 .xsd 文件上,文件位于 dubbo-config-spring 子模块下:
2.2 定义 JavaBean
dubbo-config-api 子模块中定义了 Dubbo 所有标签对应的 JavaBean,JavaBean 里面的属性一一对应标签的各配置项:
2.3 解析Schema
以如下Spring XML文件中的配置为例:
Spring是如何来解析这些配置呢?如果我们想自己定义配置该如何做呢?对于上述的XML配置,分成三个部分:
- 命名空间namespace,如tx、context
- 元素element,如component-scan、property-placeholder、annotation-driven
- 属性attribute,如base-package、location、transaction-manager
Spring定义了两个接口,来分别解析上述内容:
- NamespaceHandler:注册了一堆BeanDefinitionParser,利用他们来进行解析;
- BeanDefinitionParser:用于解析每个element的内容;
来看下具体的一个案例,就以Spring的context命名空间为例,对应的NamespaceHandler实现是ContextNamespaceHandler:
public class ContextNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
@Override
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser("property-placeholder", new PropertyPlaceholderBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("property-override", new PropertyOverrideBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation-config", new AnnotationConfigBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("component-scan", new ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("load-time-weaver", new LoadTimeWeaverBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("spring-configured", new SpringConfiguredBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("mbean-export", new MBeanExportBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("mbean-server", new MBeanServerBeanDefinitionParser());
}
}
注册了一堆BeanDefinitionParser,如果我们想看 component-scan 是如何实现的,就可以去看对应的 ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser 的源码了。
如果自定义了NamespaceHandler,如何加入到Spring中呢?Spring默认会加载jar包下的META-INF/spring.handlers文件下寻找NamespaceHandler,默认的Spring文件如下:
spring.handlers文件内容如下:相应的命名空间使用相应的NamespaceHandler
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/context=org.springframework.context.config.ContextNamespaceHandler
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/jee=org.springframework.ejb.config.JeeNamespaceHandler
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/lang=org.springframework.scripting.config.LangNamespaceHandler
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/task=org.springframework.scheduling.config.TaskNamespaceHandler
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/cache=org.springframework.cache.config.CacheNamespaceHandler
同时,Spring 通过 spring.schemas 文件得知,如 context 标签的 Schema 是 context.xsd,并以此校验应用 XML 配置文件的格式。spring.schemas 文件内容如下:
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd=org/springframework/context/config/spring-context-2.5.xsd
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd=org/springframework/context/config/spring-context-3.0.xsd
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.1.xsd=org/springframework/context/config/spring-context-3.1.xsd
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd=org/springframework/context/config/spring-context-3.2.xsd
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd=org/springframework/context/config/spring-context-4.0.xsd
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.1.xsd=org/springframework/context/config/spring-context-4.1.xsd
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd=org/springframework/context/config/spring-context-4.2.xsd
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd=org/springframework/context/config/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd=org/springframework/context/config/spring-context-4.3.xsd
......
文件位置如下:
Spring框架初始化时会加载所有classpath的spring.handlers文件,把namespace URL和namespace处理器的映射存到一个Map中,Spring框架在解析bean定义文档时,遇到了非IOC内置(beans名称空间下)的标签,会在这个Map中查找namespace处理器,使用这个自定义的处理器来进行标签解析工作。可以在 DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader 和 BeanDefinitionParserDelegate 类中看到相关逻辑的代码:
// org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java
/**
* Parse the elements at the root level in the document:
* "import", "alias", "bean".
* @param root the DOM root element of the document
*/
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate); //解析默认标签
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele); //解析自定义标签
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
// org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.java
public BeanDefinition parseCustomElement(Element ele) {
return parseCustomElement(ele, null);
}
public BeanDefinition parseCustomElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBd) {
String namespaceUri = getNamespaceURI(ele);
NamespaceHandler handler = this.readerContext.getNamespaceHandlerResolver().resolve(namespaceUri);
if (handler == null) {
error("Unable to locate Spring NamespaceHandler for XML schema namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]", ele);
return null;
}
return handler.parse(ele, new ParserContext(this.readerContext, this, containingBd));
}
3 Dubbo的Schema解析
以如下Dubbo Provider的Spring配置为例:
3.1 XML转化beanDefinition
根据Spring可扩展Schema,我们先去dubbo.jar内的META-INF/spring.handlers配置内容:
http\://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo=com.alibaba.dubbo.config.spring.schema.DubboNamespaceHandler
我们从这个类(DubboNamespaceHandler)开刀吧,DubboNamespaceHandler代码:
public class DubboNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
static {
// 确保系统中只存在一份解析处理器类定义
Version.checkDuplicate(DubboNamespaceHandler.class);
}
public void init() {
// DubboBeanDefinitionParser定义了如何解析dubbo节点信息
// DubboBeanDefinitionParser的第一个参数是beanclass
//配置标签解析器
registerBeanDefinitionParser("application", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ApplicationConfig.class, true));
//配置标签解析器
registerBeanDefinitionParser("module", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ModuleConfig.class, true));
//配置标签解析器
registerBeanDefinitionParser("registry", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(RegistryConfig.class, true));
//配置标签解析器
registerBeanDefinitionParser("monitor", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(MonitorConfig.class, true));
//配置标签解析器
registerBeanDefinitionParser("provider", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ProviderConfig.class, true));
//配置标签解析器
registerBeanDefinitionParser("consumer", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ConsumerConfig.class, true));
//配置标签解析器
registerBeanDefinitionParser("protocol", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ProtocolConfig.class, true));
//配置标签解析器
registerBeanDefinitionParser("service", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ServiceBean.class, true));
//配置标签解析器
registerBeanDefinitionParser("reference", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ReferenceBean.class, false));
//配置标签解析器
registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(AnnotationBean.class, true));
}
}
按照Spring提供的机制,Dubbo把每个自定义的可使用配置元素和对应的解析器绑定到一起。而真正负责把配置文件中声明的内容解析成对应的BeanDefinition(可以想象为Bean的模子)是靠DubboBeanDefinitionParser.parse类完成,所有dubbo的标签,都统一用DubboBeanDefinitionParser进行解析,基于一对一属性映射,将XML标签解析为Bean对象。具体代码如下:
/**
* 解析dubbo自定义标签,往BeanDefinition设置属性值,这个时候bean还没有创建
* @param element
* @param parserContext
* @param beanClass
* @param required
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private static BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext, Class beanClass, boolean required) {
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setBeanClass(beanClass);
// 设置懒加载为false,表示立即加载,spring启动时,立刻进行实例化
// 如果设置为true,那么要第一次向容器通过getBean索取bean时实例化,在spring bean的配置里可以配置
// 这里会设置懒加载为false,其实还可以得到一个推断就是dubbo标签创建的bean就是单例bean(singleton bean)
// 因为lazy-init的设置只对singleton bean有效,对原型bean(prototype无效)
beanDefinition.setLazyInit(false);
String id = element.getAttribute("id");
// 如果没有设置bean的id
if ((id == null || id.length() == 0) && required) {
String generatedBeanName = element.getAttribute("name");
// 如果name没有配置
if (generatedBeanName == null || generatedBeanName.length() == 0) {
// 如果是ProtocolConfig类型,bean name默认为 dubbo,其他的为配置的interface值
if (ProtocolConfig.class.equals(beanClass)) {
generatedBeanName = "dubbo";
} else {
generatedBeanName = element.getAttribute("interface");
}
}
/*
* 如果generatedBeanName仍为null,那么取 beanClass 的名字,beanClass 其实就是要解析的类型
* 如:com.alibaba.dubbo.config.ApplicationConfig
*/
if (generatedBeanName == null || generatedBeanName.length() == 0) {
generatedBeanName = beanClass.getName();
}
//如果id没有设置,那么 id = generatedBeanName,如果是ProtocolConfig类型的话,自然就是 dubbo
id = generatedBeanName;
int counter = 2;
/*
* 由于spring的bean id不能重复,但有些标签可能会配置多个如:dubbo:registry
* 所以 id 在后面加数字 2、3、4 区分
*/
while(parserContext.getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(id)) {
id = generatedBeanName + (counter ++);
}
}
if (id != null && id.length() > 0) {
// 检查是否有 bean id 相同的
if (parserContext.getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(id)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Duplicate spring bean id " + id);
}
/*
* 注册 bean 定义
* org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#registerBeanDefinition
* 会按照 id 即beanName做一些检查,判断是否重载已加载过的bean等等
* 跟到代码里其实 bean 的注册也是放到 ConcurrentHashMap 里
* beanName也就是这里的 id 会放到 list 里
*/
parserContext.getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(id, beanDefinition);
// 给bean添加属性值
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("id", id);
}
if (ProtocolConfig.class.equals(beanClass)) { //解析 0) {
RootBeanDefinition classDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition();
// 通过反射获取类
classDefinition.setBeanClass(ReflectUtils.forName(className));
classDefinition.setLazyInit(false);
/*
* 解析子节点,有些配置可能是:
*
*
*/
parseProperties(element.getChildNodes(), classDefinition);
/*
* ref直接设置成了 接口名 + Impl 的bean
*/
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("ref", new BeanDefinitionHolder(classDefinition, id + "Impl"));
}
} else if (ProviderConfig.class.equals(beanClass)) {
/*
* props = new HashSet();
ManagedMap parameters = null;
for (Method setter : beanClass.getMethods()) {
String name = setter.getName();
// 给model注入值时,如ServiceConfig,方法必须是set开头,并且参数数量只能为1
if (name.length() > 3 && name.startsWith("set")
&& Modifier.isPublic(setter.getModifiers())
&& setter.getParameterTypes().length == 1) {
// 方法参数类型,因为参数只能是1,所以直接取[0]
Class type = setter.getParameterTypes()[0];
// 根据set方法名获取属性值,如:setListener 得到的属性为:listener
String property = StringUtils.camelToSplitName(name.substring(3, 4).toLowerCase() + name.substring(4), "-");
props.add(property);
Method getter = null;
try {
getter = beanClass.getMethod("get" + name.substring(3), new Class[0]);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
try {
getter = beanClass.getMethod("is" + name.substring(3), new Class[0]);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e2) {
}
}
if (getter == null
|| ! Modifier.isPublic(getter.getModifiers())
|| ! type.equals(getter.getReturnType())) {
continue;
}
if ("parameters".equals(property)) {
/*
* 如果属性为 parameters,如ProtocolConfig里的setParameters(Map parameters)
* 那么去子节点获取
*
*/
parameters = parseParameters(element.getChildNodes(), beanDefinition);
} else if ("methods".equals(property)) {
/*
* 解析 0) {
// 不发布到任何注册中心时 registry = "N/A"
if ("registry".equals(property) && RegistryConfig.NO_AVAILABLE.equalsIgnoreCase(value)) {
RegistryConfig registryConfig = new RegistryConfig();
registryConfig.setAddress(RegistryConfig.NO_AVAILABLE);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(property, registryConfig);
} else if ("registry".equals(property) && value.indexOf(',') != -1) {
// 多注册中心用 , 号分隔
parseMultiRef("registries", value, beanDefinition, parserContext);
} else if ("provider".equals(property) && value.indexOf(',') != -1) {
parseMultiRef("providers", value, beanDefinition, parserContext);
} else if ("protocol".equals(property) && value.indexOf(',') != -1) {
// 同上 多协议暴露
parseMultiRef("protocols", value, beanDefinition, parserContext);
} else {
Object reference;
if (isPrimitive(type)) {//如果参数类型为 java 的基本类型
if ("async".equals(property) && "false".equals(value)
|| "timeout".equals(property) && "0".equals(value)
|| "delay".equals(property) && "0".equals(value)
|| "version".equals(property) && "0.0.0".equals(value)
|| "stat".equals(property) && "-1".equals(value)
|| "reliable".equals(property) && "false".equals(value)) {
/*
* 兼容旧版本xsd中的default值,以上配置的值在xsd中有配置defalt值
*
*/
value = null;
}
reference = value;
} else if ("protocol".equals(property)
// 如果属性为 protocol 那么要判断protocol对应的拓展点配置有没有
&& ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).hasExtension(value)
// 检查当前使用的协议是否已经解析过 可能在这里被解析过");
}
}
reference = new RuntimeBeanReference(value);
}
/*
* 设置属性,值为另外一个关联的bean
* RuntimeBeanReference 固定占位符类,当在beanfactory中作为另外一个bean的引用时,作为属性值对象,将在运行时进行解析
*/
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(property, reference);
}
}
}
}
}
}
NamedNodeMap attributes = element.getAttributes();
int len = attributes.getLength();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
Node node = attributes.item(i);
String name = node.getLocalName();
// 经过上面的解析,如果还有一些属性没有解析到的
if (! props.contains(name)) {
if (parameters == null) {
parameters = new ManagedMap();
}
String value = node.getNodeValue();
parameters.put(name, new TypedStringValue(value, String.class));
}
}
if (parameters != null) {
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("parameters", parameters);
}
return beanDefinition;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private static void parseMultiRef(String property, String value, RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition,
ParserContext parserContext) {
// 解析 registries 、providers、protocols 时支持多引用
String[] values = value.split("\\s*[,]+\\s*");
ManagedList list = null;
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++) {
String v = values[i];
if (v != null && v.length() > 0) {
if (list == null) {
list = new ManagedList();
}
list.add(new RuntimeBeanReference(v));
}
}
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(property, list);
}
private static void parseNested(Element element, ParserContext parserContext, Class beanClass,
boolean required, String tag, String property, String ref, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
NodeList nodeList = element.getChildNodes();
if (nodeList != null && nodeList.getLength() > 0) {
boolean first = true;
for (int i = 0; i < nodeList.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nodeList.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
if (tag.equals(node.getNodeName())
|| tag.equals(node.getLocalName())) {
if (first) {
first = false;
String isDefault = element.getAttribute("default");
/*
* 如果 0) {
subDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(property, new RuntimeBeanReference(ref));
}
}
}
}
}
}
private static void parseProperties(NodeList nodeList, RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
if (nodeList != null && nodeList.getLength() > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < nodeList.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nodeList.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
// 如果是 0) {
String value = ((Element) node).getAttribute("value");
// 获取 ref
String ref = ((Element) node).getAttribute("ref");
if (value != null && value.length() > 0) {
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(name, value);
} else if (ref != null && ref.length() > 0) {
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(name, new RuntimeBeanReference(ref));
} else {
/*
* 只支持两种property的设置方法:
*
*
*/
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Unsupported sub tag, Only supported 0) {
ManagedList methods = null;
for (int i = 0; i < nodeList.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nodeList.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element element = (Element) node;
// name attribute == null");
}
if (methods == null) {
methods = new ManagedList();
}
// 解析 解析的最终目的是返回 RootBeanDefinition 对象,RootBeanDefinition包含了解析出来的关于bean的所有信息,注意,在bean的解析完后其实只是spring将其转化成spring内部的一种抽象的数据对象结构,bean的创建(实例化)是第一次调用 getBean 时创建的。
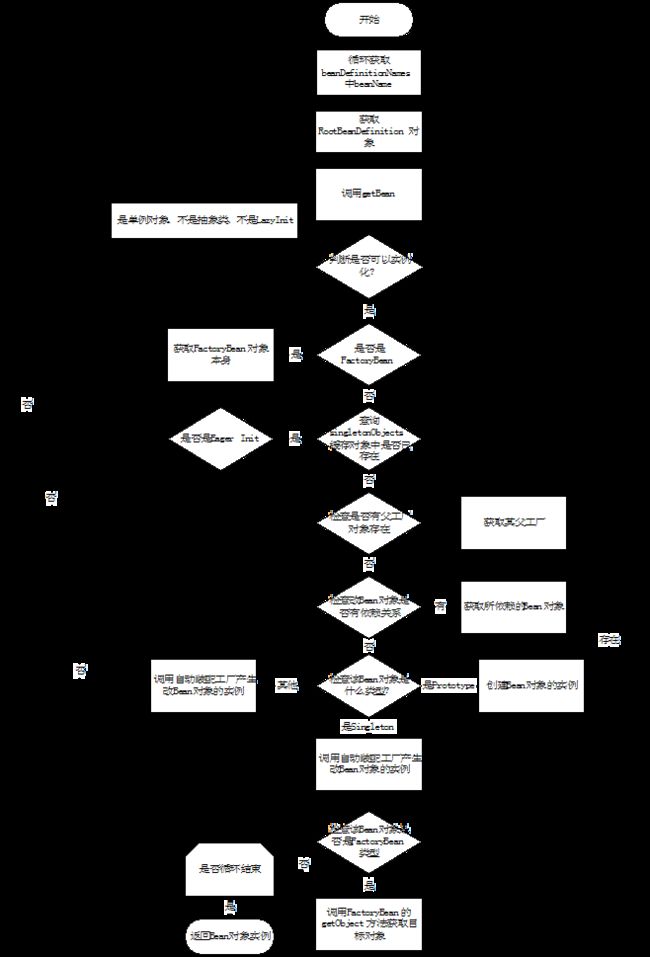
3.2 beanDefinition转化Bean
beanDefinition转化bean的过程其实都是有Spring来完成的,这部分是属于Spring的内容,下图大体描述了Spring内部是如何初始化bean: