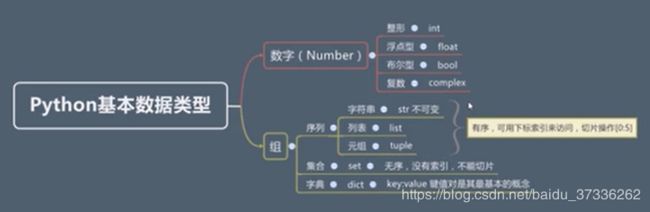
python 基本数据类型
#两个变量交换
x,y = 1,2
x,y = y,x
print('{:d},{:d}'.format(x,y))
#数据类型 值类型(不可变)int str tuple 引用类型 (可变) list set dict
print (type(2/2),type(2//2))
#进制 转义字符 \n换行 \r回车
print(0b10,10,0o10,0x1f,bin(10),bin(0o7),bin(0x11),int(0o111),hex(0o23),oct(0b1001))
print(type(True),type(False),'let\'s go ')
print('''ssss \n sss''','hello\world','hello \\n world')
#原始字符串及字符串操作
a,b= 'hello', 'world'
a1 = a + b
print(r'hello \n world')
print('拼接:hello' + 'world','a'*3,a[0:3],b[0],b[-3:-1])
for i in b:
if i == 'w':
print(i)
#列表操作
from collections import Counter
sample = [1,2,3,3,3,4,5,5]
print(Counter(sample).most_common(2))#出现次数最多的前两个元素及出现次数
max(set(sample), key=sample.count) #出现次数最多的元素
#int str list 列表[],元组(),
c,d,e = [1,2,3,4,5,1.9,True],[[1,2],['a','f'],[True,False]],['f','d','g']
f = (1,2,3,4)
print(c,d,c + e,type(c),f,type(f),(1,),c[2],a1[1:8:2],3 in c,'e' in a,9 not in c)
#len() max() min() ord() 集合set(特点无序,不重复)
g = {1,2,3,4,5}
h = {1,2,1,2,3,4,3,6,5}#剔除重复元素
print(type(g),ord('w'),h,h-g,h&g,h|g,type(set()))
python 变量赋值反映在内存中
import sys
x = 100 #分配存储空间
k = x
print(id(x))
x = 'abc'#新的存储空间
print(id(x),k)#x重命名不影响先前赋值的k
#变量赋值为存储块重新关联操作,而非更改原存储空间内的值
y = x
print(x is y,id(x))#y关联到与x相同的存储块内
print(sys.getrefcount(x))
x = 1234
y = 1234
print(x is y,id(x),id(y))#x y值相同,引用对象不同(存储空间不同)
#弱引用不增加引用计数,不影响目标生命周期
#循环引用会引起引用计数垃圾回收机制的内存泄漏(彼此引用计数永不归0,造成内存泄漏)
python 计算
#两点间距离计算
import numpy as np
import math
p1 = np.array([0, 0])
p2 = np.array([1000, 2000])
p3 = p2 - p1
p4 = math.hypot(p3[0], p3[1])
print(p4)
#小数的三种取整方式
from math import trunc, floor, ceil
x = 3.7
y = -3.7
print(trunc(x),trunc(y))#截断小数部分
print(floor(x),floor(y))#向下取整,变小
print(ceil(x),ceil(y))#向上取整,变大
#浮点数存储方式与比较
from decimal import Decimal
0.1 + 0.1 + 0.1 == 0.3 #浮点数以二进制存储十进制数的近似值
Decimal('0.1') + Decimal('0.1') + Decimal('0.1') == Decimal('0.3')
print(Decimal(0.1),Decimal('0.1'))
python 字符串操作
#字符串拼接
target_directory = "Base33"
filename = 'right.png'
print('image/resource/'+ target_directory + '/rest/' + filename)
route1 = "image/resource/{target_d}/rest/{file}".format(target_d = target_directory,file = filename)
print(route1)
python 列表操作
#列表指定元素获取
from collections import Counter
sample = [1,2,3,3,3,4,5,5]
print(Counter(sample).most_common(2))#出现次数最多的前两个元素及出现次数
max(set(sample), key=sample.count) #出现次数最多的元素
#列表元素去重
import numpy as np
a = [0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,2,2,3,4]
np.unique(a)
#filter的使用,元素过滤
lis = [1,0,0,0,1,1,2]
result = filter(lambda x: True if x != 0 else False, lis)
print(list(result))
python 字典操作
#字典dict{key:value,}key 不能重复,不可变类型
i = {'1':'potato','2':'tomato','3':'banana',4:'salad'}
print(i['1'])
#字典的插入及排序
dict = {}
dict['1'] = 'halu'
print(dict)
#key value 都是变量 (可以使用循环插入)
dict1 = {}
key = 'chinese'
value = 'china'
dict1[key] = value
print(dict1)
#字典排序
nameset = sorted(nameset.items(),key = lambda x:float(x[1]), reverse = True)
python 保留关键字
35 ['False', 'None', 'True', 'and', 'as', 'assert', 'async', 'await', 'break', 'class', 'continue', 'def', 'del', 'elif', 'else', 'except', 'finally', 'for', 'from', 'global', 'if', 'import', 'in', 'is', 'lambda', 'nonlocal', 'not', 'or', 'pass', 'raise', 'return', 'try', 'while', 'with', 'yield']
import keyword
print(len(keyword.kwlist),keyword.kwlist)
keyword.iskeyword("is")
python 内置函数
在这里插入代码片
lamda表达式降低了python可读性,慎用
#负载
app_citrix_apps = [{'citrix_name':'geou'},
{'citrix_name':'geou1'},
{'citrix_name':'geou2'},
{'citrix_name':'geou3'},]
app_citrix_apps = map(lambda x:{x['citrix_name']:0},app_citrix_apps)
print app_citrix_apps
citrix_app_runlinks={'HyperView': 1, 'Abq_cae_open_1': 1,'geou1':0,'geou':1, 'HyperMesh_1': 1, 'FLUENT 140': 1, 'Workbench 140': 1, 'FLUENT 140_1': 0}
citrix_app_links = map(lambda x:{x.keys()[0]:citrix_app_runlinks[x.keys()[0]]} if x.keys()[0] in citrix_app_runlinks.keys() else x,app_citrix_apps)
print citrix_app_links[0]
citrix_app_links = sorted(citrix_app_links, key=lambda x: x[x.keys()[0]])
loading_citrix_app = citrix_app_links[0]
print loading_citrix_app.keys()[0]
python函数中使用全局变量时,列表和元组可以很好地解决
#! /usr/bin/python
draw_point_C = [] #全局列表控制画点
k = []
def test():
if(len(k) < 4 and len(draw_point_C) == 0):
print('true')
else:
draw_point_C.insert(0,1)
#print(len(draw_point_C))
if __name__ == '__main__':
while(len(k) < 4):
test()
k.append(1)
__init__.py文件
__init__.py文件将包含py文件的文件夹变为一个python模块,每个模块中都有__init__.py文件。
批量引入
import sys
import datetime
import io
import math
__all__ = ['01']
print(sys.path)
print(math.floor(1.4))
函数及参数
import sys
sys.setrecursionlimit(1000000) #设置最大递归深度,默认最大深度998
#函数
def add(x,y): #x,y形式参数
term = x +y
return term
def defa(m = 'ysl',n = 'mac'):#默认参数
return m+n
result,result1 = add(2,3),defa() #2,3实际参数 add(y = 2,x = 3)
print(result,result1)
#序列解包
d = 1,2,3
a,b,c = d
e,f,*g = 4,5,6,7
h,*i,j = 8,9,10,11
(k,l),(m,n) = (12,13),(14,15)#嵌套解包
print(a,b,c,e,f,g,h,i,j)
print(k,l,m,n)
枚举类型
用于定义常量
from enum import Enum,unique
from enum import IntEnum #值只能为int类型
HERO = Enum('List',('a','b','c','d','e','g','f',))#常量
class STATUS(Enum):#
GAS = 1
GAS_sec = 1 #value 相同,GAS_sec为GAS的别名
LIQUID = 2
STRONE = 3
SAND = 4
@unique #不允许重复值出现
class STATUS1(IntEnum):#枚举类型:值不可变
GAS = 1
#GAS_sec = 1
GAS_sec = 2
print(HERO.a,STATUS.GAS,STATUS.GAS.name,STATUS.GAS.value,STATUS['SAND'],)
for i in STATUS:
print(i)
for i in STATUS.__members__: #.items()
print(i)
#枚举之间的比较,不能做大小(<>)比较,可以身份比较和等值比较
result = STATUS.GAS == STATUS.SAND
r = STATUS.GAS is STATUS.GAS
a = 4
print(result,r,STATUS(a),'数字转为枚举类型')
