Siamese 详解
本博客引用:
https://blog.csdn.net/ybdesire/article/details/84072339
https://blog.csdn.net/u011808673/article/details/84025349
摘要
Siamese网络用途,原理,如何训练?
背景
在人脸识别中,存在所谓的one-shot问题。举例来说,就是对公司员工进行人脸识别,每个员工只给你一张照片(训练集样本少),并且员工会离职、入职(每次变动都要重新训练模型)。有这样的问题存在,就没办法直接训练模型来解决这样的分类问题了。
为了解决one-shot问题,我们会训练一个模型来输出给定两张图像的相似度,所以模型学习得到的是similarity函数。
哪些模型能通过学习得到similarity函数呢?Siamese网络就是这样的一种模型。
Siamese网络原理
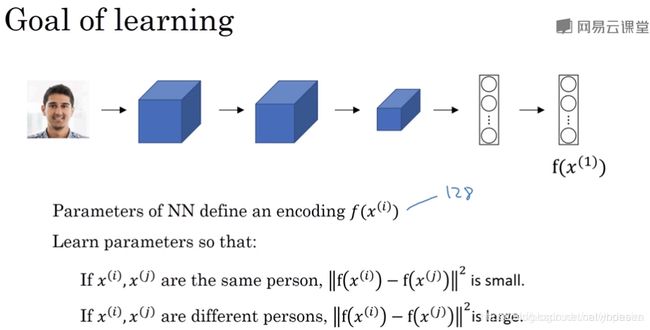
Siamese网络要给出输入图像X1和X2的相似度,所以它必须能接受两个图像作为输入,如下图:

图中上下两个模型,都由CNN构成,两个模型的参数值完全相同。不同于传统CNN的地方,是Siamese网络并不直接输出类别,而是输出一个向量(比如上图中是128个数值组成的一维向量):
若输入的图像X1和X2为同一个人,则上下两个模型输出的一维向量欧氏距离较小
若输入的图像X1和X2不是同一个人,则上下两个模型输出的一维向量欧氏距离较大
所以通过对上下两个模型输出的向量做欧氏距离计算,就能得到输入两幅图像的相似度。
又因为上下两个模型具有相同的参数,所以训练模型时,只需要训练一个模型即可。那问题来了,这样的模型该怎么训练呢?模型的输出label该标注为什么呢?
如何训练Siamese网络
模型的训练,就是给定cost function后,用梯度下降法寻找最优值的过程。
训练Siamese网络,需要引入新的cost function。我们先看模型的学习目标(下图),再一步一步讲解cost function的最终表达式。

对图中的一幅照片A,如果给定了同一个人的另一幅照片P,则模型的输出向量f(A)和f§应该是距离比较小的。如果给定了另一个人的照片N,则模型的输出向量f(A)和f(N)之间的距离就比较小。所以 d ( A , P ) < d ( A , N ) d(A,P)<d(A,N) d(A,P)<d(A,N)。
根据这个目标,就得到了cost function的定义:
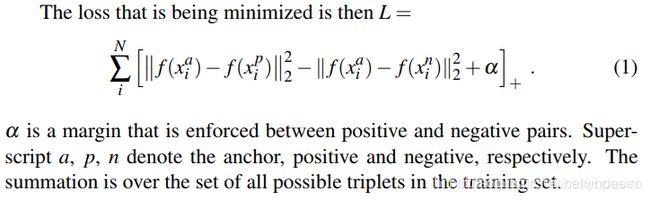
其目的,是遍历所有三元组(A,P,N),求其L的最小。公式中的参数α,是一个超参数,用于做margin,能避免模型输出的都是零向量。
有了这个cost function,用梯度下降法就能找到模型的最优值。这个过程是不需要我们对模型的向量值进行人工标注的。
Siamese 网络
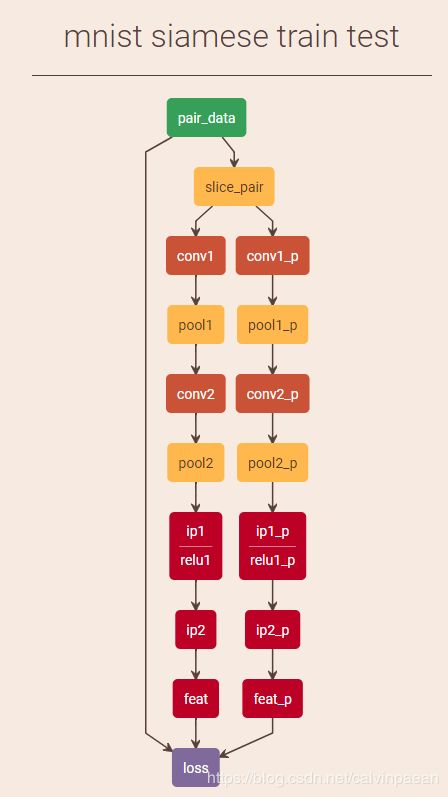
下面为Siamese网络在Caffe上的Prototxt文件:
name: "mnist_siamese_train_test"
layer {
name: "pair_data"
type: "Data"
top: "pair_data"
top: "sim"
include {
phase: TRAIN
}
transform_param {
scale: 0.00390625
}
data_param {
source: "examples/siamese/mnist_siamese_train_leveldb"
batch_size: 64
}
}
layer {
name: "pair_data"
type: "Data"
top: "pair_data"
top: "sim"
include {
phase: TEST
}
transform_param {
scale: 0.00390625
}
data_param {
source: "examples/siamese/mnist_siamese_test_leveldb"
batch_size: 100
}
}
layer {
name: "slice_pair"
type: "Slice"
bottom: "pair_data"
top: "data"
top: "data_p"
slice_param {
slice_dim: 1
slice_point: 1
}
}
layer {
name: "conv1"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "data"
top: "conv1"
param {
name: "conv1_w"
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
name: "conv1_b"
lr_mult: 2
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 20
kernel_size: 5
stride: 1
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "pool1"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv1"
top: "pool1"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "conv2"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "pool1"
top: "conv2"
param {
name: "conv2_w"
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
name: "conv2_b"
lr_mult: 2
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 50
kernel_size: 5
stride: 1
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "pool2"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv2"
top: "pool2"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "ip1"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "pool2"
top: "ip1"
param {
name: "ip1_w"
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
name: "ip1_b"
lr_mult: 2
}
inner_product_param {
num_output: 500
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu1"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "ip1"
top: "ip1"
}
layer {
name: "ip2"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "ip1"
top: "ip2"
param {
name: "ip2_w"
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
name: "ip2_b"
lr_mult: 2
}
inner_product_param {
num_output: 10
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "feat"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "ip2"
top: "feat"
param {
name: "feat_w"
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
name: "feat_b"
lr_mult: 2
}
inner_product_param {
num_output: 2
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "conv1_p"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "data_p"
top: "conv1_p"
param {
name: "conv1_w"
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
name: "conv1_b"
lr_mult: 2
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 20
kernel_size: 5
stride: 1
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "pool1_p"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv1_p"
top: "pool1_p"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "conv2_p"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "pool1_p"
top: "conv2_p"
param {
name: "conv2_w"
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
name: "conv2_b"
lr_mult: 2
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 50
kernel_size: 5
stride: 1
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "pool2_p"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv2_p"
top: "pool2_p"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "ip1_p"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "pool2_p"
top: "ip1_p"
param {
name: "ip1_w"
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
name: "ip1_b"
lr_mult: 2
}
inner_product_param {
num_output: 500
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu1_p"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "ip1_p"
top: "ip1_p"
}
layer {
name: "ip2_p"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "ip1_p"
top: "ip2_p"
param {
name: "ip2_w"
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
name: "ip2_b"
lr_mult: 2
}
inner_product_param {
num_output: 10
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "feat_p"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "ip2_p"
top: "feat_p"
param {
name: "feat_w"
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
name: "feat_b"
lr_mult: 2
}
inner_product_param {
num_output: 2
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "loss"
type: "ContrastiveLoss"
bottom: "feat"
bottom: "feat_p"
bottom: "sim"
top: "loss"
contrastive_loss_param {
margin: 1
}
}