Mybatis源码分析之Spring与Mybatis整合MapperScannerConfigurer处理过程源码分析
前面文章分析了这么多关于Mybatis源码解析,但是我们最终使用的却不是以前面文章的方式,编写自己mybatis_config.xml,而是最终将配置融合在spring的配置文件中。有了前面几篇博客的分析,相信这里会容易理解些关于Mybatis的初始化及其执行,但是仍旧需要Spring的很多知识,用到的时候会简略提到下。下面先看下我们具体使用Mybatis时候是怎样配置的。
mysql
SqlSessionFactoryBean类
负责Mybatis的初始化,最终会初始化出一个Configuration
MapperScannerConfigurer类
负责创建接口的代理,可以看到上面类实例化的时候传入的参数就是接口包
下面开始源码的具体分析。
(1)SqlSessionFactoryBean
从上面的配置文件可以看到这个类有几个属性,dataSource,plugin都比较熟悉,就不说了。主要讲解mapper.xml文件的初始化。
看一下这个类的继承结构
public class SqlSessionFactoryBean implements FactoryBean, InitializingBean, ApplicationListener 1.FactoryBean
工厂bean,实例化的时候不是返回对象本身,而是调用它的方法getObject()方法返回的对象,如果要获取FactoryBean对象,可以在id前面加一个&符号来获取
public SqlSessionFactory getObject() throws Exception {
if (this.sqlSessionFactory == null) {
afterPropertiesSet();
}
return this.sqlSessionFactory;
}2.InitailizingBean
实现这个接口的bean,会在其实例化完成后,初始化阶段调用他的方法afterPropertiesSet()(可以看下spring bean的生命周期)
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
notNull(dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required");
notNull(sqlSessionFactoryBuilder, "Property 'sqlSessionFactoryBuilder' is required");
this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();
}3.ApplicationListener
是一个接口,里面只有一个onApplicationEvent方法。所以自己的类在实现该接口的时候,要实装该方法。如果在上下文中部署一个实现了ApplicationListener接口的bean,那么每当在一个ApplicationEvent发布到 ApplicationContext时,这个bean得到通知。其实这就是标准的Oberver设计模式。
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (failFast && event instanceof ContextRefreshedEvent) {
// fail-fast -> check all statements are completed
this.sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration().getMappedStatementNames();
}
}下面从初始化入口开启分析:
this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();protected SqlSessionFactory buildSqlSessionFactory() throws IOException {
Configuration configuration;
XMLConfigBuilder xmlConfigBuilder = null;
if (this.configLocation != null) {
xmlConfigBuilder = new XMLConfigBuilder(this.configLocation.getInputStream(), null, this.configurationProperties);
configuration = xmlConfigBuilder.getConfiguration();
} else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Property 'configLocation' not specified, using default MyBatis Configuration");
}
configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.setVariables(this.configurationProperties);
}
if (this.objectFactory != null) {
configuration.setObjectFactory(this.objectFactory);
}
if (this.objectWrapperFactory != null) {
configuration.setObjectWrapperFactory(this.objectWrapperFactory);
}
if (hasLength(this.typeAliasesPackage)) {
String[] typeAliasPackageArray = tokenizeToStringArray(this.typeAliasesPackage,
ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS);
for (String packageToScan : typeAliasPackageArray) {
configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAliases(packageToScan,
typeAliasesSuperType == null ? Object.class : typeAliasesSuperType);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Scanned package: '" + packageToScan + "' for aliases");
}
}
}
if (!isEmpty(this.typeAliases)) {
for (Class typeAlias : this.typeAliases) {
configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAlias(typeAlias);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Registered type alias: '" + typeAlias + "'");
}
}
}
if (!isEmpty(this.plugins)) {
for (Interceptor plugin : this.plugins) {
configuration.addInterceptor(plugin);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Registered plugin: '" + plugin + "'");
}
}
}
if (hasLength(this.typeHandlersPackage)) {
String[] typeHandlersPackageArray = tokenizeToStringArray(this.typeHandlersPackage,
ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS);
for (String packageToScan : typeHandlersPackageArray) {
configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry().register(packageToScan);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Scanned package: '" + packageToScan + "' for type handlers");
}
}
}
if (!isEmpty(this.typeHandlers)) {
for (TypeHandler typeHandler : this.typeHandlers) {
configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry().register(typeHandler);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Registered type handler: '" + typeHandler + "'");
}
}
}
if (xmlConfigBuilder != null) {
try {
xmlConfigBuilder.parse();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Parsed configuration file: '" + this.configLocation + "'");
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse config resource: " + this.configLocation, ex);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
if (this.transactionFactory == null) {
this.transactionFactory = new SpringManagedTransactionFactory();
}
Environment environment = new Environment(this.environment, this.transactionFactory, this.dataSource);
configuration.setEnvironment(environment);
if (this.databaseIdProvider != null) {
try {
configuration.setDatabaseId(this.databaseIdProvider.getDatabaseId(this.dataSource));
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed getting a databaseId", e);
}
}
if (!isEmpty(this.mapperLocations)) {
for (Resource mapperLocation : this.mapperLocations) {
if (mapperLocation == null) {
continue;
}
try {
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(mapperLocation.getInputStream(),
configuration, mapperLocation.toString(), configuration.getSqlFragments());
xmlMapperBuilder.parse();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse mapping resource: '" + mapperLocation + "'", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Parsed mapper file: '" + mapperLocation + "'");
}
}
} else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Property 'mapperLocations' was not specified or no matching resources found");
}
}
return this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(configuration);
}分析一下这个方法的逻辑,第一个if语句,调到了else分支实例化了一个Configuration类出来,下一步将数据库的初始化读入进来。
if (this.transactionFactory == null) {
this.transactionFactory = new SpringManagedTransactionFactory();
}
Environment environment = new Environment(this.environment, this.transactionFactory, this.dataSource);
configuration.setEnvironment(environment);if (!isEmpty(this.mapperLocations)) {
for (Resource mapperLocation : this.mapperLocations) {
if (mapperLocation == null) {
continue;
}
try {
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(mapperLocation.getInputStream(),
configuration, mapperLocation.toString(), configuration.getSqlFragments());
xmlMapperBuilder.parse();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse mapping resource: '" + mapperLocation + "'", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Parsed mapper file: '" + mapperLocation + "'");
}
}
} (2) MapperScannerConfigurer
下面看这个类是怎么将接口创建为代理的。首先也看下这个类的继承结构。
public class MapperScannerConfigurer implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor, InitializingBean, ApplicationContextAware, BeanNameAware1.Aware接口
实现这些 Aware接口的Bean在被实例化 之后,可以取得一些相对应的资源,例如实现BeanFactoryAware的Bean在实例化后,Spring容器将会注入BeanFactory的实例,而实现ApplicationContextAware的Bean,在Bean被实例化后,将会被注入 ApplicationContext的实例等等。
2.InitalizingBean
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
notNull(this.basePackage, "Property 'basePackage' is required");
}3.BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
这个接口:public interface BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor。
实现该接口,可以在spring的bean创建之前,修改bean的定义属性。也就是说,Spring允许BeanFactoryPostProcessor在容器实例化任何其它bean之前读取配置元数据,并可以根据需要进行修改,例如可以把bean的scope从singleton改为prototype,也可以把property的值给修改掉。可以同时配置多个BeanFactoryPostProcessor,并通过设置'order'属性来控制各个BeanFactoryPostProcessor的执行次序。注意:BeanFactoryPostProcessor是在spring容器加载了bean的定义文件之后,在bean实例化之前执行的。
这个类的执行就是从这个后处理开始的:
/**
*
* @param registry 这个参数是spring注册beanDefiniton的地方,这个类里面有一个缓存map,专门存储beanDefinition
* @throws BeansException
*/
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
//解决${jdbc.username}这种占位符的复制问题
if (this.processPropertyPlaceHolders) {
processPropertyPlaceHolders();
}
//这个类就是将接口扫描为BeanDefinition,并且最终被代理
ClassPathMapperScanner scanner = new ClassPathMapperScanner(registry);
scanner.setAddToConfig(this.addToConfig);
scanner.setAnnotationClass(this.annotationClass);
scanner.setMarkerInterface(this.markerInterface);
scanner.setSqlSessionFactory(this.sqlSessionFactory);
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplate(this.sqlSessionTemplate);
scanner.setSqlSessionFactoryBeanName(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName);
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplateBeanName(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName);
scanner.setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(this.nameGenerator);
scanner.registerFilters();
//扫描器的scan方法将basePackage扫描为beanDefinition
scanner.scan(StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.basePackage, ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS));
}
//逻辑转移到了doScan方法
public int scan(String... basePackages) {
int beanCountAtScanStart = this.registry.getBeanDefinitionCount();
doScan(basePackages);
// Register annotation config processors, if necessary.
if (this.includeAnnotationConfig) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
}
return this.registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() - beanCountAtScanStart;
}
@Override
public Set doScan(String... basePackages) {
//首先调用了父类的doScan方法,下面具体分析,比较关键,转化为了spring bean的形式
Set beanDefinitions = super.doScan(basePackages);
if (beanDefinitions.isEmpty()) {
logger.warn("No MyBatis mapper was found in '" + Arrays.toString(basePackages) + "' package. Please check your configuration.");
} else {
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : beanDefinitions) {
//这里就转化为了正常的spring中的bean的形式了,spring就是最开始将配置文件初始化为了一个GenericBeanDefinition
GenericBeanDefinition definition = (GenericBeanDefinition) holder.getBeanDefinition();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating MapperFactoryBean with name '" + holder.getBeanName()
+ "' and '" + definition.getBeanClassName() + "' mapperInterface");
}
// the mapper interface is the original class of the bean
// but, the actual class of the bean is MapperFactoryBean
//这种就是对MapperFactoryBean中的一些属性的赋值,(可以看些BeanWrapperImpl的相关知识)
definition.getPropertyValues().add("mapperInterface", definition.getBeanClassName());
//最最关键的一步,这就是beanDefintion的真正的类型,这里也就是将所有的接口类最终都按照MapperFactoryBean处理的
definition.setBeanClass(MapperFactoryBean.class);
definition.getPropertyValues().add("addToConfig", this.addToConfig);
boolean explicitFactoryUsed = false;
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName)) {
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName));
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
} else if (this.sqlSessionFactory != null) {
//在MapperFactoryBean中找了一下sqlSessionFactory这个属性,没有找到,他的父类SqlSessionDaoSupport中也没有这个属性
//但是有sqlSession这个属性,其实这里给sqlSessionFactory赋值,就是调用他的set方法,看到这个类虽然没有这个属性,但是确实有这个
//属性的set方法,玄机都在这个 set方法里,最终跟踪下去实例化了蛮多对象
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", this.sqlSessionFactory);
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName)) {
if (explicitFactoryUsed) {
logger.warn("Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored.");
}
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName));
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
} else if (this.sqlSessionTemplate != null) {
if (explicitFactoryUsed) {
logger.warn("Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored.");
}
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", this.sqlSessionTemplate);
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
}
if (!explicitFactoryUsed) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Enabling autowire by type for MapperFactoryBean with name '" + holder.getBeanName() + "'.");
}
definition.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE);
}
}
}
return beanDefinitions;
} //看返回值就看得出,将传入的dao接口,最终扫描为BeanDefinitionHolder,这个类里包含这BeanDefinition属性
protected Set doScan(String... basePackages) {
Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified");
Set beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet();
//显然basePackages也是可以配置为数组形式的
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
//靠这个函数就将basePackage转化为最基本的beanDefinition
Set candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
//过滤处理所有生成的基本beanDefinition
for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) {
//bean是单例还是原型判断
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(candidate);
candidate.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
//取得beanName
String beanName = this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(candidate, this.registry);
if (candidate instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
postProcessBeanDefinition((AbstractBeanDefinition) candidate, beanName);
}
if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidate);
}
if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) {
//封装到holder类中
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName);
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder);
//注册到registry中
registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
}
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
public Set findCandidateComponents(String basePackage) {
Set candidates = new LinkedHashSet();
try {
//basePackage路径构造
String packageSearchPath = ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX +
resolveBasePackage(basePackage) + "/" + this.resourcePattern;
//将路径转化为资源
Resource[] resources = this.resourcePatternResolver.getResources(packageSearchPath);
boolean traceEnabled = logger.isTraceEnabled();
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
//遍历每一个文件资源
for (Resource resource : resources) {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Scanning " + resource);
}
if (resource.isReadable()) {
try {
//对资源内容的一个转化
MetadataReader metadataReader = this.metadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(resource);
if (isCandidateComponent(metadataReader)) {
//用传入的资源构建出基本的BeanDefinition,初始化bean的名称,注解等一些基本字段
ScannedGenericBeanDefinition sbd = new ScannedGenericBeanDefinition(metadataReader);
sbd.setResource(resource);
sbd.setSource(resource);
if (isCandidateComponent(sbd)) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Identified candidate component class: " + resource);
}
candidates.add(sbd);
}
else {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Ignored because not a concrete top-level class: " + resource);
}
}
}
else {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Ignored because not matching any filter: " + resource);
}
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to read candidate component class: " + resource, ex);
}
}
else {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Ignored because not readable: " + resource);
}
}
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("I/O failure during classpath scanning", ex);
}
return candidates;
}
public class MapperFactoryBean extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements FactoryBean {
private Class mapperInterface;
private boolean addToConfig = true;
/**
* Sets the mapper interface of the MyBatis mapper
*
* @param mapperInterface class of the interface
*/
public void setMapperInterface(Class mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
/**
* If addToConfig is false the mapper will not be added to MyBatis. This means
* it must have been included in mybatis-config.xml.
*
* If it is true, the mapper will be added to MyBatis in the case it is not already
* registered.
*
* By default addToCofig is true.
*
* @param addToConfig
*/
public void setAddToConfig(boolean addToConfig) {
this.addToConfig = addToConfig;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
protected void checkDaoConfig() {
super.checkDaoConfig();
notNull(this.mapperInterface, "Property 'mapperInterface' is required");
Configuration configuration = getSqlSession().getConfiguration();
if (this.addToConfig && !configuration.hasMapper(this.mapperInterface)) {
try {
configuration.addMapper(this.mapperInterface);
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Error while adding the mapper '" + this.mapperInterface + "' to configuration.", t);
throw new IllegalArgumentException(t);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
public T getObject() throws Exception {
return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
public Class getObjectType() {
return this.mapperInterface;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
相信大家也看出来了这个类上的玄机,继承了一个类,同时实现了FactoryBean。首先看下继承的这个类,
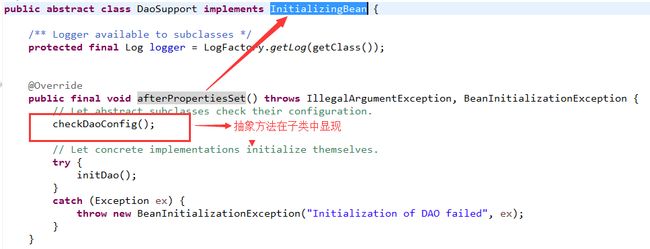
public abstract class SqlSessionDaoSupport extends DaoSupport,是一个抽象类,同时又继承了另一个类
感觉以这种截图的方式讲解还蛮清晰的。看到这个类是不是明白了,最终相当于MapperFactoryBean实现了InitializingBean,看到afterProperties方法中调用了一个抽象方法,这个方法实在哪个子类中实现的呢?
mybatis与sping结合的所有初始化就结束了,到这里不仅早就有了Configuration类,sqlSession也被初始化完成了,下面就是用sqlSession调用执行方法的起始,getMapper的时候了,那么这个是怎么处理的呢,上面看到MapperFactoryBean还继承了工厂bean,所以这个bean被实例化的时候会调用他的getObeject方法,在这个方法中移花接木,生成了代理。
public T getObject() throws Exception {
return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}其实只有这么一句,不过也看到了通过接口,调用getMapper方法了,这样就又归到了前面博客执行接口方法的流程里了,在这个方法调用完最终返回的是一个传入接口的动态代理。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------20170910凌晨2:09的分割线----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
没什么想说的,其实也没有想象中的那么逻辑复杂,只是需要一点spring源码的知识。下一步期望可以分析一下Mybatis的sqlNode的问题,感觉这里还是不行,还有就是下一个系列SpringMVC的源码分析。